Assisted Natural Regeneration of Degraded Land [布基纳法索]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Franziska Kaguembèga-Müller
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Fabian Ottiger
technologies_1358 - 布基纳法索
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
Book project: SLM in Practice - Guidelines and Best Practices for Sub-Saharan Africa (SLM in Practice)有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
newTree - nouvelarbre (newTree - nouvelarbre) - 瑞士1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
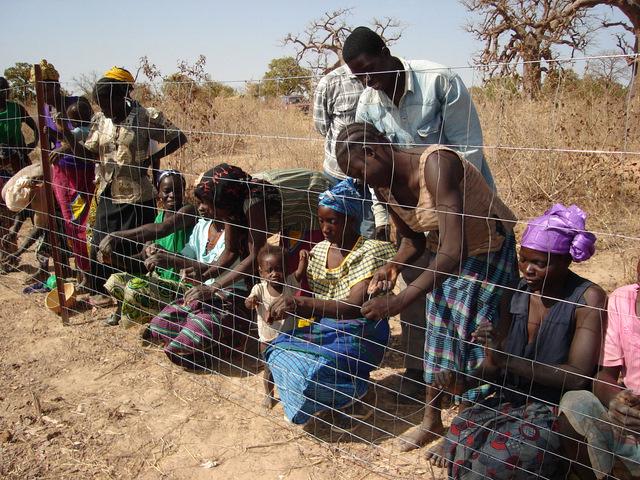
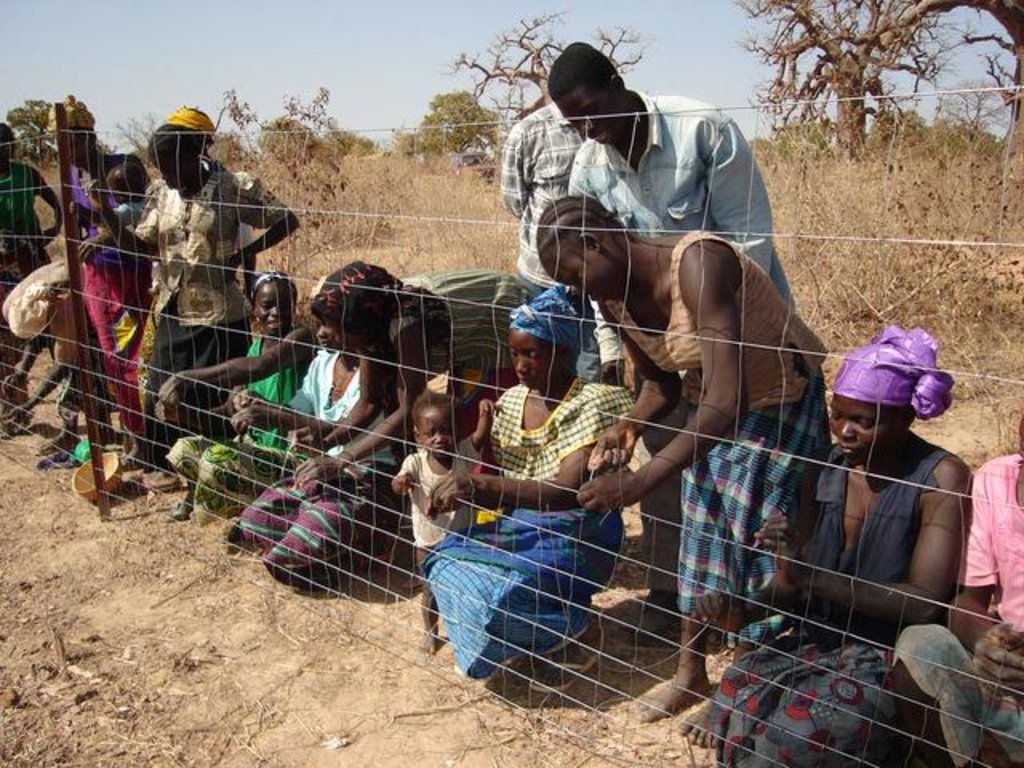
Fenced 3 ha plots are set aside to allow for natural regeneration of highly diverse forests.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
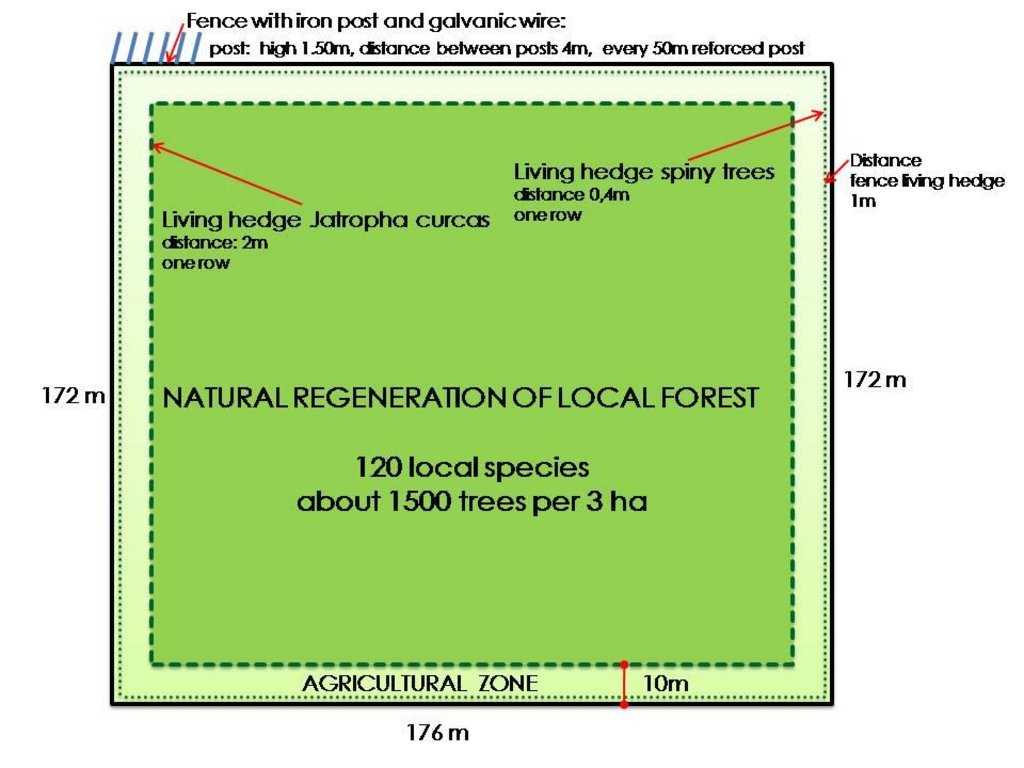
Assisted natural regeneration, as promoted by newTree in Burkina Faso, starts with enclosing 3 ha of degraded land with a solid fence. Fence materials (iron posts and galvanic wire) are externally sponsored and locally assembled and installed. Along the fence a dense living hedge of thorny trees (local tree species: e.g. Acacia nilotica, A. senegal, Prosopis sp, Ziziphus mauritiana) is planted. A strip of 10 m along the hedge is dedicated to agriculture. This area is equivalent to approximately 10% of the protected area. The rest is dedicated to natural regeneration of the local forest. Once protected, natural vegetation rich in endogenous species can actively regenerate. Annual vegetation species inventories are made to monitor the biomass, biodiversity and the growth rate of the trees. The forest reaches a tree density of approximately 500 trees per hectare and consists of around 120 local species. Some enrichment planting of rare species enhances the allotments. The protected area is of paramount importance for biodiversity conservation. Management activities in the protected area includes (1) seeding / planting of improved fodder species; and (2) establishing stone lines and half-moons (demi-lunes) for soil erosion control and water harvesting, (3) installing bee hives for honey production; and (4) fodder production: the grass is cut, tied and carried to feed livestock outside the regeneration area. Property rights for the protected area are clearly established through a contractual agreement that includes/respects traditional and government land rights. The local land users select the area, provide all labour inputs and ensure the long-term management of the sites according to mutually agreed goals. Training is provided to enhance income generating activities – ranging from beekeeping and the production of high-value vegetable crops to the processing of non timber forestry products – and to promote the use of fuel-efficient cooking stoves.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
布基纳法索
区域/州/省:
Soum Province
2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 不到10年前(最近)
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过项目/外部干预
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
- 保护生态系统
- 保持/提高生物多样性
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

农田
- 一年一作

森林/林地
- Assisted regeneration of natural forest
产品和服务:
- 木材
- 薪材
- 水果和坚果
- 其它森林产品
- 放牧/啃牧
- 自然保持/保护
注释:
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Soil erosion by water and wind; Fertility decline; Sealing and crusting; Reduction of vegetation cover; Aridification
Plantation forestry: Yes
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Forests / woodlands: Fn: Natural
如果由于技术的实施而导致土地用途发生变化,则在技术实施前说明土地利的用途。:
Mixed: Ma: Agro-silvopastoralism
3.3 有关土地利用的更多信息
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
3.4 该技术所属的SLM组
- 区域封闭(停止使用,支持恢复)
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

植物措施
- V1:乔木和灌木覆盖层

管理措施
- M1:改变土地使用类型
注释:
Main measures: vegetative measures, management measures
Type of vegetative measures: in blocks
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀

土壤风蚀
- Et:表土流失

化学性土壤退化
- Cn:肥力下降和有机质含量下降(非侵蚀所致)

物理性土壤退化
- Pk:熟化和结壳

生物性退化
- Bc:植被覆盖的减少
- Bq:数量/生物量减少
- Bs:质量和物种组成/多样性的下降

水质恶化
- Ha:干旱化
注释:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Et: loss of topsoil, Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content, Pk: sealing and crusting, Bc: reduction of vegetation cover, Bq: quantity / biomass decline, Bs: quality and species composition /diversity decline, Ha: aridification
Main causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires), overgrazing
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 修复/恢复严重退化的土地
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
4.2 技术规范/技术图纸说明
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: control of raindrop splash, improvement of ground cover, improvement of surface structure (crusting, sealing), increase in organic matter, increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), increase of infiltration, reduction in wind speed, increase of biomass (quantity), promotion of vegetation species and varieties (quality, eg palatable fodder), spatial arrangement and diversification of land use
Secondary technical functions: increase of groundwater level / recharge of groundwater
Scattered / dispersed
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
In blocks
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 500
Trees/ shrubs species: Acacia nilotica, A. senegal, Prosopis sp, Ziziphus mauritiana
4.4 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Select an area of 3 ha of degraded land | 植物性的 | |
| 2. | Establish a 1.5 m high fence around the selected area: install metal posts, manufacture / assemble chain-link fence materials (manually) | 植物性的 | |
| 3. | Plant a living hedge of spiny trees at a distance of 1 m to the fence, plants spaced at 0.4 m | 植物性的 | |
| 4. | Reserve a 10 m strip along the fence / hedge for improved agriculture / Plant a living hedge of Jatropha curcas to separate cropland from regeneration area | 植物性的 | |
| 5. | Seed / plant improved fodder species within protected area / Establish stone lines and half-moons for soil erosion control and water harvesting within protected area | 植物性的 | |
| 6. | Install beehives (2-10 hives per protected area) | ||
| 7. | Purchase protection and harvesting equipment | ||
| 8. | Construct fuel efficient cooking stoves |
4.5 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Labour | ha | 1.0 | 1300.0 | 1300.0 | 33.0 |
| 设备 | Tools | ha | 1.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 33.0 |
| 施工材料 | Material for fence construction | ha | 1.0 | 2900.0 | 2900.0 | 33.0 |
| 其它 | Training, seeds, compost | ha | 1.0 | 260.0 | 260.0 | 33.0 |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 4560.0 | |||||
注释:
Components for fence construction: sand, gravel, rock and water, poles, galvanised wire, cement, tree seedlings
4.6 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Supervise fence and protected area; repairing where necessary | 植物性的 | |
| 2. | Replant / replace dead seedlings in living hedges | 植物性的 | |
| 3. | Improved agriculture: agroforestry, water harvesting, compost application | 植物性的 | |
| 4. | Beekeeping: monthly control of beehive; yield 2-3 times per year (manually with protection equipment) | 植物性的 | |
| 5. | Improved fodder production: cut grass and tie hay with simple tying machine (once a year after rainy season) | 植物性的 |
4.7 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Labour | ha | 1.0 | 730.0 | 730.0 | 95.0 |
| 植物材料 | Seedlings | ha | 1.0 | 40.0 | 40.0 | 95.0 |
| 其它 | Training, seeds, compost | ha | 1.0 | 40.0 | 40.0 | 95.0 |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 810.0 | |||||
注释:
Machinery/ tools: pick, shovel, hammer, glove, tong, iron rod
A unit relates to a protected area of 3 hectares (average size; feasible and beneficial for participating land users, namely farm families / womens’ groups).
4.8 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
Labour for establishment includes: digging of planting pits/ditches, post installation, fabrication of chain-link fence materials, all plantations, stone lines, half-moons, etc. Components for fence construction are locally available.
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
有关降雨的规范/注释:
300-600 mm
农业气候带
- 半干旱
Thermal climate class: tropics
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 细粒/重质(粘土)
表土有机质:
- 低(<1%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Soil fertility: Low
Soil drainage/infiltration: Poor
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
生产系统的市场定位:
- 生计(自给)
- 混合(生计/商业
个人或集体:
- 团体/社区
机械化水平:
- 手工作业
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly disadvantaged land users
Difference in the involvement of women and men: some of the plots are managed by women's groups
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者拥有或租用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 小规模的
注释:
3 ha per household
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 州
土地使用权:
- 个人
注释:
traditional family property rights (factually)
land use rights: families
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
饲料生产
饲料质量
木材生产
收入和成本
农业收入
社会文化影响
食品安全/自给自足
健康状况
SLM/土地退化知识
社会经济弱势群体的情况
生态影响
水循环/径流
水的回收/收集
地表径流
蒸发
土壤
土壤水分
土壤覆盖层
土壤流失
土壤压实
养分循环/补给
土壤有机物/地下C
生物多样性:植被、动物
生物量/地上C
植物多样性
有益物种
栖息地多样性
减少气候和灾害风险
风速
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 气候变化/极端天气的类型 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年温度 | 增加 | 好 |
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气象灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 局地暴雨 | 好 |
| 局地风暴 | 好 |
气候灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 干旱 | 好 |
水文灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 比较和缓的(河道)洪水 | 好 |
其他气候相关的后果
其他气候相关的后果
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 缩短生长期 | 好 |
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
中性/平衡
长期回报:
非常积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
非常积极
6.5 技术采用
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发地采用该技术,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 0-10%
注释:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
There is a strong trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: All land users have implemented the technology through receiving incentives (payment for labour and other inputs). Regeneration sites have been established in 5 different provinces (Soum in the North, Kadiogo, Kourweogo, Boulkiemde and Oubritenga in the centre of Burkina Faso). There is high demand for establishment of further sites. The demonstration effect of improved agriculture within the fence (agroforestry, etc. resulting in higher yields) encourages farmers to adopt these measures in their fields outside the protected area also
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| High investment cost | introduce income generating activities which amortise (help pay off) the initial investments and the waiting time until land users can harvest non-woody products from the forest; relocate the fence to enclose other degraded land when the living hedge is dense enough and takes over the function of protection. |
| Insecurity of land rights is a constraint for implementation (government is official land owner) | Conclude contractual agreements which include/respect traditional and government land rights |
7. 参考和链接
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Diatta, M; Albergel, J.; Perez, P.; Faye, E.; Séne, M. et Grouzis, M. 2000. Efficacité de la mise en défens testée dans l’aménagement d’un petit bassin versant de Thysse Kaymor (Sénégal). 15 p.
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Guinko S., 1984. Végétation de Haute Volta, Volume I. Thèse de Doctorat : Université de Bordeaux III (France). Tome, 394p.
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块