Post-fire Forest Residue Mulch [葡萄牙]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Sergio Prats Alegre Prats
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Fabian Ottiger
acolchoado, aplicação de restos vegetais
technologies_1186 - 葡萄牙
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
SLM专业人员:
Keizer Jan Jacob
Universidade de Aveiro-CESAM
Campus Universitário de Santiago, 3810-193 Aveiro, Portugal
葡萄牙
SLM专业人员:
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
Preventing and Remediating degradation of soils in Europe through Land Care (EU-RECARE )有助于对技术进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
Catastrophic shifts in drylands (EU-CASCADE)有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
University of Aveiro (University of Aveiro) - 葡萄牙1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
25/04/2013
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
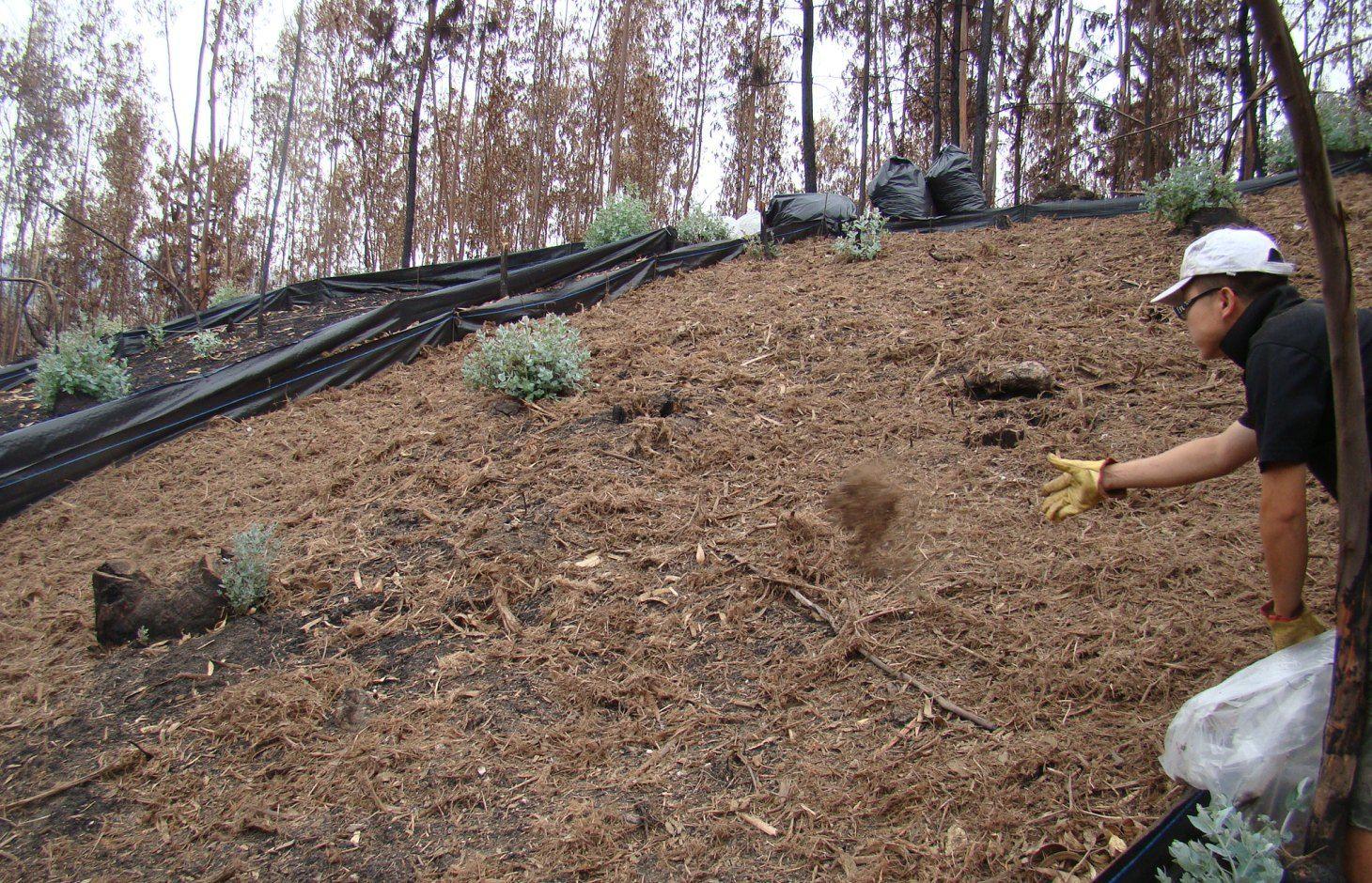
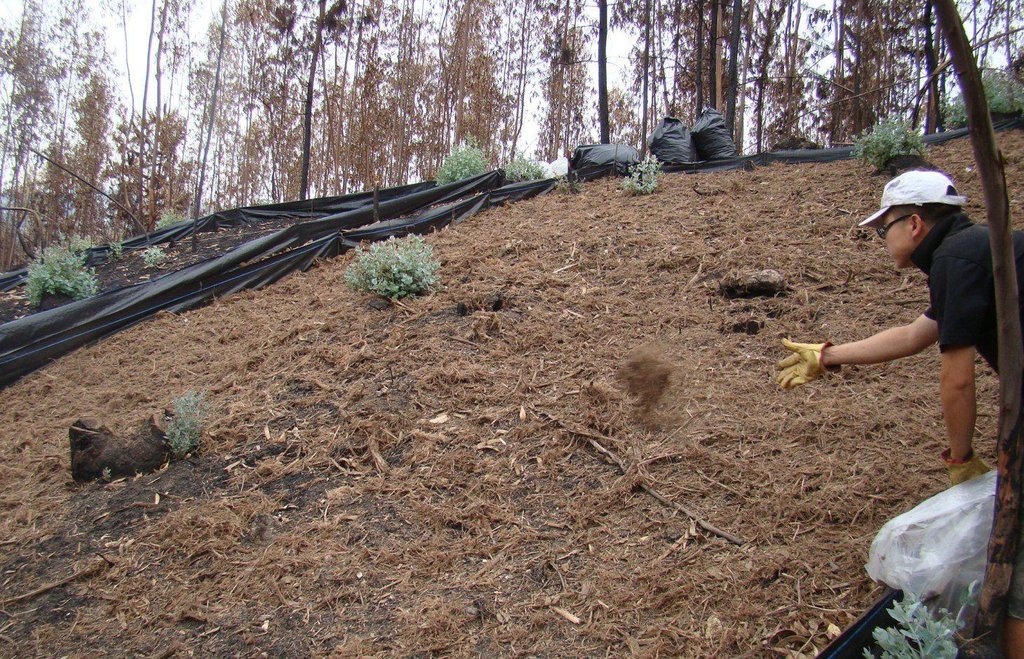
Forest residue mulch is spread immediately after a wildfire in order to prevent soil erosion and reduce overland flow.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
In two areas of eucalypt plantations affected by wildfires in central Portugal in 2007 and 2010, the research team of the University of Aveiro set up two experiments in order to test the effect of forest residue mulching as a soil erosion mitigation technique. Forest residues such as chopped eucalypt bark mulch was spread over a group of erosion plots, and was compared to an untreated group of plots.
The mulching was applied at ratios of 8.7 and 10.8 Mg ha-1 provided an initial ground cover of 70 to 80%, and was found to reduce post-fire runoff by 40-50% and soil erosion by 85-90%, respectively.
Purpose of the Technology: The increase in ground cover will decrease post-fire soil erosion by reducing raindrop impact over the ashes and bare soil, and decrease the runoff amount by increasing water surface storage, decreasing runoff velocity, and increase infiltration.
Ideally, post-fire mulching must be carried out immediately after the fire, in order to prevent that the first autumn rainfall events fall over the bare and unprotected burnt soils. It is intended for places in which burnt severity was moderate to high and where there are important values at risk, such as water reservoirs, populations, industries, human and wild life.
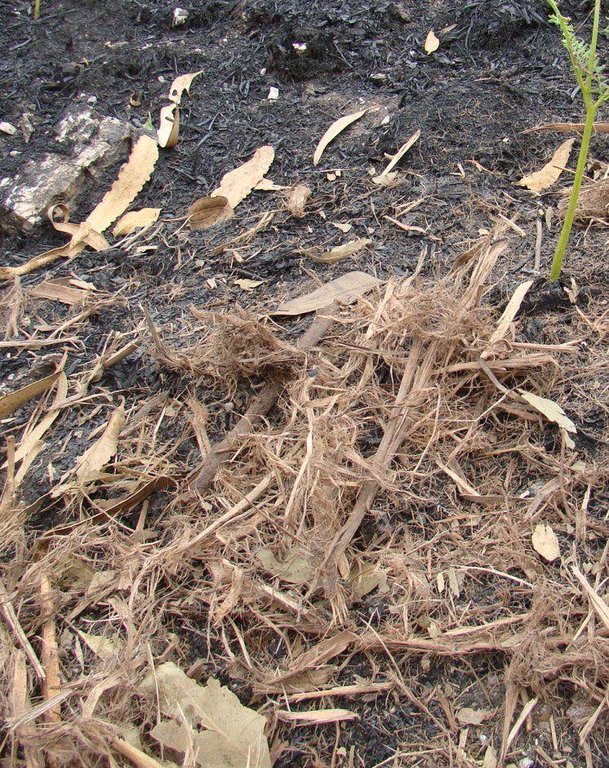
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The chopped bark mulch was obtained at a depot 20 km from the burnt area, where eucalypt logs are debarked and then transported to a paper pulp factory. The bark is chopped into fibers and are typically transported to a biomass energy plant. We used these 10–15 cm wide 2–5 cm long bark fibers as the source for our mulching experiment. The chopped bark mulch decays very slowly (around 20% less ground cover per year) which was very useful in cases of low re-growth of natural vegetation.
Natural / human environment: The eucalypt trees in the region are typically planted as monocultures for paper pulp production, and harvested every 7-14 years. The landscape reflects a long history of intense land management, with a mosaic of (semi-)natural and man-made agricultural and afforested lands. Since the 1980´s, however, wildfires have increased dramatically in frequency and extent, aided by a general warming and drying trend but driven primarily by socio-economic changes.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
葡萄牙
区域/州/省:
Portugal/Beira Litoral
有关地点的进一步说明:
Sever do vouga/ Pessegueiro do Vouga, Ermida
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 不到10年前(最近)
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 在实验/研究期间
注释(项目类型等):
The first experiment was carried out in 2007.
3. SLM技术的分类
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

森林/林地
产品和服务:
- 木材
- 薪材
注释:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Increased runoff and soil erosion, resulting in a decrease of on-site fertility and derived off-site effects such as loss of water quality, reservoirs water volume storage, higher risk of flooding and human beings damage.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Loss of wood resources and productivity.
Plantation forestry: eucalypt are logged and left to regrow from stumps each 7-10 years
Forest products and services: timber, fuelwood
3.3 有关土地利用的更多信息
每年的生长季节数:
- 1
3.4 该技术所属的SLM组
- 改良的地面/植被覆盖
3.5 技术传播
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果该技术均匀地分布在一个区域上,请注明覆盖的大致区域。:
- < 0.1 平方千米(10 公顷)
注释:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 1.0E-5 m2.
The experiment was carried out in grous of small bounded plots of 0.25, 16 and 100 m2.
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

农艺措施
- A1:植被和土壤覆盖层
注释:
Main measures: agronomic measures
Type of agronomic measures: mulching
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀
- Wo:场外劣化效应

化学性土壤退化
- Cn:肥力下降和有机质含量下降(非侵蚀所致)

水质恶化
- Hs:地表水良变化
- Hp:地表水水质下降
注释:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Hs: change in quantity of surface water, Hp: decline of surface water quality
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wo: offsite degradation effects, Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content
Main causes of degradation: crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (Eucalypt monocultures are prone to suffer wildfires), deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires), disturbance of water cycle (infiltration / runoff) (Increased runoff is observed after wildfires), Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts) (Burnt areas are very sensitive to high intensity events), other natural causes (avalanches, volcanic eruptions, mud flows, highly susceptible natural resources, extreme topography, etc.) specify (Sediment deposition can decrease the storage volume of reservoirs.)
Secondary causes of degradation: floods (Overland flow can be extremely high after forest fires), inputs and infrastructure: (roads, markets, distribution of water points, other, …) (Roads concentrated the runoff and are greatly degraded.)
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 防止土地退化
- 减少土地退化
注释:
Main goals: prevention of land degradation, mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
4.2 技术规范/技术图纸说明
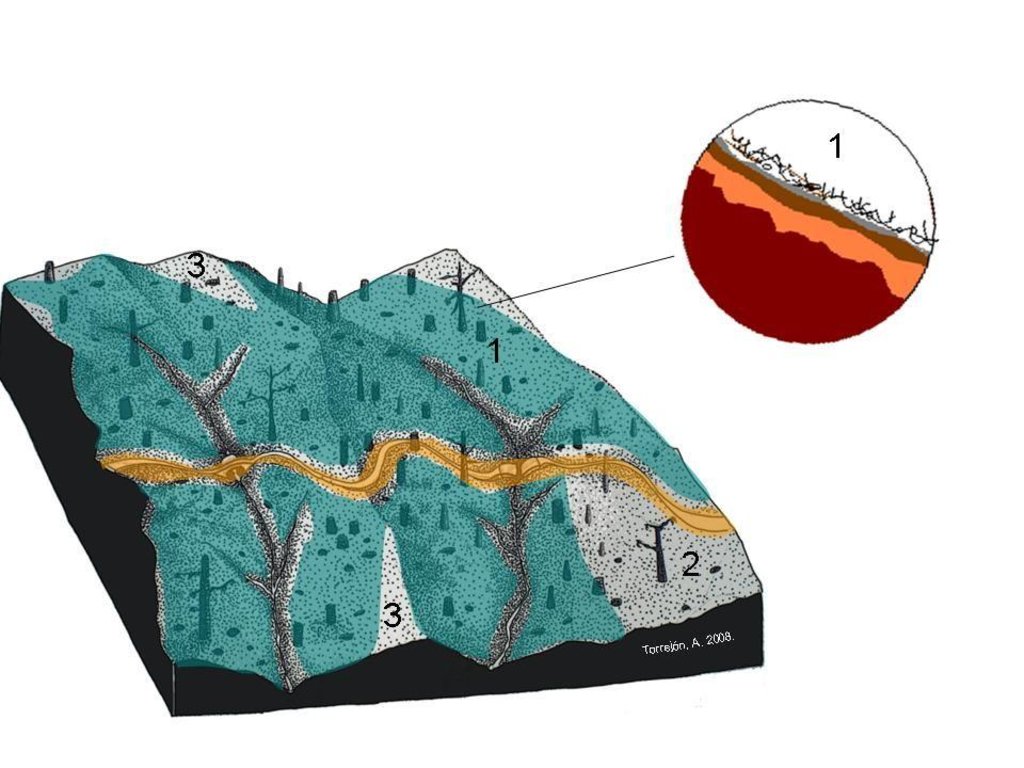
Forest residue mulch is spread as homogeneous as possible over steep areas (steeper than 15º) burnt at high fire severity (represented in green and 1). Other areas which are flat (2) and burnt at low severity or only partially burnt (3) must be avoided.
Location: Ermida. Sever do Vouga/ Portugal
Date: 15 9 2010
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: low (forest residue mulching is highly effective in all situations, but applications using short fibres mulching as well as low intensity burning should be avoided.)
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: control of raindrop splash, control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap, control of concentrated runoff: impede / retard, control of concentrated runoff: drain / divert, improvement of ground cover, improvement of water quality, buffering / filtering water, sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting
Secondary technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, reduction of slope angle, increase of surface roughness, increase in organic matter, increase of infiltration, increase / maintain water stored in soil, increase of groundwater level / recharge of groundwater
Mulching
Material/ species: chopped bark, cork, stems, leaves, straw/eucalypt, pine, oaks, shrubs
Quantity/ density: 2-10t/ha
Remarks: material with low density (straw) need less weight for achieving the final goal: 70% ground cover.
4.3 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
Euro
注明美元与当地货币的汇率(如相关):1美元=:
0.78
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
64.00
4.4 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Labour | 农业学的 | |
| 2. | Transportation (small truck for carrying persons and material) | 农业学的 | |
| 3. | Eucalypt chopped bark mulch | 农业学的 | |
| 4. | Others | 农业学的 |
4.5 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Labour | ha | 1.0 | 192.0 | 192.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Machine use | ha | 1.0 | 51.2 | 51.2 | 100.0 |
| 其它 | Forest residue mulch | ha | 1.0 | 307.6 | 307.6 | 100.0 |
| 其它 | Others | ha | 1.0 | 64.1 | 64.1 | 100.0 |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 614.9 | |||||
注释:
Duration of establishment phase: 1 month(s)
4.7 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
注释:
The prices were determined in winter 2012 for central Portugal. It is intended that mulch is applied only once, and thus maintenance is not needed. In other regions other forest residues can have a higher availability. Straw, needles, deciduous leaves or chopped shrubs are lighter compared to eucalypt chopped bark, slash stems or wood chips, and thus, can be easier to apply and transport. However, the lighter the material, the easier it can be blown away in windy areas.
4.8 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
Accessibility and steepness will raise the costs, but selecting forest residues with lower densities as well as applying them in horizontal strips along the slope can reduce the application rates and the costs.
For large and inaccessible areas some researchers indicated that helicopters can reduce the costs.
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
农业气候带
- 潮湿的
- 半湿润
Thermal climate class: subtropics
Thermal climate class: temperate
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
关于地形的注释和进一步规范:
Altitudinal zone: 101-500 m a.s.l. (300m)
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 粗粒/轻(砂质)
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 高(>3%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Topsoil organic matter is high (Around 10 % between 0 to 5 cm of soil depth)
Soil fertility is high-medium
Soil drainage/infiltration is medium (Dependent on the soil water repellence cycles, characteristics of eucalypt and pine plantations on the area.)
Soil water storage capacity is medium
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
5-50米
地表水的可用性:
好
水质(未处理):
良好饮用水
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 中等
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
生产系统的市场定位:
- 混合(生计/商业
- 商业/市场
非农收入:
- 低于全部收入的10%
相对财富水平:
- 贫瘠
- 平均水平
个人或集体:
- 员工(公司、政府)
性别:
- 女人
- 男人
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: 50-100 persons/km2
Annual population growth: negative
50% of the land users are average wealthy.
40% of the land users are poor.
10% of the land users are poor.
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者拥有或租用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 小规模的
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 社区/村庄
土地使用权:
- 社区(有组织)
- 个人
用水权:
- 自由进入(无组织)
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
水资源可用性和质量
家畜用水的可用性
灌溉用水的可用性
灌溉用水需求
收入和成本
农业投入费用
注释/具体说明:
Eucalypt chopped bark mulch increases expenses if not funded by the Government
社会文化影响
SLM/土地退化知识
冲突缓解
注释/具体说明:
Less damage to off-site neighbouring properties
Improved livelihoods and human well-being
注释/具体说明:
Public awareness of the technology is very limited. It is necessary to show it to landowners and stakeholders and increase dissemination.
生态影响
水循环/径流
水质
地表径流
地下水位/含水层
蒸发
土壤
土壤水分
土壤覆盖层
土壤流失
土壤有机物/地下C
生物多样性:植被、动物
动物多样性
有益物种
其它生态影响
Hazard towards adverse events
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
水资源可用性
下游洪水
下游淤积
注释/具体说明:
If applied in large areas
地下水/河流污染
缓冲/过滤能力
风力搬运沉积物
对邻近农田的破坏
对公共/私人基础设施的破坏
注释/具体说明:
If applied in large areas upslope
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 气候变化/极端天气的类型 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年温度 | 增加 | 好 |
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气象灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 局地暴雨 | 好 |
| 局地风暴 | 好 |
气候灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 干旱 | 好 |
水文灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 比较和缓的(河道)洪水 | 不好 |
其他气候相关的后果
其他气候相关的后果
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 缩短生长期 | 未知 |
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
中性/平衡
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
稍微积极
长期回报:
稍微积极
6.5 技术采用
注释:
Comments on acceptance with external material support: The technology has been tested by scientific researchers and it is very effective, but not broadly implemented.
Comments on spontaneous adoption: The technology has been tested by scientific researchers researchers and it is very effective, but not broadly implemented.
There is no trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| It will prevent sediment movement and accumulation over roads and downslope properties |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
It is a technology very easy to apply, with low failure possibilities and a strong soil erosion control How can they be sustained / enhanced? Some researchers found better performance by grinding the mulch and selecting only the longest fibres. |
| The material is readily available (residues from the main forest specie affected by the wildfire) |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| The costs are not very high, but enough to discourage the landowners to cover the expenses. | Look for Government funding, educate land owners about soil erosion conservation techniques. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| When applying high density mulches the application labour requirements and costs will be higher | Distribute the mulch in strips, use lighter mulches, grind to remove the fine fibres or maybe try to reduce the application rate. It is also possible to use in-situ chopping tree machines or to use aerial application methods, such as helicopters to reduce the application costs. |
7. 参考和链接
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Prats S. A., Macdonald L.H., Monteiro M.S.V., Ferreira A.J.D., Coelho C.O.A., Keizer J.J.,
2012. Effectiveness of forest residue mulching in reducing post-fire runoff and erosion
in a pine and a eucalypt plantation in north-central Portugal. Geoderma 191, 115-124.
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
Internet
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Shakesby R.A., Boakes D.J., Coelho C.O.A., Gonçalves A.J.B., Walsh R.P.D., 1996. Limiting
the soil degradational impacts of wildfire in pine and eucalyptus forests in Portugal.
Applied Geography 16, 337-335.
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
Internet
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Robichaud, P.R., Lewis, S.A., Ashmun, L.E., Wagenbrenner, J.W., Brown, R.E., 2013a.
Postfire mulching for runoff and erosion mitigation Part I: Effectiveness at reducing
hillslope erosion rates. Catena 105, 75–92.
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
Internet
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块