Dugout Pond [印度]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Mulchand Kag
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Fabian Ottiger
Talawadi
technologies_1472 - 印度
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
30/09/2002
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.5 请参阅有关SLM方法的问卷

Comprehensive watershed development [印度]
Participatory approach that includes a package of measures leading to empowerment of communities to implement and sustain watershed development.
- 编制者: David Gandhi
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
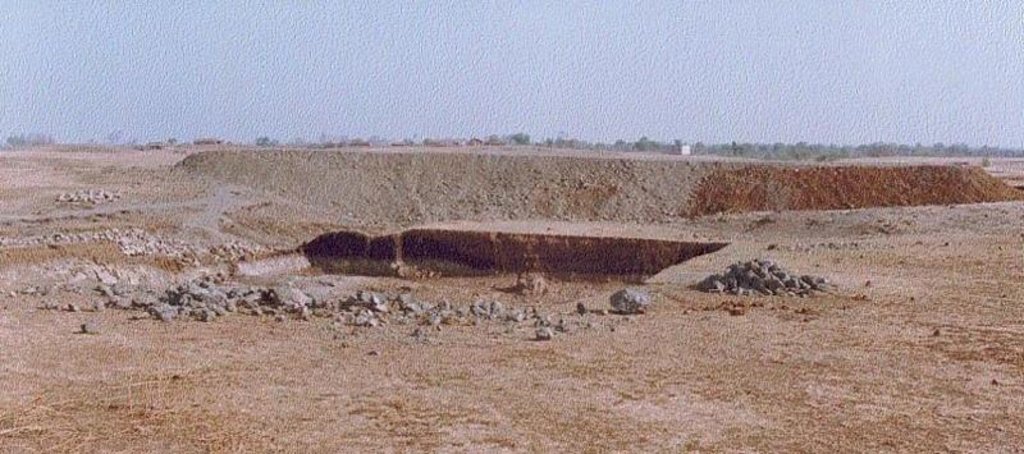
Dugout pond is a sunken water harvesting structure constructed along the rills in upper catchment for the purpose of storage of runoff and recharge of ground water.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
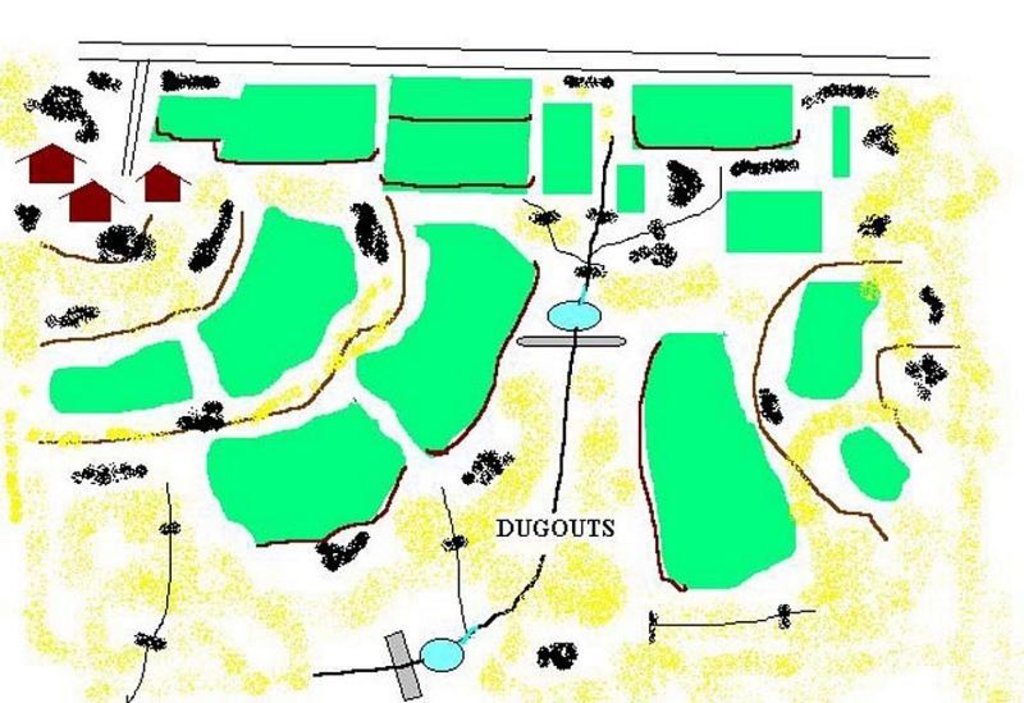
Dugout pond is a rectangular shape subsurface pond with the excavated material forming an embankment down stream. It is constructed in the upper catchment of the watershed, along the rill/shallow gully. The site for the pond should be where there is a depression. The size may vary from small to large depending on the size of catchment, needs of the farmers, availability of finance, bed rock strata.
Purpose of the Technology: 1- Storage of runoff. 2- Increase in water levels of shallow wells 'odees' through increased percolation. 3- Flood control through series of such structures. 4- Low cost, low risk alternative for poor community. 5- Benefits to community living in upper catchment.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: 1- Site selection with community. 2- Design and preparation of estimate by the project staff. 3- Descussion with VWDC and community, identification of users, descussion regarding contribution, agreement, work plan. 4- Layout and construction under VWDC supervision with technical support from the project. 5- Treatment of catchment.
Natural / human environment: Responsibility of user group.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
印度
区域/州/省:
Madhya Pradesh
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 不到10年前(最近)
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过项目/外部干预
注释(项目类型等):
The technology has been developed by the project as modification/improvement to Dugout pond constructed under NWDPRA (National Watershed Development Program for Rainfed Areas).
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 适应气候变化/极端天气及其影响
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

牧场
注释:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): 1. Utilisation of slopy and stony (class VI) land for agriculture. 2. Agriculture practices along the slope, use of erosion permitting crop eg. Cotton, Maize. 3. Excessive grazing of grass land.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): shallow soils, low soil moisture , low yields , non-availability of grazing land.
Type of cropping system and major crops comments: Monsoon - Cotton + Maize + Blackgram /Soyabean. Winter (with irrigation) - Wheat + Gram (excluding Cotton fields).
3.3 有关土地利用的更多信息
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
注释:
Water supply: Also mixed rainfed - irrigated
每年的生长季节数:
- 2
具体说明:
Longest growing period in days: 150 Longest growing period from month to month: Nov - Mar Second longest growing period in days: 135 Second longest growing period from month to month: Jun - Sep
3.4 该技术所属的SLM组
- 集水
- 灌溉管理(包括供水、排水)
- 地下水管理
3.5 技术传播
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果该技术均匀地分布在一个区域上,请注明覆盖的大致区域。:
- 10-100 平方千米
注释:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 48 m2.
The area comprises 36 villages with 1632 household mainly tribal. Villages comprise a larger settlement along with a number of hamlets. The topography is rolling and gently undulating. The area forms the catchment of the Larki stream, which forms the upper catchment of the river Mahi.
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wg:冲沟侵蚀/沟蚀

水质恶化
- Ha:干旱化
注释:
Main type of degradation addressed: Ha: aridification
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wg: gully erosion / gullying
Main causes of degradation: other human induced causes (specify) (Social causes - Lack of awareness and mobilisation amongst the communities.), Top down approach (Macro planning rather than micro (village level) planning.)
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
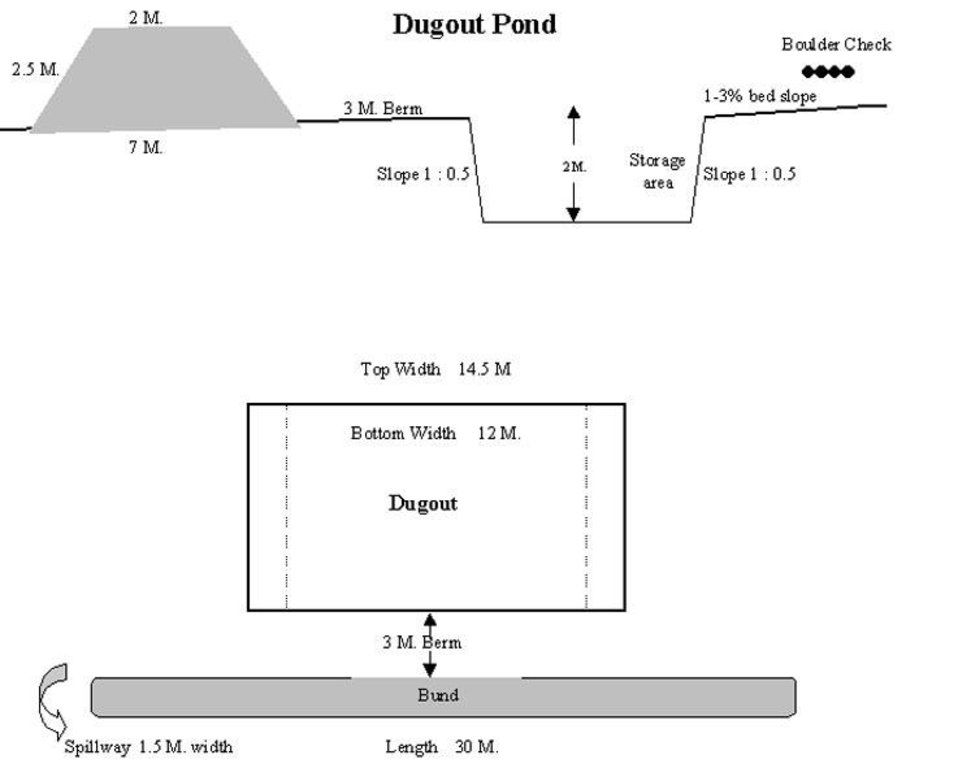
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
4.2 技术规范/技术图纸说明
Technical Drawing of Dugout Pond
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: increase of infiltration
Secondary technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, water harvesting / increase water supply
Construction material (earth): Excavated material used for embankment.
Construction material (stone): Excavated stones used for pitching.
4.3 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
Rupees
注明美元与当地货币的汇率(如相关):1美元=:
48.85
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
1.00
4.4 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Discussion in VWDC meeting | 结构性的 | March-April |
| 2. | Site selection | 结构性的 | March-April |
| 3. | Identification of beneficiaries, users group formation | 结构性的 | March-April |
| 4. | Design & estimate | 结构性的 | March-April |
| 5. | Agreement with VWDC | 结构性的 | March-April |
| 6. | Treatment of catchment area | 结构性的 | April-May |
| 7. | Construction of dugout pond | 结构性的 | April-May |
| 8. | Seeding of embankment | 结构性的 | June-July |
4.5 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
注释:
Duration of establishment phase: 12 month(s)
4.6 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Monitoring by users group | 结构性的 | Year around/Regular |
| 2. | Report of damage, breakage in VWDC | 结构性的 | Rainy season/After heavy shower |
| 3. | Decision regarding repair by VWDC/UG | 结构性的 | Rainy season/After heavy shower |
| 4. | Necessary repaires carried out | 结构性的 | Rainy season/After heavy shower |
| 5. | Desilting | 结构性的 | Dry season/annual |
4.7 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
注释:
The size of dugout described in 2.7.1 is :- Excavated area - 13m long X 12m wide X 2.5m Bund - 30m long X2.5m height X 2m top width X 7m bottom width
4.8 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
1- Cost of excavation increases with hardness of strata. 2- Non availability of stones locally for pitching.
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
指定年平均降雨量(若已知),单位为mm:
800.00
有关降雨的规范/注释:
However for the past 4 years the area has received below average rainfall.
农业气候带
- 半干旱
90 - 120 days LGP - monsoon
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
关于地形的注释和进一步规范:
Landforms: Ridges (ranked 1, gradually undulating topography) and hill slopes (ranked 2)
Slopes on average: Moderate (ranked 1, fields in upper catchment) and gentle (ranked 2, fields in valley portion)
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 低(<1%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Soil depth on average: Shallow (ranked 1, fields on ridge/slopes), very shallow (ranked 2, ridge portion) and moderately deep (ranked 3, fields in valley)
Soil fertility: Medium (ranked 1) and low (ranked 2, fields on ridge/slopes, grass land)
Soil drainage/infiltration: Good (ranked 1, sloping land, shallow soils) and medium (ranked 2, fields in valley)
Soil water storage capacity: Low (ranked 1, shallow soils) and medium (ranked 2, deep soils)
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
非农收入:
- 收入的10-50%
相对财富水平:
- 贫瘠
- 平均水平
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Population density: 200-500 persons/km2
Annual population growth: > 4%
33% of the land users are average wealthy and own 33% of the land (Few farmers with wells, fields in valley.).
50% of the land users are poor and own 57% of the land (Majority of farmers.).
17% of the land users are poor and own 10% of the land (Very small holding.).
Off-farm income specification: While main income is from rainfed agriculture, significant income is obtained during migration, which increases during drought periods.
Level of mechanization: Animal traction (ranked 1, land preparation), manual labour (ranked 2, land preparation, weeding, harvesting) and mechanised (ranked 3, threshing)
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 社区/村庄
土地使用权:
- 自由进入(无组织)
- 个人
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
中性/平衡
长期回报:
积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
积极
6.5 技术采用
如若可行,进行量化(住户数量和/或覆盖面积):
1672
注释:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
1632 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: estimates
40 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: survey results
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: The community is very poor and hence requires some financial support to offset loss of wages.
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接

Comprehensive watershed development [印度]
Participatory approach that includes a package of measures leading to empowerment of communities to implement and sustain watershed development.
- 编制者: David Gandhi
模块
无模块