Multistorey Gardens [肯尼亚]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Paul Kahiga
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Fabian Ottiger
Multistorey Gardens
technologies_1322 - 肯尼亚
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
SLM专业人员:
Gathenya Mwangi
Jomo Kenyatta University of Agriculture and Technology
P.O.Box, 62000-00200, Nairobi, Juja, Kenya
肯尼亚
SLM专业人员:
Home Patrick
Jomo Kenyatta University of Agriculture and Technology
P.O.Box, 62000-00200, Nairobi, Juja, Kenya
肯尼亚
SLM专业人员:
Chege Timothy
Jomo Kenyatta University of Agriculture and Technology
P.O.Box, 62000-00200, Nairobi, Juja, Kenya
肯尼亚
SLM专业人员:
Adamba Omwange
Jomo Kenyatta University of Agriculture and Technology
P.O.Box, 62000-00200, Nairobi, Juja, Kenya
肯尼亚
SLM专业人员:
Baobab Kimengich
Jomo Kenyatta University of Agriculture and Technology
P.O.Box, 62000-00200, Nairobi, Juja, Kenya
肯尼亚
SLM专业人员:
Wamuongo Jane
Kenya Agricultural Research Institute
Nairobi
肯尼亚
SLM专业人员:
Karanja Andrew
Kenya Agricultural Research Institute
Nairobi
肯尼亚
SLM专业人员:
Namirembe Sara
+254 20 7224000
World Agroforestry Centre (ICRAF)
United Nations Avenue, P. O. Box 30677, Nairobi
肯尼亚
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Jomo Kenyatta University (Jomo Kenyatta University) - 肯尼亚有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
KARI Headquarters (KARI Headquarters) - 肯尼亚有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
International Centre for Research in Agroforestry (ICRAF) - 肯尼亚1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
19/09/2012
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.4 所述技术的可持续性声明
这里所描述的技术在土地退化方面是否存在问题,导致无法被认为是一种可持续的土地管理技术?:
否
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
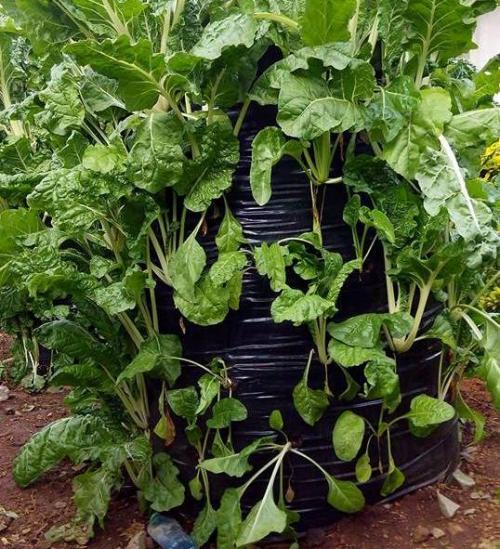
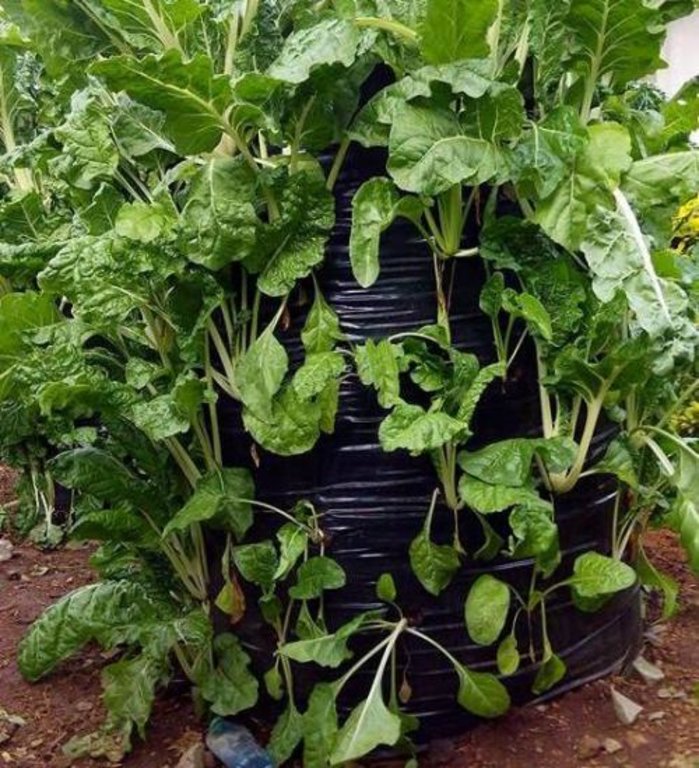
Multistory gardens refer to upright polythene sack filled with soil, in which food crops like vegetables, kales, carrots or onions grow on its sides.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
Multistory gardening is an innovative and exciting technology for year round vegetable gardening. Multi-storey farming not only makes efficient use of water but it is also safe from droughts and floods
Purpose of the Technology: This micro-gardening concept being a low input activity is ideal where labor and other resources are scarce. Multi-storey gardens lead to development of self reliance in vegetables for nutrition and food security in the vulnerable households.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Materials required for multi-storey gardening include empty cereal bag or animal feed bag, one empty oil can or 6”PVC pipe with holes, 2buckets small stones, 6 buckets soil, 6 buckets manure, seeds, adequate water to irrigate the bag garden and gardening tools. The following procedure is used to set up the garden. 1) Mix the soil and well decomposed manure thoroughly. 2) Cut out the bottom of the oil can and make holes on the sides. 3) Fold back the bag and fill the bottom 15cm with small stones. 4) Place the can on top of the small stones in the center of the bag. 5) Fill the oil can with small stones 6) Fill the area between the oil can and the bag with the soil-manure mixture up to the can level. 7) Pull up the can to the level of the soil compost mixture with a tilting motion. Repeat steps 5, 6 and 7 until the bag is full and a central core of stones is formed leaving the tin at the top of the bag garden. Pour water into the tin through the central core till the soil is soaked.
Natural / human environment: Multistory gardens technology is suitable for urban gardening in Kenya where land for farming has greatly reduced due to urbanization.These bag gardens are also suitable for dry, non fertile areas where soils are not suitable for conventional gardening, areas with water scarcity..
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
肯尼亚
区域/州/省:
Eastern Province
有关地点的进一步说明:
Embu
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 不到10年前(最近)
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过项目/外部干预
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 改良生产
- 适应气候变化/极端天气及其影响
- 创造有益的经济影响
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

农田
- 一年一作
注释:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Effects of strong moving wind causes great soil erosion, but the presence of multistorey crops alternates the wind energy, hence lowering its effects.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Greatest soil erosion and also bending of crops in the farms
Constraints of settlement / urban
3.3 有关土地利用的更多信息
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 混合雨水灌溉
每年的生长季节数:
- 1
具体说明:
Longest growing period in days: 180, Second longest growing period in days: 180
3.4 该技术所属的SLM组
- 家庭花园
3.5 技术传播
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果该技术均匀地分布在一个区域上,请注明覆盖的大致区域。:
- < 0.1 平方千米(10 公顷)
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

农艺措施
- A1:植被和土壤覆盖层

植物措施
- V2:草和多年生草本植物
注释:
Type of agronomic measures: better crop cover
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤风蚀
- Et:表土流失
注释:
Main causes of degradation: soil management, urbanisation and infrastructure development, land tenure
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 防止土地退化
- 修复/恢复严重退化的土地
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
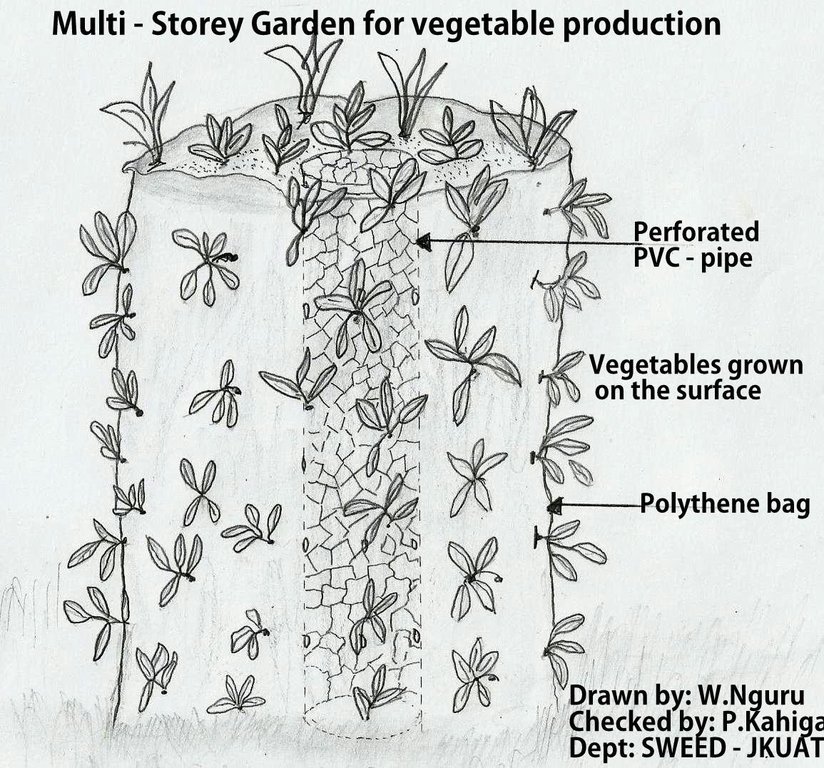
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
4.2 技术规范/技术图纸说明
This is a technical drawing showing a typical multi-storey garden technology for vegetable production. It comprises of a perforated polythene bag with a central Perforated PVC pipe (for water application) and vegetables planted on the outer surfaces.
Location: Mbeere South District. Eastern Province
Main technical functions: spatial arrangement and diversification of land use
Better crop cover
Material/ species: vegetables (kales and spinach)
Quantity/ density: 8
Remarks: per line
4.3 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
Kshs
注明美元与当地货币的汇率(如相关):1美元=:
100.0
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
500.00
4.4 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Purchase polythene bag | 农业学的 | |
| 2. | Purchase manure (FYM) | 农业学的 | |
| 3. | Purchase seedlings | 农业学的 |
注释:
Lifespan of the polythene bag: 5 years
Lifespan of the manure: 1 year
Lifespan of the seedlings: 1 year
4.5 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Labour | Labour per 10 bags | 2.0 | 2.5 | 5.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Tools | ha | 1.0 | 20.0 | 20.0 | 100.0 |
| 植物材料 | Seedlings | Seedlings | 320.0 | 0.00156 | 0.5 | 92.0 |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | Manure | 20.0 | 0.05 | 1.0 | 100.0 | |
| 施工材料 | Polythene bag | Bags | 10.0 | 0.25 | 2.5 | 100.0 |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 29.0 | |||||
注释:
Duration of establishment phase: 1 month(s)
4.6 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | weeding | 农业学的 | 2 |
| 2. | harvesting | 农业学的 | 3 per week |
4.7 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Weeding | Mandyas | 3.0 | 0.8333 | 2.5 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Harvesting | Mandays | 1.0 | 2.5 | 2.5 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Tools | Ha | 1.0 | 2.0 | 2.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 7.0 | |||||
4.8 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
Labor is the most determinate factor affecting the costs.
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
农业气候带
- 半干旱
Thermal climate class: tropics
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 中(1-3%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Soil fertility: Medium
Soil drainage/infiltration: Medium
Soil water storage capacity: Medium
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
5-50米
地表水的可用性:
中等
水质(未处理):
仅供农业使用(灌溉)
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 中等
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
生产系统的市场定位:
- 混合(生计/商业
非农收入:
- 低于全部收入的10%
相对财富水平:
- 平均水平
个人或集体:
- 个人/家庭
机械化水平:
- 手工作业
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: < 0.5%
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者拥有或租用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 小规模的
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地使用权:
- 个人
用水权:
- 个人
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
生产故障风险
水资源可用性和质量
灌溉用水需求
收入和成本
收入来源的多样性
社会文化影响
食品安全/自给自足
Improved livelihoods and human well-being
注释/具体说明:
Improves dietary diversification
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气象灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 局地暴雨 | 好 |
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
积极
6.5 技术采用
注释:
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: It is a new technology
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Growing of vegetables all year round and less water is used for irrigation |
| Labour efficient means of increasing food security |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Multi-storey gardens contributes to dietary diversification among the practicing communities. |
| Contributes to income generation. |
| Encourages self reliance and empowers women in rural areas. |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
- 实地考察、实地调查
- 与土地使用者的访谈
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块