Small Water Impounding Project (SWIP) [菲律宾]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Philippine Overview of Conservation Approaches and Technologies
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Deborah Niggli
technologies_1507 - 菲律宾
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
SLM专业人员:
Teresita Sandoval
632-923-0459
Bureau of Soils and Water Management
Diliman, Quezon City, Philippines
菲律宾
SLM专业人员:
Rondal Jose
923-04-59
bswm@pwolrd.net / ph joron @pacific.net.ph
Bureau of Soils and Water Management
SRDC Bldg., Elliptical Road Diliman, Quezon City, Philippines
菲律宾
SLM专业人员:
Lucas Rodolfo
Bureau of Soils and Water Management
Visayas Avenue, Vasra, Quezon City, Philippines
菲律宾
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Bureau of Soils and Water Management (Bureau of Soils and Water Management) - 菲律宾1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
16/05/2000
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.4 所述技术的可持续性声明
这里所描述的技术在土地退化方面是否存在问题,导致无法被认为是一种可持续的土地管理技术?:
否
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
Development of micro-catchment for soil and water conservation and for the provision of supplementary irrigation during the dry season.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
Small Water Impounding Project (SWIP) is a water harvesting and storage structure consisting of an earth embankment spillway, outlet works and canal facilities. It is designed for soil and water conservation and flood control by holding as much water as possible during the rainy season. The reduced volume and force of runoff subsequently reduced their eroding power of water thereby minimizing soil erosion and silting of fertile bottom lands. The reservoir with its stored water is an important supplemental source of water for agriculture and is also used for fisheries. SWIP development involves a holistic approach. The watershed is developed for land use that enhances water infiltration and minimizes soil erosion (for the long life of the reservoir). The most common use of the watershed is agro-forestry. The service area is used for high value crops that minimizes the use of water on a controlled basis. A holistic and integrated approach is done in managing the micro-watershed. The farmer-beneficiaries of the irrigation water and those of the watershed are organized into an association. They maintain the system and protect the watershed by advocating sustainable agriculture.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
菲律宾
区域/州/省:
Nueva Ecija
有关地点的进一步说明:
Nueva Ecija
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 不到10年前(最近)
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过项目/外部干预
注释(项目类型等):
From other areas with simlar condition (areas where runoff can be collected and impounded and used for supplementary irrigation)
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 改良生产
- 保护生态系统
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

农田
- 一年一作
- 多年一作(非木材)
注释:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Long term sustainability of agricultural system is seriously in doubt. Because farmers cannot practice intensive agriculture, income is low.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Low yield and cannot raise two crops of rice in one year. High inputs required. Small farm area and lack of irrigation facilities.
3.3 有关土地利用的更多信息
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 混合雨水灌溉
每年的生长季节数:
- 2
具体说明:
Longest growing period in days: 180, Longest growing period from month to month: May - Oct; Second longest growing period in days: 120, Second longest growing period from month to month: Nov - Feb
3.4 该技术所属的SLM组
- 灌溉管理(包括供水、排水)
- 地表水管理(泉、河、湖、海)
3.5 技术传播
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果该技术均匀地分布在一个区域上,请注明覆盖的大致区域。:
- 1-10 平方千米
注释:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 10 m2.
Because of the recurring El Nino phonomenon, the government fast-tracked the development of small water impounding projects during the 90's to counteract severe water shortages especially for upland areas.
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀

化学性土壤退化
- Cn:肥力下降和有机质含量下降(非侵蚀所致)

水质恶化
- Ha:干旱化
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 修复/恢复严重退化的土地
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
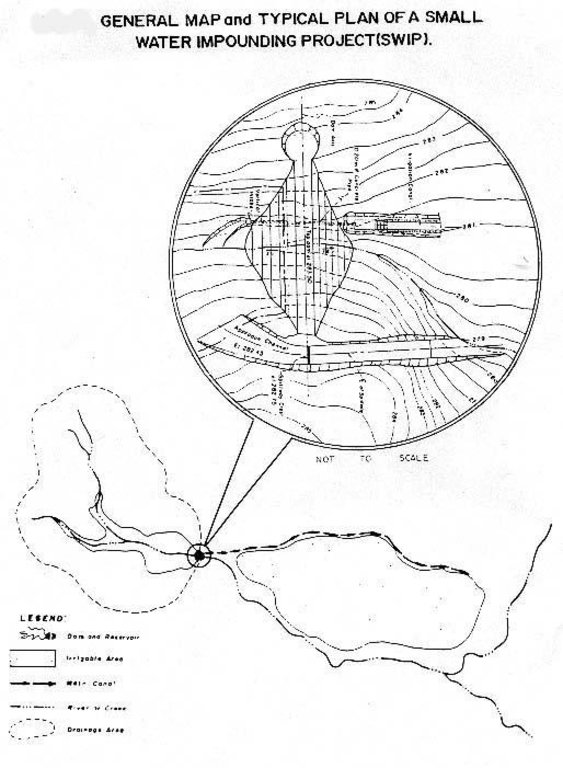
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
4.2 技术规范/技术图纸说明
General map and typical plan of a Small Water Impounding Project (SWIP)
Location: Talugtug. Nueva Ecija
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: water harvesting / increase water supply
Secondary technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, increase of infiltration
Vegetative measure: contour
Vegetative material: F : fruit trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 100
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 10
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 10
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 10
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 10
Vegetative measure: downstream side of the dam
Vegetative material: F : fruit trees / shrubs
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.5
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.5
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.5
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.5
Vegetative measure: forest trees
Vegetative material: F : fruit trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 4,000
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 2
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 2
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 2
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 2
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: F : fruit trees / shrubs
Trees/ shrubs species: mahogany, G-melina
Fruit trees / shrubs species: mango
Grass species: vetive (to protect the downstream slope of dam)
Other species: banana
4.3 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
Phil. Peso
注明美元与当地货币的汇率(如相关):1美元=:
40.0
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
4.00
4.4 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | clearing | 植物性的 | onset of rains May-June) |
| 2. | layout/staking | 植物性的 | onset of rains |
| 3. | digging of holes | 植物性的 | onset of rains |
| 4. | basal fertilization | 植物性的 | onset of rains |
| 5. | planting | 植物性的 | onset of rains |
4.5 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | labour | ha | 1.0 | 39000.0 | 39000.0 | |
| 设备 | machine use | ha | 1.0 | 55000.0 | 55000.0 | |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 94000.0 | |||||
注释:
Duration of establishment phase: 12 month(s)
4.6 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Weeding | 植物性的 | rainy season /monthly |
| 2. | Fertilization | 植物性的 | /twice a year |
| 3. | Irrigation | 植物性的 | dry season /weekly |
4.7 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | labour | ha | 1.0 | 900.0 | 900.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | animal traction | ha | 1.0 | 375.0 | 375.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 1275.0 | |||||
注释:
Length, height and width of structure and the source of materials like gravels and stones.
4.8 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
The source of materials like stones/gravels affect the cost. Usually, these are hauled from long distances. Also the construction of access roads adds substantially to the cost.
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
农业气候带
- 潮湿的
- 半湿润
Thermal climate class: tropics
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
- 细粒/重质(粘土)
表土有机质:
- 中(1-3%)
- 低(<1%)
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
生产系统的市场定位:
- 生计(自给)
- 混合(生计/商业
非农收入:
- 收入的10-50%
相对财富水平:
- 贫瘠
- 平均水平
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Population density: 50-100 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 1% - 2%
5% of the land users are very rich and own 25% of the land (4).
10% of the land users are rich and own 25% of the land.
50% of the land users are average wealthy and own 40% of the land.
30% of the land users are poor and own 5% of the land.
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者拥有或租用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
注释:
Only a small part of the landholding can be cultivated intensively.
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 个人,未命名
- 个人,有命名
土地使用权:
- 自由进入(无组织)
- 个人
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
注释/具体说明:
rice production
饲料生产
饲料质量
木材生产
生产区域
收入和成本
农业收入
其它社会经济效应
Fish production
注释/具体说明:
Fish culture
社会文化影响
娱乐机会
注释/具体说明:
Picnic grounds
社区机构
注释/具体说明:
Farmers are organized into an association
SLM/土地退化知识
注释/具体说明:
Including soil fertility management
Employment creation
注释/具体说明:
During construction
生态影响
土壤
土壤水分
土壤覆盖层
注释/具体说明:
Woodland taking over grassland
土壤流失
注释/具体说明:
reservoir area
生物多样性:植被、动物
植物多样性
其它生态影响
Soil fertility
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
水资源可用性
注释/具体说明:
Increased groundwater recharge
旱季稳定可靠的水流
注释/具体说明:
dry season flow
下游洪水
下游淤积
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
轻度消极
长期回报:
非常积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
非常积极
长期回报:
非常积极
6.5 技术采用
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发地采用该技术,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 0-10%
注释:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
180 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Increase in farm income |
| Opportunity for other farming opportunities (fish including shell farming) |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| It is a holistic and integrated approach to watershed management/development |
| Immediate economic impact |
| Institutional strengthening |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| High establishment cost |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| High initial investment cost | Cost-sharing among different agencies. Beneficiaries to subsidize labor |
| Loss of productive land (reservoir area) | Compensation of affected farmers |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
- 实地考察、实地调查
- 与土地使用者的访谈
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Small Water Impounding Project (SWIP) for Productivity Improvement of Paddy Soils: The case of Talugtug, Nueva Ecija, Philippines, 2000, Rodolfo M. Lucas, Samuel Contreras, Teresita Sandoval
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块