Jatropha curcas hedge [埃塞俄比亚]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Simon Bach
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Fabian Ottiger
Agulo Keter
technologies_1524 - 埃塞俄比亚
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
SLM专业人员:
Ayele Habtamu
+251 92 592 0594
Haramaya University
Haramaya University, P.O. Box 138, Dire Dawa, Ethiopia
埃塞俄比亚
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Haramaya University (HU) - 埃塞俄比亚1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
30/04/2011
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
Gully rehabilitation and hill stabilization with Jatropha hedges.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
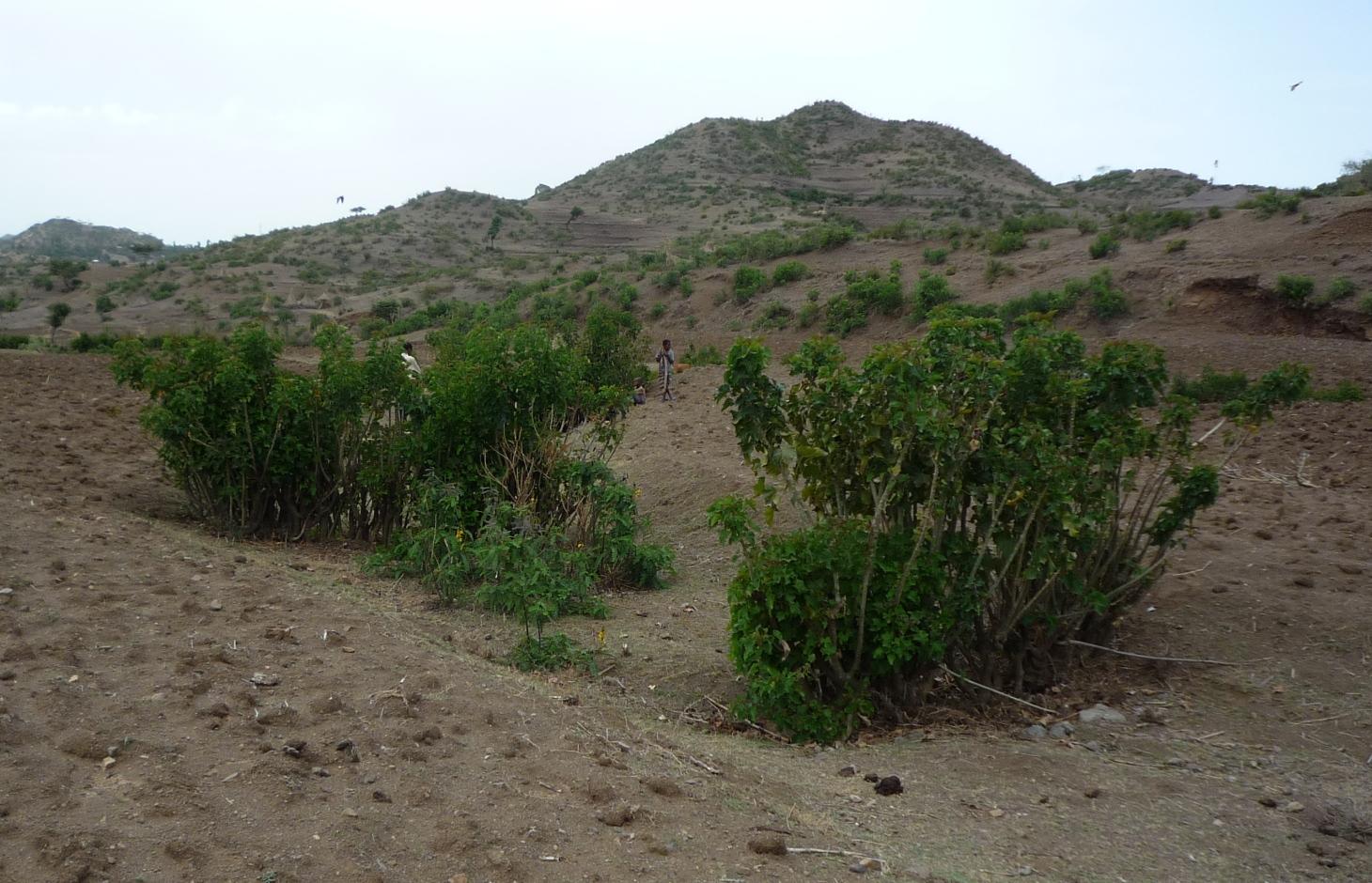
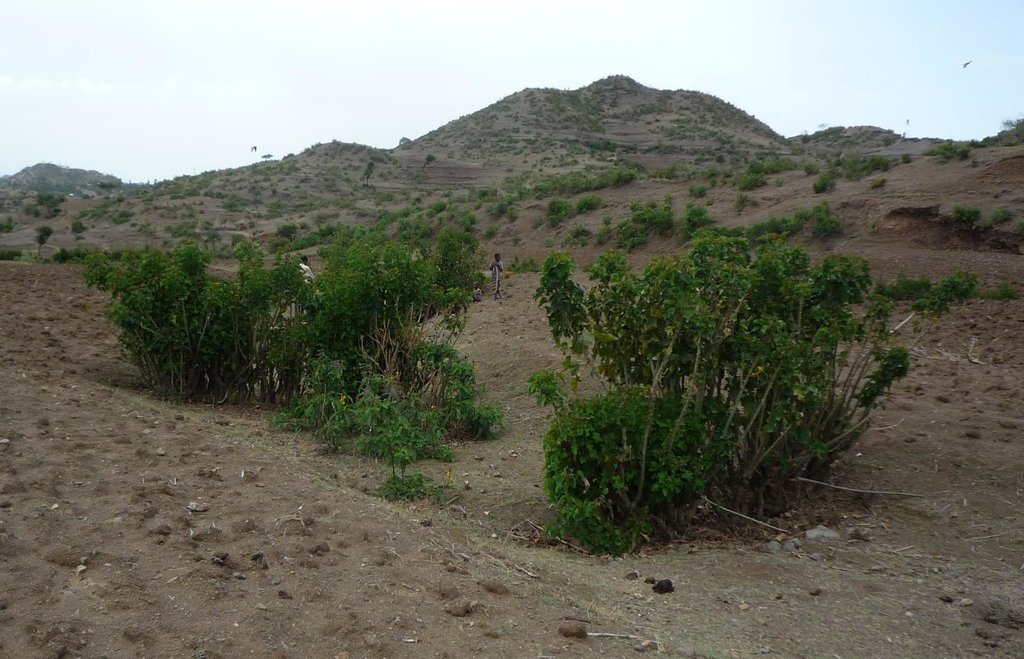
In the area around Bati in Ethiopia, Jatropha is used to stabilize hills ore to rehabilitate gullies. The technology was introduced during the last decade by local farmers on their plots. The advantage of Jatropha against other shrubs is that it is poisonous and therefore not browsed by animals. Additionally the seeds can be collected by household members and sold on the local market. The seed's oil can be used as a lamp oil or even for the production of bio-fuel.
Purpose of the Technology: Besides hedges and living fences, Jatropha is used for combating sheet or gully erosion. To stop erosion processes the Jatropha cuttings are planted across a gully or along hill sides to stabilize them in the same manner as check dams or terraces do. The plant is chosen because of its very tolerant character, rather high accessibility in the area and because it is easy to propagate by cuttings. Often Jatropha is used in combination with traditional stone check dams or terraces aiming for an increased stability of the technology itself. For that purpose Jatropha is planted in front of the stone walls or also on top of them.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: In earlier times Jatropha was planted by seeds but nowadays, since there are a lot of plants in the area, propagation by cuttings is the more prominent form. Since the plants are pruned every year anyway, the cuttings are accessible almost in any case for free. At markets further away, the cuttings cost around one cent per piece. In order to rehabilitate a gully Jatropha cuttings are planted as near as possible in the selected area in a row across the gully. After rooting, the spaces between the plants are filled up with litter, shrubs or stones. In order to have a thick stem and avoid competition with crops, the plants are pruned every year. The thick main stems reach a height of approximately one meter which delineates the maximum height of possible soil collection. If the area behind the filled up gaps and the cuttings has silted up, the height is increased by adding new litter in the higher up gaps. In off farming season, the Jatropha seeds are collected and sold on the market to create additional income.
Natural / human environment: The case study site, Bati, lays in an semiarid climatic zone on 1600 m a.s.l. Rainfalls are erratic and the rain sum per year is between 500-1000 mm. The landscape is very hilly with rather steep slopes. The area has a high population density and growth. The agricultural sector is very dominant and lead by a lot of small scale farming with a lot of livestock and small plots of cropland.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
埃塞俄比亚
区域/州/省:
Ethiopia / Amhara Region
有关地点的进一步说明:
Bati
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 10-50年前
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过土地使用者的创新
注释(项目类型等):
Farmers are using Jatropha curcas since approximately 30 years in the research area in Bati mostly for fencing. Innovative farmers started using the plant for stabilizing existing physical structures (stone walls, terraces, gully check dams) or using it as a complete substitute for these physical structures.
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
- 创造有益的经济影响
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

农田
- 一年一作
主要农作物(经济作物及粮食作物):
Major food crop: Sorghum
Major other crop: Corn

混合(作物/放牧/树木),包括农林
- 林牧业
主要产品/服务:
Major food product: Cattle, goat, sheep, camel
Major other product: Chicken
注释:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Deforestation, overgrazing, cultivation of erosion-sensitive areas or steep slopes.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Too much soil loss and land degradation, no vegetation cover and poor soil moisture.
Grazingland comments: Livestock is not fenced in. Children herd the animals and watch out that they do not browse through crop fields. In off-farming season crop residues are collected from the field and stored next to the field. Animals are allowed to eat the still remaining residues on the field. After that, the animals are fed by the collected crop residues.
Livestock is grazing on crop residues
Type of grazing system comments: Livestock is not fenced in. Children herd the animals and watch out that they do not browse through crop fields. In off-farming season crop residues are collected from the field and stored next to the field. Animals are allowed to eat the still remaining residues on the field. After that, the animals are fed by the collected crop residues. Ge: Extensive grazing land
3.3 有关土地利用的更多信息
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
注释:
Water supply: Also mixed rainfed - irrigated
每年的生长季节数:
- 1
具体说明:
Longest growing period in days: 90 Longest growing period from month to month: June until September
牲畜密度(如相关):
> 100 LU /km2
3.4 该技术所属的SLM组
- 横坡措施
3.5 技术传播
注释:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.7 m2.
Size of the case study watershed.
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

植物措施
- V1:乔木和灌木覆盖层

结构措施
- S1:阶地
- S6:墙、障碍物、栅栏、围墙
注释:
Main measures: vegetative measures, structural measures
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -contour
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀
- Wg:冲沟侵蚀/沟蚀
注释:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wg: gully erosion / gullying
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion
Main causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (Deforestation for the past 30 years.), over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use (Wood collection for cooking and construction.), overgrazing (60% of the watershed area are cultivated - big grazing pressure on remaining land), other human induced causes (specify) (Cultivation of very steep slopes.), change of seasonal rainfall (Erratic rainfall.), Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts) (If there is rain, it is intensive.), population pressure (High population pressure.), poverty / wealth (Poor facilities.)
Secondary causes of degradation: soil management (Poor soil management practices and lack of awareness.), crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (Annual cropping.), droughts (The research area is considered rather dry.), land tenure (If the land is rented, it is poorly managed.), inputs and infrastructure: (roads, markets, distribution of water points, other, …) (Poor access to fertilizer. Bad infrastructures.), education, access to knowledge and support services (Lack of awareness for soil degradation.), Low productivity of the land (As a consequence seeking for new/larger areas to increase production.)
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 减少土地退化
- 修复/恢复严重退化的土地
注释:
Main goals: rehabilitation / reclamation of denuded land
Secondary goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
4.2 技术规范/技术图纸说明
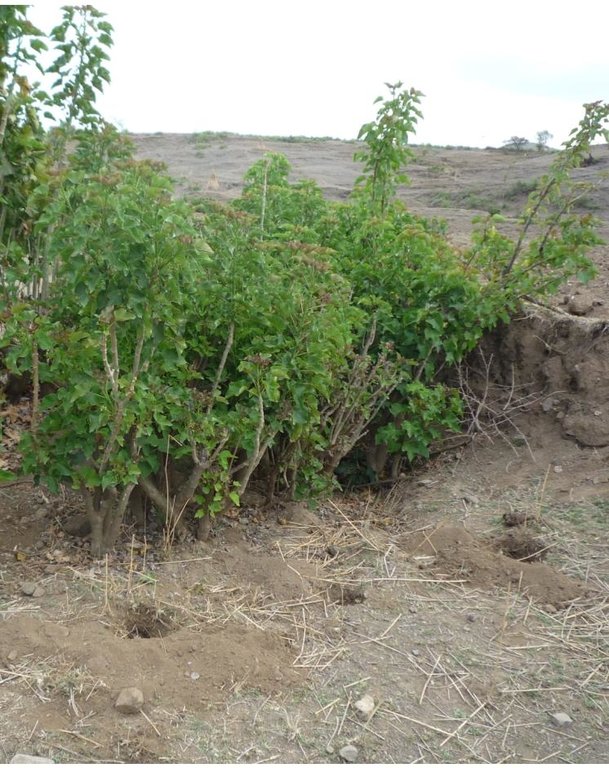
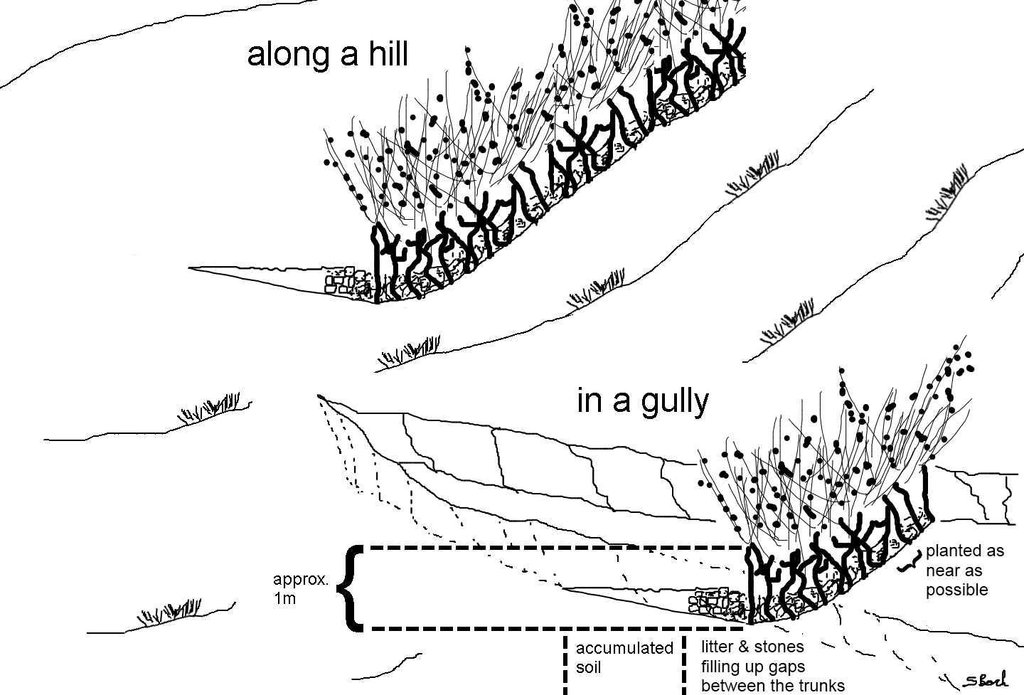
Jatropha hedges as they can be found in the region of Bati. Often the plant is used for gully rehabilitation. For that purpose it is planted (mostly by cuttings) with a minimal interval between each plant to create a barrier-like hedge. The gaps are filled up with litter or stones.
Approximately 1 m of soil can be collected by the trunk - above that height it is too thin. The Jatropha seed can create additional income besides the purpose of soil and water conservation. Often, the plant is used in combination with traditional technologies (terraces, stone walls) and planted on top or in front of these traditional structures to improve their stability.
Location: South of Bati. Bati Woreda, Amhara Region, Ethiopia
Date: 05.05.2011
Technical knowledge required for land users: low (Planting takes place rather randomly in places of needs.)
Main technical functions: control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap, control of concentrated runoff: impede / retard, reduction of slope angle, increase / maintain water stored in soil, increase of groundwater level / recharge of groundwater, sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting
Secondary technical functions: reduction of slope length, improvement of ground cover, improvement of topsoil structure (compaction), increase in organic matter, increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), increase of infiltration, water harvesting / increase water supply, improvement of water quality, buffering / filtering water, reduction in wind speed, increase of biomass (quantity)
Aligned: -contour
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 10 per m
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): ~1m
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): ~20m
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.1
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 1.5
Vegetative measure: filling material
Vegetative material: O : other
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: O : other
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: O : other
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: O : other
Trees/ shrubs species: Jatropha curcas
Other species: Stones, shrubs, sticks - things that can be found and utilized to fill up gaps between each plant.
4.3 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
Ethiopian Birr
注明美元与当地货币的汇率(如相关):1美元=:
16.82
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
1.00
4.4 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | One time initial sawing of Jatropha seeds (30 years ago). | 植物性的 | Initial. Wet season. |
| 2. | Cutting of the Jatropha cuttings (12.5 person days needed). | 植物性的 | dry season |
| 3. | Planting of the Jatropha cuttings (12.5 person days needed). | 植物性的 | dry season |
4.5 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Seeding | person day | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Cutting of the Jatropha cuttings | person day | 12.5 | 1.0 | 12.5 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Planting of the Jatropha cuttings | person day | 12.5 | 1.0 | 12.5 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Tools for cutting | 500m | 1.0 | 5.0 | 5.0 | 100.0 |
| 植物材料 | Seeds | kg | 1.0 | 2.0 | 2.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 33.0 | |||||
4.6 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Collection of Jatropha seeds (5 person days needed). | 植物性的 | Off farming season(Okt.) |
| 2. | Filling up the gaps with litter (5 person days needed). | 植物性的 | If necessary |
| 3. | Pruning of the Jatropha hedges (15 person days needed). | 植物性的 | Yearly before wet season. |
4.7 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Collection of Jatropha seeds | Person days | 5.0 | 1.0 | 5.0 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Filling up the gaps with litter | Person days | 5.0 | 1.0 | 5.0 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Pruning of the Jatropha | person days | 15.0 | 1.0 | 15.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Tools | Person days | 15.0 | 0.333333333 | 5.0 | 100.0 |
| 施工材料 | Wood | 500m | 1.0 | 100.0 | ||
| 施工材料 | Stone | 500m | 1.0 | 100.0 | ||
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 30.0 | |||||
注释:
Machinery/ tools: saw, axe
Total costs of a hectare are calculated for a hedge of 100 m length every 20 m (500 m total hedge) in the year 2011. Tool prices were estimated and labor costs were calculated with a daily wage of 1$.
4.8 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
Rough topology in the area, questionable availability of construction materials if they are not found nearby.
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
有关降雨的规范/注释:
Erratic rainfall (rainseason from June until September)
751-1000 mm ranked 1
501-750 mm ranked 2
农业气候带
- 半干旱
Thermal climate class: tropics
LGP shorter than 90 days.
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
关于地形的注释和进一步规范:
Altitudinal zone: 1501-2000 m a.s.l. (The study site is located at 1600m a.s.l.)
Landforms: Hill slopes (ranked 1) and valley floors (ranked 2)
Slopes on average: Hilly (ranked 1), rolling (ranked 2) and steep (ranked 3)
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 粗粒/轻(砂质)
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 低(<1%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Soil depth on average: Very shallow (ranked 1), shallow (ranked 2)
Soil texture: Coarse/light (ranked 1) and medium (ranked 2)
Soil fertility is low
Soil drainage/infiltration is good
Soil water storage capacity is medium
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
5-50米
地表水的可用性:
匮乏/没有
水质(未处理):
不良饮用水(需要处理)
关于水质和水量的注释和进一步规范:
Ground water table is unknown.
Availability of surface water: Only during rainy season
Water quality (untreated): Poor drinking water (treatment required, mostly groundwater)
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 低
关于生物多样性的注释和进一步规范:
Relative to other parts of Ethiopia.
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
生产系统的市场定位:
- 生计(自给)
非农收入:
- 低于全部收入的10%
相对财富水平:
- 丰富
个人或集体:
- 个人/家庭
机械化水平:
- 手工作业
- 畜力牵引
性别:
- 男人
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: 100-200 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 6%
1% of the land users are rich (Adopt the most of SWC technologies).
19% of the land users are average wealthy.
89% of the land users are poor.
Off-farm income specification: Off-farm income has low importance.
Level of mechanization: Animal traction (plowing by oxen, ranked 1) and manual work (ranked 2)
Market orientation: Mixed (subsistence and commercial) Goat/sheep are main meat source (in household or on market).
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者拥有或租用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 小规模的
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 个人,有命名
用水权:
- 自由进入(无组织)
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
注释/具体说明:
gullies are transformed to fields
生产故障风险
注释/具体说明:
improving soil moisture
产品多样性
注释/具体说明:
selling the Jatropha curcas seeds
生产区域
注释/具体说明:
gullies are transformed to fields. Structure needs space but also gains space
土地管理
注释/具体说明:
gully is now flat land and traversable, structure as a new obstacle
能源生产
注释/具体说明:
Jatropha curcas seed oil as a biofuel
水资源可用性和质量
饮用水的可用性
收入和成本
农业投入费用
注释/具体说明:
alluvial soil is relatively fertile
农业收入
注释/具体说明:
new fields lead to higher productivity
收入来源的多样性
注释/具体说明:
selling the Jatropha curcas seeds
经济差异
注释/具体说明:
additional income by selling Jatropha seeds
工作量
注释/具体说明:
slightly labor increase, establishment and maintenance work
社会文化影响
食品安全/自给自足
注释/具体说明:
additional space for new fields
社区机构
国家机构
SLM/土地退化知识
注释/具体说明:
positive examples for other land users
社会经济弱势群体的情况
注释/具体说明:
up -downstream problems may be solved
Improved livelihoods and human well-being
注释/具体说明:
Accumulation of soil leads to new space for fields and additional food security or even income (if crop surplus is sold). Collection of Jatropha curcas seeds - they can be sold (additional income) or processed to oil (lamp oil etc.)
生态影响
水循环/径流
水量
注释/具体说明:
increased soil moisture
水的回收/收集
注释/具体说明:
Jatropha curcas dam blocks water flow
地表径流
注释/具体说明:
increased infiltration, reduced flow velocity
地下水位/含水层
注释/具体说明:
increased infiltration
蒸发
注释/具体说明:
maybe due to the Jatropha curcas canopy
土壤
土壤水分
注释/具体说明:
Jatropha curcas dam blocks water flow,. But additional groundwater may be logged
土壤覆盖层
注释/具体说明:
Jatropha curcas canopy
土壤流失
注释/具体说明:
alluvial accumulation behind the structure
土壤结壳/密封
注释/具体说明:
increased rooting
土壤压实
注释/具体说明:
increased rooting
养分循环/补给
注释/具体说明:
Jatropha curcas leaves & litter
土壤有机物/地下C
注释/具体说明:
Jatropha curcas leaves & litter
生物多样性:植被、动物
生物量/地上C
注释/具体说明:
Jatropha curcas biomass
植物多样性
注释/具体说明:
Jatropha curcas as a new habitat
动物多样性
注释/具体说明:
Jatropha curcas as a new habitat
有益物种
注释/具体说明:
Jatropha curcas new habitat for worms etc
栖息地多样性
注释/具体说明:
Jatropha curcas as a new habitat
害虫/疾病控制
注释/具体说明:
new habitat for rodents etc.
减少气候和灾害风险
洪水影响
注释/具体说明:
flood controll by Jatropha curcas dams
碳和温室气体的排放
注释/具体说明:
little effect by additional plants
火灾风险
注释/具体说明:
Jatropha curcas wood is a bad fire wood
风速
注释/具体说明:
Jatropha curcas shrub as a wind breaker
其它生态影响
Increased competition
注释/具体说明:
Over water and sunlight
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
水资源可用性
注释/具体说明:
possibility of spring development
旱季稳定可靠的水流
注释/具体说明:
if a spring can develop
下游洪水
注释/具体说明:
increased infiltration/reduced flooding
下游淤积
注释/具体说明:
trapping of the sediments by the structure
地下水/河流污染
注释/具体说明:
trapping of the sediments by the structure
缓冲/过滤能力
注释/具体说明:
increased infiltration
风力搬运沉积物
对邻近农田的破坏
注释/具体说明:
due to gully rehabilitation
对公共/私人基础设施的破坏
注释/具体说明:
due to gully rehabilitation
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 气候变化/极端天气的类型 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年温度 | 增加 | 好 |
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气象灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 局地暴雨 | 好 |
| 局地风暴 | 好 |
气候灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 干旱 | 好 |
水文灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 比较和缓的(河道)洪水 | 未知 |
其他气候相关的后果
其他气候相关的后果
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 缩短生长期 | 好 |
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
轻度消极
长期回报:
非常积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
非常积极
长期回报:
非常积极
注释:
Establishment needs a little time, although not very much. Maintenance work is very little needed and can be done if needed or in off-farming season. Establishment and mainentance costs are none or very little.
6.5 技术采用
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发地采用该技术,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 90-100%
注释:
Comments on acceptance with external material support: Local technology spread from farmer to farmer.
Comments on spontaneous adoption: Completely based on farmer's initiative.
There is a strong trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: A lot of farmer are adopting (or already have adopted) Jatropha curcas as a SWC technology in the region.
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
Soil and water conservation are very important. Also the conservation of soil moisture. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Create farmer's awareness that SWC is very important for a sustainable land management. |
|
In combination, Jatropha curcas can also be used to stabilize traditional stone structuress (terraces, dams). These physical structures are not consideret very stable and need a lot of work to establish and maintain. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Further research to improve physical structures, Jatropha curcas structures as well as their combination. |
|
The roots bind the soil and holding it together and help collecting additional soil that otherwise would be washed out. The root and the plant also help to slow down flowing water. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Research on how tolerant is the plant on flooding etc. |
|
Jatropha curcas is also a very good life fence that animals do not browse through because the leaves are poisonous. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Create awareness in the society that the plant is poisonous and should not be eaten. |
|
The seeds can be sold. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Creating and improving markets, infrastructures and technologies that need Jatropca curcas oil or biofuel. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
Very low labor and money input for establishment and maintenance. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Keep the technology as simple as it is today. |
|
Easy to atopt in a wide range of environments (Jatroha curcas is a rather tolerant plant). How can they be sustained / enhanced? Additional research to improve knowledge of Jatropha curcas. |
|
Selling of the seeds is an additional income. If the seeds are crushed to oil it can substitute for example lamp oil that has to be bought. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Improve market situation and find technologies suitable to use Jatropha curcas oil or biofuel. |
|
The plant can be used in a wide range of rehabilitation purposes (gully rehabilitation, hill stabilization, improvment of micro climate etc.) How can they be sustained / enhanced? Create and maintain awareness of the farmers. |
|
If plantet on bare land only, the plant does not compete with food production. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Sensitize the farmers that food is more important than gaining an extra income so they do not give up their fields for Jatropha seed production. |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| If children eat the seeds they get sick. | Rise awareness that the plant is poisonous. |
| Plant competes for soil moisture. | Find a good compromise betweeen pruning and maximum toleratet shade as well as maximum soil moisture that can be taken by the plant to maximize yield. |
| Plant competes for sun light. | Find a good compromise betweeen pruning and maximum toleratet shade as well as maximum soil moisture that can be taken by the plant to maximize yield. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Jatropha curcas is an alien plant although it is used for more than 30 years in the region. | Research on the long term effects of Jatropha curcas in specific areas. |
| If the plant should reach maximum yields inputs have to be increased as well and it has to be planted on fertile soil (food competition). | Make shure people only use it as fence or as a SWC plant on bare land. |
| To avoid shading the plant is often pruned every year and the yield is therefore very small (economically irrelevant). | Find a good compromise betweeen pruning and maximum toleratet shade to maximize yield. |
| The plant is poisonous. People have to take care and children have to be sensitized. But acording to the farmers eating the leaves or the seeds leads to stomach ache and is not too dangerous. | Create awareness in the society that the plant is poisonous and should not be eaten. |
| Farmers plant and use Jatropha curcas quite randomly and without any specific approach. | The role of science: find the best practice. |
7. 参考和链接
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Bach S. (2012) Potentials and limitations of Jatropha curcas as a multipurpose crop for sustainable energy supply and soil and water conservation - a case study in Bati, Ethiopia, using the WOCAT approach. Unpublished master’s thesis, Centre for Development and Environment, University of Bern.
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块