Degraded communal pasture Obishur [塔吉克斯坦]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Malgorzata Conder
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Fabian Ottiger
technologies_1545 - 塔吉克斯坦
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
NCCR North-South (NCCR North-South) - 吉尔吉斯斯坦有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
CDE Centre for Development and Environment (CDE Centre for Development and Environment) - 瑞士1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
28/07/2012
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
Degraded communal pasture without grazing management and sufficient waterpoints
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
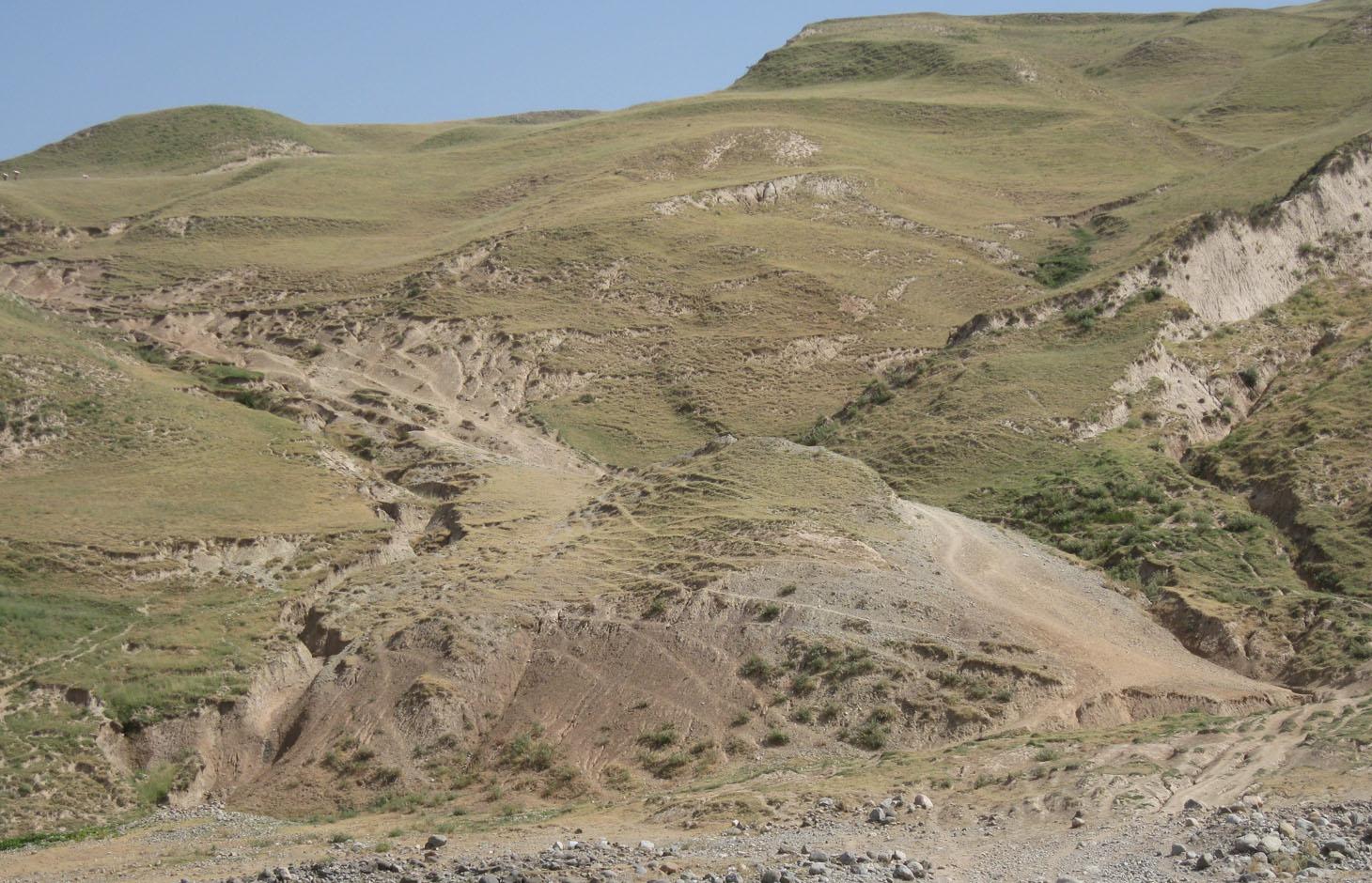
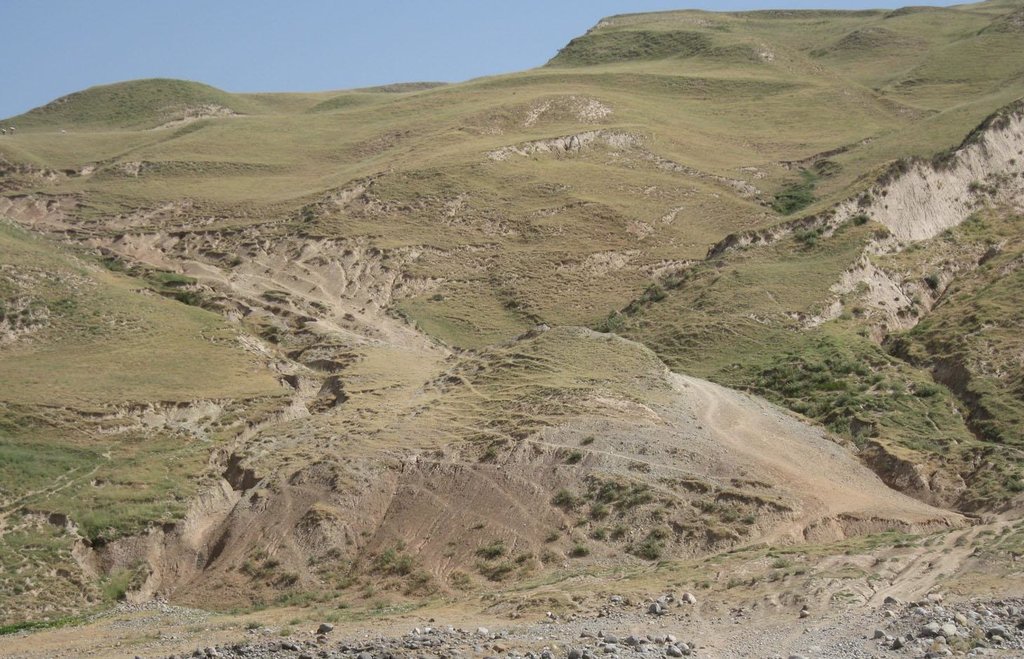
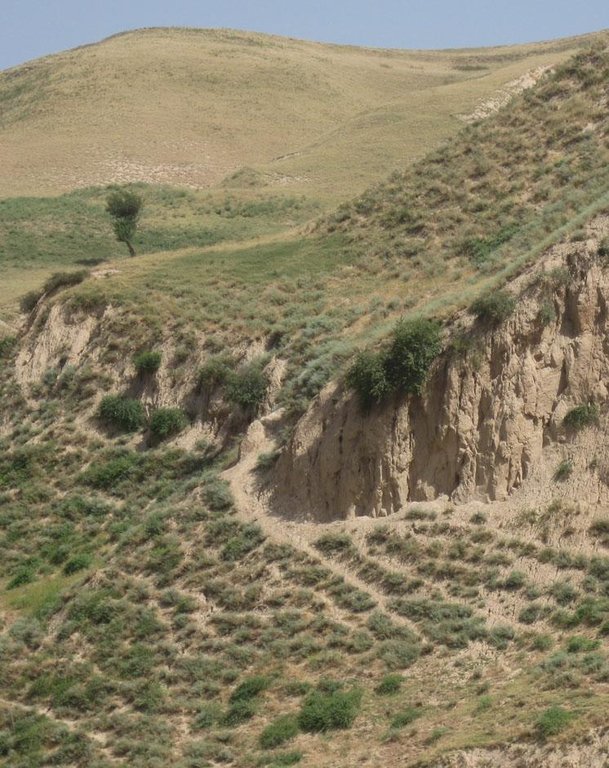
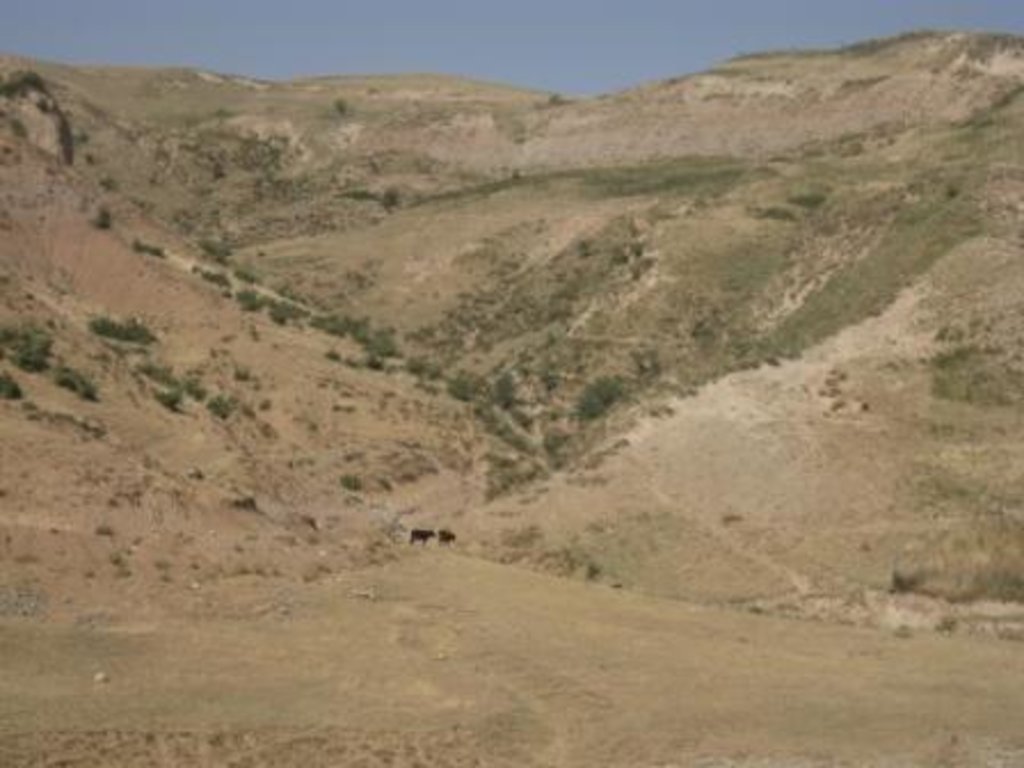
On the communal pasture, located at the foothill around 85 households graze their livestock totally 500 cows and 100 sheep and goats. Half of the households of the village Momandion have livestock which is meant to graze at different places on that pasture. As there is no water point higher up in the pasture area, livestock grazes near the village where a water point is installed. The rolling zone is totally overgrazed and shows several deep gullies. Cows and the small livestock are divided for grazing. Every family is looking after a herd for a day every month. Although the families of the herding livestock communicate with each other, there is no planning for a sustainable grazing management.
Purpose of the Technology: The whole plot is overgrazed and livestock is increasing, so at least controlled pasture management could be expected to decrease the degradation process. Additionally, more vegetation would be available for feeding livestock. More water points have to be installed higher up in the pasture, to decrease pressure on soil and vegetation. More waterpoints would extend the area to be used for grazing. Another issue is that nobody really feels responsible for the pasture and its management. This explains why no pasture management exists at Jamoat level. Farmers are not organized in terms of pasture rotation and control. Livestock owners pay very small rent, which does not make them vakue the pastureland. Additionally, the tax is not enough for projects or investments (like installing water points).
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Every household pays 12 Somoni per year for pasture rent, which is in total around 1000 Somoni. Rent is per household not per livestock number. No maintenance is done.
Natural / human environment: The pasture extends from the foothill to the upper parts of the hill with a high percentage of overgrazed, trampled, erosive area. Except for the water point near the village, there is no water and no shady points for livestock. 85 households graze their livestock, which total 1500 cows and small livestock. Every household is responsible for grazing the herd one day every month. Apart from that, no management exists between the families and Jamoat.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
塔吉克斯坦
区域/州/省:
Khatlon, Tajikistan
有关地点的进一步说明:
Muminabad
Map
×3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

牧场
主要动物种类及产品:
Main animal species: Cow, sheep, goat
注释:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Overgrazing, soil compaction, soil and gully erosion, increasing vegetation cover and hence lower resilience for disaster risks
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): More livestock reduces vegetation cover through overgrazing and trampling. Gully formation. Not enough water acces in the pastureland.
Semi-nomadism / pastoralism: cow, sheep, goat
Grazingland comments: Evtl. summer pasture
semi-nomadism within an delimited communal area, intensive pastoralism due to overgrazing
Type of grazing system comments: Evtl. summer pasture
semi-nomadism within an delimited communal area, intensive pastoralism due to overgrazing
3.3 有关土地利用的更多信息
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
每年的生长季节数:
- 1
具体说明:
Longest growing period in days: 180 Longest growing period from month to month: March-Sept
牲畜密度(如相关):
50-100 LU /km2
3.4 该技术所属的SLM组
- 畜牧业和牧场管理
- Water points
3.5 技术传播
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果该技术均匀地分布在一个区域上,请注明覆盖的大致区域。:
- 0.1-1 平方千米
注释:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.94 km2.
Farmer (Vakil) did not know at all the area extent, data based on Google Earth
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

管理措施
- M2:改变管理/强度级别
- M3:根据自然和人文环境进行布局
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀
- Wg:冲沟侵蚀/沟蚀

土壤风蚀
- Eo:场外劣化效应

物理性土壤退化
- Pc:压实

生物性退化
- Bc:植被覆盖的减少

水质恶化
- Hs:地表水良变化
注释:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Eo: offsite degradation effects, Bc: reduction of vegetation cover, Hs: change in quantity of surface water
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wg: gully erosion / gullying, Pc: compaction
Main causes of degradation: overgrazing (No controlled grazing), population pressure (Increasing livestock), land tenure (Communal property=No individual responsibility)
Secondary causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (one or two decades ago), disturbance of water cycle (infiltration / runoff), poverty / wealth
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 减少土地退化
- 修复/恢复严重退化的土地
注释:
Main goals: rehabilitation / reclamation of denuded land
Secondary goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
4.2 技术规范/技术图纸说明
Bare vegetation cover, no trees, soil erosion, trampled paths, rill building, no waterpoints are all calling for pasture management among the villages.
Location: Obishur watershed, Momandion. Muminabad, Khatlon, Tajikistan
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: control of concentrated runoff: impede / retard, improvement of ground cover, stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides), increase of infiltration
Secondary technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, increase of surface roughness, improvement of surface structure (crusting, sealing), improvement of topsoil structure (compaction), increase in organic matter, increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), increase / maintain water stored in soil, increase of biomass (quantity), spatial arrangement and diversification of land use
Change of land use practices / intensity level: Controlled access, staged grazing
4.3 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
Somoni
注明美元与当地货币的汇率(如相关):1美元=:
4.83
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
12.40
4.4 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Possible solutions: Pasture ManagementWorkshops, Meetings, Round table | 管理 | |
| 2. | Water points | 管理 | |
| 3. | Reduce Livestock quantity | 管理 |
4.8 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
It wouldn not be expensive to hold regular meetings between the livestock keeping families for a better organization of the grazing area. The installation of a water point is very costly and labour intensive in contrast.
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
有关降雨的规范/注释:
Totally 800 mm: 700mm in winter-spring, July-Sept dry season
农业气候带
- 半湿润
Thermal climate class: temperate, LPG from end of March until September
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
关于地形的注释和进一步规范:
Slopes on average: Steep (ranked 1, approx. 40%) and hilly (ranked 2)
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 粗粒/轻(砂质)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Soil fertility: Low
Soil drainage/infiltration: Poor
Soil water storage capacity: Very low
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
> 50米
地表水的可用性:
匮乏/没有
水质(未处理):
不可用
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 低
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
生产系统的市场定位:
- 生计(自给)
非农收入:
- 低于全部收入的10%
相对财富水平:
- 平均水平
个人或集体:
- 团体/社区
性别:
- 男人
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: 100-200 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 1% - 2%
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者拥有或租用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 小规模的
注释:
2.4 ha, if 7.7 pers/household counted. In total 3040 ha pasture
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 社区/村庄
土地使用权:
- 个人
用水权:
- 租赁
注释:
Land ownership is based on Land user certificates
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
畜牧生产
注释/具体说明:
Less forage available for livestock due to reduce vegetation cover
木材生产
注释/具体说明:
important clear-cutting in the past
土地管理
SLM之前的数量:
no organizational task without pasture management
注释/具体说明:
no organizational task without pasture management
水资源可用性和质量
家畜用水的可用性
注释/具体说明:
lack of water points for livestock
家畜用水的质量
注释/具体说明:
lack of water points for livestock
收入和成本
农业投入费用
注释/具体说明:
more fodder has to be bought, because grazing is insufficient
农业收入
注释/具体说明:
Less forage for livestock
工作量
注释/具体说明:
no organizational task without pasture management / feeding animals
社会文化影响
食品安全/自给自足
注释/具体说明:
More difficult to feed livestock
Improved livelihoods and human well-being
生态影响
水循环/径流
地表径流
地下水位/含水层
土壤
土壤水分
土壤覆盖层
土壤结壳/密封
土壤压实
土壤有机物/地下C
减少气候和灾害风险
风速
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
下游洪水
缓冲/过滤能力
对公共/私人基础设施的破坏
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 气候变化/极端天气的类型 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年温度 | 增加 | 好 |
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气象灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 局地暴雨 | 不好 |
气候灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 干旱 | 不好 |
水文灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 比较和缓的(河道)洪水 | 不好 |
注释:
Pasture rotation would improve vegetation cover, infiltration, slope stabilization and natural disaster resilience
Rotate within the grazing land and less energy needed by livestock, which leads also to less consumption and hence overgrazing
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
Establishment of rotational grazing is not expensive and does not require further equipment How can they be sustained / enhanced? Empower communication and decision-making also between the farmers |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Importance of rotational grazing depends on Jamoat and farmers level | Strengthen communication between Jamoat and farmers through consultancy, meetings etc. Farmer as tenants should get a voice. |
| Pastureland rent is too cheap and is not valued. There is no incentive to change, because nobody feels responsible for that area. | Increase the rent and discuss communally where money should go to (e.g. water points). |
| Pasture management does not show benefits immediately which makes it difficult to evidence good Technology. | Explanation/ education about short and long-term benefits |
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块