Composting using Indigenous Microorganism (IMO) [菲律宾]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Philippine Overview of Conservation Approaches and Technologies
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Fabian Ottiger
technologies_1317 - 菲律宾
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
关键资源人
SLM专业人员:
Penaranda Melijoy
Department of Agriculture-Bureau of Soils and Water Management
5th Floor, Department of Agriculture Building, Elliptical Road, Quezon City, 1100 Metro Manila, Philippines
菲律宾
SLM专业人员:
Bernardino Renel
Department of Agriculture-Bureau of Soils and Water Management
5th Floor, Department of Agriculture Building, Elliptical Road, Quezon City, 1100 Metro Manila, Philippines
菲律宾
SLM专业人员:
Magno Beatriz
Department of Agriculture-Bureau of Soils and Water Management
5th Floor, Department of Agriculture Building, Elliptical Road, Quezon City, 1100 Metro Manila, Philippines
菲律宾
土地使用者:
Ambrocio Acosta
09179258499
Master's Garden
Lamtang - Pico Road, Sitio Piinalayok, Pugis, La Trinidad, Benguet, Philippines
菲律宾
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Bureau of Soils and Water Management (Bureau of Soils and Water Management) - 菲律宾有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
The Master's Garden - 菲律宾1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
15/09/2013
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
Composting is the natural process of decomposition of organic matter by microorganisms under controlled conditions.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
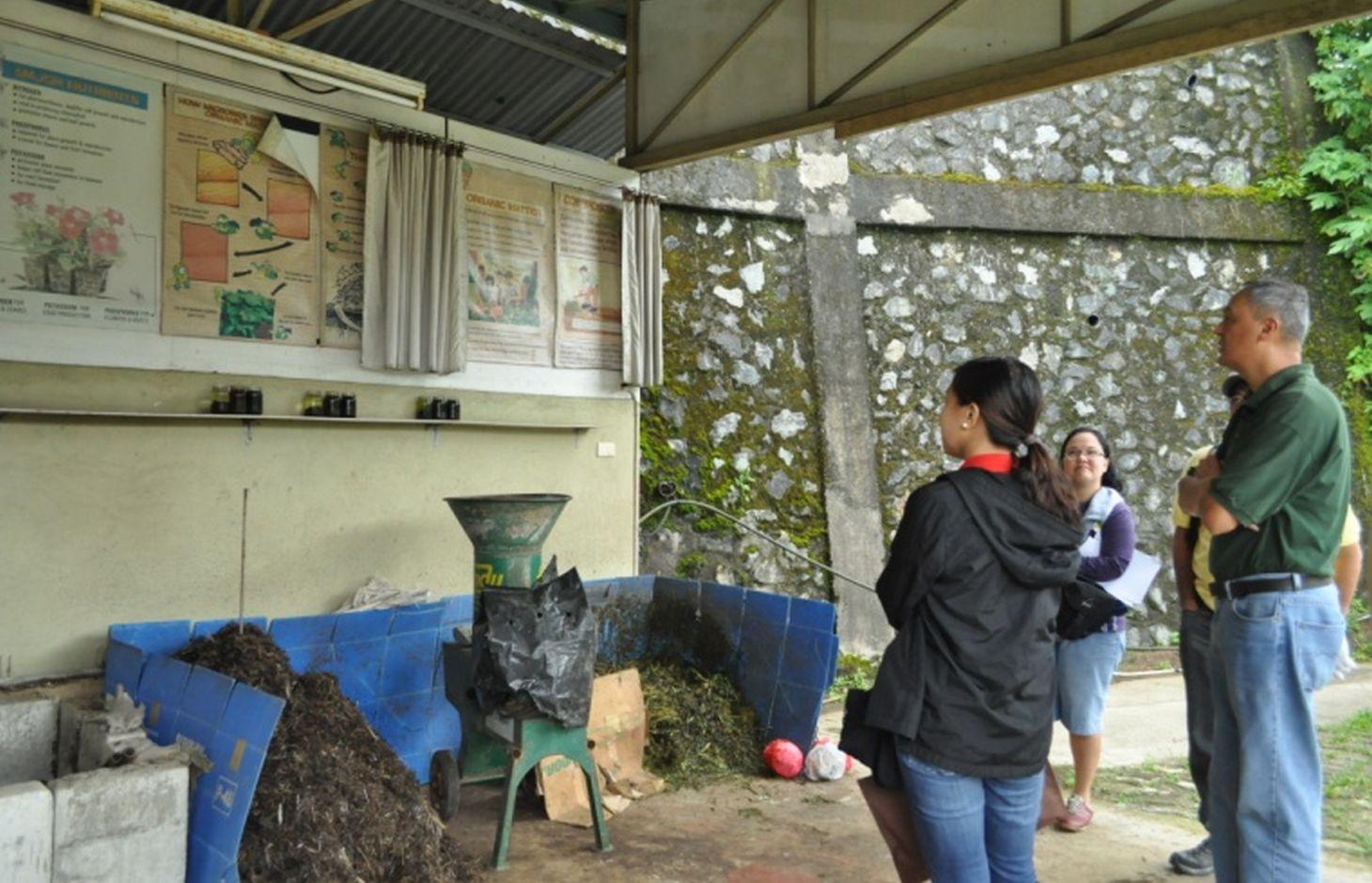
Composting is the decomposition of grass and weeds as fertilizer with the aid of indigenous microorganisms (IMO). This technology is practiced to produce compost used in the farm. Compost is a rich source of organic matter which improves soil tilth. Its decomposition slowly release available nutrients for plant uptake.Material used in the production are weeds and bio waste available in the farm which include Agetarum houstonianum, Dentella repens, Setaria palmifolia, Ipomea aquatica, Echinochloa crusgali, Helianthus annuus and Digitaria ciliaris. The compost is applied in the organic vegetable production of the farm. Vegetables planted include lettuce, herbs, kale and others that are used for garden salads.
Purpose of the Technology: The purpose of composting is to produce compost that is utilized as fertilizer for the soil. It is done to reduce the input cost of using chemical fertilizer and to avoid lasting harms to the soils and the environment (e.g. formation of impermeable layer "hardpan", affection of micro-organisms, and upsetting of pH).
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The initial step in making compost is gathering of raw materials such as weeds and grasses available in the farm. Then, these are shredded and sprayed with IMO to hasten the decomposition. IMO is produced by mixing one tablespoon of forest soil and one tablespoon of sugar/molasses in one liter of water. A portion of the mixture (250ml) is extracted and diluted in a 16 liter knapsack sprayer. The diluted mixture is sprayed to the shredded grasses/weeds and left to decompose for 14 days. For a 1 ton of shredded grass and weeds, 16L of diluted mixture is needed.
Natural / human environment: Master’s Garden of Mr. Ambrocio Acosta is located at Barangay Puguis, La Trinidad, Benguet. The province is under Type I climate by the Coronas system of classification with distinct wet and dry seasons with an average annual rainfall of 3,879 mm. The dry season is from November to April while the wet season is from May to October. The farm has an elevation of 1,342 meters above sea level with less than 40% slope. The farm was manually terraced and arranged into beds with UV treated plastic shed. The production system is managed and cultivated by Mr. Acosta and his two farm laborers.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
菲律宾
区域/州/省:
La Trinidad, Benguet
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 10-50年前
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过土地使用者的创新
注释(项目类型等):
Composting was practice since they started developed the farm on year 2000.
3. SLM技术的分类
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

农田
- 一年一作
- 多年一作(非木材)
主要农作物(经济作物及粮食作物):
Major cash crop annual cropping: lettuce, tomatoes, cucumber, sugar beets, salad pe
Major cash crop perennial (non woody) cropping: Thyme, mint, tarragon and chives
Major food crop annual cropping: lettuce and tomato
注释:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Since the farm has steep slope, soil erosion was prevalent resulting to low fertility of the soil
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Soil erosion caused by rainfall leaving them nothing but an exposed subsoil layer.
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Cropland: Ca: Annual cropping
如果由于技术的实施而导致土地用途发生变化,则在技术实施前说明土地利的用途。:
Grazing land: Ge: Extensive grazing land
3.3 有关土地利用的更多信息
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 充分灌溉
每年的生长季节数:
- 2
3.4 该技术所属的SLM组
- 土壤肥力综合管理
3.5 技术传播
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果该技术均匀地分布在一个区域上,请注明覆盖的大致区域。:
- < 0.1 平方千米(10 公顷)
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

农艺措施
- A2:有机质/土壤肥力
注释:
Main measures: agronomic measures
Type of agronomic measures: manure / compost / residues
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀

化学性土壤退化
- Cn:肥力下降和有机质含量下降(非侵蚀所致)
注释:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content
Main causes of degradation: Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts) (Average annual rainfall is 3,879 mm), other natural causes (avalanches, volcanic eruptions, mud flows, highly susceptible natural resources, extreme topography, etc.) specify (extreme topography(steep slope >40%)
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 减少土地退化
注释:
Main goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
4.2 技术规范/技术图纸说明
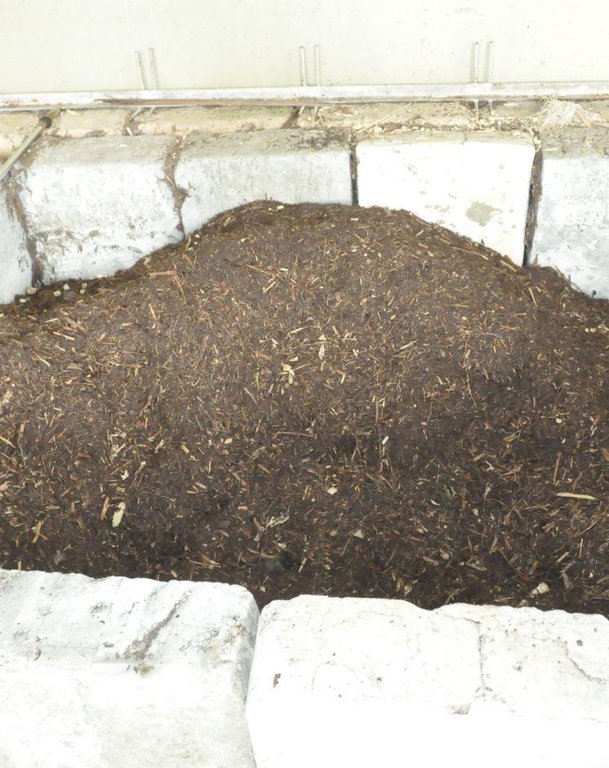
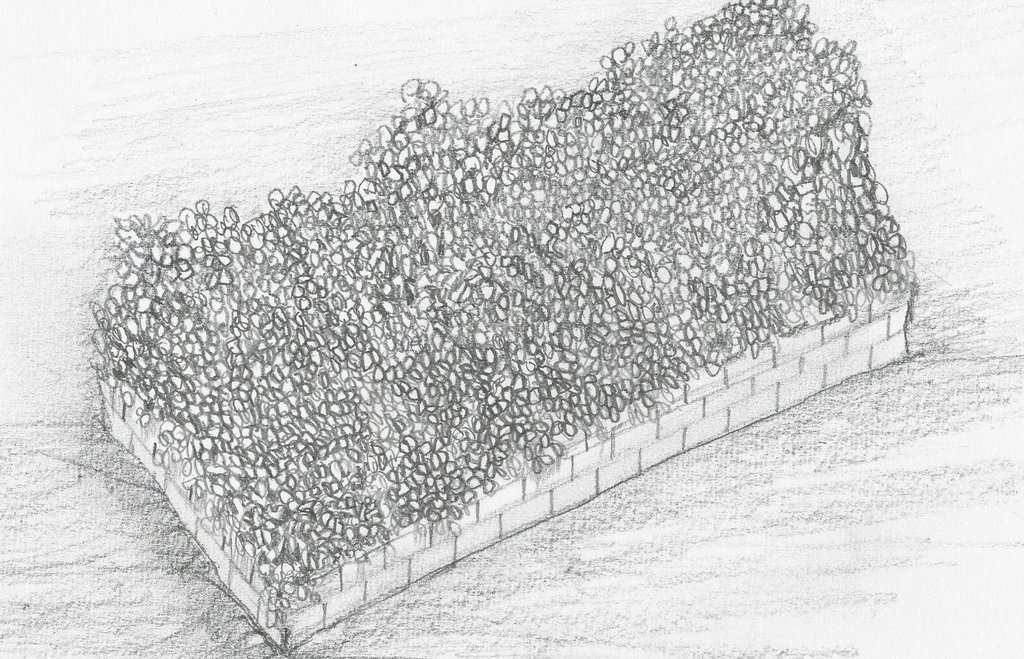
Compost piled in a cemented box.
Location: Brgy. Puguis. La Trinidad, Benguet
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: increase in organic matter, increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…)
Secondary technical functions: improvement of topsoil structure (compaction), increase of infiltration
Manure / compost / residues
Material/ species: Grass and weeds available in the farm( Ageratum houstonianum, Dentella repens, Setaria palmifolia,
Quantity/ density: 500kg
Remarks: the pile to be converted into compost should be under a shed protected from rain to prevent the avai
Agronomic measure: Indigenous microorganism (IMO) solution
Material/ species: forest soil, sugar/molasses, water
4.3 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
pesos
注明美元与当地货币的汇率(如相关):1美元=:
45.0
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
5.56
4.4 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Procurement of sprayer, shredder, seedling pots and trays | 农业学的 | |
| 2. | Establishment of composite chamber (shed) | 农业学的 |
4.5 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 设备 | Sprayer | ha | 1.0 | 22.22 | 22.22 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Shredder | ha | 1.0 | 2222.22 | 2222.22 | 100.0 |
| 其它 | Compost chamber | ha | 1.0 | 155.56 | 155.56 | 100.0 |
| 其它 | Seedling trays | ha | 1.0 | 55.56 | 55.56 | 100.0 |
| 其它 | Seedling pots | ha | 1.0 | 2.22 | 2.22 | 100.0 |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 2457.78 | |||||
注释:
Life span of sprayer and shredders more than 20 years
4.6 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Hauling of grass and weeds available in the farm | 农业学的 | Once a month |
| 2. | Shredding of grass and weeds | 农业学的 | Once a month |
| 3. | Spraying the shredded grass and weeds with indigenous microorganisms (IMO) | 农业学的 | |
| 4. | Leave for 14 days to decompose | 农业学的 | |
| 5. | Application of Compost | 农业学的 |
4.7 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Labour | ha | 1.0 | 55.57 | 55.57 | 100.0 |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 55.57 | |||||
注释:
Machinery/ tools: shredder
The calculation is based on the initial establishment cost (e.g. machine and tools) spend by Mr. Acosta on 2003.
4.8 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
The determinate factor affecting the cost is the cost of mechanical shredder. This machine is considered as important investment to those who is serious in engaging and practicing organic farming in a sizable farm like Mr. Ambrocio Acosta.
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
农业气候带
- 潮湿的
Thermal climate class: tropics
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
关于地形的注释和进一步规范:
Altitudinal zone: 1001-1500 m a.s.l. (1,342 meters above sea level)
Landfroms: Mountain slopes (the technology was applied at the farm with > 25 ° or >40 % slope and in concave situation)
Slopes on average: steep (31-60%) (the mean slope is 40%)
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 中(1-3%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Soil fertility is medium
Soil drainage/infiltration is medium
Soil water storage is low
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
5-50米
地表水的可用性:
好
水质(未处理):
仅供农业使用(灌溉)
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 高
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
生产系统的市场定位:
- 混合(生计/商业
非农收入:
- 低于全部收入的10%
相对财富水平:
- 平均水平
个人或集体:
- 个人/家庭
机械化水平:
- 手工作业
性别:
- 男人
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 3% - 4%
100% of the land users are average wealthy and own 100% of the land.
Level of mechanization: manual labour (Vegetables and herbs were planted at beds which were cultivated manually)
Market orientation: Mixed (subsistence and commercial) ( Harvested vegetables and herbs were for the subsistence of his family and were sold commercially at leading groceries and supermarket through a private marketing corporation known as KIAS Organic Gree)
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者拥有或租用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 中等规模的
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 个人,有命名
土地使用权:
- 个人
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
注释/具体说明:
Increase in yield was observed as response to compost especially as a source of N and P on the soil
收入和成本
农业投入费用
注释/具体说明:
Grass and weeds are free and readily available in the environment thus reducing the expenses.
农业收入
社会文化影响
健康状况
文化机会
娱乐机会
Improved livelihoods and human well-being
注释/具体说明:
Composting is the decomposition of organic matter into compost which is the alternate for chemical/inorganic fertilizer as source of nutrients for crops. The use of compost prevents the farmers from exposure to harmful effects of chemical fertilizer and protects the consumer on the adverse effects of chemicals on the farm produce. Increased awareness and market demands including premium price for organic crops makes the Organic Farming an impressive source of livelihood and business.
生态影响
土壤
土壤压实
注释/具体说明:
Soil aggregation was enhanced because of the added organic matter from compost
生物多样性:植被、动物
生物量/地上C
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 气候变化/极端天气的类型 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年温度 | 增加 | 好 |
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气象灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 局地暴雨 | 好 |
| 局地风暴 | 好 |
气候灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 干旱 | 好 |
水文灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 比较和缓的(河道)洪水 | 不好 |
其他气候相关的后果
其他气候相关的后果
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 缩短生长期 | 好 |
注释:
The pile of shredded grass and weeds that will be decomposed into compost were housed under a shed protected from rain and exposure from heat of the sun.
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
非常积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
非常积极
长期回报:
非常积极
6.5 技术采用
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发地采用该技术,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 90-100%
注释:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
1 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: Voluntary adoption of the technology was observed since the land owner, Mr. Ambrosio Acosta , was a member and a previous officer of a small group of organic farmers, the La Trinidad Organic Producers (LATOP) and was also an accredited resource speaker/ trainer for Organic Agriculture-related events/forum.
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: It was observed that there is an increased awareness on the harmful effects of chemical inputs on the soil and its negative impact on human health. There is also an increase in demand for organically grown vegetables in the local market.
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Compost increases the organic matter of the soil thus improving soil tilth. Also, it contributes to prevent incidence of plant pathogens,and insect diseases, infestation. |
| Compost as fertilizer provides nutrients to the crops |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Application of compost increases soil organic matter that promotes soil aggregation and improves soil condition. |
| Decomposition of the compost slowy releases nutrients like N, P and K that were readily available to plants. |
| It reduces farm production cost. |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| High initial investment cost in the purchase of equipment, tools and other supplies to start the technology. | Equipment and materials purchased are used for long term. |
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块