Gully Rehabilitation [埃塞俄比亚]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Unknown User
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Fabian Ottiger
Kitir (Amharic)
technologies_1469 - 埃塞俄比亚
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
10/12/2005
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
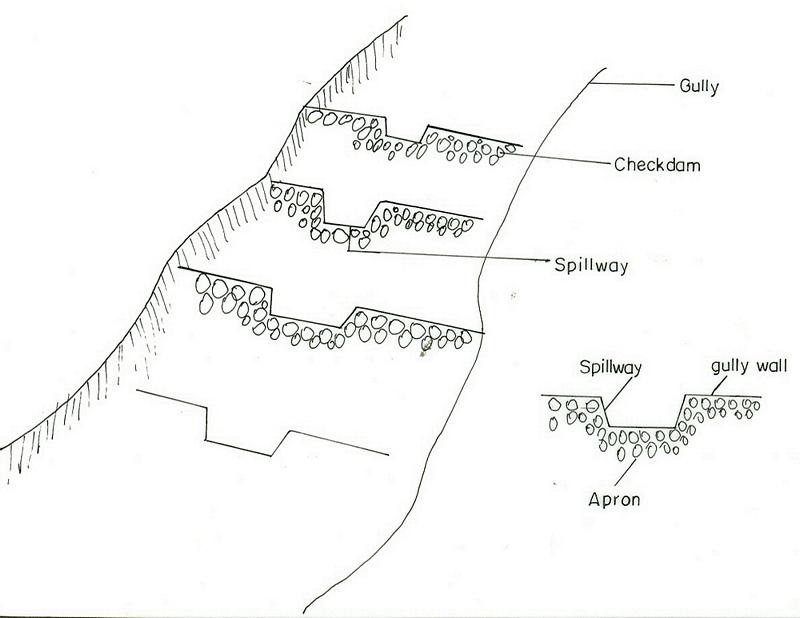
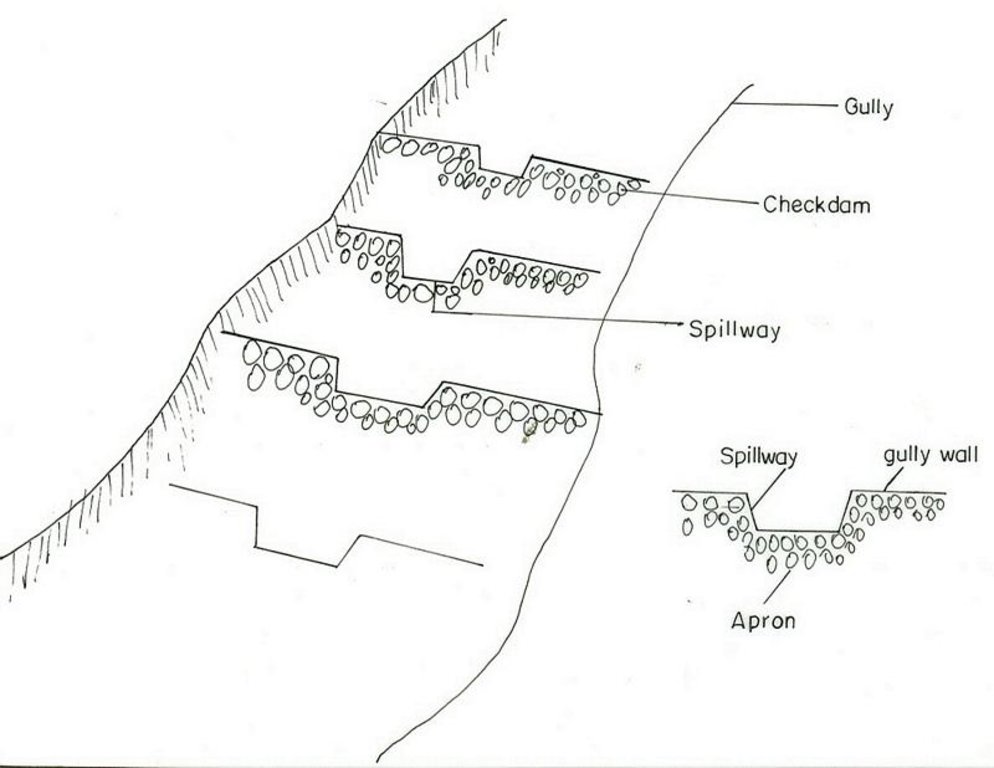
It is a barrier of stone/wood/earth placed across a gully to control runoff and sediment passing through.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
A checkdam constructed from stone, wood or branches of trees. It has an average height of 1m and is spaced at 1m vertical interval. The purpose is to reclaim gully lands to productive lands by controllong the rate of runoff and trapping the soil. By plugging the gully using different checkdams the gully gradient is brought to a gentle slope and flow rates and soil movment is regulated. Constructing of checkdam in a gully starts with smaller checkdams which are regularly maintained and up graded of their heights. Gully plugging by checkdams and vegetative material is suitable to all agro-climatic conditions but the choice of material for establishment depends on the availability of material in the nearby and rate of flow. For a high rate and volume of flows stone checkdams are prefered to wooden or earth chekdams.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
埃塞俄比亚
区域/州/省:
South Gonder
有关地点的进一步说明:
Meher, Gurara, Melo, Rib, Sebat Wodel, Hamus Wonz
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 50多年前(传统)
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过项目/外部干预
注释(项目类型等):
Introduced to the country about 30 years ago from other countries exprience.
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

农田
- 一年一作
主要农作物(经济作物及粮食作物):
Major food crop: Barley, wheat

混合(作物/放牧/树木),包括农林
- 农林牧业
注释:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Open grazing, bare land, high erosion risk
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): land slide, erosion
Nomadism: Yes
Grazingland comments: grazing lands are replaced by other land use system or degraded irreversibly and also the number and productivity of livestock is reduced due to shortage of feed and fodder.
Other type of forest: selective felling of natural forests: charcoal
Problems / comments regarding forest use: The communities assigned guards for area closures in order to protect them from illegal cutting and conversion to other land uses. Government or projects used to employ site guards for protecting the enclosures at the initial stage. When the communities started to get benefit from enclosures then decided to take responsibility to protecting them.
Forest products and services: fuelwood, grazing / browsing, protection against natural hazards
Type of cropping system and major crops comments: Barley-teff
Constraints of settlement / urban
Constraints of infrastructure network (roads, railways, pipe lines, power lines)
3.3 有关土地利用的更多信息
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
每年的生长季节数:
- 1
具体说明:
Longest growing period in days: 210 Longest growing period from month to month: May - Dec
3.4 该技术所属的SLM组
- 横坡措施
- 地表水管理(泉、河、湖、海)
3.5 技术传播
注释:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.42 km2.
The area is calculated based on gully size.
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

植物措施

结构措施
- S5:大坝、集水斗、水池
注释:
Main measures: structural measures
Secondary measures: vegetative measures
Type of vegetative measures: scattered / dispersed
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀
- Wg:冲沟侵蚀/沟蚀

化学性土壤退化
- Cn:肥力下降和有机质含量下降(非侵蚀所致)
注释:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wg: gully erosion / gullying, Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 减少土地退化
注释:
Secondary goals: prevention of land degradation, rehabilitation / reclamation of denuded land
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
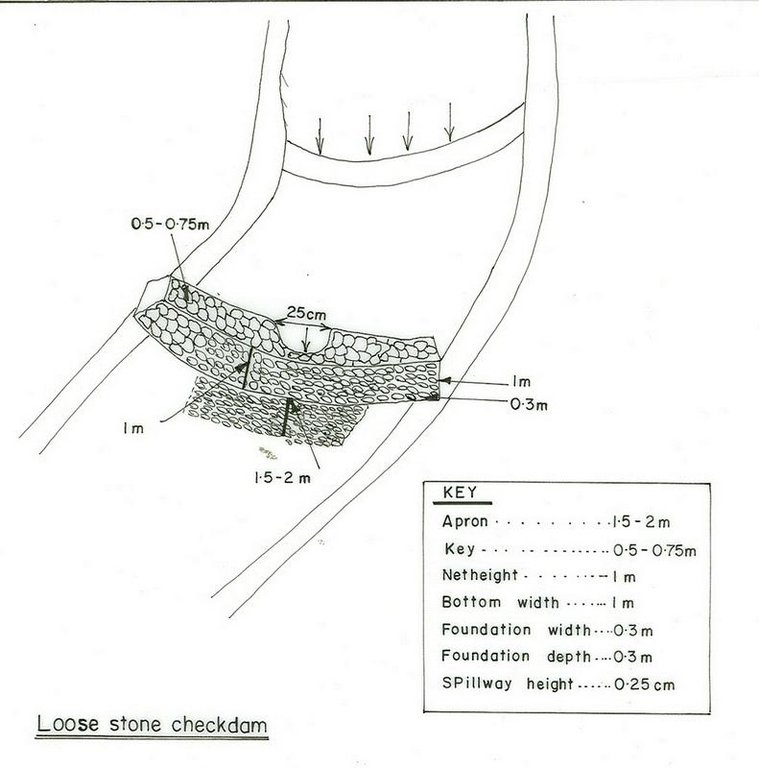
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
4.2 技术规范/技术图纸说明
Amhara
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap
Secondary technical functions: increase of infiltration, water harvesting / increase water supply
Scattered / dispersed
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 400
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 1m
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 5m
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 1m
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 5m
Vegetative measure: plantation
Vegetative material: F : fruit trees / shrubs, G : grass
Number of plants per (ha): 2500
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 1m
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 1m
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 1m
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 1m
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: F : fruit trees / shrubs, G : grass
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: F : fruit trees / shrubs, G : grass
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: F : fruit trees / shrubs, G : grass
Trees/ shrubs species: saligna, dicurense
Grass species: Bana, vetiver, serdo
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 12.00%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is (see figure below): 10.00%
Gradient along the rows / strips: 0.00%
Structural measure: checkdam
Vertical interval between structures (m): 1
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 1
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 1
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 1
Vegetation is used for stabilisation of structures.
4.3 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
Birr
注明美元与当地货币的汇率(如相关):1美元=:
8.6
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
0.80
4.4 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | collect planting materials | 植物性的 | onset of rain |
| 2. | planting | 植物性的 | during rain |
| 3. | construction | 结构性的 | dry season/after crop harvest |
| 4. | fencing | 结构性的 | dry season/after crop harvest |
| 5. | Stone collection | 结构性的 | January-March |
| 6. | gully reshaping | 结构性的 | January-March |
| 7. | dig foundation | 结构性的 | dry season/after crop harvest |
| 8. | Fencing (live or wood) | 管理 | dry season |
4.6 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | replanting | 植物性的 | rainy season /as required |
| 2. | fencing | 植物性的 | dry season /once |
| 3. | stone collection | 结构性的 | as required |
| 4. | construction | 结构性的 | as required |
| 5. | maintaining breaks in fence | 管理 | dry season / as required |
4.7 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
注释:
Length and width of the structure.
4.8 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
slope, labour, time of cost recovery payment (period), width (length) of the gully, availability of construction materials.
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
有关降雨的规范/注释:
It ranges from 1250-1599 mm
农业气候带
- 潮湿的
- 半湿润
Subhumid: It is woina dega and dega
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
关于地形的注释和进一步规范:
Altitudinal zone: It ranges between 1500-4033 m a.s.l.
Landforms: Mountain slopes (ranked 1), ridges (ranked 2) and plateau/plains as well as hill slopes (both ranked 3)
Slopes on average: Hilly (ranked 1), steep (ranked 2) and rolling (ranked 3)
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 细粒/重质(粘土)
表土有机质:
- 低(<1%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Soil depth on average: Very shallow (More in hilly slopes/steep slopes, ranked 1) and shallow (on rolling areas, ranked 2)
Soil texture: Fine/heavy (At gentle slopes, ranked 1), medium (rolling slopes, ranked 2) and coarse/ light (at the bottom of the gully)
Soil fertility: Medium (ranked 1), low (ranked 2) and high (ranked 3)
Topsoil organic matter is low (continuous cropping and erosion)
Soil drainage/infiltration is medium (steep slopes , ranked 1) and good (ranked 2)
Soil water storage capacity is medium (ranked 1) and high (clay soils, ranked 2)
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
生产系统的市场定位:
- 生计(自给)
非农收入:
- 低于全部收入的10%
相对财富水平:
- 非常贫瘠
- 贫瘠
机械化水平:
- 手工作业
- 畜力牵引
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Population density: 200-500 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2% - 3%
60% of the land users are poor and own 30% of the land.
40% of the land users are poor and own 20% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: No apparent differences could be observed.
Level of mechanization is aniaml traction (ploughing using oxen, horses and cow, ranked 1) and human labour (digging by hoe, ranked 2)
Market orientation of production system: Also mixed (subsistence/ commercial), subsistence in agro-silvopastoralism (farm implements, feul, charcoal)
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者拥有或租用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
注释:
Average area of land owned or leased by land users applying the Technology: Mostly from 0.5-0.75 ha
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 州
- 个人,未命名
土地使用权:
- 个人
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
注释/具体说明:
no annual crop grown
饲料生产
饲料质量
木材生产
收入和成本
农业收入
工作量
注释/具体说明:
More labour needed for the technology means shortage of labour for farm activities.
社会文化影响
社区机构
国家机构
SLM/土地退化知识
冲突缓解
注释/具体说明:
At the boundray of two holdings and questions as to who will have to ues the gully.
生态影响
水循环/径流
水的回收/收集
多余水的排放
土壤
土壤水分
注释/具体说明:
Due to more water retention.
土壤覆盖层
土壤流失
其它生态影响
Biodiversity enhancement
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
旱季稳定可靠的水流
下游洪水
下游淤积
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
稍微积极
长期回报:
积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
长期回报:
积极
6.5 技术采用
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发地采用该技术,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 90-100%
注释:
35 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Soil erosion control and prevention of gully expansion. |
|
sources of fodder How can they be sustained / enhanced? plant more forage trees |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
Fodder production and soil formation rate enhanced How can they be sustained / enhanced? make frequent maintenance |
|
Moisture and water harvesting enhanced How can they be sustained / enhanced? plant useful trees/ nitrogen fixing trees |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| rodents |
7. 参考和链接
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Ethiopia Federal RDS, Rural Rural Development policy Strategy and Methods. 2001.
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Soil and water management manual, Alemaya. 2003.
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块