Saxaul plantation for stabilisation of sandy soils [塔吉克斯坦]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Firdavs Faizulloev
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: David Streiff
technologies_1461 - 塔吉克斯坦
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
SLM专业人员:
SLM专业人员:
SLM专业人员:
Najmiddin Abdurakhimov
najmiddin.abdurakhimov@undp.org
UNDP
塔吉克斯坦
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
CDE Centre for Development and Environment (CDE Centre for Development and Environment) - 瑞士有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Central Asian Countries Initiative for Sustainable Land Management - Multicountry Capacity Building (CACILM - MCB) - 吉尔吉斯斯坦有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
United Nations Development Program (United Nations Development Program) - 塔吉克斯坦1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
13/04/2011
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
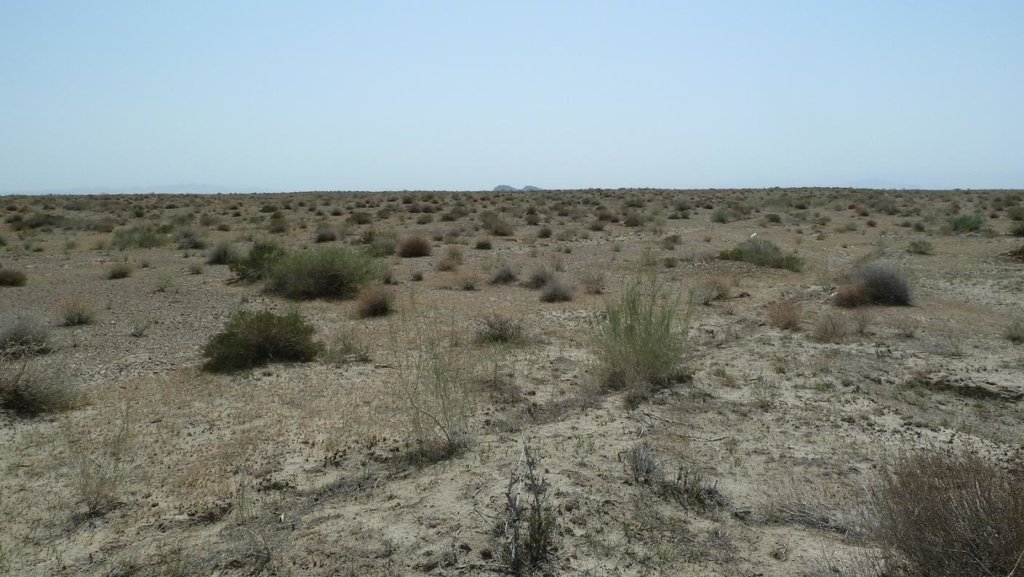
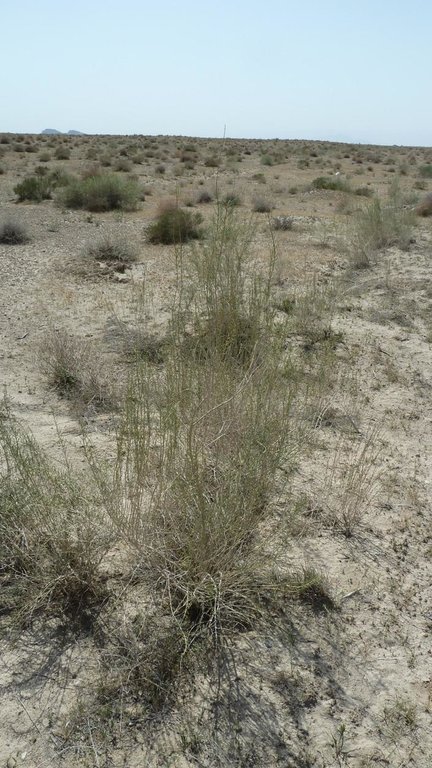
Saxaul (Haloxylon ammodendron) bushes are planted on denuded sandy soils with the aim to reduce the rate of desertification.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
On 15 ha of denuded land, prone to wind erosion the Saxaul bush (Haloxylon ammodendron) which is native to Central Asia was planted in order to stabilise the soils and halt desertification. Over two years 25 ha of Saxaul plantation was established through natural spreading of the plant. The idea came from UNDP who also funded the purchase of seeds, fuel and fertilisers. UNDP further conducted an awareness raising campaign among local land users and members of dekhkan farms about the role of Saxaul bushes in combating land degradation and techniques of planting Saxaul plantations.
Purpose of the Technology: The Shaartuz area has repeatedly suffered from droughts, and the natural vegetation cover is highly degraded due to overexploitation for firewood. This renders the sandy soils very susceptible to wind erosion. Saxaul plantations have been widely applied in other arid areas of Central Asia to combat desertification, and were selected as an appropriate method for soil fixation around Shaartuz.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Saxaul seeds have to be collected in November, and need to be planted immediately, as otherwise they lose their viability. A tractor was used to plough the land, and the seeds were planted manually. 15 ha of plantation were planted in one single day. As they are not irrigated in this area, the Saxaul bushes are entirely dependent on winter rain and dew for their water supply. The trees grow slowly and need protection from roaming cattle. As the forestry department (leskhoz) responsible for the protection of the plantation has no guards, the project employed a local forester from the Jamoat to protect the area. Meetings were held with surrounding villages to discuss the risk of wind erosion, and the need for the plantations. Also a mobile theatre was involved in order to raise the public awareness with regards to deforestation and desertification issues. An agreement was achieved with the local residents to help protect the newly planted trees from cattle.
Natural / human environment: Saxaul plantations improve vegetation cover, and therefore also increase water infiltration into the soil and improve soil structure. Once the soil has stabilised with the help of the Saxaul bushes, other herbs and bushes will regenerate in the area, and reinforce the vegetation cover. Moreover, different wild animals and birds are already nesting in the area as the vegetation increases.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
塔吉克斯坦
区域/州/省:
Shaartuz, Khatlon
有关地点的进一步说明:
Jura Nazarov Jamoat
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 不到10年前(最近)
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过项目/外部干预
注释(项目类型等):
2009
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

牧场
粗放式放牧场:
- 半游牧/游牧

森林/林地
产品和服务:
- 自然保持/保护
注释:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): removal of natural vegetation cover, loss of topsoil through wind erosion
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): wind erosion, droughts,
Plantation forestry: Yes
Forest products and services: nature conservation / protection
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Forests / woodlands: Fp: Plantations, afforestations
如果由于技术的实施而导致土地用途发生变化,则在技术实施前说明土地利的用途。:
Grazing land: Ge: Extensive grazing land
3.3 有关土地利用的更多信息
每年的生长季节数:
- 1
具体说明:
Longest growing period in days: 240Longest growing period from month to month: March-October
3.4 该技术所属的SLM组
- 防风林/防护林带
- 改良的地面/植被覆盖
- 改良植物品种/动物品种
3.5 技术传播
注释:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.15 m2.
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

植物措施
- V1:乔木和灌木覆盖层
注释:
Main measures: vegetative measures
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -linear
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤风蚀
- Et:表土流失
- Ed:风蚀风积

生物性退化
- Bc:植被覆盖的减少
- Bh:栖息地丧失
- Bq:数量/生物量减少
注释:
Main type of degradation addressed: Et: loss of topsoil, Ed: deflation and deposition, Bc: reduction of vegetation cover
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Bh: loss of habitats, Bq: quantity / biomass decline
Main causes of degradation: over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use, overgrazing
Secondary causes of degradation: droughts, population pressure (high demand for firewood)
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 减少土地退化
- 修复/恢复严重退化的土地
注释:
Main goals: rehabilitation / reclamation of denuded land
Secondary goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
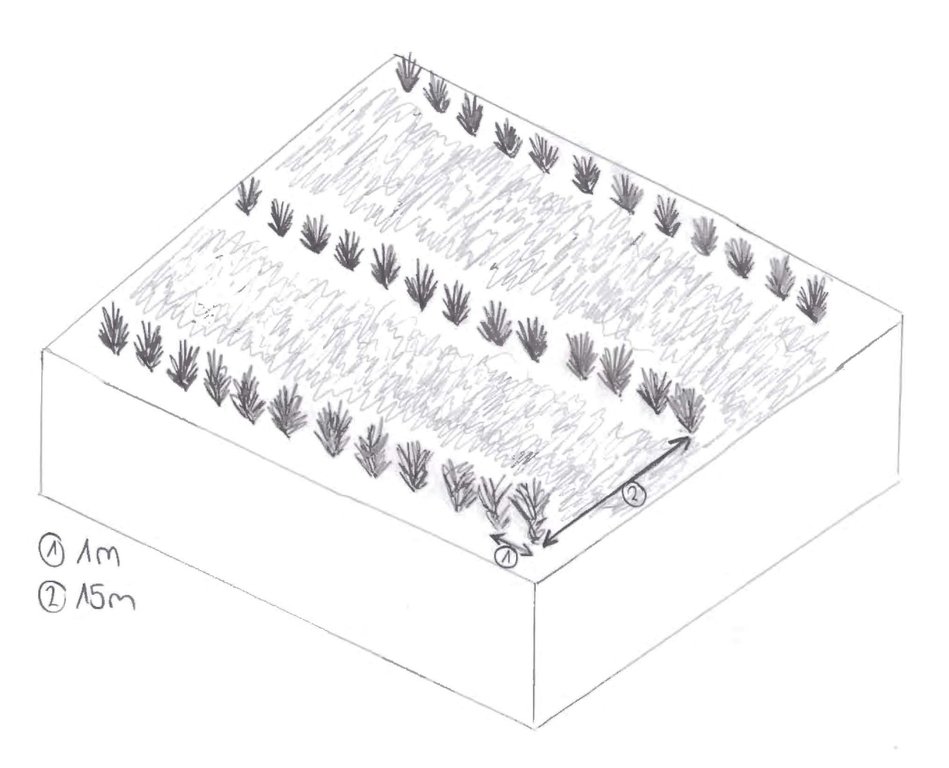
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
4.2 技术规范/技术图纸说明
Saxaul seeds are planted in parallel rows, with 15 m spacing between each row. The interval between seeds within each row is 1m.
Location: Jura Nazarov Jamoat. Shaartuz, Khatlon
Date: 27.05.2011
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: low
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: improvement of ground cover, stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides)
Secondary technical functions: increase of infiltration, reduction in wind speed, increase of biomass (quantity)
Aligned: -linear
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 667
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 15
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 1
Trees/ shrubs species: Saxaul (Haloxylon ammodendron)
4.3 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
Somoni
注明美元与当地货币的汇率(如相关):1美元=:
4.5
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
5.50
4.4 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Collect Saxaul seeds | 植物性的 | November |
| 2. | Plant seeds using tractor with automated seed planter | 植物性的 | December |
| 3. | Application of carbamide fertiliser once after planting seeds | 植物性的 | December |
4.5 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Collect Saxaul seeds | Persons/day | 16.0 | 20.0 | 320.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Tractor for seed planting | Persons/day | 1.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Fuel | ha | 15.0 | 6.666666 | 100.0 | |
| 植物材料 | Seeds | kg | 13.0 | 15.0 | 195.0 | |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | Fertilizer | kg | 3.3 | 2.42424242 | 8.0 | |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 723.0 | |||||
如果土地使用者负担的费用少于100%,请注明由谁负担其余费用:
UNDP
4.6 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Protection of plantation from roaming cattle by local forestry employee | 植物性的 | ongoing |
4.7 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Protection of plantation from cattle | ha/month | 15.0 | 16.666667 | 250.0 | |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 250.0 | |||||
注释:
Machinery/ tools: tractor with automated seed planter
Costs for the purchase of seeds and fertilisers were calculated for one ha of plantation.
However, the costs indicated for machinery and labour regarding the seed collection and planting process are with respect to the whole plantation of 15 ha.
The costs for labour during maintenance are for the monthly salary of an employee who is needed to protect the plantation from outsiders.
4.8 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
For this technology, costs are related to the use of a tractor for planting of seeds and for the purchase of seeds and fertiliser. As the plantation was implemented by the forestry agency, labour used was provided by current employees of the agency.
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
指定年平均降雨量(若已知),单位为mm:
100.00
农业气候带
- 干旱
Thermal climate class: temperate
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 粗粒/轻(砂质)
表土有机质:
- 低(<1%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Soil fertility is low
Soil drainage / infiltration is good
Soil water storage capacity is very low
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
> 50米
地表水的可用性:
匮乏/没有
水质(未处理):
不良饮用水(需要处理)
关于水质和水量的注释和进一步规范:
Water quality (untreated) is poor and groundwater
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 低
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
生产系统的市场定位:
- 商业/市场
个人或集体:
- 员工(公司、政府)
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Difference in the involvement of women and men: forestry agency
Annual population growth: 1% - 2%
Off-farm income specification: It is not the land users who apply the technology, but forestry agency employees.
Market orientation of production system: only protection function
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 州
土地使用权:
- 社区(有组织)
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
生产区域
注释/具体说明:
Loss of grazing land due to restricted access, however, land was already degraded.
收入和成本
农业投入费用
注释/具体说明:
Fertilisers are needed during the establishment phase
工作量
注释/具体说明:
A guard is needed to protect the plantation all day long from roaming cattle.
生态影响
水循环/径流
蒸发
土壤
土壤覆盖层
土壤流失
生物多样性:植被、动物
生物量/地上C
栖息地多样性
注释/具体说明:
provides a habitat for a bird species that are dependent on the tree (Passer ammodendri)
减少气候和灾害风险
风速
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
风力搬运沉积物
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 气候变化/极端天气的类型 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年温度 | 增加 | 好 |
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气象灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 局地暴雨 | 好 |
| 局地风暴 | 好 |
气候灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 干旱 | 好 |
水文灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 比较和缓的(河道)洪水 | 不好 |
其他气候相关的后果
其他气候相关的后果
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 缩短生长期 | 好 |
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
中性/平衡
长期回报:
积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
中性/平衡
长期回报:
积极
6.5 技术采用
如若可行,进行量化(住户数量和/或覆盖面积):
NA
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发地采用该技术,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 0-10%
注释:
Comments on acceptance with external material support: the technology was implemented by the forestry agency, not the land users
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Farmers have understood the importance of Saxaul plantations, and the role Saxaul bushes can play in combating sand drifts. There has been a trend towards growing spontaneous adoption of the technology by others.
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
Effective fixation of sandy soils, protecting them from wind storms and preventing erosion. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Increase plantation areas in the region |
| Use of native tree species which are very well adapted to arid ecosystems |
| Through the plantation of Saxaul, the establishment of other plant species follows on naturally. |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Decline of areas suitable for cattle grazing | Developing a management plan which could include restricted user rights for cattle grazing |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| The plantation only has protective function, but there is no aim to introduce a sustainable management scheme which would allow for the extraction of firewood. | Develop a management plan |
| The area covered by the plantation is very small so the impacts might be minimal. | Increase the plantation area |
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块