Rockwall Terracing [菲律宾]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Philippine Overview of Conservation Approaches and Technologies
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Fabian Ottiger
technologies_1700 - 菲律宾
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
关键资源人
SLM专业人员:
Luistro Aida
273-2474
Department of Agriculture-STIARC, RFO IVA
RMIC Bldg., BPI Compound Visayas Ave Quezon City
菲律宾
SLM专业人员:
Gregorio Elizabeth
Department of Agriculture-STIARC, RFO IVA
RMIC Bldg., BPI Compound Visayas Ave Quezon City
菲律宾
SLM专业人员:
Dinamling Djolly Ma.
Bureau of Soils and Water Management
Visayas Avenue, Vasra, Quezon City, Philippines
菲律宾
SLM专业人员:
Guttierez Albert
alfergu@yahoo.com
LGU of La Libertad
Negros Oriental
菲律宾
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Bureau of Soils and Water Management (Bureau of Soils and Water Management) - 菲律宾有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Southern Tagalog Integrated Agricultural Research Center (STIARC) - 菲律宾有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
LGU of La Libertad - 菲律宾1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
28/05/2015
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
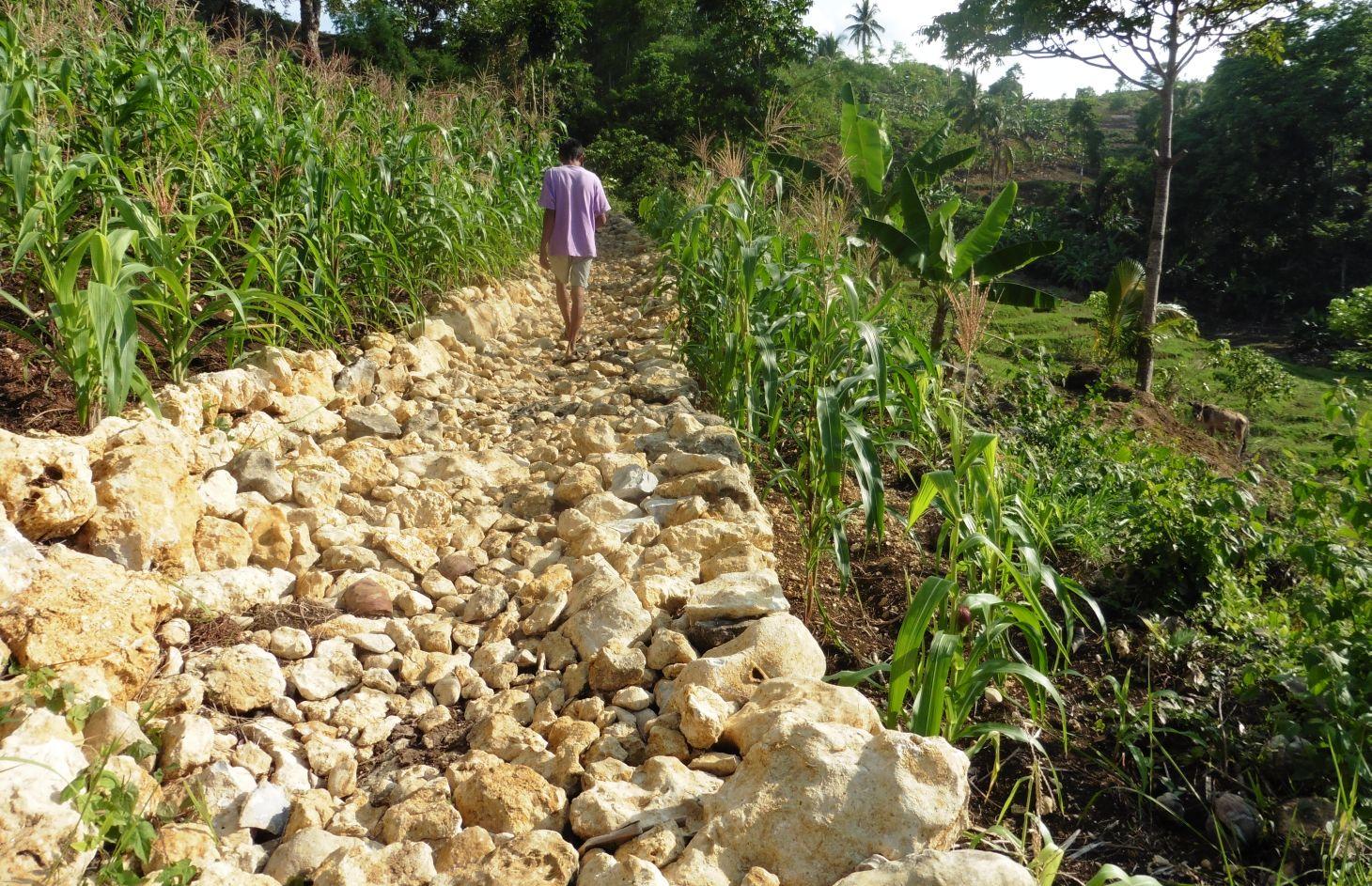
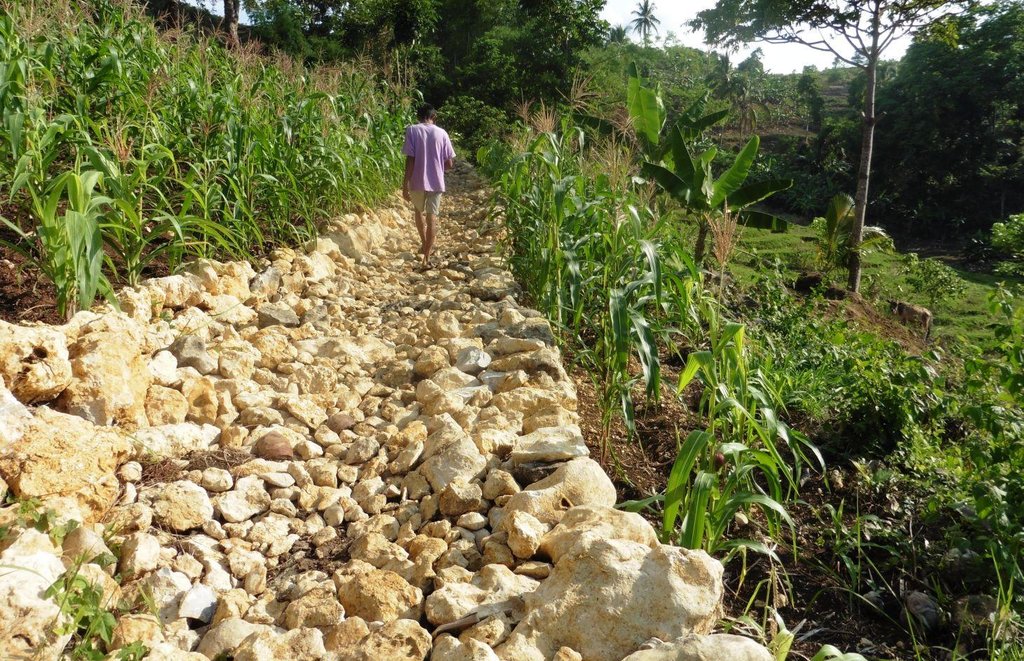
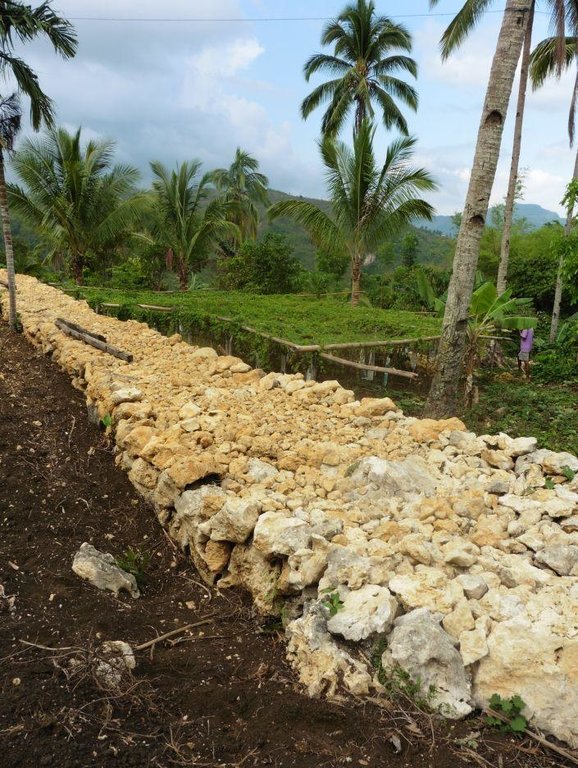
Rockwall terracing refers to the piling of stones or rocks along contour lines to reduce soil erosion in hilly areas.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
Rockwall terracing technology is widely practiced by farmers in hilly area of Barangay Nasunggan, La Libertad, Negros Oriental. Rocks piled along contours are indigenous to the area. The terrace bed is cultivated and planted with corn, watermelon, and vegetables. In some areas, livestock like cattle and native pigs are being raised. The technology is a traditional practice in the Philippines and one of the conservation techniques under the Conservation Farming Village (CFV) approach.
Purpose of the Technology: Rockwall terraces are built to reduce soil erosion and provide ease in land preparation through the removal of naturally present rocks in the cultivated area.It also contributes to the partial arrangement and diversification of land use. Before the implementation of the technology, the physical condition of the area is not recommended for farming practices due to the presence of rocks scattered all over the area.Dispersed and concentrated runoff are controlled in this technology. Raindrop splash is also restrained. Moreover, water storage is maintained in the soil.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: With the aid of an A-Frame, contours are determined. Rocks and/or stones are gathered from the area and piled along contours to form walls 1.10 m wide and 1.50 m high. It requires 14 person-day for a month to construct a 50-meter rockwall with a cost of 800 USD. Maintenance of the structure is done three times a year by repiling of dislodged rocks.
Natural / human environment: The area is classified under a humid agro-climate condition where an average annual rainfall of 1000-1500 mm per year are observed. The average cropland size of land user ranges from 0.5-1 hectare with a slope of 18-25%. Majority of their income are derived from on-farm activities. Crops planted in the terraced bed are sold in the town market and is also utilized for consumption.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
菲律宾
区域/州/省:
La Libertad
有关地点的进一步说明:
Negros Oriental
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 不到10年前(最近)
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过土地使用者的创新
3. SLM技术的分类
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

农田
- 一年一作
主要农作物(经济作物及粮食作物):
Major cash crop: Vegetable, banana, cacao, coffee
Major food crop: Corn, forage legumes

混合(作物/放牧/树木),包括农林
- 农牧业
主要产品/服务:
Main livestock species: swine, cattle, chicken
注释:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): The area is prone to soil erosion and land degradation due to absence of vegetation.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Not suitable for crop production because of the rocks or stones scattered in the area.
Mixed: (eg agro-pastoralism, silvo-pastoralism): swine, cattle, chicken
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Mixed: Mo: Other
如果由于技术的实施而导致土地用途发生变化,则在技术实施前说明土地利的用途。:
Cropland: Ca: Annual cropping
3.3 有关土地利用的更多信息
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
注释:
Water supply: rainfed, mixed rainfed - irrigated
Water supply: rainfed, post-flooding
牲畜密度(如相关):
10-25 LU /km2
3.4 该技术所属的SLM组
- 横坡措施
3.5 技术传播
注释:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.278 m2.
At present, rockwalls are not constructed in contiguous manner. Construction were done prioritizing those highly eroded areas but the plan is to build and expand in the barangay, smallest administrative division in the Philippines.
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

结构措施
- S6:墙、障碍物、栅栏、围墙
注释:
Main measures: structural measures
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀

化学性土壤退化
- Cn:肥力下降和有机质含量下降(非侵蚀所致)

生物性退化
- Bc:植被覆盖的减少
注释:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content, Bc: reduction of vegetation cover
Main causes of degradation: soil management (intensive soil cultivation/tillage)
Secondary causes of degradation: crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (inappropriate cropping system), deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (logging), education, access to knowledge and support services (limited access to learning facilities)
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 修复/恢复严重退化的土地
注释:
Main goals: rehabilitation / reclamation of denuded land
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
作者:
Patricio A. Yambot, Bureau of Soils and Water Management
4.2 技术规范/技术图纸说明
Rockwall terrace built to utilize the rocks in the area.
Location: Brgy. Nasunngan. La Libertad, Negros Oriental
Date: May 25,2015
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap, control soil erosion
Secondary technical functions: control of raindrop splash, reduction of slope angle, reduction of slope length, increase / maintain water stored in soil, promotion of vegetation species and varieties (quality, eg palatable fodder), spatial arrangement and diversification of land use, serve as access road
Wall/ barrier
Spacing between structures (m): 3-5m
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 1.5
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 1.1
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 50 m
Construction material (stone): limestones
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 18%
4.3 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
Pesos
注明美元与当地货币的汇率(如相关):1美元=:
45.0
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
2.22
4.4 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Contouring | 结构性的 | 1 day |
| 2. | Digging along contour, Gathering and piling of stones along contours | 结构性的 | 3 months |
4.5 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | labour | dam | 1.0 | 804.44 | 804.44 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Tools | dam | 1.0 | 22.22 | 22.22 | 100.0 |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 826.66 | |||||
注释:
Duration of establishment phase: 5 month(s)
4.6 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Repiling of stones and rocks that were dislodged | 结构性的 | 3 times a year |
4.7 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Labour | 50m | 1.0 | 13.33 | 13.33 | 100.0 |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 13.33 | |||||
注释:
Machinery/ tools: A-Frame, Mattock, Shovel
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
农业气候带
- 潮湿的
Thermal climate class: tropics
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
关于地形的注释和进一步规范:
Altiudinal zones: 501-100 m a.s.l. (600m)
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 中(1-3%)
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
> 50米
地表水的可用性:
匮乏/没有
水质(未处理):
良好饮用水
关于水质和水量的注释和进一步规范:
Seasonality of water quality and source of pollution (good drinking water, year round, spring water )
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 低
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
生产系统的市场定位:
- 生计(自给)
- 混合(生计/商业
非农收入:
- 低于全部收入的10%
相对财富水平:
- 贫瘠
- 平均水平
个人或集体:
- 个人/家庭
机械化水平:
- 手工作业
- 畜力牵引
性别:
- 女人
- 男人
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly disadvantaged land users
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Level of mechanization: Manual work, animal traction
Market orientation: subsistence (self-supply)
Market orientation: Mixed (subsistence/commercial)
Annual population growth: 1% - 2%; 2%
30% of the land users are average wealthy and own 30% of the land.
70% of the land users are poor and own 70% of the land.
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者拥有或租用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 小规模的
注释:
1-2ha of cropland and <0.5ha grazing land per household
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 个人,未命名
土地使用权:
- 个人
用水权:
- 个人
注释:
Sharing of water from spring during summer
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
SLM之前的数量:
5000 ears for corn/ha
SLM之后的数量:
10000 ears for corn/ha
饲料生产
饲料质量
产品多样性
生产区域
收入和成本
农业投入费用
农业收入
收入来源的多样性
其它社会经济效应
crop production area
注释/具体说明:
Reduced crop production area: medium (20-50%)
社会文化影响
食品安全/自给自足
文化机会
社区机构
国家机构
冲突缓解
社会经济弱势群体的情况
Improved livelihoods and human well-being
注释/具体说明:
yes, greatly
生态影响
土壤
土壤流失
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
下游淤积
缓冲/过滤能力
对邻近农田的破坏
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 气候变化/极端天气的类型 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年温度 | 增加 | 好 |
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气象灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 局地暴雨 | 不好 |
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
积极
6.5 技术采用
如若可行,进行量化(住户数量和/或覆盖面积):
10 land user families/households
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发地采用该技术,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 50-90%
注释:
63% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
10 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
37% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
6 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Even without LGU assistance, rockwall technology will continue since most of the landusers in the area were trained on how to construct with the use of A-frame.
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Rockwall terraces prevent downstream siltation thus preserving the topsoil in the upper part of the area. |
| Ease of land preparation since rocks are not scattered in the field.It improves the soil condition for crop establishment. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
The technology involves indigenous material such as rocks and stones from the area. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Improvement of piling rocks/stones |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Production area is reduced due to the rock wall structure. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Durability of the structure. | This could be improved by cementing the gaps between rocks (riprapping) to enhance durability, thus reducing maintenance cost. |
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块