Agroforestry system [意大利]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Nicola Dal Ferro
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Fabian Ottiger
Sistema agroforestale su terreni agricoli
technologies_1230 - 意大利
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
SLM专业人员:
Morari Francesco
francesco.morari@unipd.it
University of Padova
Via 8 Febbraio 1848, 2, 35122 Padova PD, Italy
意大利
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
Preventing and Remediating degradation of soils in Europe through Land Care (EU-RECARE )有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
University of Padova (UNIPD) - 意大利1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
20/10/2014
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.5 请参阅有关SLM方法的问卷

Rural development programme in the Veneto region [意大利]
Developing rural areas in the Veneto region through sustainable land management policies
- 编制者: Nicola Dal Ferro
Carbon farming [意大利]
Managing land, water, plants and animals to meet the landscape restoration, climate change and food security.
- 编制者: Nicola Dal Ferro
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
Silvo-arable systems for production of annual crops on tree plots
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
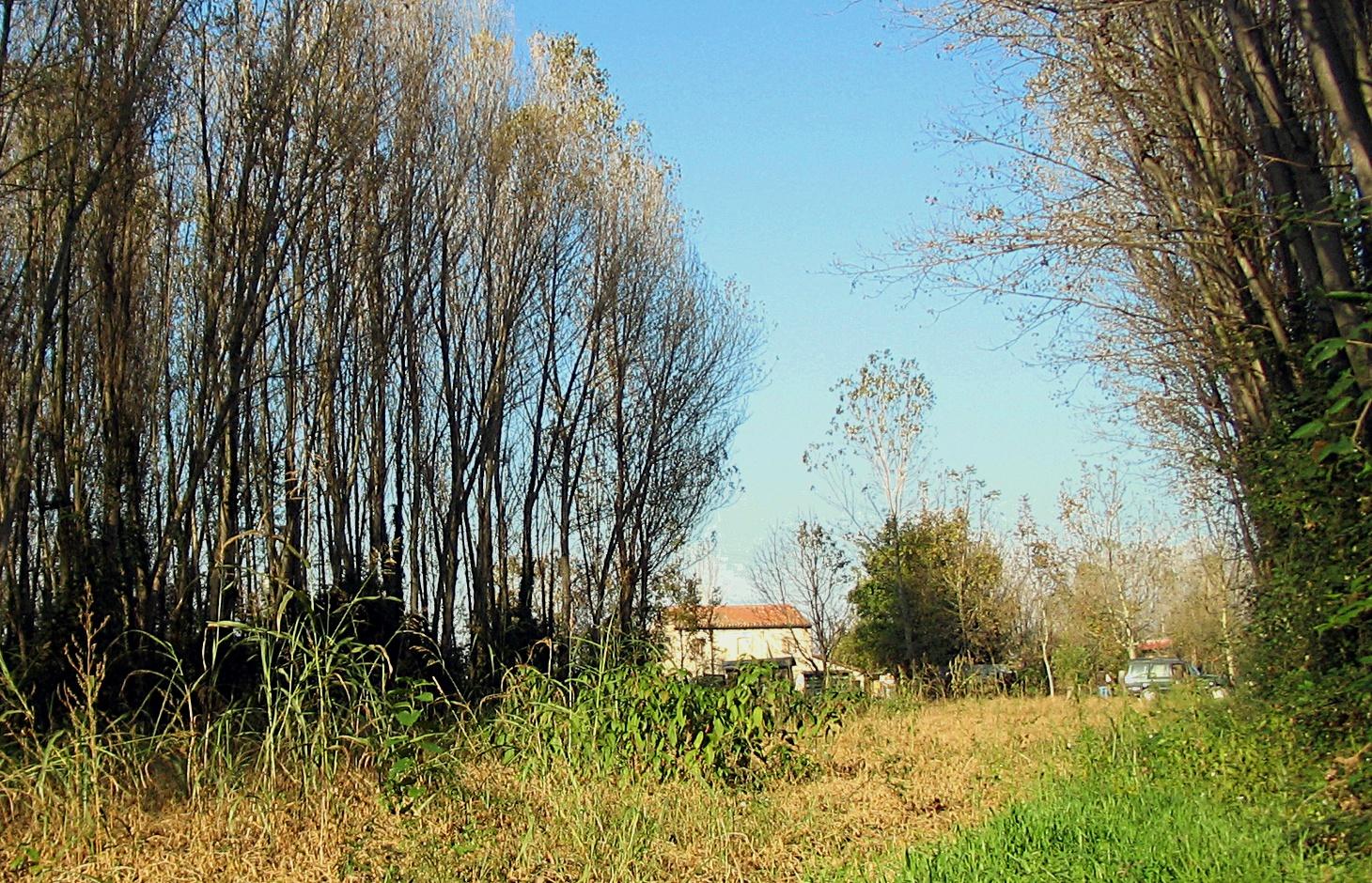
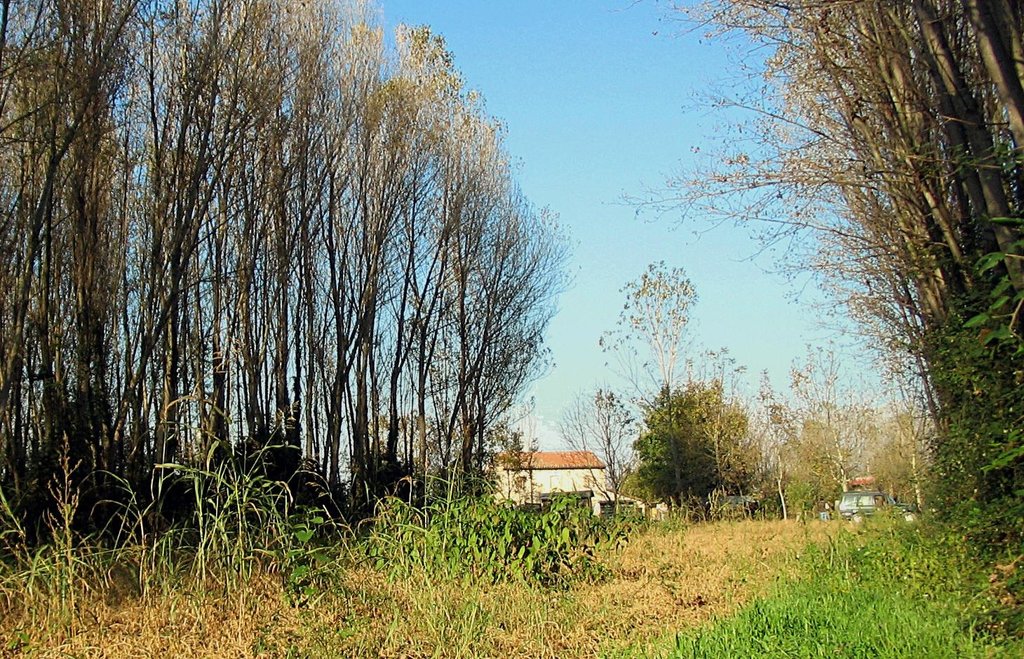
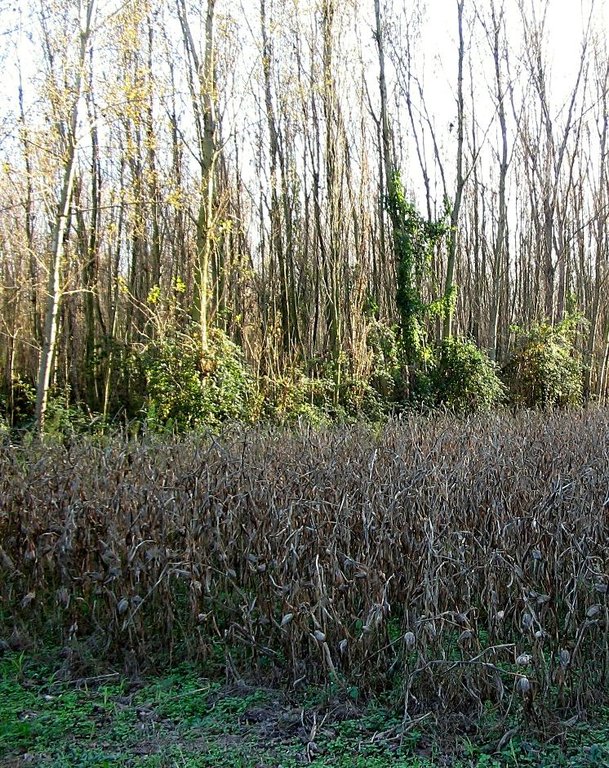
Agroforestry systems (AS) are the mixed cultivation of annual crops and trees in a single field. Historically, agroforestry has been used as a land management system that allowed the integration and diversification of productivity while maintaining the ecosystem biodiversity and diversifying farm landscape. Over the last fifty years the number of trees in agroecosystems in Italy was reduced of 75% due to the advent of intensive cropping systems and mechanisation, with significant changes to agriculture and landscape. In recent years, re-introduction of silvo-arable systems in the Veneto region have been supported as an agri-environmental measure of the Rural Development Programme (RDP) to improve sustainable land management.
Purpose of the Technology: Tree and crop production in the same area are compatible and combine environmental and economic benefits. As a result, ASs have been proposed to the farmers with the aim of reducing environmental impacts and energy inputs as well as improving biodiversity and agricultural landscape.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Agroforestry systems are adjusted to the needs of modern and sustainable agriculture and farmers who adopt this technology take advantage of higher ecosystem biodiversity, incomes and labour diversification, lower energy inputs and reinforcement of natural pest control. The systems are managed with low tree intensity (50-100 trees/ha) and large planting systems (up to 14 m in the row and 40 m inter-row) in order to simplify mechanisation of field practices, depending on machinery and cultivated crops.
Natural / human environment: Adopting agroforestry systems achieves several environmental benefits that have been widely demonstrated worldwide: regulation of nutrient cycling and adsorption of nonpoint source pollution (phytoremediation) thanks to the effect of deep rooting systems; reduction of soil surface erosion and sedimentation in rivers and lakes, improvement of micro-climate conditions, soil and ecosystem biodiversity. Reforestation of agroecosystems was recommended by Kyoto Protocol to mitigate global warming. Finally, agrisilviculture systems improve socio-cultural aspects as they contribute to differentiate and enrich the agricultural landscape.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
意大利
区域/州/省:
Italy
有关地点的进一步说明:
Veneto region
2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 不到10年前(最近)
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过项目/外部干预
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 保持/提高生物多样性
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

农田
- 一年一作
主要农作物(经济作物及粮食作物):
Major cash crop: Maize
Other crops: Wheat, soybean

混合(作物/放牧/树木),包括农林
- 农林业
注释:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Soils in the low Venetian plain of the Veneto region generally suffer from a loss of soil organic matter (SOM) that is strongly affected by their natural texture and climatic conditions. Moreover in the last 50 years high intensive monoculture practices and mechanisation implied a further decrease of SOM (estimated 0.02-0.58 t/ha/y of carbon lost), soil habitats and surface water quality.
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Mixed: Mf: Agroforestry
如果由于技术的实施而导致土地用途发生变化,则在技术实施前说明土地利的用途。:
Cropland: Ca: Annual cropping
3.3 有关土地利用的更多信息
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 混合雨水灌溉
注释:
Water supply: Also rainfed, full irrigation
每年的生长季节数:
- 1
具体说明:
Longest growing period in days: 210 Longest growing period from month to month: March to OctoberSecond longest growing period in days: 180
3.4 该技术所属的SLM组
- 农业林学
- 改良的地面/植被覆盖
3.5 技术传播
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果该技术均匀地分布在一个区域上,请注明覆盖的大致区域。:
- 1-10 平方千米
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

植物措施
- V1:乔木和灌木覆盖层

管理措施
- M2:改变管理/强度级别
注释:
Main measures: vegetative measures, management measures
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -linear
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

化学性土壤退化
- Cn:肥力下降和有机质含量下降(非侵蚀所致)

生物性退化
- Bh:栖息地丧失

水质恶化
- Hp:地表水水质下降
注释:
Main type of degradation addressed: Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content, Bh: loss of habitats, Hp: decline of surface water quality
Main causes of degradation: soil management (lack of organic input with fertilizations), population pressure (High demand for agricultural products and competition for land in densely populated area)
Secondary causes of degradation: crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (crop monoculture instead of crop rotation), deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (mechanisation)
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 防止土地退化
- 减少土地退化
注释:
Main goals: prevention of land degradation
Secondary goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
作者:
Nicola Dal Ferro
4.2 技术规范/技术图纸说明
Agroforestry systems are mainly characterised by low tree density, with crops growing within tree belts 25-50 m wide.
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides), improvement of water quality, buffering / filtering water, sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting
Secondary technical functions: control of raindrop splash, control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, control of concentrated runoff: impede / retard, improvement of ground cover, increase of surface roughness, improvement of surface structure (crusting, sealing), increase in organic matter
Aligned: -linear
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 50-100
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 20-40
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 10
Trees/ shrubs species: poplar, oak, walnut etc.
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 0%
4.3 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
Euro €
注明美元与当地货币的汇率(如相关):1美元=:
0.8
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
21.00
4.4 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | System planning | 植物性的 | |
| 2. | Tillage and soil preparation | 植物性的 | |
| 3. | Tree planting and fertilisation | 植物性的 | |
| 4. | Mulching | 植物性的 |
4.5 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | System planning | ha | 1.0 | 102.0 | 102.0 | |
| 劳动力 | Tillage and soil preparation | ha | 1.0 | 102.0 | 102.0 | |
| 劳动力 | Tree planting and fertilisation | ha | 1.0 | 127.0 | 127.0 | |
| 劳动力 | Mulching | ha | 1.0 | 1220.0 | 1220.0 | |
| 设备 | Tillage and soil preparation | ha | 1.0 | 254.0 | 254.0 | |
| 植物材料 | Seedlings | ha | 1.0 | 175.0 | 175.0 | |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | Fertilizer | ha | 1.0 | 21.0 | 21.0 | |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 2001.0 | |||||
4.6 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Pruning, replanting, additional irrigation, weed control | 植物性的 | |
| 2. | Crop management | 植物性的 |
4.7 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Pruning, replanting, additional irrigation, weed control | ha | 1.0 | 250.0 | 250.0 | |
| 劳动力 | Crop management | ha | 1.0 | 850.0 | 850.0 | |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 1100.0 | |||||
4.8 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
The establishment of SLT is the most determinate factor affecting the costs, particularly soil preparation and mulching.
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
农业气候带
- 半湿润
Thermal climate class: temperate
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
关于地形的注释和进一步规范:
Altitudinal zone: 0-100 m a.s.l. (the low Venetian does not exceed 50 m above sea level)
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 粗粒/轻(砂质)
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 中(1-3%)
- 低(<1%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Soil fertility is low-medium
Soil drainage/infiltration is medium
Soil water storage capacity is medium
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
< 5米
地表水的可用性:
好
水质(未处理):
良好饮用水
关于水质和水量的注释和进一步规范:
Ground water table: <5m (The area surrounding the Venice lagoon (1240 km2) is even below the sea level (down to -2 m) and currently cultivated due to land reclamation. As a result water table is kept artificially low)
Water quality (untreated) is good drinking water (groundwater) or for agricultural use only (surface water can be used for agricultural purposes but not as drinking water)
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 中等
关于生物多样性的注释和进一步规范:
High population density, infrastructures and intensive agriculture practices affect the state of biodiversity.
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
生产系统的市场定位:
- 商业/市场
非农收入:
- 低于全部收入的10%
相对财富水平:
- 平均水平
个人或集体:
- 个人/家庭
机械化水平:
- 机械化/电动
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: 200-500 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 0.5% - 1%
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者拥有或租用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 中等规模的
注释:
Average area of land owned or leased by land users applying the Technology: Also 50-100 ha, 100-500 ha
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地使用权:
- 个人
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
木材生产
产品多样性
收入和成本
农业投入费用
收入来源的多样性
社会文化影响
健康状况
文化机会
娱乐机会
SLM/土地退化知识
Improved livelihoods and human well-being
注释/具体说明:
The technology is recognized by the EU CAP as a system of high ecological and social value due to increased biodiversity, improved rural landscape and environmental quality. However, the technology has been little adopted in Veneto region due to scarce technical expertise and very few fundings, resulting in a limited improvement of livelihoods and human well-being.
生态影响
水循环/径流
水质
地表径流
土壤
土壤覆盖层
养分循环/补给
土壤有机物/地下C
生物多样性:植被、动物
生物量/地上C
植物多样性
栖息地多样性
减少气候和灾害风险
碳和温室气体的排放
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
地下水/河流污染
缓冲/过滤能力
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 气候变化/极端天气的类型 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年温度 | 增加 | 好 |
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气候灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 干旱 | 不好 |
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
轻度消极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
消极
长期回报:
稍微积极
6.5 技术采用
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发地采用该技术,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 10-50%
注释:
80% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
20% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
improves water and soil quality How can they be sustained / enhanced? spread over larger territories and integration with other sustainable land practices (e.g. conservation agriculture, cover crops etc.) |
|
enhances agro-ecosystem biodiversity How can they be sustained / enhanced? improve connecting corridors between habitats |
|
income generation and diversification opportunity How can they be sustained / enhanced? stimulation of alternative markets |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Increases difficulties in handling machinery | Improvement of technical knowledge and planning |
| Increases establishment costs | Increase funding for implementation |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| excessive shading for crop production | lower tree density and enlarge inter-row; improve system design |
| high investment and income reduction in the short-term | economic support |
| low efficacy due to short-term cycles of the technology and replacement with traditional cropping systems | improve the effectiveness of subsidies to keep the technology in the log-term |
7. 参考和链接
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Agroforestazione - Produrre con gli alberi per un'agricoltura differente, Veneto Agricoltura, 2011.
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Programma di sviluppo rurale per il veneto 2007-2013, Regione Veneto, 2007. Dipartimento Agricoltura e Sviluppo Rurale.
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接

Rural development programme in the Veneto region [意大利]
Developing rural areas in the Veneto region through sustainable land management policies
- 编制者: Nicola Dal Ferro

Carbon farming [意大利]
Managing land, water, plants and animals to meet the landscape restoration, climate change and food security.
- 编制者: Nicola Dal Ferro
模块
无模块




