Integrated Production and Pest Management (IPPM) [马里]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Dieter Nill
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Fabian Ottiger
Gestion intégrée de la production et des déprédateurs (GIPD) (French)
technologies_1653 - 马里
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
SLM专业人员:
Dako Jean Parfait
parfaitdako@yahoo.fr
Direction Nationale de l'Agriculture
马里
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
Manual of Good Practices in Small Scale Irrigation in the Sahel (GIZ )有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ) GmbH (GIZ) - 德国有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Direction Nationale de l'Agriculture (DNA) - 马里1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
01/07/2012
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.4 所述技术的可持续性声明
这里所描述的技术在土地退化方面是否存在问题,导致无法被认为是一种可持续的土地管理技术?:
否
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
IPPM reduces the negative impact wrought by pesticides on the environment (wildlife, water, soil) and on humankind
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
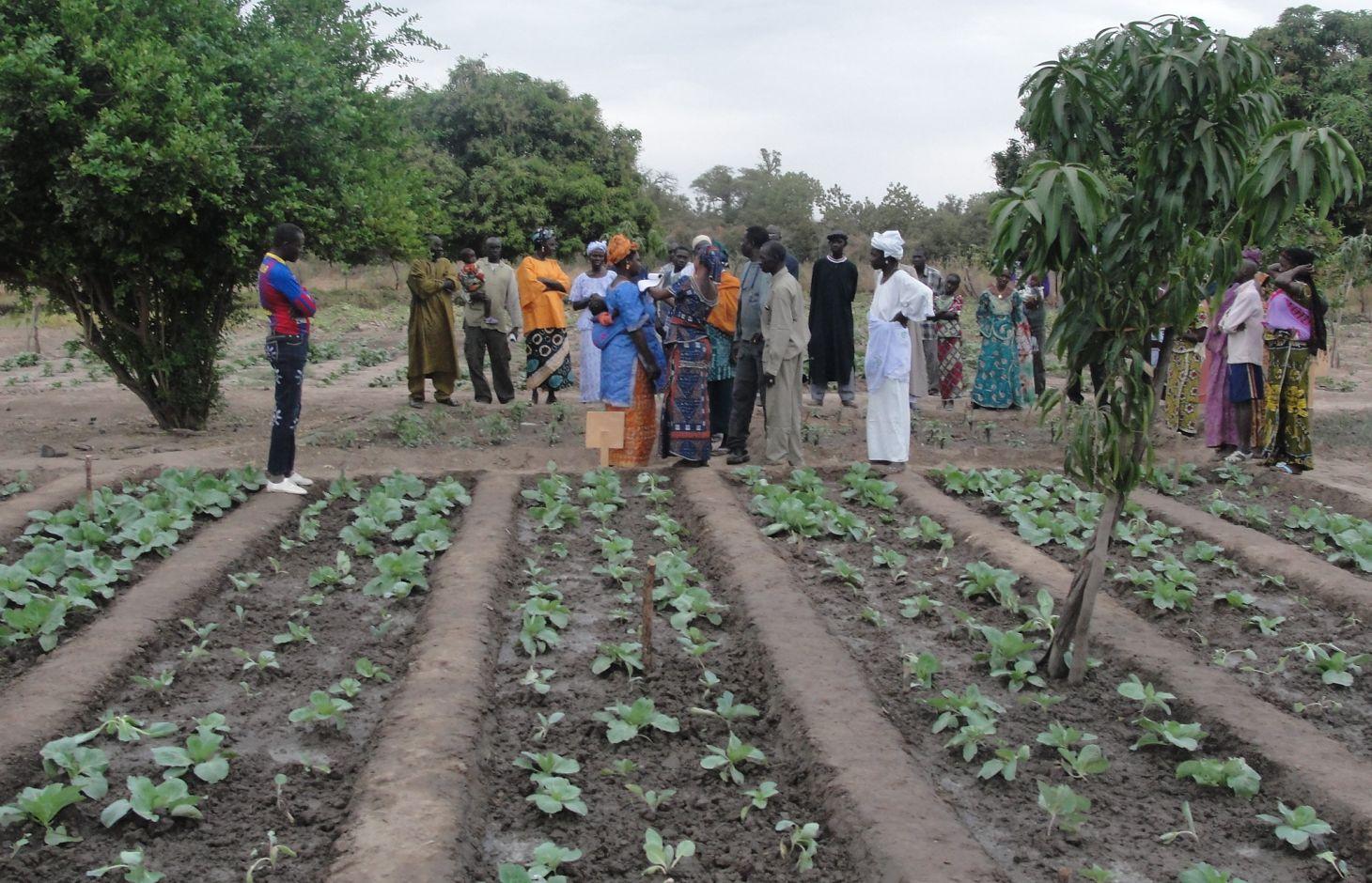
Integrated Production and Pest Management (IPPM) curbs the environmental degradation caused by current farming practices (intensive and extensive), reducing the negative impact wrought by pesticides on the environment (wildlife, water, soil) and on humankind. IPPM promotes the adoption of farming practices that are as respectful of the environment as they are productive and profitable.
Purpose of the Technology: IPPM works with all available techniques for combatting pests, while keeping pesticide use at economically justified levels. It reduces risks to human and animal health and to the environment. It is put into practice in farmer field schools (FFSs).
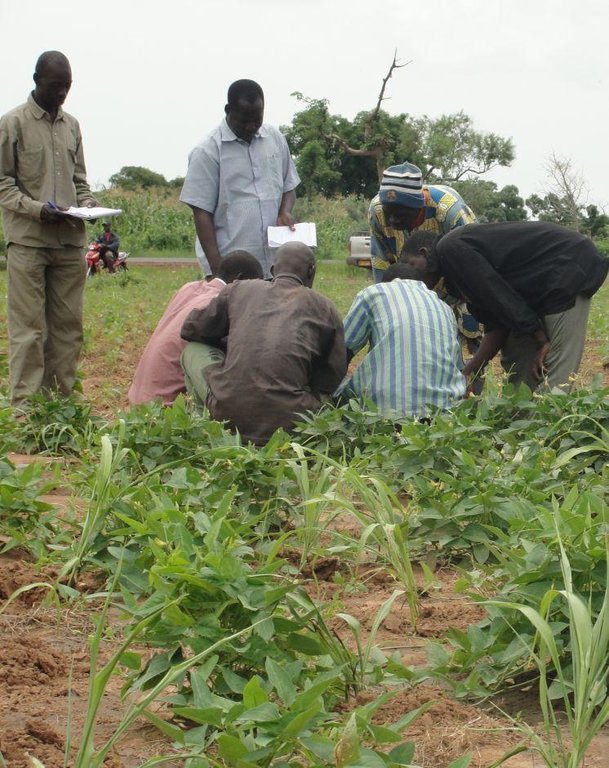
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Implementation: Men and women farmers are informed about the harmful effects of pesticide use. A group of local farmers are offered the opportunity to form a farmer field school led by a facilitator (with 25 farmers in each FFS group). The weekly sessions of the FFS focus on studying the presence
of insects and diseases and the condition of plants. The results are recorded in a study-findings logbook. Biopesticides like neem extract are used and their effectiveness is studied. Operation: Setting the critical thresholds for pest infestation of crops and evaluating the treatments required; Composing and applying pesticides according to the level of infestation.
Roles of the actors involved: Producers participate in the FFS and apply the techniques on their lands. Technical services provide training in good farming practices and link up the plant-disease and insect experts with the FFS facilitators. Research institutions make their plant-disease and insect experts
available and train up the technical services.
Natural / human environment: Implementation locations: All regions throughout Mali. On going for around 12 years. This technique is particularly popular with farmers. Trained facilitators and farming advisors are available.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
马里
区域/州/省:
Mali
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 10-50年前
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过项目/外部干预
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
- 保持/提高生物多样性
- 创造有益的社会影响
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

农田
- 一年一作
注释:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): environmental degradation caused by current farming practices (intensive and extensive)
3.3 有关土地利用的更多信息
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 混合雨水灌溉
每年的生长季节数:
- 1
具体说明:
Longest growing period in days: 120, Longest growing period from month to month: August-November
3.4 该技术所属的SLM组
- 病虫害综合管理(包括有机农业)
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

管理措施
- M7:其它
注释:
Specification of other management measures: combatting pests
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

生物性退化
- Bp:害虫/疾病增加,捕食者减少
注释:
Main causes of degradation: soil management (Unadapted landuse methods, reduced or abandoned fallow periods), crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (negative impact of pesticides, neglect of fallow periods and crop rotation), droughts (due to heat waves), population pressure (rapidly growing population increasing pressure on land), land tenure (insecure access to land and collectively managed communal land), poverty / wealth (very poor population)
Secondary causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (deforestation through overgrazing and fire wood collection), over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use (firewood collection), overgrazing (cattle, sheep and goats), change in temperature (Climate change: heat waves), change of seasonal rainfall (more variable onset of rain), Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts) (more variable and intensive rains), wind storms / dust storms (frequent storms), floods (due to intensive rain storms), labour availability (some migration of men to nearby cities), education, access to knowledge and support services (high level of illiteracy)
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 防止土地退化
- 减少土地退化
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.2 技术规范/技术图纸说明
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: combatting pests, change in farming practices
Other type of management: IPPM works with all available techniques for combatting pests, while keeping pesticide use at economically justified levels. Adoption of respectful farming practices.
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
农业气候带
- 半干旱
Thermal climate class: tropics
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
- 细粒/重质(粘土)
表土有机质:
- 中(1-3%)
- 低(<1%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Soil fertility: Medium
Soil drainage/infiltration: Medium and poor
Soil water storage capacity: Medium
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
5-50米
地表水的可用性:
中等
水质(未处理):
仅供农业使用(灌溉)
关于水质和水量的注释和进一步规范:
Availability of surface water: Also poor/ none
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 中等
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
生产系统的市场定位:
- 混合(生计/商业
非农收入:
- 收入的10-50%
相对财富水平:
- 贫瘠
- 平均水平
机械化水平:
- 手工作业
性别:
- 男人
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Population density: < 10 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2% - 3%
10% of the land users are rich.
50% of the land users are average wealthy.
30% of the land users are poor.
10% of the land users are poor.
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者拥有或租用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 小规模的
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
注释:
The irrigated area is allocated by the chief
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
生产故障风险
水资源可用性和质量
家畜用水的可用性
家畜用水的质量
收入和成本
农业投入费用
注释/具体说明:
Reduced use of pesticides
社会文化影响
食品安全/自给自足
健康状况
注释/具体说明:
Reduced risk to human and animal health and to the environment
SLM/土地退化知识
社会经济弱势群体的情况
Improved livelihoods and human well-being
注释/具体说明:
IPPM promotes the adoption of farming practices that are as respectful of the environment as they are productive and profitable. It reduces risks to human and animal health and to the environment.
生态影响
水循环/径流
水质
生物多样性:植被、动物
植物多样性
动物多样性
有益物种
栖息地多样性
害虫/疾病控制
减少气候和灾害风险
碳和温室气体的排放
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 气候变化/极端天气的类型 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年温度 | 增加 | 好 |
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气象灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 局地暴雨 | 不好 |
| 局地风暴 | 好 |
气候灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 干旱 | 好 |
水文灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 比较和缓的(河道)洪水 | 好 |
其他气候相关的后果
其他气候相关的后果
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 缩短生长期 | 好 |
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
非常积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
非常积极
长期回报:
非常积极
6.5 技术采用
注释:
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Implementation locations: All regions throughout Mail.
Scope of application: All farmed basins.
Duration of application: On going for around 12 years
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Reduction in pest control costs |
| Farm production is healthier and the environment is better protected |
| The use of pesticides for safeguarding production in rural areas is now very low. |
| Reduction of the negative impact wrought by pesticides on the environment (wildlife, water, soil) and on humankind |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| The village facilitators and farmers participating in the FFS must be literate | |
| IPPM requires inputs from plant-disease and insect experts |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
- 实地考察、实地调查
- 与土地使用者的访谈
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Annual reports for 2010, 2011 and 2012 – IPPM/DNA
7.3 链接到网络上可用的相关信息
标题/说明:
Manual of Good Practices in Small Scale Irrigation in the Sahel. Experiences from Mali. Published by GIZ in 2014.
URL:
http://star-www.giz.de/starweb/giz/pub/servlet.starweb
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块