Intercropping of grass and corn to increase soil organic matter [荷兰]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Jason Stuka
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Fabian Ottiger
Gras onderzaai bij mais (NL)
technologies_1248 - 荷兰
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
SLM专业人员:
Smit Annemieke
Wageningen Environmental Research (Alterra)
Droevendaalsesteeg 4, 6708 PB Wageningen
荷兰
SLM专业人员:
Leever Henk
HOEDuurzaam
荷兰
SLM专业人员:
Rienks Willem
Rom3D
Dorshorst 1a 7217 PH Harfsen
荷兰
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
Preventing and Remediating degradation of soils in Europe through Land Care (EU-RECARE )有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Provincie Gelderland - 荷兰有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Hoe Duurzaam - 荷兰有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Ministerie van Economische Zaken - 荷兰有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Vitens - Laat Water Voor Je Werken - 荷兰有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Wageningen Environmental Research (Alterra) - 荷兰1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
20/03/2015
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.5 请参阅有关SLM方法的问卷

Regional process, social innovation [荷兰]
Social innovation for sustained soil organic matter, clean drinking water and sustainable crop production
- 编制者: Simone Verzandvoort
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
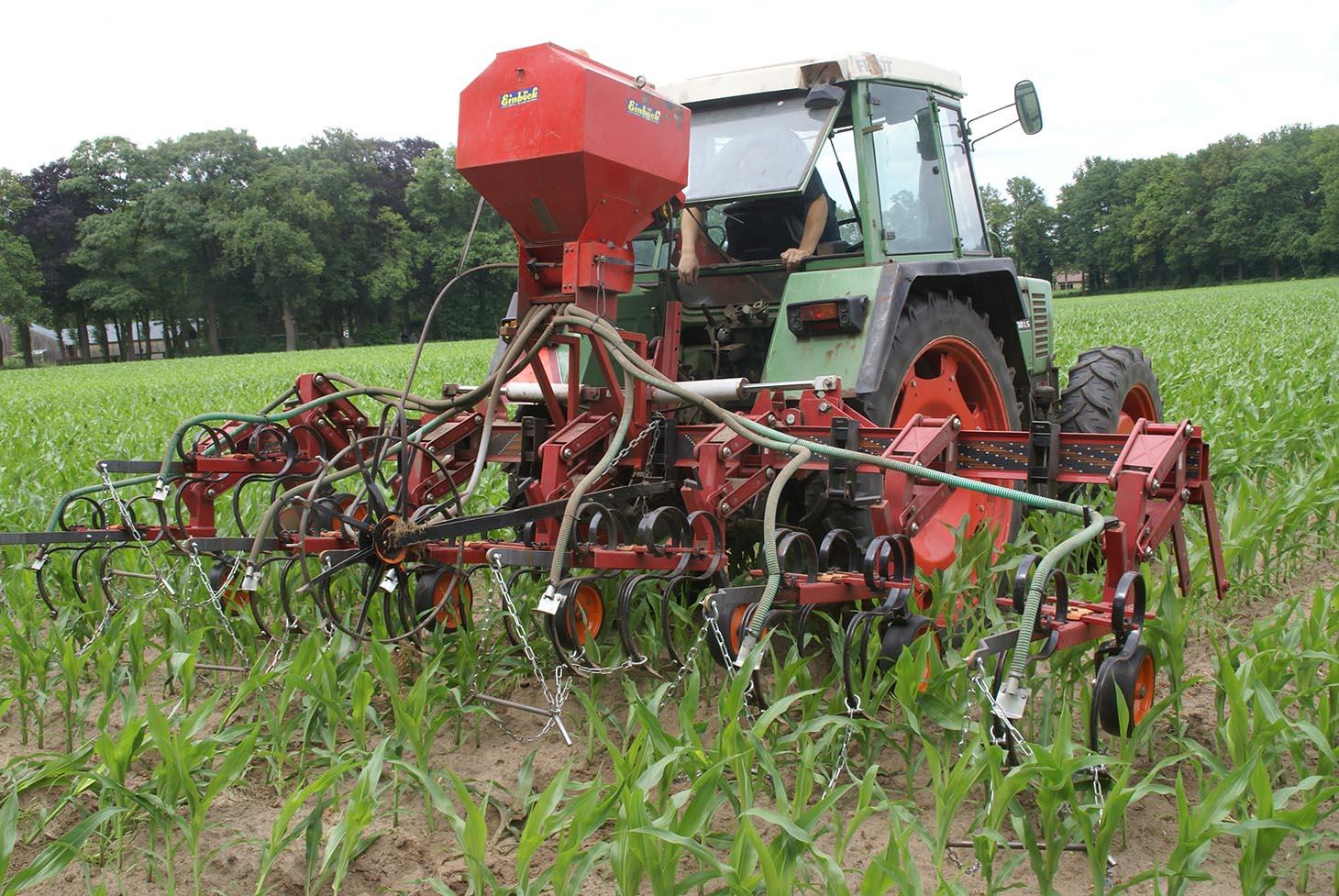
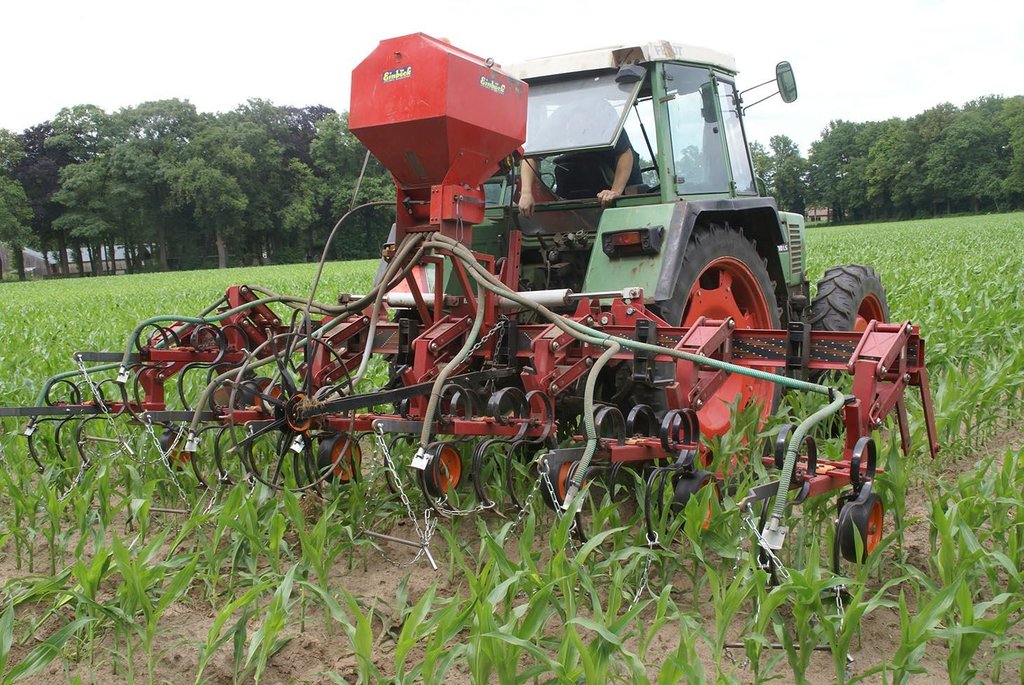
Grass intercropping on corn fields
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
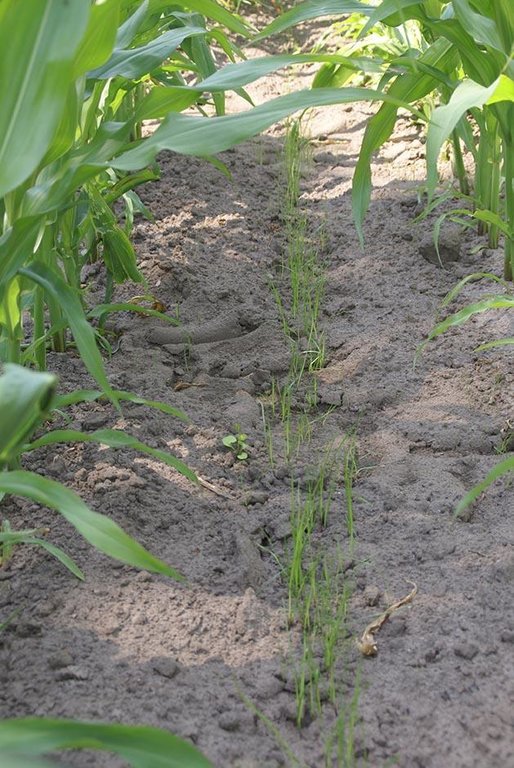
Italian rye grass is sown when the corn has grown to knee height, and has not yet developed a closed cover. The grass is plowed into the soil several months after the harvest of the corn crop.
Purpose of the Technology: The purpose of the technology is to enable a good growth of the catch crop (the grass) and to increase root biomass production after the corn is harvested. This will contribute to the organic mater content of the soil, and reduce the leaching of nitrogen and potassium. After underplowing of the grass, the nitrogen and potassium will be released to the soil and become available for the next crop.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: When corn is well established (between 30-60 cm height), grass is seeded between rows. A special seeder is required. Tractor must have tires that fit between corn rows. Grass germinates, but growth is reduced as corn matures and creates shade. When corn is harvested, grass continues to grow as a winter catch-crop. Some years, grass is sprayed with fertiliser to increase mineralisation. Grass is cultivated into the soil in early spring.
Natural / human environment: Multi-functional rural area with land use for agriculture, recreation, residence and nature. Dairy agriculture in small farms for Dutch standards combined with arable cropping. High livestock density.
Undulating landscape with cover sands and clayey and loamy sediments. Podzols and cambisols developed in sandy substrate. The area also has patches of anthroposols, soils enriched in Medieval times with manure and organic residues. Phosphate and nitrogen levels in these soils are in general high.
Mean monthly temperature varies between 2 and 17°C. The long-term mean annual precipitation is between 800 and 825 mm, with the lowest amounts in spring, and the highest in autumn. The long-term average annual precipitation deficit is between 200 and 240 mm.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
荷兰
区域/州/省:
Gelderland
有关地点的进一步说明:
Haarlo - Oude Eibergen
注释:
Boundary points of the Technology area: Left: 52.098865, 6.563182
Right: 52.095031, 6.634282
Top: 52.111764, 6.589390
Bottom: 52.081761, 6.620607
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 不到10年前(最近)
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过土地使用者的创新
注释(项目类型等):
The land users's initiative was through the application for the project Healthy Sand by a group of farmers. During the Gezond Zand Project the group organised themselves in the Foundation HOEDuurzaam. The project ran from 2012-2014 and is followed by the new project BodemRijk.
The external initiative was from the drinking water company Vitens and the Province of Gelderland in the same period.
3. SLM技术的分类
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

农田
- 一年一作
主要农作物(经济作物及粮食作物):
Major cash crop: potatoes
Major food crop: Maize, cereals
Other: Grass
注释:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): The main soil threat in the Olden-Eibergen Case Study area is the gradual decline of soil organic matter stocks. On average, agricultural fields have lost up till 5.4% of organic matter in the last 10 years according to farmers. This threatens the agricultural potential of the soil as well as its water holding capacity, and its potential to buffer leaching of nutrients and pesticides. In the long term, agricultural productivity will fall, costs of agricultural inputs such as manure, fertilizers, pesticides and irrigation will increase and the additional costs for cleaning drinking water withdrawn from ground water will rise.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): The group of farmers in the area experience declining crop production, problems with too dry and too wet soils, and decreasing organic matter content in soil due to long-term monocultures of maize, the use of pig manure and legislation forcing farmers to process or export manure from their farms.
Grazingland comments: Nothing filled in in this section, since the technology applies specifically to maize cropping.
Type of grazing system comments: Nothing filled in in this section, since the technology applies specifically to maize cropping.
3.3 有关土地利用的更多信息
注释:
Water supply: rainfed, mixed rainfed - irrigated
每年的生长季节数:
- 1
具体说明:
Longest growing period in days: 250Longest growing period from month to month: March - November
3.4 该技术所属的SLM组
- Intercropping
3.5 技术传播
注释:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.94 m2.
94 ha over 32 fields. 20 farmers applied this technology.
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

农艺措施
- A1:植被和土壤覆盖层
- A2:有机质/土壤肥力

植物措施
- V1:乔木和灌木覆盖层
注释:
Main measures: agronomic measures
Type of agronomic measures: cover cropping, green manure, rotations / fallows
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -linear
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

化学性土壤退化
- Cn:肥力下降和有机质含量下降(非侵蚀所致)

物理性土壤退化
- Pc:压实

水质恶化
- Hq:地下水水质下降
注释:
Main type of degradation addressed: Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Pc: compaction, Hq: decline of groundwater quality
Main causes of degradation: soil management (ploughing for renewal of grassland or rotation to arable cropping), governance / institutional (Stricter manure legislation since January 2014 deriving from the EU Nitrates Directive has forced farmers to process part of the manure from their farms on-farm, or to export it from their farms.)
Secondary causes of degradation: crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (long-term monoculture of maize and intensive cropping of seed potatoes)
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 防止土地退化
- 减少土地退化
注释:
Main goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
Secondary goals: prevention of land degradation
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
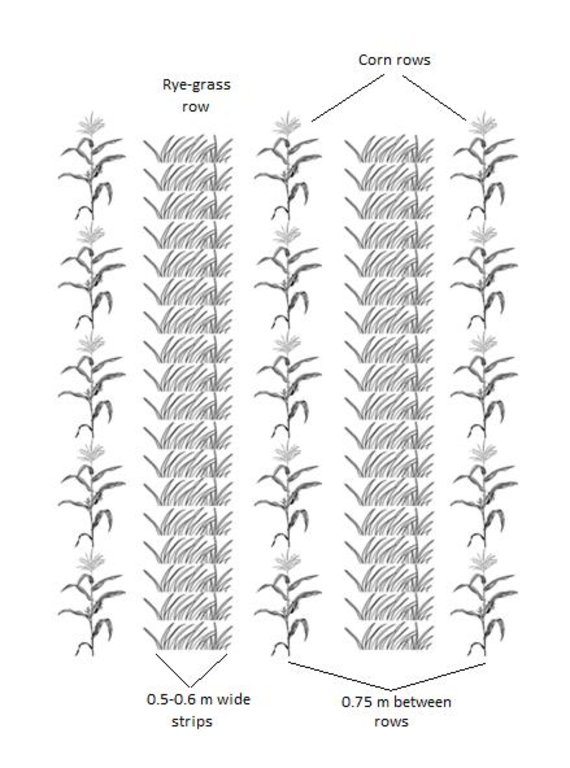
4.2 技术规范/技术图纸说明
After the corn crop is growing, a tractor with a seeder sows Italian Rye-grass seeds between the rows of corn. The grass seeds are sown in strips parallel to the corn rows. The corn rows are 0.75 metres apart. The grass strips are usually between 0.50 and 0.60 metres wide, but this is according to the farmer's preference. this means that a spacing of between 0.075 and 0.125 metres remains bare on each side of the grass strip, between the grass and the corn.
Location: Haarlo - Oude Eibergen. Gelderland
Date: April 8 2015
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Technical knowledge required for agricultural contractor: high (technical skills are required from an agricultural contractor with a special machine to sow the grass in the already standing maize crop.)
Main technical functions: increase in organic matter, increase of biomass (quantity)
Secondary technical functions: improvement of ground cover, improvement of topsoil structure (compaction), increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), increase / maintain water stored in soil, improvement of water quality, buffering / filtering water
Cover cropping
Material/ species: Italian rye-grass
Quantity/ density: 25 kg/ha
Remarks: Between corn rows width 0.075-0.125 m bare space.
Green manure
Material/ species: Italian rye-grass
Quantity/ density: 25 kg/ha
Remarks: Between corn rows width 0.075-0.125 m bare space.
Rotations / fallows
Remarks: The Italian rye grass is worked into the soil ca 5 months after the harvest of the maize.
Aligned: -linear
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): not applicable
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.75-1.25
Grass species: Italian rye grass
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): not applic%
4.3 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
Euro
注明美元与当地货币的汇率(如相关):1美元=:
0.94
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
255.70
4.4 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Buy a seeder | 农业学的 |
4.5 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 设备 | Seeder | Machine | 1.0 | 5327.05 | 5327.05 | |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 5327.05 | |||||
注释:
Duration of establishment phase: 0 month(s)
Life span of the seeder: 6 years
4.6 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Seeding | 农业学的 | After corn is established |
| 2. | Fertilizer | 农业学的 | Every other year |
4.7 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 设备 | Machine use | ha | 1.0 | 117.2 | 117.2 | 100.0 |
| 植物材料 | Seeds | ha | 1.0 | 42.62 | 42.62 | 100.0 |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | Fertilizer Hired(machine+fert) | ha | 1.0 | 9.06 | 9.06 | 100.0 |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 168.88 | |||||
注释:
Machinery/ tools: Specific tractor to perform grass undersowing (seeder), tractor, sprayer/applicator
To seed the Rye-grass strips between the corn rows. Done a few months after the corn is seeded.
4.8 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
New equipment (Seeder) - The seeding and fertilizer applications are hired from a company. The company purchases the new equipment to seed between the corn rows.
The greatest determinate factor to the land users are then the cost of hired machine hours.
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
有关降雨的规范/注释:
182 days of precipitation annually
农业气候带
- 半湿润
Thermal climate class: temperate. Mean monthly temperatures vary between 2-17 °C (LGP 240-269 days, mean monthly temperatures vary between 2-17 °C)
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
关于地形的注释和进一步规范:
Altitudinal zone: 0-100 m a.s.l. (up to 45 metres a.s.l.)
Slopes on average: Flat and gentle (Only incidental)
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 粗粒/轻(砂质)
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 高(>3%)
- 中(1-3%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Soil depth on average: Deep (A and B horizons up till 40 cm in Gleyic Podzols and Umbric Gleysols (ca 75% of the area) Hardly any soil organic matter below 15 cm. Rooting depth is up to 80 cm) and very deep (Deep topsoils rich in organic matter in the Fimic Anthrosols (12% of the area))
Soil texture is coarse/light (Most soils have a sandy texture due to the substrate consisting of cover sands) and medium (Soils in former creek valleys contain loam (Umbric Gleysols))
Soil fertility is low (most soils have a low fertility due to the sandy substrate (specifically the Gleyic Podzols, ca 40% of the area)) or very high (in Fimic Anthrosols originated due to application of farmyard manure since medieval times (12% of the area))
Topsoil organic matter is medium-high (The purpose of the pilot project is to increase soil organic matter)
Soil drainage/infiltration is good (deep ground water table (H > 40-80 cm; L>120 cm) in the sandy soils on thick substrate of cover sands (in 65% of the area)) and medium (shallow groundwater tables in the Umbric Gleysols (35% of the area))
Soil water storage capacity is very high (in the Fimic Anthrosols with high SOM in the topsoil) and medium (in the other soils, varying with the soil organic matter content)
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
< 5米
地表水的可用性:
中等
水质(未处理):
不良饮用水(需要处理)
关于水质和水量的注释和进一步规范:
Ground water table is <5m (in all soil types the highest level of the groundwater table during the year is <140 cm below the soil surface. The lowest level can be lower than 120 cm)
Availability of surface water is medium (from small rivers (De Berkel) and creeks)
Water quality (untreated) is poor drinking water (treatement required - levels of the pesticides Bentazon, and MCPP in the groundwater have incidentally exceeded the norms for drinking water production between 1985 and 2009.)
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 中等
关于生物多样性的注释和进一步规范:
Soil biodiversity is high in the Fimic Anthrosols.
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
生产系统的市场定位:
- 混合(生计/商业
非农收入:
- 低于全部收入的10%
相对财富水平:
- 平均水平
个人或集体:
- 个人/家庭
机械化水平:
- 机械化/电动
性别:
- 男人
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Difference in the involvement of women and men: Most outdoor farm operations are completed by men.
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: negative
100% of the land users are average wealthy and own 100% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: Some farmers are contractual workers. Wives of farmers often have a job, e.g. at the municipality, craft work. No B&B activities or educational services.
Market orientation: Mixed (Maize is completely used to feed cows (max 20% of the area is allowed under maize); other arable crops are sold to the market. Dairy production is commercial.)
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者拥有或租用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 中等规模的
注释:
15-50 ha 6 land owners (source: geoinformation from the project gezpnd Zand)
50-100 15 land owners (source: geoinformation from the project gezpnd Zand)
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 个人,有命名
土地使用权:
- 租赁
- 个人
注释:
All agriculture land is owned or rented by individual farmers. Some farmers lease their land to other farmers. Leased land is less well managed, resulting in lower organic matter contents. Investments in SLM would lead to a higher renting fee, or the land owner taking the land back in exploitation.
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
注释/具体说明:
Expected increase of maize production: to 6-7 tonnes/ha. Not proven yet.
Possible competition between crop and grass. Not shown yet.
生产故障风险
注释/具体说明:
Expected. Not proven yet.
水资源可用性和质量
灌溉用水需求
注释/具体说明:
Only for farmers with fields at higher elevations and drier soils.
收入和成本
工作量
注释/具体说明:
Saves seeding winter crop in autumn.
Added planning, but work is hired.
Undersowing of grass in the standing maize crops requires specific skills.
社会文化影响
社区机构
注释/具体说明:
Created farmer's foundation.
SLM/土地退化知识
注释/具体说明:
Farmers understanding ecological impacts of farming practices and organic matter in soils.
冲突缓解
注释/具体说明:
Farmers collaborating with water company.
Improved livelihoods and human well-being
注释/具体说明:
Dairy farmers have learned more about the importance of soil organic matter for their production systems, and about the consequences of soil management on soil organic matter and other aspects of soil health. This learning was brought by the exchange of knowledge between farmers and experts, and between farmers themselves. Farmers also profited from services provided to them by the farmers' foundations: shared investments (e.g. in the manure separator) and support in the application for subsidies to finance the SLM measure.
生态影响
水循环/径流
水量
注释/具体说明:
Insignificantly more water transpiration.
水质
注释/具体说明:
Expected. Not proven yet.
地表径流
注释/具体说明:
Expected. Not proven yet. Little to no slope.
多余水的排放
注释/具体说明:
Expected. Not proven yet.
地下水位/含水层
注释/具体说明:
Insignificantly more water transpiration.
土壤
土壤水分
注释/具体说明:
Expected. Not proven yet. Claimed by some farmers already.
土壤覆盖层
注释/具体说明:
Not measured but observed on photographs.
土壤压实
养分循环/补给
注释/具体说明:
Expected. Not proven yet.
土壤有机物/地下C
注释/具体说明:
Expected. Not proven yet.
生物多样性:植被、动物
生物量/地上C
注释/具体说明:
Not measured but observed on photographs.
植物多样性
有益物种
栖息地多样性
注释/具体说明:
Expected. Not proven yet.
害虫/疾病控制
注释/具体说明:
Possibly. Not proven.
减少气候和灾害风险
碳和温室气体的排放
注释/具体说明:
Expected. Not proven yet.
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
下游洪水
注释/具体说明:
Expected. Not proven yet.
地下水/河流污染
注释/具体说明:
Expected. Not proven yet.
缓冲/过滤能力
注释/具体说明:
Expected. Not proven yet.
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 气候变化/极端天气的类型 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年温度 | 增加 | 好 |
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气象灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 局地暴雨 | 好 |
气候灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 干旱 | 好 |
其他气候相关的后果
其他气候相关的后果
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 缩短生长期 | 好 |
注释:
No modifications to the technology in response to climate change.
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
中性/平衡
长期回报:
稍微积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
消极
长期回报:
中性/平衡
注释:
Farmers are subsidized for seeding rye-grass between corn rows. If not subsidized, they are unlikely to invest. Few farmers have seen short-term benefits. Their willingness to invest is based on their understanding of the long-term benefits, brought about by the Approach developed in the Project Gezond Zand (and in RECARE).
6.5 技术采用
如若可行,进行量化(住户数量和/或覆盖面积):
20
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发地采用该技术,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 0-10%
注释:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
20 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
increases soil organic matter How can they be sustained / enhanced? annual application of the measure; subsidy to execute the measure |
|
increases maize crop yield in the long term How can they be sustained / enhanced? annual application of the measure |
| reduces leaching of nitrogen, potassium and pesticides to the groundwater |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
increases soil organic matter How can they be sustained / enhanced? annual application of the measure; subsidy to execute the measure |
| increases available soil moisture |
| reduces leaching of nitrogen, potassium and pesticides to the groundwater |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Uncertainty of the success or positive effect of the measure. | |
| Uncertainty of negative effects to the crop. | |
| Uncertainty of competition between grass and crop for nutrients and moisture. | |
| Concerns about cost and labour | |
| Uncertainty of hindrance from legislation. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| technology requires hiring of skilled labour and machinery, which is not viable without subsidy in the short term | provide subsidy in the first 3-5 years of implementation |
7. 参考和链接
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
RECARE_WP3 Report: CS_11_Ouden-Eibergen_v2Annemieke Smit and Simone Verzandvoort2014
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
Freeannemieke.smit@wur.nl
7.3 链接到网络上可用的相关信息
标题/说明:
Gezond Zand: Met een verbeterde bodemkwaliteit naar een betere waterkwaliteit Haarloseveld en Olden EibergenBy Willem Rienks and Henk Leever2014
URL:
Freehttp://www.hoeduurzaam.nl/images/gallery/nieuws/Brochure/BrochureHoeduurzaam%20Definitief.pdf
标题/说明:
Unravelling changes in soil fertility of agricultural land in The NetherlandsArjan Reijneveld2013
URL:
Wageningen University Library http://library.wur.nl/WebQuery/wda/2044057
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接

Regional process, social innovation [荷兰]
Social innovation for sustained soil organic matter, clean drinking water and sustainable crop production
- 编制者: Simone Verzandvoort
模块
无模块