Micro irrigation in poplar plantation [阿富汗]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Aqila Haidery
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Deborah Niggli
Abyari joychayi
technologies_1603 - 阿富汗
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
SLM专业人员:
SLM专业人员:
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
HELVETAS (Swiss Intercooperation)1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
10/05/2014
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.4 所述技术的可持续性声明
这里所描述的技术在土地退化方面是否存在问题,导致无法被认为是一种可持续的土地管理技术?:
否
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
Micro irrigation canal system for supplying water to poplar plantations on sloping lands.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
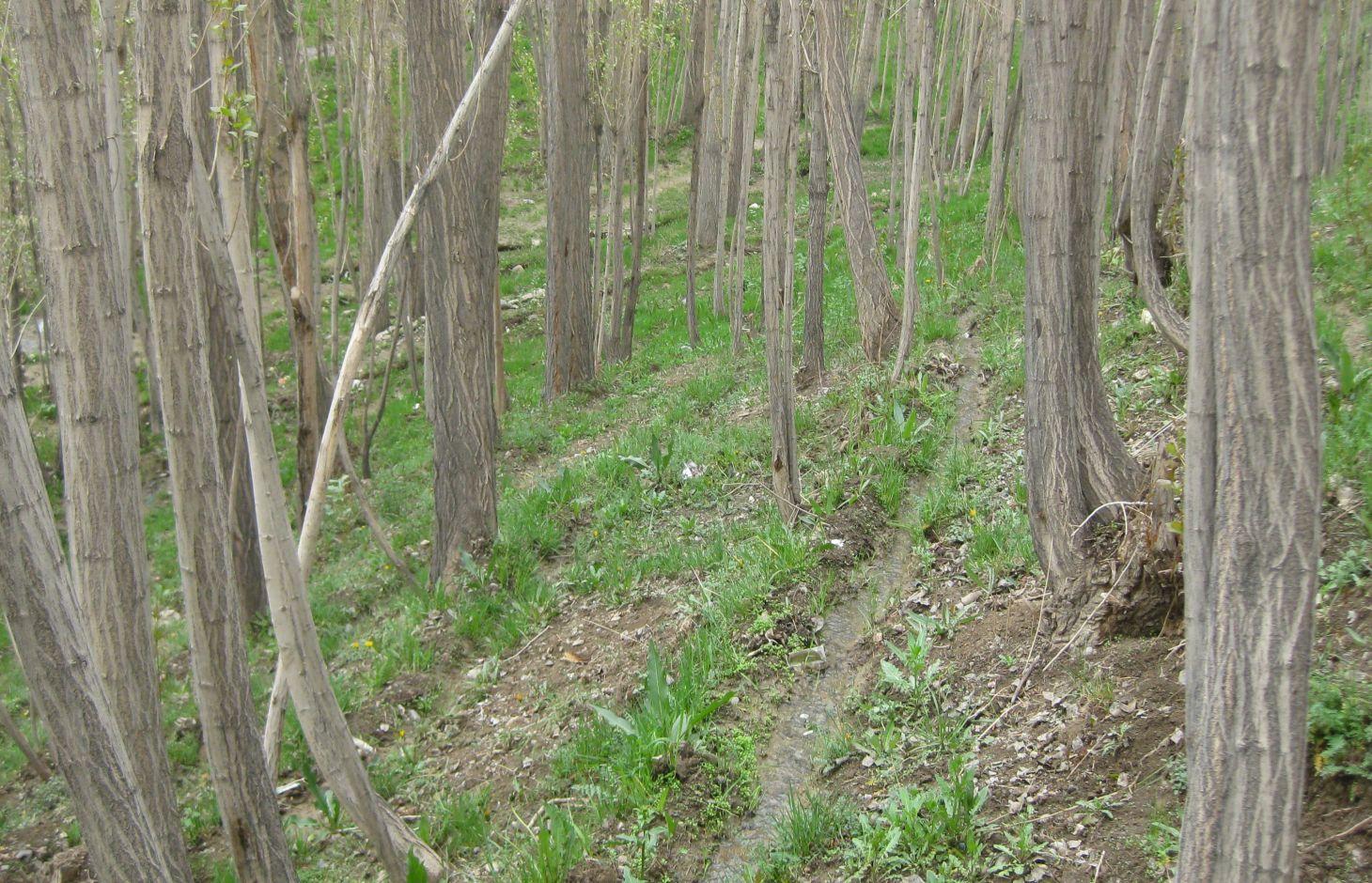
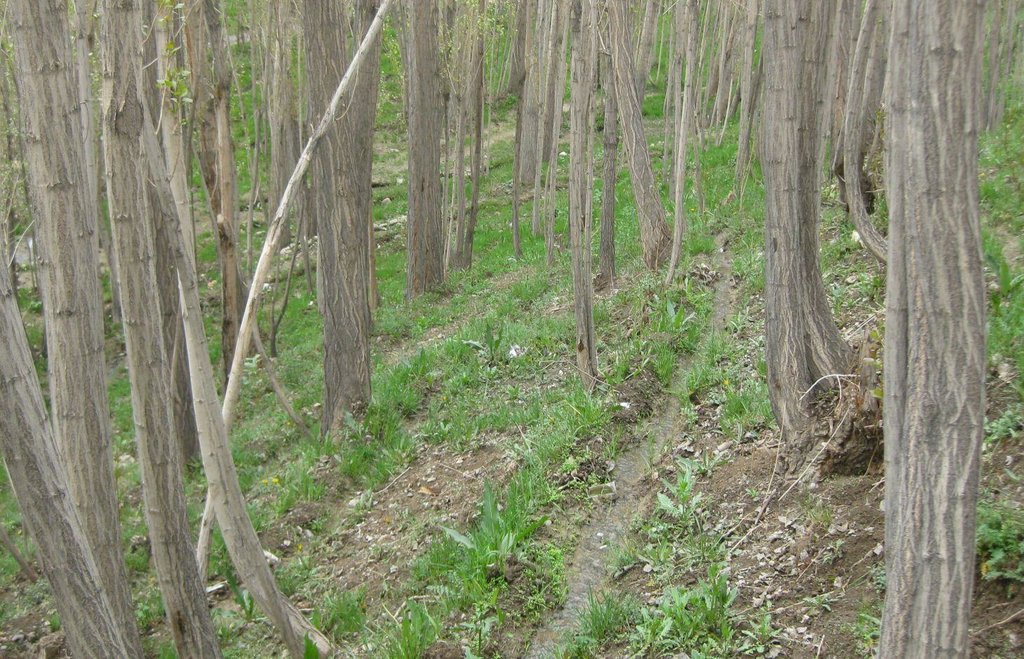
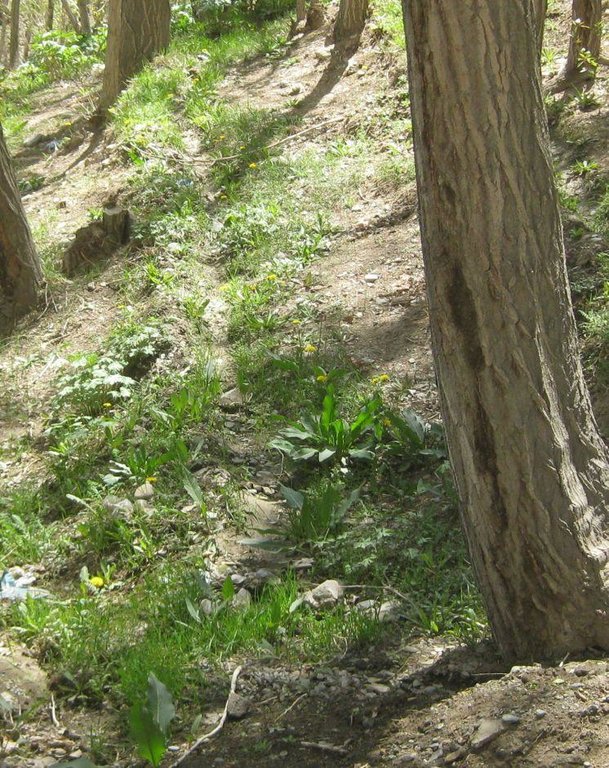
The Micro Irrigation system technology is documented by SLM Project/HELVETAS Swiss Intercooperation with financial support of Swiss Agency for Development and Cooperation (SDC). The presented micro-irrigation system, a structural SLM technology, was applied in Central Highland’s Province of Bamyan (Afghanistan). The micro-irrigation technology is applied to bring marginal land under cultivation for economic benefits, with the added benefit of rehabilitating degraded sloping land. The main irrigation canal also conveys water to agricultural land. It is a traditional technology applied by a land user without external support. It is also implemented by many other land users with some variations to the technology.
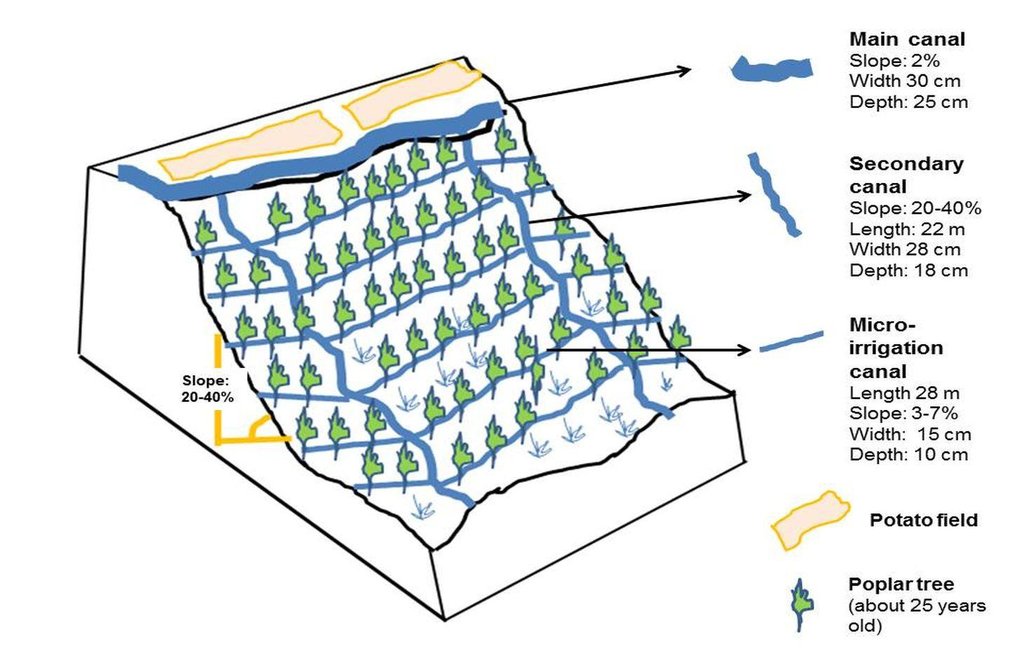
The technology consists of a network of main irrigation canal, secondary canals from which water is conveyed to sloping micro irrigation canals. The water reaches to the roots of each tree through infiltration/seepage.
The main canal has about 2% gradient and the micro-channels from 2-7% gradient. The slope of the site ranges between 20-40%. A micro irrigation canal is 28 m long, 15 cm wide and 10 cm deep. While the cross section remains same, the length can differ according to the land size.
The site was originally a degraded site with gravel soil. According to the land user, the site was not at all suitable for agriculture due to soil degradation and bad water shortage possibilities. Approximately 25 years after the plantation of poplar trees, the site's physical and biological conditions of the slope have improved due to the establishment of poplar trees. The poplar trees can be used for timber for construction and firewood. The poplar timber has good market in Bamyan and can fetch up to 35 USD per tree.
The micro-irrigation systems, which help establishing poplar plantations, contribute to multiple benefits for the land user's family and also the environment. As the poplar plantations are irrigated, their growth increases and their mortality, due to water shortage, is reduced.
As a result of re-vegetating the relatively steep slope, soil erosion from the site has reduced and the fertility of the soil has improved. Improved soil moisture and fertility has also helped in establishment of a good ground canopy. Many birds visit the site for shelter. The plantation has reached its harvesting stage and the land user is planning to cut the trees for sale, expecting an income of about 10,500 USD from the site.
A close look at this technology shows that the system works well and that it is easily managed by the land user. Some minor improvements, such as reducing the slope gradient of the micro-irrigation canals for reducing canal erosion, construction of pits to capture sediments at the drainage points and planting suitable grasses with good roots along the canal bunds could make the system more effective and sustainable. The measures could also help in reducing the sensitivity of the micro-irrigation canals towards intense rainfall.
The farmers are applying this SLM technology without any external financial or technical support and there is growing trend towards spontaneous adoption. According to the land user's estimate, of about 400 families in his village, 80 families have applied the technology
The basic purpose of the micro-irrigation system is to supply irrigation water to the poplar trees for reducing plant mortality and increasing plant growth.
The main establishment activities include layout of the micro canals across the sloping land using shovels and pick axe without use of any alignment equipment. Approximately 150 persons-days/ha were employed for constructing the micro-irrigation canals and 5 person-days/ha sufficed for on-site maintenance works. About 970 USD/ha was spent on the construction and most of the cost for labour was covered by the family of the owner.
The site is owned by a land user with clear land use rights. The water rights are common and organized as there is a traditional social water management institution (Mirab), which ensures an equitable distribution of irrigation water to all the farmers taking water from the main canal. A command area on a turn-by-turn basis exists. Water users pay service fees to the Mirab mostly in kind. The land users mentioned that they give about 14 kg of wheat and/or potato each year to the Mirab for this site. The land user has to also participate in main canal repair works on a voluntary basis. Bamyan Centre receives about 230 mm rainfall per year. Most of the rain falls in the months of April and May. Winters are severe with temperatures falling below minus 20 degrees. The area receives snowfall up to 180 cm per year in normal years. Bamyan center has an arid and temperate climate with one main growing season of about 6 months, which is from April to September. The plantation site is located at an altitude of about 2300 m. It is north-facing slope with a soil depth of about 30-50 cm. The soil is sandy loam with a medium soil fertility.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
阿富汗
区域/州/省:
Bamyan
有关地点的进一步说明:
Bamyan center
2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 10-50年前
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过土地使用者的创新
注释(项目类型等):
The technology is being applied on the site since about 25 years.
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 改良生产
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

森林/林地
(半天然)天然森林/林地:
- 选伐
植树造林:
- 单一栽培的本地品种
产品和服务:
- 木材
- 薪材
注释:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Gravely site, shortage of water for irrigation, sloping land affected by soil erosion. Heavy shrub harvesting for firewood and overgrazing on common/rangeland leading to land degradation.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Sloping land with sandy soil unsuitable for agriculture.
Plantation forestry: Plantation of poplar trees (mono culture)
Problems / comments regarding forest use: Land users do selective felling when they need cash. The trees are lopped for fuel wood.
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Forests / woodlands: Fp: Plantations, afforestations
3.3 有关土地利用的更多信息
每年的生长季节数:
- 1
具体说明:
Longest growing period in days: 170, Longest growing period from month to month: April to September in the valley bottom
3.4 该技术所属的SLM组
- 灌溉管理(包括供水、排水)
3.5 技术传播
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果该技术均匀地分布在一个区域上,请注明覆盖的大致区域。:
- 0.1-1 平方千米
注释:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.16 m2.
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

结构措施
- S3:分级沟渠、渠道、水道
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

生物性退化
- Bc:植被覆盖的减少

水质恶化
- Ha:干旱化
注释:
Main causes of degradation: over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use (Particulary for firewood), overgrazing (Mainly by sheep and goats), population pressure, inputs and infrastructure: (roads, markets, distribution of water points, other, …) (Lack of irrigation water), governance / institutional (Specifically in the case of common lands)
Secondary causes of degradation: droughts
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 减少土地退化
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
4.2 技术规范/技术图纸说明
Technical specifications of micro-irrigation system for poplar plantation. The system comprises main canal, secondary canals and micro irrigation canals which receive water from and drain into secondary canals.
Location: Tape Chauni. Bamyan Centre
Date: 10 May 2014
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: low
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: water harvesting / increase water supply
Secondary technical functions: increase of biomass (quantity)
Vertical interval between structures (m): 0.22-0.6
Spacing between structures (m): 1.8-2
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.1
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.15
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.28
Construction material (earth): Soil from the site is used for canal consturction
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 20-40%
Lateral gradient along the structure: 3-7%
4.3 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
Afghani
注明美元与当地货币的汇率(如相关):1美元=:
57.0
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
70.00
4.4 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Construction of secondary and micro-irrigation canals | 结构性的 | Spring |
4.5 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | labour | ha | 1.0 | 921.0 | 921.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | tools | ha | 1.0 | 52.0 | 52.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 973.0 | |||||
注释:
Duration of establishment phase: 0.25 month(s)
4.6 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Maintenance of canals | 结构性的 | Spring/once per year |
4.7 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | labour | ha | 1.0 | 30.0 | 30.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | tools | ha | 1.0 | 52.0 | 52.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 82.0 | |||||
注释:
Machinery/ tools: Pick axe and shovels
The presented costs were calculated on the basis of the exisiting local labour rate and the currency exchange rate which may vary from one year to another. For instance in 2010/11, 1 USD was 50 Afghani.
The cost of payment to the Mirab (Water distributor appointed by the land users) is not included. According to the land user, the Mirabs receive about 700 kg wheat/year from all the land users who use the main canal.
4.8 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
Labour is the most determinate factor affecting the costs. All the work is done manually.
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
有关降雨的规范/注释:
Most rainfall is in May. According to provincial agriculture department, Bamyan centre receives about 230 mm rain a year
农业气候带
- 半干旱
Thermal climate class: temperate. Winter temperatures can go below minus 20 degree C and maximum in summer up to 34 degree C
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 粗粒/轻(砂质)
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 中(1-3%)
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
5-50米
地表水的可用性:
好
水质(未处理):
仅供农业使用(灌溉)
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 中等
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
生产系统的市场定位:
- 混合(生计/商业
非农收入:
- 收入的10-50%
相对财富水平:
- 平均水平
个人或集体:
- 个人/家庭
性别:
- 男人
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Difference in the involvement of women and men: Women are however involved in other agriculture works but at the plantation site, they are not involved at all. The land user has about 0.4 ha irrigated crop land used for potato and wheat cultivation on a rotation basis.
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2% - 3%
Off-farm income specification: The land user family is food secure from its own production for up to 6 months only. For food security for 12 months, they have to depend on other sources of off farm income. The agriculture land is not enough to meet all the family needs.
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者拥有或租用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 小规模的
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 个人,有命名
土地使用权:
- 租赁
用水权:
- 社区(有组织)
注释:
For water distribution, there is a traditional system called as Mirab which is applied for the plantations as well. The land user applying the plantation/micro-irrigation technique have to participate in main irrigation canal repair and cleaning works. The land user also has to pay in kind or cash to the Mirab for his services.
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
饲料生产
木材生产
注释/具体说明:
Irrigation helps in Poplar establishment and growth
生产故障风险
注释/具体说明:
Important for reducing plant mortality
生产区域
注释/具体说明:
The area was degraded before
能源生产
水资源可用性和质量
灌溉用水的可用性
注释/具体说明:
For plantations
收入和成本
农业收入
注释/具体说明:
From sale of poplar trees but only in the long term
工作量
注释/具体说明:
Irrigation needs more time and labour
社会文化影响
娱乐机会
SLM/土地退化知识
注释/具体说明:
Other land users see and learn
冲突缓解
Fuel wood sufficiency
注释/具体说明:
Lopped branches are used for fuel wood
contribution to human well-being
注释/具体说明:
The technology contributes to increased household income in the long term and also towards increased production of fodder, fuel wood and timber.
生态影响
土壤
土壤水分
土壤有机物/地下C
注释/具体说明:
Due to build of humus and ground cover
生物多样性:植被、动物
生物量/地上C
注释/具体说明:
Due to plantations
植物多样性
注释/具体说明:
due to increased soil moisture
动物多样性
注释/具体说明:
habitat for birds
害虫/疾病控制
减少气候和灾害风险
风速
注释/具体说明:
Due to plantations (indirect impact)
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
缓冲/过滤能力
注释/具体说明:
Due to plantations
风力搬运沉积物
注释/具体说明:
Plantations impact
对公共/私人基础设施的破坏
注释/具体说明:
Due to less sedimentation and runoff from the site
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 气候变化/极端天气的类型 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年温度 | 增加 | 好 |
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气象灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 局地暴雨 | 不好 |
气候灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 干旱 | 不好 |
水文灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 比较和缓的(河道)洪水 | 不好 |
注释:
Stabilize the technology with grasses and reduce the slope of the channels so that it is less sensitive to increase in rainfall intensities.
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
消极
长期回报:
非常积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
轻度消极
长期回报:
非常积极
注释:
The returns in the form of cash start coming after 10-12 years with this poplar variety following a selective felling and replanting approach.
6.5 技术采用
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发地采用该技术,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 90-100%
注释:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
80 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
The total area under this plantation in the village is estimated to be 16 ha (80 jerib)
There is a small growing trend towards the adoption of the technology by communities and individuals in the area. Adoption depends on (and is hampered by) the availability of a reliable water source near the sites with potential for plantation and also about the land.
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| The technology helps successful establishment of poplar trees and also natural grasses on sloping lands. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Micro-irrigation technology is important for the establishment and maintenance of poplar plantations. The technology is adapted for afforestation of sloping land. |
| The technology does not require much maintenance once the plantations are well established. A special attention need to be given to the secondary canals. |
| No external support for establishing or maintaining the technology. |
| The technology helps in improving the site's micro climate which leads to more plant and animal (bird) diversity. |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| There is no information available regarding the land user's view on the weaknesses of this technology. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| The canals break at some weak points. Also the slopes of the micro channels is more at many places leading to some soil erosion. | Proper alignment of micro-irrigation canals. |
| Rill and gully erosion due to rapid and uncontrolled flow of excessive drainage in secondary canals. | Plant grasses with robust root system along the canals. Strengthen points where water spills from the micro-irrigation canals into the secondary canals with vegetative measures and sediment pits. |
| Due to small sizes of the channels, irrigation needs more time and labour. | Improvements in micro irrigation canals will reduce this problem considering. Interested organisations could carry out action research on how to improve this system by also incorporating efficient water use measures. |
| The technology can be applied only when there is a reliable source of running water. | Action research on soil and water conservation techniques for plantations in areas where there is no easy access to irrigation water. |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
- 实地考察、实地调查
- 与土地使用者的访谈
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块