Crop Rotation [肯尼亚]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Paul Kahiga
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Fabian Ottiger
Crop rotation
technologies_1326 - 肯尼亚
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
SLM专业人员:
Gathenya Mwangi
Jomo Kenyatta University of Agriculture and Technology
P.O.Box, 62000-00200, Juja, Nairobi Kenya
肯尼亚
SLM专业人员:
Home Patrick
Jomo Kenyatta University of Agriculture and Technology
P.O.Box, 62000-00200, Juja, Nairobi Kenya
肯尼亚
SLM专业人员:
Chege Timothy
Jomo Kenyatta University of Agriculture and Technology
P.O.Box, 62000-00200, Juja, Nairobi Kenya
肯尼亚
SLM专业人员:
Kimengich Baobab
Jomo Kenyatta University of Agriculture and Technology
P.O.Box, 62000-00200, Juja, Nairobi Kenya
肯尼亚
SLM专业人员:
Omwange Abamba
Jomo Kenyatta University of Agriculture and Technology
P.O.Box, 62000-00200, Juja, Nairobi Kenya
肯尼亚
SLM专业人员:
Karanja Andrew
+254 729 054547
Kenya Agricultural Research Institute
Nairobi
肯尼亚
SLM专业人员:
Wamuongo Jane
+254 729 054547
Kenya Agricultural Research Institute
Nairobi
肯尼亚
SLM专业人员:
Namirembe Sara
World Agroforestry Centre (ICRAF)
Nairobi
肯尼亚
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
International Centre for Research in Agroforestry (ICRAF) - 肯尼亚有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
KARI Headquarters (KARI Headquarters) - 肯尼亚有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Jomo Kenyatta University (Jomo Kenyatta University) - 肯尼亚1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
18/09/2012
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.4 所述技术的可持续性声明
这里所描述的技术在土地退化方面是否存在问题,导致无法被认为是一种可持续的土地管理技术?:
否
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
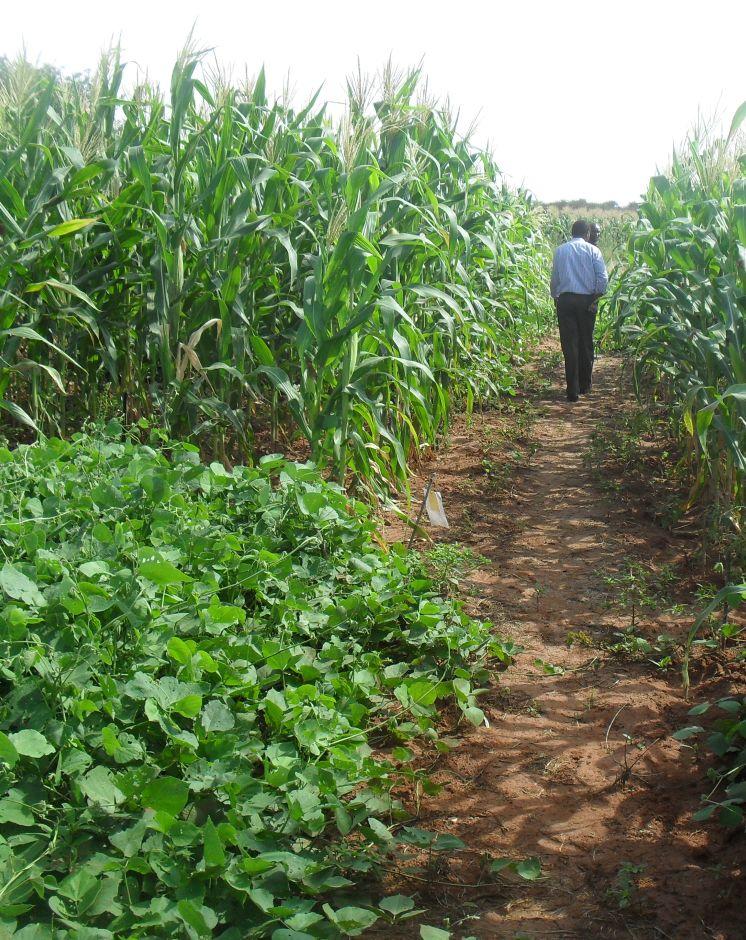
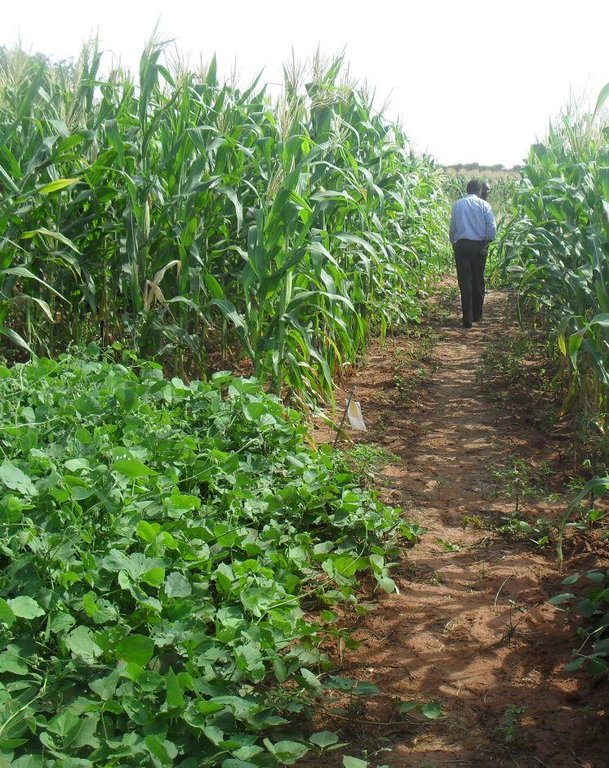
Crop rotation is the practice of growing a series of different types of crops in the same area in sequential seasons.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
Growing the same crop in the same place for many years in a row disproportionately depletes the soil of certain nutrients. With rotation, a crop that leaches the soil of one kind of nutrient is followed during the next growing season by a dissimilar crop that returns that nutrient to the soil or draws a different ratio of nutrients. Crop rotation mitigates the buildup of pathogens and pests that often occurs when one species is continuously cropped, and can also improve soil structure and fertility by increasing biomass from varied root structures.
Purpose of the Technology: Crop rotation improves crop's productivity, it reduces soil erosion and enhances maximum nutrient utilization. Crop rotation also improve soil properties and aeration. A nitrogen-fixing crop, like a legume, should always proceed a nitrogen depleting one; similarly, a low residue crop (i.e. a crop with low biomass) should be offset with a high biomass cover crop, like a mixture of grasses and legumes
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Crop rotation is practiced by subdividing the land into different portions. The portions are planted with crops e.g. cereals at first then in the next season, another plant is planted in the following manner; 1) Cereals crop with legumes, 2) Deep rooted with shallow rooted and a cover crop.
Natural / human environment: In Embu county, the main crops that are rotated includes, maize and legumes.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
肯尼亚
区域/州/省:
Eastern Province
有关地点的进一步说明:
Mbeere South District
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 10-50年前
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过土地使用者的创新
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 改良生产
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
- 保护生态系统
- 创造有益的经济影响
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

农田
- 一年一作
注释:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Soil erosion
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Soil erosion and low productivity
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Cropland: Ca: Annual cropping
如果由于技术的实施而导致土地用途发生变化,则在技术实施前说明土地利的用途。:
Cropland: Ca: Annual cropping
3.3 有关土地利用的更多信息
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 混合雨水灌溉
每年的生长季节数:
- 1
具体说明:
Longest growing period in days: 90
3.4 该技术所属的SLM组
- 轮作制度(轮作、休耕、轮垦)
3.5 技术传播
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果该技术均匀地分布在一个区域上,请注明覆盖的大致区域。:
- 10-100 平方千米
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

农艺措施
- A2:有机质/土壤肥力
注释:
Type of agronomic measures: better crop cover, rotations / fallows
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀
注释:
Main causes of degradation: soil management, crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub), land tenure
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 防止土地退化
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
4.2 技术规范/技术图纸说明
The technical drawing on the left hand side shows a typical crop rotation arrangement, a series of different types of crops in the same area are grown in sequential season. These may include, cereals, legumes, alliums and solanaceae.
Location: Embu. Eastern Province
Date: 13.02.2013
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: improvement of ground cover, increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…)
4.3 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
Kshs
注明美元与当地货币的汇率(如相关):1美元=:
100.0
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
5.00
4.4 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Land preparation | 农业学的 | |
| 2. | Buy seeds | 农业学的 |
4.5 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Land preparation | ha | 1.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Tools | ha | 1.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 |
| 植物材料 | Seeds | ha | 1.0 | 50.0 | 50.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 250.0 | |||||
注释:
Lifespan of the product: Landpreparation (3 years)
4.6 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Planting | 农业学的 | Each cropping season |
| 2. | Weeding | 农业学的 |
4.7 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Planting and weeding | ha | 1.0 | 50.0 | 50.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Tools | ha | 1.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 |
| 植物材料 | Seeds | ha | 1.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 250.0 | |||||
4.8 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
labour
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
农业气候带
- 半湿润
Thermal climate class: tropics
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 中(1-3%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Soil fertility: Medium
Soil drainage/infiltration: Good
Soil water storage capacity: Medium
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
5-50米
地表水的可用性:
中等
水质(未处理):
不良饮用水(需要处理)
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 中等
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
生产系统的市场定位:
- 混合(生计/商业
非农收入:
- 低于全部收入的10%
相对财富水平:
- 平均水平
个人或集体:
- 个人/家庭
机械化水平:
- 手工作业
性别:
- 女人
- 男人
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 0.5% - 1%
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者拥有或租用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 小规模的
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 个人,有命名
土地使用权:
- 个人
用水权:
- 个人
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
生产故障风险
产品多样性
收入和成本
农业收入
收入来源的多样性
工作量
社会文化影响
食品安全/自给自足
SLM/土地退化知识
Improved livelihoods and human well-being
生态影响
生物多样性:植被、动物
生物量/地上C
害虫/疾病控制
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
缓冲/过滤能力
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 气候变化/极端天气的类型 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年温度 | 增加 | 好 |
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
积极
6.5 技术采用
注释:
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Helps in controlling weeds. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Crop rotation prevents soil depletion of nutrients thus maintains soil fertility. |
| Crop rotation reduces soil erosion |
| Reduces pest's build-up thus prevents disease infestation. |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| The fungi and pests left behind from a previous crop can potentially harm the new crop. | Liase with agronomist for advice on appropriate pesticides and fungicides to use. |
| More time is required in preparing fields for crops ahead of rotations. | Proper timing of farm operations in preparation of rotations |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
- 实地考察、实地调查
- 与土地使用者的访谈
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块