Stone bunds and small basins [菲律宾]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Philippine Overview of Conservation Approaches and Technologies
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Deborah Niggli
Pamugong sa yuta (Cebuano)
technologies_1424 - 菲律宾
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
关键资源人
SLM专业人员:
Rondal Jose
Bureau of Soils and Water Management
Elliptical Road, Diliman, Quezon City, Philippines
菲律宾
1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
02/08/2002
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.4 所述技术的可持续性声明
这里所描述的技术在土地退化方面是否存在问题,导致无法被认为是一种可持续的土地管理技术?:
否
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
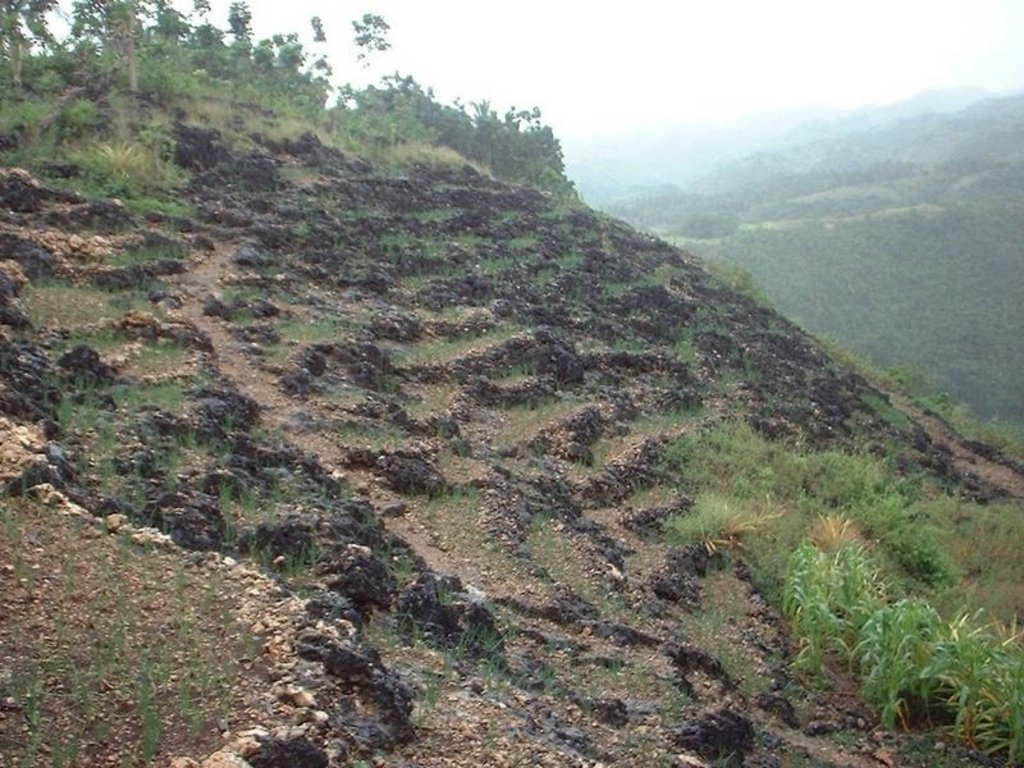
Piling of stones and rocks along the contour to control run-off and soil erosion. It is also about the creation of small basins by removing stones and using them as barriers.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
This is a low-cost erosion control technology by piling stones/rocks along the contour. The spacing of the piles depends on the slope and the availability/abundance of surface rocks. The stone bunds, usually 0.4 meter wide is intended to slow down run-off and catch/impound soil that moves downslope, etiher by water or by gravity. The technology is also about the creation of small basins by removing rocks and using them as barrier. In these small basins, water is impounded and allow to infiltrate. Soil carried with the run-off is deposited in these basins for the raising of high value crops. The technology is most especially applicable in areas where limestone and other rock outcrops and where the soil is commonly shallow and skeletal. With time, natural terraces can form. Limestone/rock outcrops are also used in the construction of check dams along small waterways. These check dams will result in the formation of flat-bottom valleys where transplanted rice is usually grown. Series of check dams will form terraces along valley floor in the long run.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
菲律宾
有关地点的进一步说明:
Siquijor, Cebu, Bohol, Negros Oriental
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 50多年前(传统)
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 作为传统系统的一部分(> 50 年)
注释(项目类型等):
Indigenous to the area.
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

农田
- 一年一作
注释:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Soil erosion/degradation, soil fertility decline
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): productivity decline, increasing levels of input to maintain yield.
Type of cropping system and major crops comments: Two (2) crops of onion or two crops of corn or one crop of corn followed by vegetables.
3.3 有关土地利用的更多信息
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
每年的生长季节数:
- 2
具体说明:
Longest growing period in days: 270, Longest growing period from month to month: May - Jun; Second longest growing period in days: 240, Second longest growing period from month to month: May - Dec
3.4 该技术所属的SLM组
- 横坡措施
3.5 技术传播
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果该技术均匀地分布在一个区域上,请注明覆盖的大致区域。:
- > 10,000 平方千米
注释:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 31 m2.
The technology of pilling stones along the contour has been praticed for generation. However, it was given an added push through the Central Visayas Resources Project (CVRP). It is a case of promoting farmers' initiative (PFI).
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

结构措施
- S2:堤、岸
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀
- Wg:冲沟侵蚀/沟蚀

水质恶化
- Ha:干旱化
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 修复/恢复严重退化的土地
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
4.2 技术规范/技术图纸说明
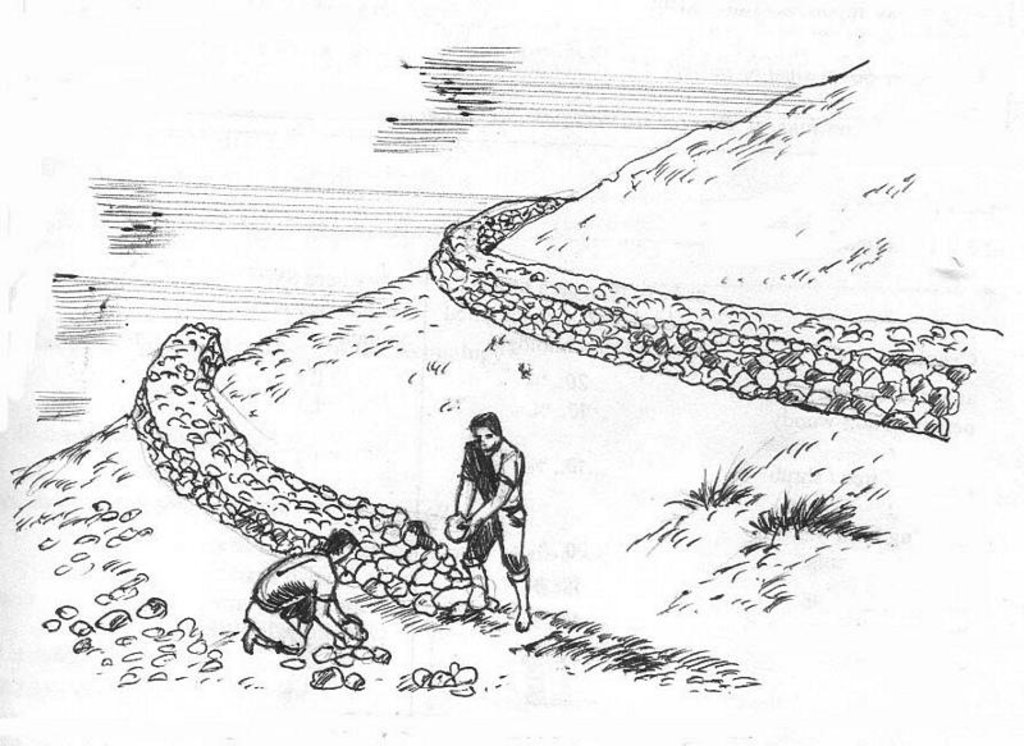
Construction of stone bunds along the contour for run-off and erosion control
Date: 8-22-2002
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap
Secondary technical functions: reduction of slope length, increase / maintain water stored in soil
4.3 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
Philippine peso
注明美元与当地货币的汇率(如相关):1美元=:
50.0
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
4.00
4.5 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | labour | ha | 1.0 | 1000.0 | 1000.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | tools | ha | 1.0 | 20.0 | 20.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 1020.0 | |||||
4.7 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | labour | ha | 1.0 | 40.0 | 40.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 40.0 | |||||
注释:
The volume of stones to be removed, gathered and piled to create a wall.
4.8 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
Labor for the removal and collection of stones for piling.
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
农业气候带
- 潮湿的
- 半湿润
Thermal climate class: tropics
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
- 细粒/重质(粘土)
表土有机质:
- 中(1-3%)
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
生产系统的市场定位:
- 混合(生计/商业
- 商业/市场
非农收入:
- 收入的10-50%
相对财富水平:
- 贫瘠
- 平均水平
机械化水平:
- 手工作业
- 畜力牵引
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Population density: 100-200 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2% - 3%
30% of the land users are rich and own 20% of the land.
10% of the land users are average wealthy and own 30% of the land.
60% of the land users are poor and own 50% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: retailing, carpentry, dressmaking, fishing, overseas employment, etc.
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者拥有或租用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 个人,有命名
土地使用权:
- 个人
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
注释/具体说明:
from nothing to something
生产区域
注释/具体说明:
area occupied by stone wall
土地管理
注释/具体说明:
stone wall is also on obstruction
收入和成本
农业收入
注释/具体说明:
from nothing to something
社会文化影响
冲突缓解
生态影响
水循环/径流
地表径流
SLM之前的数量:
40
SLM之后的数量:
10
土壤
土壤水分
注释/具体说明:
Better infiltration
土壤覆盖层
注释/具体说明:
Better crop growth
土壤流失
注释/具体说明:
Almost zero soil loss
其它生态影响
Soil fertility
注释/具体说明:
Build-up of nutrients
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
下游洪水
地下水/河流污染
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
稍微积极
长期回报:
非常积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
积极
6.5 技术采用
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发地采用该技术,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 90-100%
注释:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
200 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology. When other farmers saw the effect of the technology, they adopted spontaneously.
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Permanent |
| Clears the land for cultivation |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Once established, it becomes permanent |
| Very effective in trapping sediment |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Sancturies for pests | Cleanliness of the surroundings |
| Laborious during establishment | labor sharing |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Stone wall serve as sanctuary for pests like rats and snakes | Cleanliness of the surroundings |
| Stone wall can be an obstruction in cultivation and mobility |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
- 实地考察、实地调查
- 与土地使用者的访谈
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块