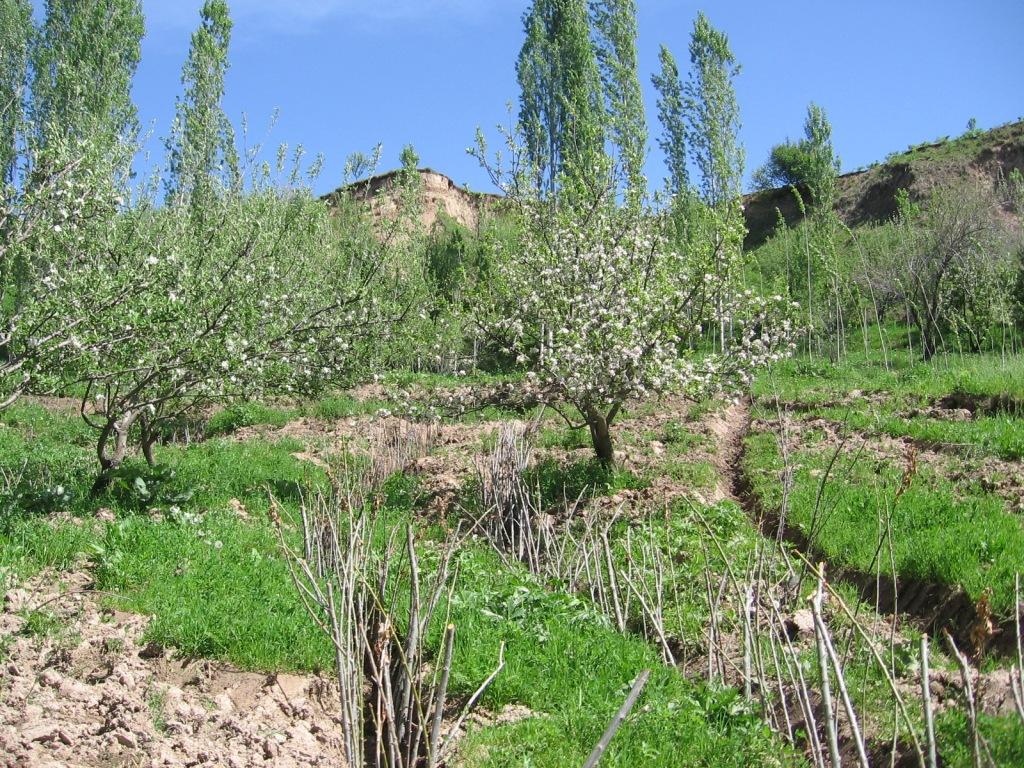
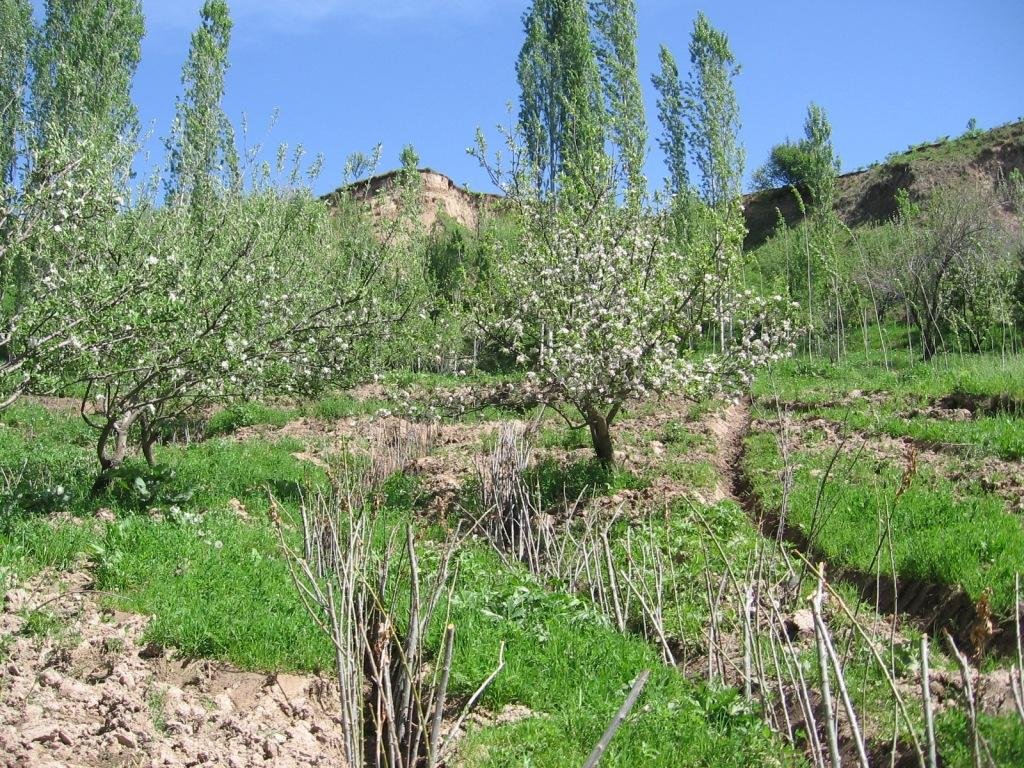
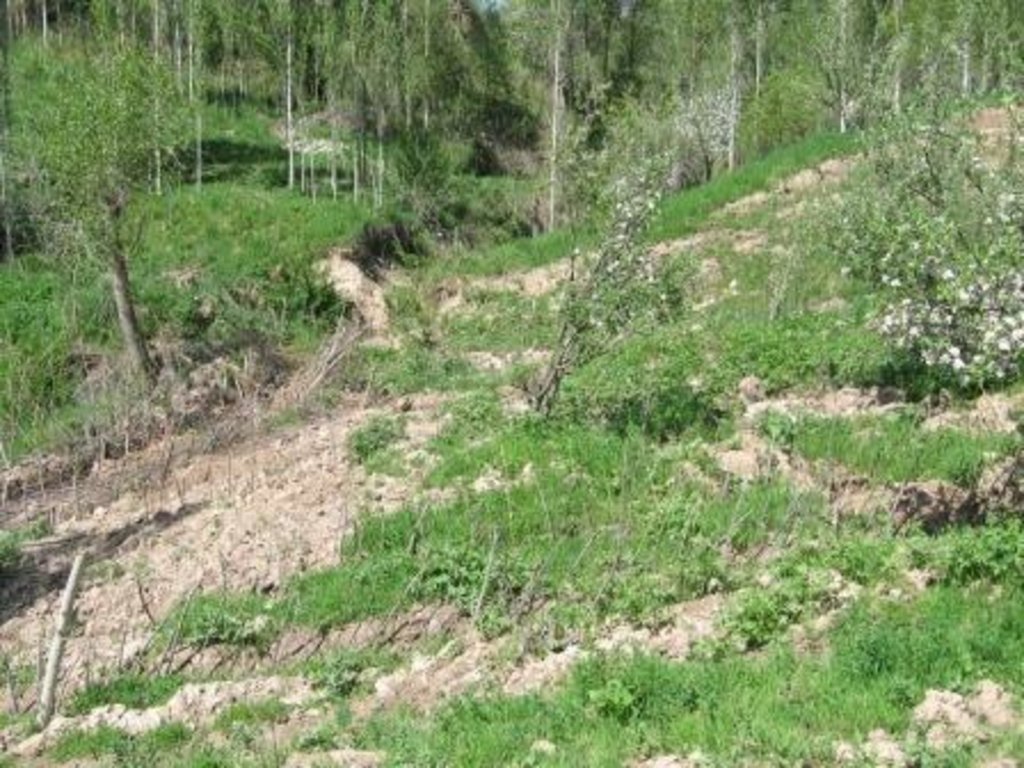
Landslide prevention using drainage trenches lined with fast growing trees. [塔吉克斯坦]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Giuseppe Bonati
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: David Streiff
technologies_1457 - 塔吉克斯坦
- Landslide prevention using drainage trenches lined with fast growing trees.: March 16, 2017 (inactive)
- Landslide prevention using drainage trenches lined with fast growing trees.: July 21, 2017 (inactive)
- Landslide prevention using drainage trenches lined with fast growing trees.: Aug. 19, 2019 (inactive)
- Landslide prevention using drainage trenches lined with fast growing trees.: Nov. 2, 2021 (public)
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
SLM专业人员:
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
CESVI (CESVI) - 塔吉克斯坦1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
30/04/2011
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
The construction of linear gravel bed ditches lined with local tree species, at angles across a hill slope to channel the surface water.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
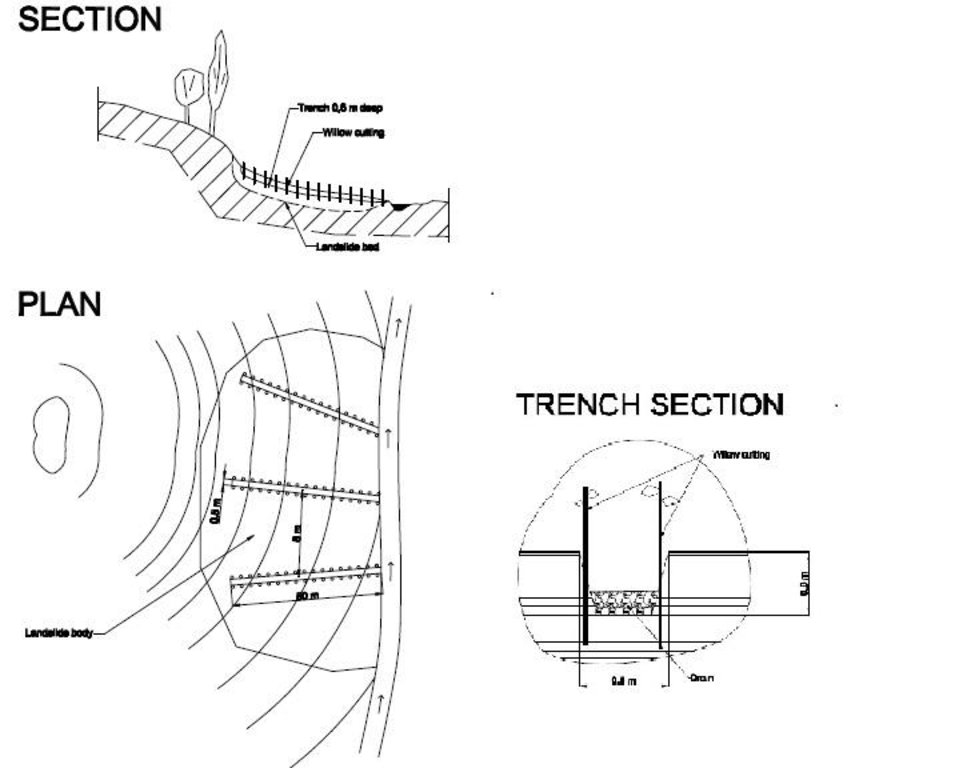
A series of 80m long ditches are constructed at angles of approximately 30 degrees, across a hill slope at the base of the watershed. This land is prone to waterlogging, therefore several ditches approximately 0.5m deep, with a gravel bed to prevent erosion, drain the excess surface water away to the main tributary of the watershed. The edge of the ditches are further lined with fast growing tree species such as willow and poplar for stabilisation and afforestation purposes.
Purpose of the Technology: The purpose of the ditches is two fold, firstly to channel the surface water to prevent waterlogging that had previously led to landslides and small mud flows. Secondly, to enable cultivation on land that was previously unusable.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The technology is very simple and cost effective. Initially there needs to be an assessment of the amount of surface water that runs over the slope, this will determine the number of ditches required. The ditches are marked out, running at approximately 30 degrees perpendicular to the slope. The ditches are dug to a depth of 0.5m (or deeper) and filled with a base layer of stone to prevent the bed of the ditch from being eroded. Once the ditch is established, preferably in the spring time, fast growing and naturally available cuttings from trees such as poplars and willows are planted alongside the edge of the ditch at 0.2m intervals. These will stabilise the ditch bank and as the trees become established some thinning out will be required due to their close proximity to each other.
Natural / human environment: The area used is a hillside slope, subject to substantial amounts of surface water run off due to its location at the base of the watershed. The region suffers from a lack of accessible irrigation water, especially during the hot summer months. This technology allows land to be brought into cultivation that has natural access to water and is able to sustain vegetation during the dry months.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
塔吉克斯坦
区域/州/省:
Khatlon
有关地点的进一步说明:
Khovaling
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 不到10年前(最近)
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过土地使用者的创新
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

森林/林地
(半天然)天然森林/林地:
- 选伐
产品和服务:
- 木材
- 薪材
- 水果和坚果
注释:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Due to a lack of drainage in the existing soil, surface flow collects and becomes concentrated leading to top soil washing and gulleying. Animal paths across the slope exacerbate the erosion process.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): In Soviet times the land was not used due to waterlogging, but the land had good potential to plant trees and produce an income.
Selective felling of (semi-) natural forests: Yes
Problems / comments regarding forest use: Collection of fruit; apple, pear and other trees that can be used for construction purposes. These can be cut after 15yrs to provide income.
Forest products and services: timber, fuelwood, fruits and nuts
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Cropland: Ct: Tree and shrub cropping
如果由于技术的实施而导致土地用途发生变化,则在技术实施前说明土地利的用途。:
Forests / woodlands: Fn: Natural
3.3 有关土地利用的更多信息
每年的生长季节数:
- 1
具体说明:
Longest growing period in days: 180Longest growing period from month to month: April - October
3.4 该技术所属的SLM组
- 横坡措施
- 引水和排水
3.5 技术传播
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果该技术均匀地分布在一个区域上,请注明覆盖的大致区域。:
- 0.1-1 平方千米
注释:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0,1 m2.
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

农艺措施
- A1:植被和土壤覆盖层

植物措施
- V1:乔木和灌木覆盖层

结构措施
- S3:分级沟渠、渠道、水道

管理措施
- M7:其它
注释:
Main measures: structural measures
Secondary measures: vegetative measures
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -contour
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀
- Wm:块体运动/滑坡
注释:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Wm: mass movements / landslides
Main causes of degradation: overgrazing (The land is used for grazing and livestock migration.), Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts) (Heavy rainfall events add to the degradation process.), other natural causes (avalanches, volcanic eruptions, mud flows, highly susceptible natural resources, extreme topography, etc.) specify (Topological situation at the base of the watershed means it is susceptible to mud flows and other natural disasters)
Secondary causes of degradation: inputs and infrastructure: (roads, markets, distribution of water points, other, …) (access to animal water points and pastures.)
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 减少土地退化
注释:
Secondary goals: prevention of land degradation, rehabilitation / reclamation of denuded land
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
4.2 技术规范/技术图纸说明
The drawing shows the layout of the trench and the lining with fast growing native trees.
Location: JONBKHAT. KHOVALING TAJIKISTAN
Date: 2011-04-30
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: low (Simple technology.)
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: control of concentrated runoff: drain / divert, stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides)
Secondary technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, control of concentrated runoff: impede / retard, water spreading, improvement of water quality, buffering / filtering water, promotion of vegetation species and varieties (quality, eg palatable fodder)
Aligned: -contour
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.2
Trees/ shrubs species: willows, bed, poplar are planted in 0.2m intervals along the ditch.
Diversion ditch/ drainage
Spacing between structures (m): 20
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.6
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.5
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 80
Construction material (stone): stones were used to line the bed of the drainage ditch to reduce scouring.
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 20%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is: 18%
Vegetation is used for stabilisation of structures.
4.3 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
Tajik Somoni
注明美元与当地货币的汇率(如相关):1美元=:
4.5
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
5.50
4.4 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Tree planting | 植物性的 | Spring |
| 2. | Construction of the drainage ditches | 结构性的 | spring |
4.5 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Planting trees | Persons/day | 3.0 | 25.0 | 75.0 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Building drainage ditches | Persons/day | 3.0 | 25.0 | 75.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Tools | Pieces | 1.0 | 20.0 | 20.0 | 100.0 |
| 植物材料 | Tree seedlings | pieces | 800.0 | 1.0 | 800.0 | 100.0 |
| 施工材料 | Stone | cub m | 3.0 | 100.0 | 300.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 1270.0 | |||||
注释:
Duration of establishment phase: 1 month(s)
4.6 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | tree maintenance | 植物性的 | spring |
| 2. | clearance of ditches | 结构性的 | annual |
4.7 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Tree maintenance | Persons/day | 2.0 | 25.0 | 50.0 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Clearing ditches | Persons/day | 1.0 | 25.0 | 25.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 75.0 | |||||
注释:
Machinery/ tools: Shovel
The costs are calculated for an 80m trench based on 2010 prices in rural Tajikistan.
4.8 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
The cost of an 80m ditch is mainly determined by labour and seedlings. Labour can be provided by the land owner and seedlings for willows and poplars can be found locally and therefore are of no cost. The stone may occur naturally but there may be transport costs.
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
有关降雨的规范/注释:
heavy rainfall in spring.
农业气候带
- 半干旱
Thermal climate class: temperate
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
关于地形的注释和进一步规范:
Altitudinal zone: Just at the foot of the hill slopes.
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 中(1-3%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Soil fertility is high because of loess soils
Soil drainage / infiltration is poor
Soil water storage capacity is low
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
< 5米
地表水的可用性:
好
水质(未处理):
不良饮用水(需要处理)
关于水质和水量的注释和进一步规范:
Availability of surface water: Also medium
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 中等
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
生产系统的市场定位:
- 生计(自给)
非农收入:
- 低于全部收入的10%
个人或集体:
- 团体/社区
性别:
- 男人
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 1% - 2%
90% of the land users are poor (low income rural families).
10% of the land users are poor.
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者拥有或租用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 小规模的
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 州
土地使用权:
- 社区(有组织)
用水权:
- 自由进入(无组织)
注释:
Water user right refer to the water running over the land
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
注释/具体说明:
Fruit tree yields
木材生产
注释/具体说明:
Fire wood and construction materials
生产区域
能源生产
注释/具体说明:
Generation of the wood for fuel
收入和成本
农业收入
收入来源的多样性
社会文化影响
SLM/土地退化知识
注释/具体说明:
Better understanding of how to control erosion
生态影响
水循环/径流
水的回收/收集
地表径流
多余水的排放
地下水位/含水层
土壤
土壤覆盖层
土壤流失
减少气候和灾害风险
滑坡/泥石流
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
缓冲/过滤能力
对邻近农田的破坏
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 气候变化/极端天气的类型 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年温度 | 增加 | 好 |
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气象灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 局地暴雨 | 不好 |
气候灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 干旱 | 不好 |
水文灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 比较和缓的(河道)洪水 | 不好 |
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
稍微积极
长期回报:
非常积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
非常积极
6.5 技术采用
- 单例/实验
如若可行,进行量化(住户数量和/或覆盖面积):
1 household
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发地采用该技术,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 90-100%
注释:
There is no trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| It is easy to build and cheap. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
It is a basic and easy technology that could be easily replicated, over larger areas. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Further training on the correct angles to build channels and dimensions |
|
The technogy is low cost and potentially quick to build. How can they be sustained / enhanced? It can be built on many different slopes types, angles and heights. |
|
It allows the land to be used for growing fruit trees and timber. There is the opportunity to sell the products. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Training could be provided on tree cultivation. |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| The trench may be inefffective if there is a heavy deluge of surface water, and may in fact concentrate the surface water run off. | The trenches could be filled with gravel and rocks, and intertwined in a grid network, this is a common practice for railway embankements in Europe. The slope has to be shallow enough to prevent the gravel material being washed away. |
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块