Lining irrigation canals [马里]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Dieter Nill
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Deborah Niggli
Revêtement des canaux d’irrigation (French)
technologies_1651 - 马里
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
SLM专业人员:
Traore Minamba
tbaminan@gmail.com
IICEM
马里
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
Manual of Good Practices in Small Scale Irrigation in the Sahel (GIZ )有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ) GmbH (GIZ) - 德国1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
01/07/2012
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.4 所述技术的可持续性声明
这里所描述的技术在土地退化方面是否存在问题,导致无法被认为是一种可持续的土地管理技术?:
否
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
Lining canals is a powerful way to save irrigation water by minimising seepage losses, and to reduce pumping time and costs.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
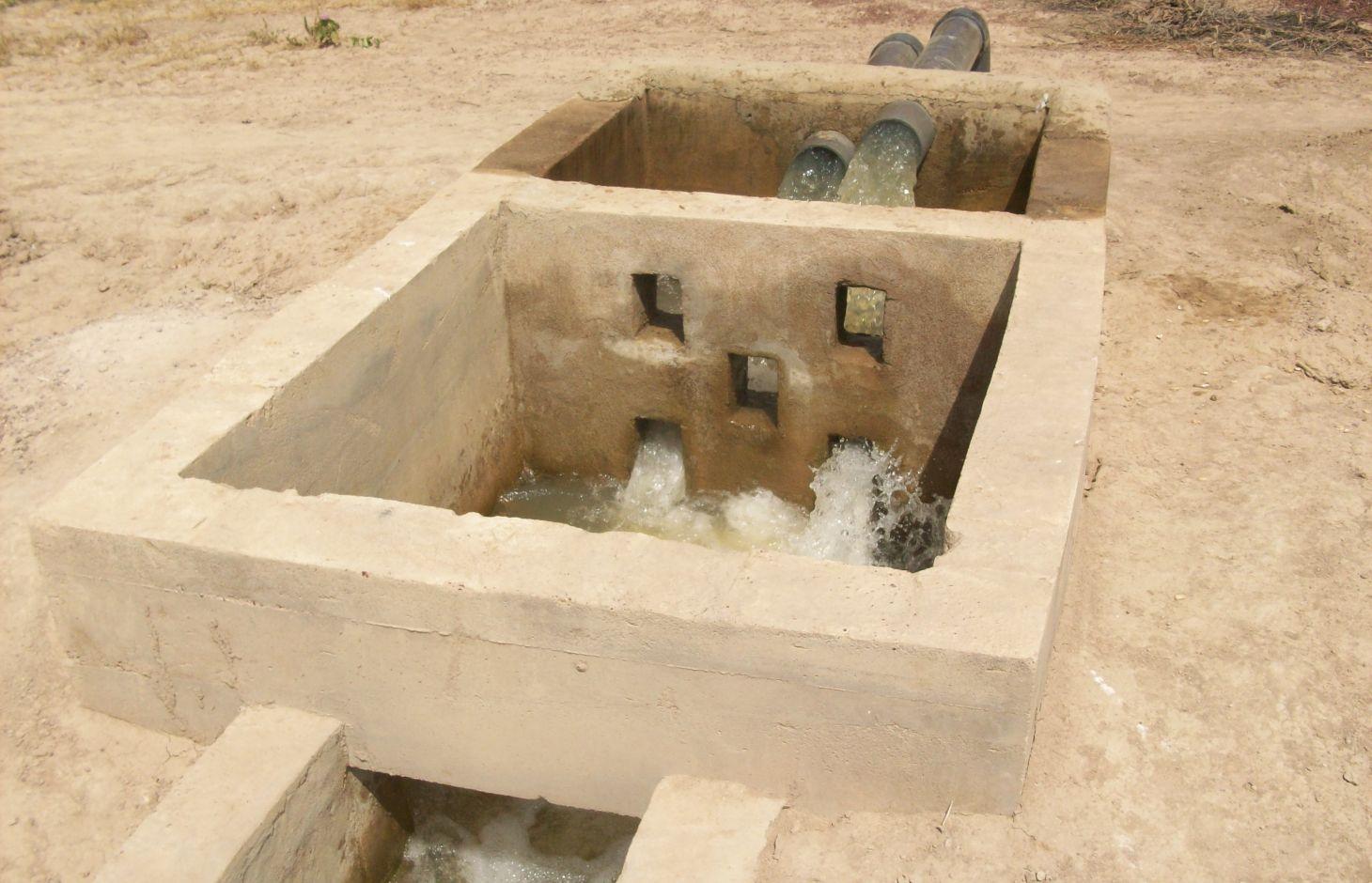
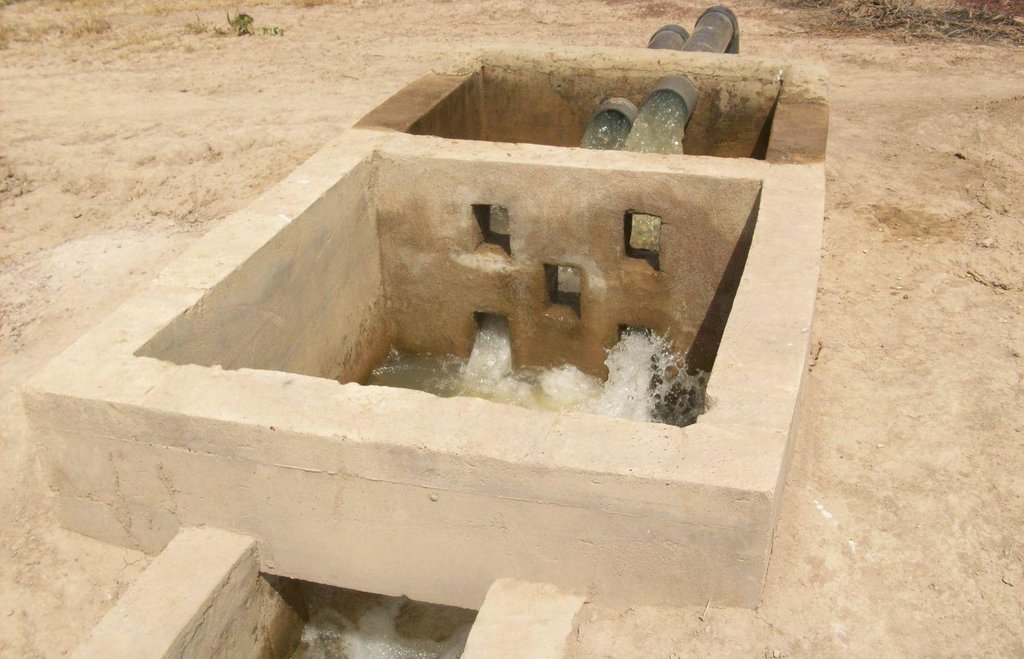
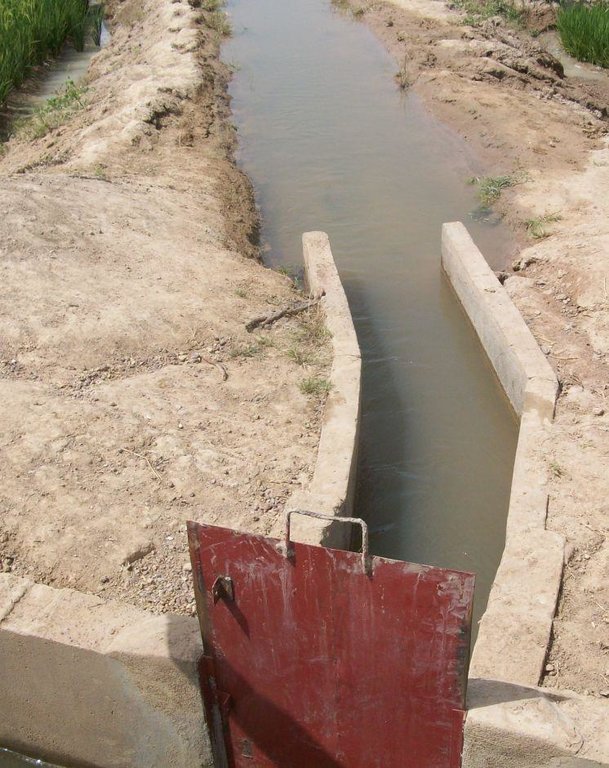
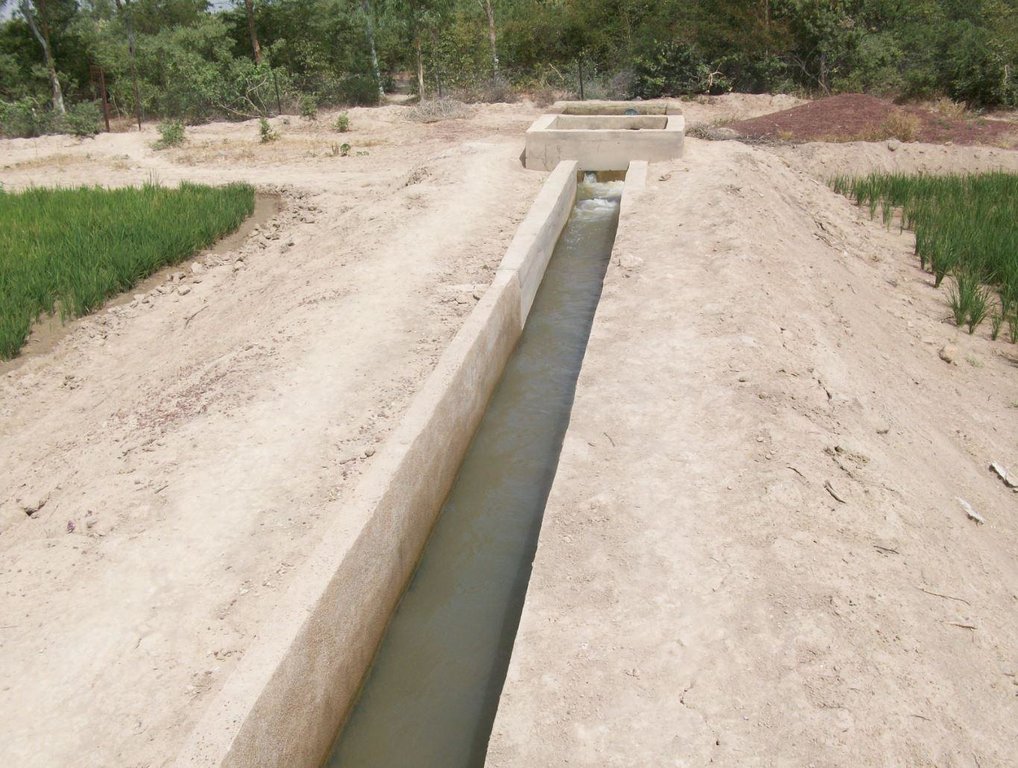
The irrigation area’s main earthen canals have their inverts lined in concrete and their sides lined with solid cement blocks. Concrete support posts are set at intervals and capped in concrete. Each lined main canal should be no longer than two kilometres. The main canal’s turnouts into the secondary canals are built in cement and are equipped with gates that can be opened and closed as required.
Each turnout’s outflow area is protected by a rockfill structure that is built right up to the top of the canal wall to prevent the canal banks at the head of the secondary canals from becoming degraded.
Lining is mainly used to improve the efficiency of existing irrigation systems. Once the canal has been lined, yields increase by between 35% and 80%. This is because crops receive the water they need to ripen as and when it is required. Often, lining also makes it possible to extend the irrigated area. Pumping hours per hectare are considerably reduced (by 25% in the rainy season) because the canals ensure the correct distribution of irrigation water. Consequently, irrigation costs per tonne of produce drop due to the reduction in pumping hours and the costs of periodical maintenance and increases in yields.
Together with the growers, a memorandum of understanding was drawn up with IICEM and then signed by the mayor. The memorandum describes all the activities that form part of the collaboration between IICEM and the various beneficiaries. The works were carried out either in-company or constituted part of the highly labour-intensive work (HLIW).
a) Work delivered in-company (turnkey basis): Works are carried out in several stages: 1) Identifying the sites requiring lining. This involves locating the sites to develop and making contact with the NGOs that represent the project in the region, as well as regional directorates of rural engineering and economic operators working with the farming organisations in question. 2) The delimited sites chosen for development must undergo technical studies, which are entrusted to engineering consultancies recruited through an open tender process in accordance with the terms of reference for the studies to be conducted. 3) The technical feasibility studies comprise topographical, geotechnical, soil and environmental studies, as well as the creation of a development plan and quantification of materials required for the construction work. 4) Drawing up the invitation to tender (ITT) documents and communicating the tender process to businesses. In lieu of a ToR, an ITT is created by the project according to the requirements of the site. It is then published so that interested consultancies can put forward their bids. 5) Works are carried out under the control and supervision of the oversight office to ensure they adhere to professional standards.
b) Highly labour-intensive work: 1) The same as above. 2) Topographical surveys are carried out by IICEM specialists to calculate the calibration of the canals to ensure they are able to submerge plots over a large area. 3) After calibrating the schemes (energy dissipation basin and division box, main canal and secondary canal turnout, channel), a work plan is drawn up. This uses the measurements calculated to quantify construction material and equipment requirements. 4) Teams of (preferably local) builders are recruited to line the canals. The teams comprise master builders, reinforcing ironworkers, bricklayers and surveyors. 5) The materials and equipment required for each site are provided by an appropriate supplier recruited through a tendering process. 6) Provision of labour and farmer participation. Only the building contractors are paid for working on the project. Labour is supplied by the local community who are provided with lunch to maintain motivation and to prevent lost time caused by workers going off-site. 7) In villages where schemes are proposed, teams of shift workers from the local community are set up and trained in proper conduct for working on a canal lining project and in the keeping of a construction project log book.
Once the canal lining works are complete, IICEM provides a pump unit and subsidises the required fuel and consumables for one growing season. Training in how to run and maintain pump units is provided for the local beneficiaries tasked with their upkeep. Furthermore, training in the management and maintenance of irrigation schemes is delivered to the farming organisations’ steering committee.
The lifespan of a canal lining ranges from 10 to 20 years if small repairs are regularly undertaken. Ensuring linings are impermeable is of the utmost importance because water penetrating through micro-cracks as it flows through the network can lead to rapid and major water loss. It is therefore essential that producers can maintain installations and repair cracks.
The Sahel is a region where the population has always faced a high degree of climate variability, manifested both in terms of time (unexpected dry spells can occur during the rainy season) and in terms of space (rainfall can vary greatly from one area to another). The population is mainly composed of small farmers and livestock keepers.
Over the last two decades, the effects of climate change have exacerbated the already difficult conditions. Accord¬ing to projections made by climatologists, the Sahel will experience a rise in temperatures combined with highly variable rainfall and an increase in extreme weather events.
The Soil and Water conservation and rehabilitation techniques have helped people in the Sahel to manage their ecosystems more effectively and improve their productive land. As a result, communities are better prepared to cope with environmental changes (changes in the climate, land degradation, etc.) and the im¬pact of shocks, particularly droughts
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
马里
区域/州/省:
Mali
有关地点的进一步说明:
Mopti, Timbuktu, Gao, Sikasso
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 不到10年前(最近)
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过项目/外部干预
注释(项目类型等):
This kind of practice has been carried out by IICEM since 2009.
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 改良生产
- 保护生态系统
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

农田
- 一年一作

混合(作物/放牧/树木),包括农林
- 农牧业
- 林牧业
注释:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): unequal distribution of irrigation water, ineffective irrigation systems (water loss)
3.3 有关土地利用的更多信息
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 混合雨水灌溉
每年的生长季节数:
- 1
具体说明:
Longest growing period in days: 120Longest growing period from month to month: August-November
牲畜密度(如相关):
1-10 LU /km2
3.4 该技术所属的SLM组
- 畜牧业和牧场管理
- 灌溉管理(包括供水、排水)
- 引水和排水
3.5 技术传播
注释:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 12 m2.
Around 50 sites covering approximately 1200 hectares have had their canals lined
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

结构措施
- S3:分级沟渠、渠道、水道
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wr:河岸侵蚀

化学性土壤退化
- Cn:肥力下降和有机质含量下降(非侵蚀所致)

生物性退化
- Bc:植被覆盖的减少

水质恶化
- Ha:干旱化
注释:
Main causes of degradation: soil management (Unadapted landuse methods, reduced or abandoned fallow periods), crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (Neglect of fallow periods and crop rotation), over abstraction / excessive withdrawal of water (for irrigation, industry, etc.), droughts (due to heat waves), population pressure (rapidly growing population increasing pressure on land), land tenure (insecure access to land and collectively managed communal land), poverty / wealth (very poor population)
Secondary causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (deforestation through overgrazing and fire wood collection), over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use (firewood collection), overgrazing (cattle, sheep and goats), change in temperature (Climate change: heat waves), change of seasonal rainfall (more variable onset of rain), Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts) (more variable and intensive rains), wind storms / dust storms (frequent storms), floods (due to intensive rain storms), labour availability (some migration of men to nearby cities), education, access to knowledge and support services (high level of illiteracy)
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 防止土地退化
- 减少土地退化
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
4.2 技术规范/技术图纸说明
The irrigation area’s main earthen canals have their inverts lined in concrete and their sides lined with solid cement blocks. Concrete support posts are set at intervals and capped in concrete. Each lined main canal should be no longer than two kilometres. The main canal’s turnouts into the secondary canals are built in cement and are equipped with gates that can be opened and closed as required. Each turnout’s outflow area is protected by a rockfill structure that is built right up to the top of the canal wall to prevent the canal banks at the head of the secondary canals from becoming degraded.
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: water harvesting / increase water supply, water spreading
4.3 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
CFA Franc
注明美元与当地货币的汇率(如相关):1美元=:
512.0
4.4 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Identifying the sites requiring lining | 结构性的 | |
| 2. | Launching the invitation to tender for the technical studies / Undertaking topographical surveys to calibrate schemes | 结构性的 | |
| 3. | Performing the technical studies / Quantifying building material requirements | 结构性的 | |
| 4. | Drawing up the invitation to tender (ITT) documents and communicating the tender process to businesses / Recruitment of masons, bricklayers and reinforcing ironworkers | 结构性的 | |
| 5. | Delivery of works under the supervision of the oversight office / Invitation to tender for the provision of materials and equipment | 结构性的 | |
| 6. | Provision of labour and farmer participation | 结构性的 | |
| 7. | Training workers from the local community in building site conduct | 结构性的 |
4.6 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | small repairs are regularly undertaken | 结构性的 |
4.8 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
Around 50 sites covering approximately 1,200 hectares have had their canals lined. Total costs: 1,587,865.50 US Dollar
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
农业气候带
- 半干旱
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
- 细粒/重质(粘土)
表土有机质:
- 中(1-3%)
- 低(<1%)
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
5-50米
地表水的可用性:
中等
水质(未处理):
仅供农业使用(灌溉)
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 中等
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
定栖或游牧:
- 定栖的
生产系统的市场定位:
- 混合(生计/商业
非农收入:
- 收入的10-50%
相对财富水平:
- 贫瘠
- 平均水平
机械化水平:
- 手工作业
性别:
- 男人
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Population density: < 10 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2% - 3%
10% of the land users are rich.
50% of the land users are average wealthy.
30% of the land users are poor.
10% of the land users are poor.
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者拥有或租用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 小规模的
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
注释:
The irrigated land is allocated by the chief
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
生产故障风险
生产区域
收入和成本
工作量
社会文化影响
食品安全/自给自足
冲突缓解
生态影响
水循环/径流
水量
水的回收/收集
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
旱季稳定可靠的水流
地下水/河流污染
风力搬运沉积物
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 气候变化/极端天气的类型 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年温度 | 增加 | 好 |
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气象灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 局地暴雨 | 不好 |
| 局地风暴 | 好 |
气候灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 干旱 | 好 |
水文灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 比较和缓的(河道)洪水 | 不好 |
其他气候相关的后果
其他气候相关的后果
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 缩短生长期 | 未知 |
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
轻度消极
长期回报:
稍微积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
稍微积极
长期回报:
非常积极
6.5 技术采用
注释:
Comments on spontaneous adoption: Lining of canals is an investment which is generally only feasible with external assistance.
There is no trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Irrigation system canals in Mopti, Timbuktu, Gao and Sikasso have been lined.
Around 50 sites covering approximately 1,200 hectares have had their canals lined. This kind of practice has been carried out by IICEM since 2009.
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Lining canals is a powerful way to save irrigation water by minimising seepage losses. |
| Pumping time and costs are also greatly reduced through the speedy distribution of irrigation water supplies, and reducing the use of motorised pumps lowers maintenance costs. |
| Yields increase by between 35% and 80%. Often, lining also makes it possible to extend the irrigated area. |
| Training in how to run and maintain pump units is provided for the local beneficiaries tasked with their upkeep. Furthermore, training in the management and maintenance of irrigation schemes is delivered to the farming organisations’ steering committee |
| The lifespan of a canal lining ranges from 10 to 20 years |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
- 实地考察、实地调查
- 与土地使用者的访谈
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Manual of Good Practices in Small Scale Irrigation in the Sahel. Experiences from Mali. Published by GIZ in 2014.
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
http://star-www.giz.de/starweb/giz/pub/servlet.starweb
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
www.iicem.net
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块