Reforestation [西班牙]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Artemi Cerda
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Fabian Ottiger
Reforestación
technologies_1267 - 西班牙
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
SLM专业人员:
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Universidad de Valencia (Universidad de Valencia) - 西班牙1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
24/10/2014
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
Reforestation refers to establishment of forest on land that had recent tree cover.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
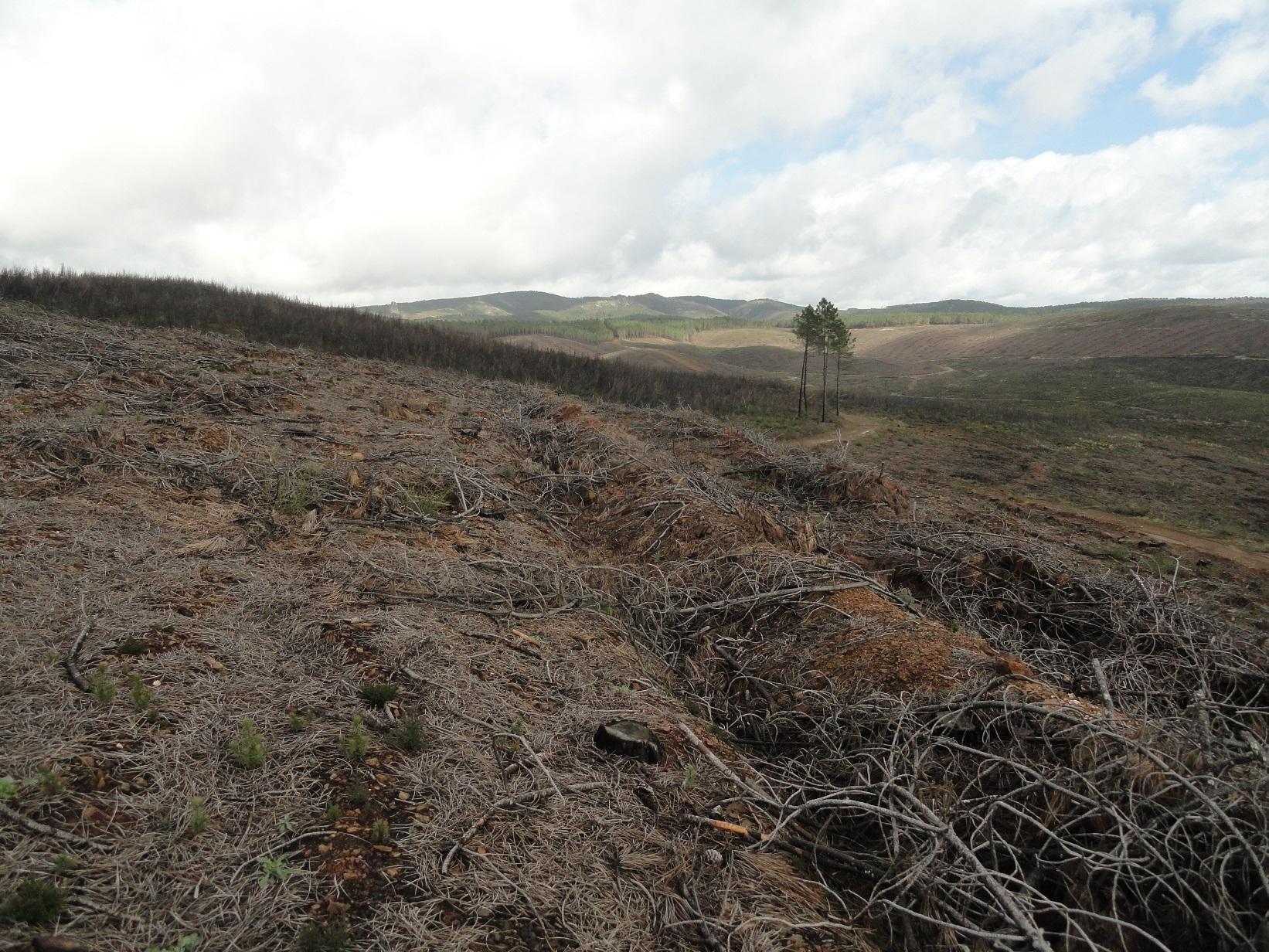
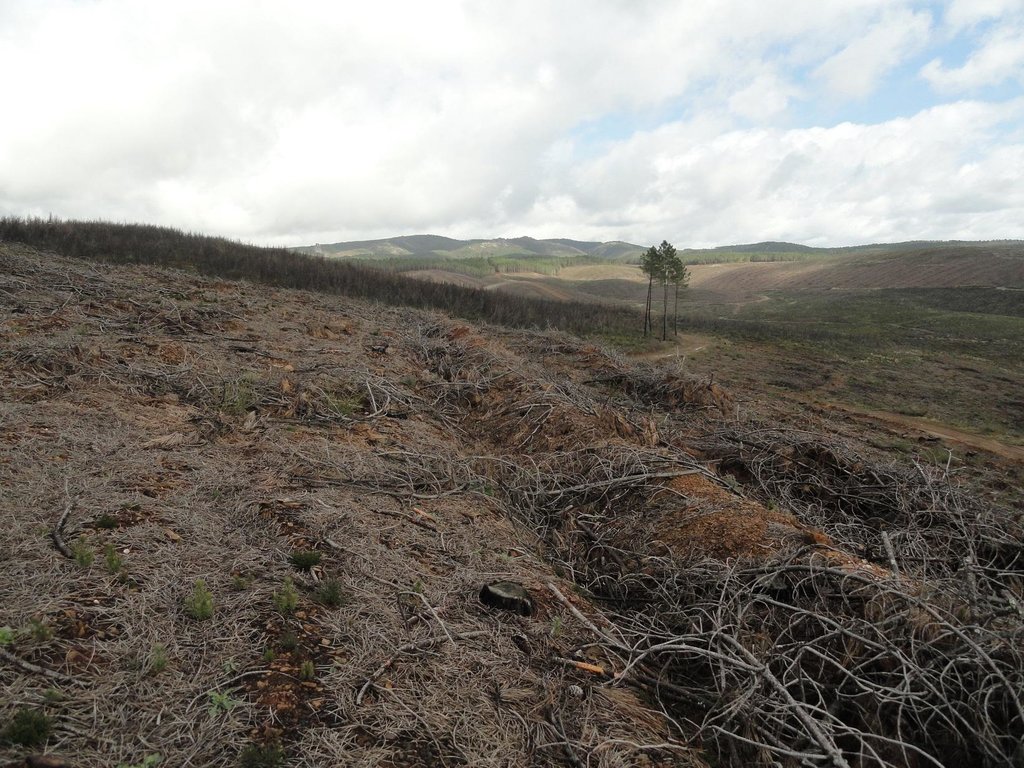
A wildfire is expected for summer 2015 in the Caroig mountain range. The area was afforested with Aleppo pines during the 20th century and nowadays the landscape is composed by mature Aleppo pines at different stages of development with shrub vegetation in the understorey.
Purpose of the Technology: The post-fire area is expected to be reforested with local shrubs species and Aleppo pines.
Perturbation by machinery when reforesting is expected to increase soil erosion.
The research team of the University of Valencia will implement an experiment based on the sediment fences technique to capture and measure post-fire soil losses in a reforested burned landscape.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Maintenance activity deals with the plantation scheme which includes man-power, machinery, access to remote areas and cost of plants, as main expenses.
Natural / human environment: The Aleppo pine trees in the region are typically planted as monoculture for wood production. The landscape reflects a long history of intense land management, with a mosaic of (semi-) natural and man-made agricultural (terraces) and afforested lands. Since the 1970´s, however, wildfires have increased dramatically in frequency and extent, driven primarily by socio-economic changes.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
西班牙
区域/州/省:
Spain
有关地点的进一步说明:
Valencia
Map
×3. SLM技术的分类
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

森林/林地
注释:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): It is expected that after a wildfire runoff and soil erosion will increase, resulting in a decrease of on-site fertility and derived off-site effects such as loss of water quality, soil water storage, higher risk of flooding and damage to human life.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Loss of wood resources.
Plantation forestry: Aleppo pine plantations
Forest products and services: timber, fuelwood, fruits and nuts, grazing / browsing, other forest products / uses (honey, medical, etc.), nature conservation / protection, recreation / tourism, protection against natural hazards
3.3 有关土地利用的更多信息
具体说明:
Longest growing period in days: 180 Longest growing period from month to month: February to july
3.4 该技术所属的SLM组
- 天然和半天然森林管理
- 减少基于生态系统的灾害风险
3.5 技术传播
注释:
A wildfire is expected in the study area for summer 2015.
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

植物措施
- V1:乔木和灌木覆盖层

结构措施
- S3:分级沟渠、渠道、水道
注释:
Main measures: vegetative measures, structural measures
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -graded strips *<sup>3</sup>
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀

生物性退化
- Bc:植被覆盖的减少
注释:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Bc: reduction of vegetation cover
Main causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (forest fires), Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts), droughts, population pressure (depopulation)
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 修复/恢复严重退化的土地
注释:
Main goals: rehabilitation / reclamation of denuded land
Secondary goals: prevention of land degradation, mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
作者:
Gonzalez-Pelayo, O., University of Valencia. Dept. of Geography. Blasco Ibañez 28. 46010. Valencia. Spain
4.2 技术规范/技术图纸说明
Bench terraces construction promotes water and sediment deposition and reduces slope lenght.
Location: Valencia. Spain
Date: 02-02-2014
Secondary technical functions: reduction of slope angle, reduction of slope length
Aligned: -graded strips
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Trees/ shrubs species: Aleppo pine, quercus ilex, quercus coccifera, pistacia lentiscus, rosmarinus officinalis
Grass species: brachypodium retusum
Bund/ bank: graded
Vertical interval between structures (m): 10
Spacing between structures (m): 3
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.5
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 1
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 50
Construction material (earth): ripped soil surface by specialized machinery
4.8 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
Costs will be affected by slope angle, soil depth which reverts in manpower and specialized machinery.
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
有关降雨的规范/注释:
Mediterranean climate with concentred precipitation in february-may and september-december months. Drought from june to september
农业气候带
- 半湿润
- 半干旱
Thermal climate class: temperate (Transition zone between smi-arid and sub-humid)
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
关于地形的注释和进一步规范:
Landforms: Also footslopes
Altitudinal zone: 501-1000 m a.s.l. (650-700 metres above sea level)
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 高(>3%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Soil depth on average: Very shallow(Leptool) and shallow (Cambiosol)
Soil fertility is medium
Soil drainage/infiltration is medium
Soil water storage capacity is high
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
5-50米
地表水的可用性:
匮乏/没有
水质(未处理):
仅供农业使用(灌溉)
关于水质和水量的注释和进一步规范:
Availability of surface water: Poor/none (only when rainfalls)
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 中等
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者拥有或租用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
木材生产
社会文化影响
娱乐机会
生态影响
土壤
土壤流失
生物多样性:植被、动物
生物量/地上C
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
风力搬运沉积物
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气象灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 局地暴雨 | 不好 |
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
Local species and new tree plantations are seen as future local production. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Selecting local species. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
Reforestation with local species must to be done based on a previous assessment of the fire effects on environment. Removing burned logs and planting trees and shrubs with heavy machinery could lead the system to a degradation stage instead of decrease soil losses. How can they be sustained / enhanced? It could be enhanced by the evaluation and preselection of areas suitable to be reforested. |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Impacts of heavy machinery in a fragil post-fire environment. |
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块