Flood Irrigation for salinity control [阿曼]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Hamood Al-Hashmi
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: David Streiff
التحكم في الملوحة باستخدام ري بالغمر
technologies_1312 - 阿曼
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
SLM专业人员:
SLM专业人员:
SLM专业人员:
SLM专业人员:
SLM专业人员:
SLM专业人员:
AL Abri Fatima
MOAF
阿曼
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Test institution (TI) - 阿尔巴尼亚有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Sultan Qaboos University (SQU) - 阿曼1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
06/01/2016
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
Using saline ground water for controlling soil salinity
2.2 技术的详细说明
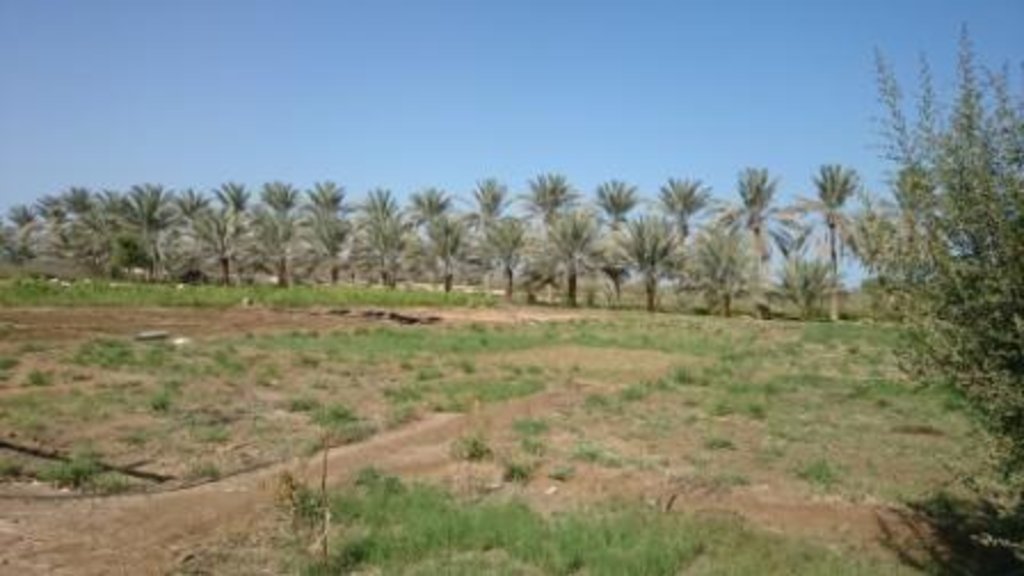
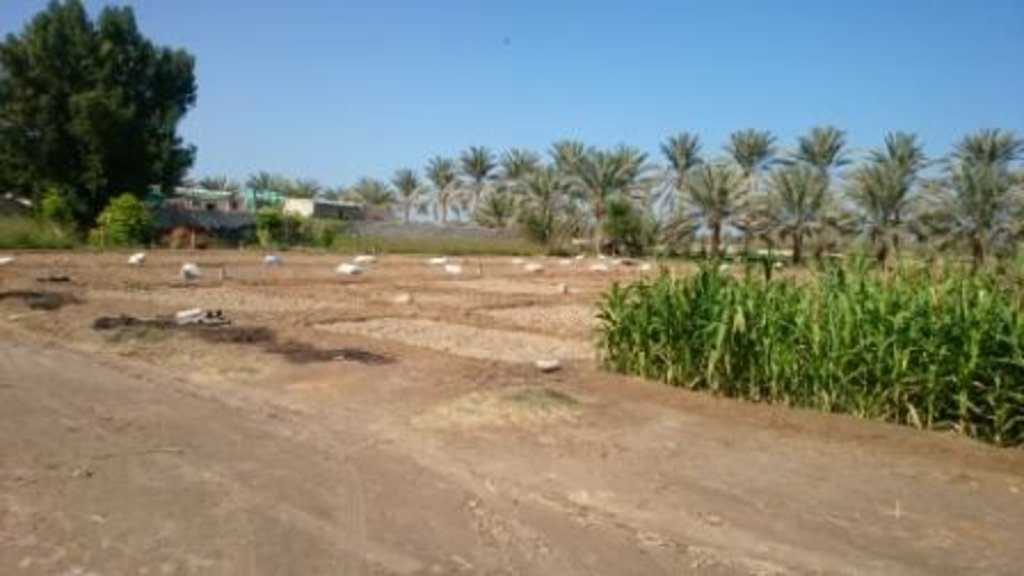
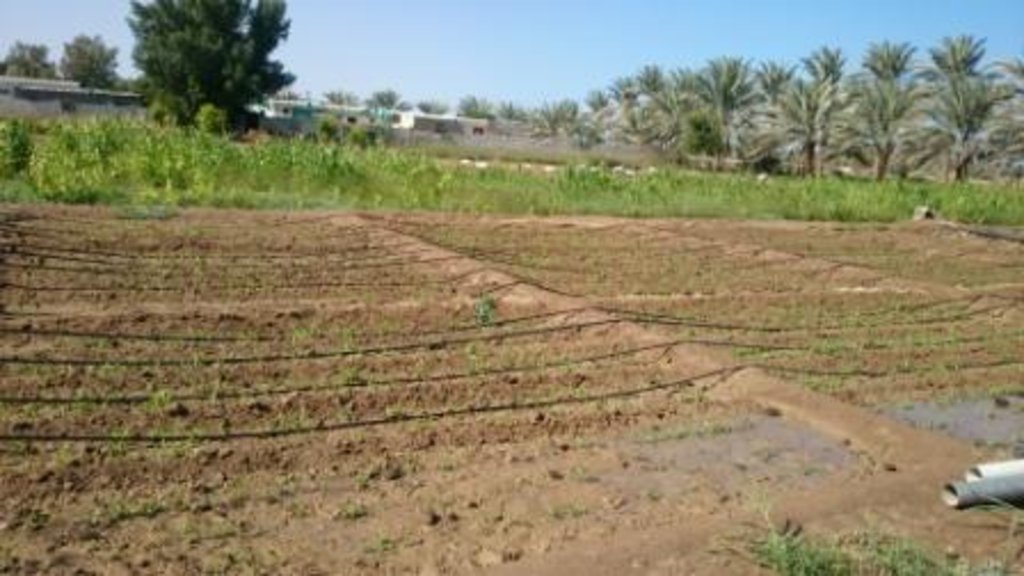
说明:
The farm total area is 7 fadan. The farm was established 40 years ago. Two labors are working in the farm. The income is low just covering the farm inputs.
Crops planted are alfalfa, Rhodes grass, corn, Mango, Pomegranate, Date Palm, Henna tree, Buckthorn tree
Purpose of the Technology: Using saline ground water through flood irrigation for leaching salt accumulation and soil sustainability.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Main inputs are labors, tractor, date palm processing unit and machinery. the maintenance is doing for pipes and machinery.
Natural / human environment: Well water having salinity of 7.13 ds/m is used to irrigate the land also leach the soil. This has resulted an accumulated salt in the soil. Due to increase in soil salinity the cropping pattern has changed drastically. Some years ago the farm was cultivated with a variety of crops but now is limited to growing perennial crops that are salt tolerant. Date palm are the most salt tolerant plants followed by Rhodes and Alfalfa. Mangoes are sensitive to salts compared with other fruit trees.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
阿曼
区域/州/省:
Al Batinah South
有关地点的进一步说明:
Al Massena/ Al Sheeba
Map
×3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 适应气候变化/极端天气及其影响
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

混合(作物/放牧/树木),包括农林
注释:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): soil and water salinity
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Mixed: Mp: Agro-pastoralism
如果由于技术的实施而导致土地用途发生变化,则在技术实施前说明土地利的用途。:
Cropland: Ca: Annual cropping
3.3 有关土地利用的更多信息
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 充分灌溉
具体说明:
Longest growing period in days: 60; Longest growing period from month to month: october to december; Second longest growing period in days: 45; Second longest growing period from month to month: february to mid of march
3.4 该技术所属的SLM组
- 灌溉管理(包括供水、排水)
3.5 技术传播
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果该技术均匀地分布在一个区域上,请注明覆盖的大致区域。:
- < 0.1 平方千米(10 公顷)
注释:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.0294 km2.
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

农艺措施
- A2:有机质/土壤肥力

植物措施
- V1:乔木和灌木覆盖层

管理措施
- M2:改变管理/强度级别
注释:
Secondary measures: vegetative measures, management measures
Type of agronomic measures: mixed cropping / intercropping, manure / compost / residues, mineral (inorganic) fertilizers
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -against wind, in blocks
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

水质恶化
- Hq:地下水水质下降
注释:
Main causes of degradation: droughts, population pressure
Secondary causes of degradation: soil management, crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub), deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires), over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use, urbanisation and infrastructure development
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 修复/恢复严重退化的土地
注释:
Secondary goals: prevention of land degradation, mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
4.2 技术规范/技术图纸说明
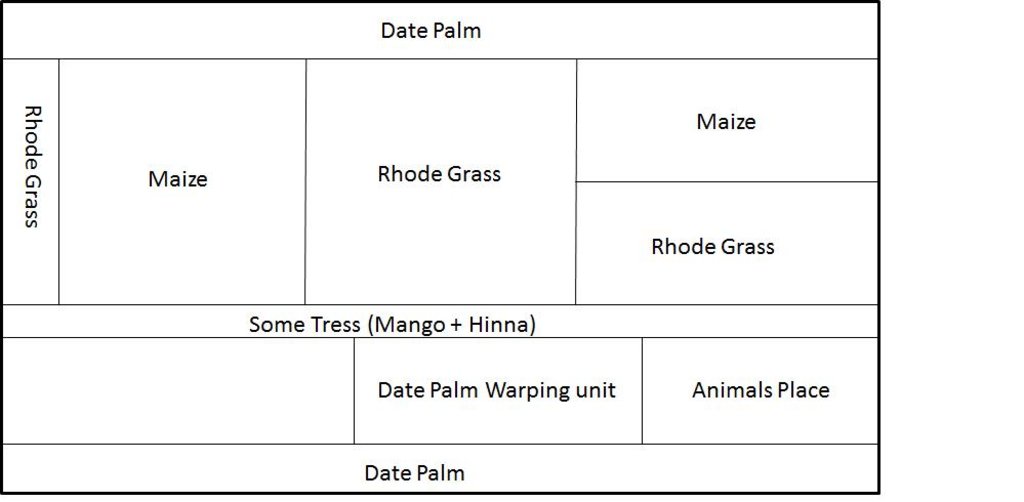
a farm of 7 feddan mainly grown date palm, rhode grass and ,maize. the farm also a small animal yard.
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Secondary technical functions: control of raindrop splash, control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap, control of concentrated runoff: impede / retard, control of concentrated runoff: drain / divert, improvement of ground cover, improvement of surface structure (crusting, sealing), increase in organic matter
Aligned: -against wind
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
In blocks
Vegetative material: G : grass
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 0-2%
Change of land use practices / intensity level: land used for planting Rhodes grass and seasonal crops (recently maize was grown).
4.3 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
Omani Rial
注明美元与当地货币的汇率(如相关):1美元=:
0.39
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
10.40
4.4 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | 结构性的 | all day around |
4.5 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Labour | ha | 1.0 | 120.0 | 120.0 | |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 120.0 | |||||
4.7 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Labour | ha | 1.0 | 120.0 | 120.0 | |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 120.0 | |||||
4.8 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
labour, seeds, fertilizer and electricty
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
农业气候带
- 干旱
Thermal climate class: subtropics
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 低(<1%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Soil fertility is very low
Soil drainage / infiltration is good
Soil water storage capacity is medium
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
> 50米
水质(未处理):
不可用
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 中等
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
生产系统的市场定位:
- 混合(生计/商业
非农收入:
- > 收入的50%
相对财富水平:
- 平均水平
个人或集体:
- 个人/家庭
性别:
- 男人
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Population density: 50-100 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 1% - 2%
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者拥有或租用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 小规模的
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 个人,未命名
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
饲料生产
生产故障风险
产品多样性
生产区域
土地管理
水资源可用性和质量
灌溉用水的可用性
灌溉用水的质量
灌溉用水需求
收入和成本
农业投入费用
农业收入
收入来源的多样性
工作量
社会文化影响
食品安全/自给自足
健康状况
娱乐机会
社区机构
SLM/土地退化知识
livelihood and human well-being
注释/具体说明:
The technology has improve livelihoods and human well-being of the owner and his family, increasing income of the farmer changed his family lifestyle and a farm become a place for family gathering.
生态影响
水循环/径流
水量
水质
多余水的排放
地下水位/含水层
蒸发
土壤
土壤水分
土壤覆盖层
土壤流失
土壤结壳/密封
养分循环/补给
盐度
土壤有机物/地下C
生物多样性:植被、动物
生物量/地上C
植物多样性
动物多样性
减少气候和灾害风险
干旱影响
碳和温室气体的排放
火灾风险
风速
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 气候变化/极端天气的类型 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年温度 | 增加 | 不好 |
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气象灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 局地暴雨 | 未知 |
| 局地风暴 | 未知 |
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
积极
注释:
due to many different type of crops and grass and trees in the farm, and having date processor increase profit and maintenance is low.
6.5 技术采用
- 大于 50%
如若可行,进行量化(住户数量和/或覆盖面积):
75 percent of stated area
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发地采用该技术,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 90-100%
注释:
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: farmers in this area strongly will like to do the same due to high water salinity, in order to wash down salinity, thus, they use flood irrigation technology.
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| easily implemented |
| costly effective and every farmer can implement it |
| resist to hard weather condition |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| in long term, ground water will be more deep | reduce over pumping |
| ground water salinity will increase | reduce over pumping |
| salt accumulation in the soil will increase | by using different soil conditioner, gypsum and soil mulch and organic manure |
| soil degradation will be the final result |
7. 参考和链接
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Oman Salinity Strategy, Ministry of Agriculture and Fisheries, 2012
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
South Batinah Integrated Study, Ministry of Agriculture and Fisheries, 1993
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Oman General Soil Map, Ministry of Agriculture and Fisheries. 1993
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块