Littuko Growing for Forest Enhancement [菲律宾]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Philippine Overview of Conservation Approaches and Technologies
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: David Streiff
technologies_1708 - 菲律宾
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
关键资源人
SLM专业人员:
Dacumos Evangeline
Department of Agriculture-Bureau of Soils and Water Management
菲律宾
SLM专业人员:
Dinamling Djolly Ma.
Department of Agriculture-Bureau of Soils and Water Management
SLM专业人员:
Espanto Patrick Benson
Department of Agriculture-Bureau of Soils and Water Management
菲律宾
Mento Dopinio
SLM专业人员:
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Bureau of Soils and Water Management (Bureau of Soils and Water Management) - 菲律宾有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Forest Management Bureau (Forest Management Bureau) - 菲律宾1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
23/06/2015
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.5 请参阅有关SLM方法的问卷

Community-Based Forest Management [菲律宾]
Community-Based Forest Management (CBFM) refers to the organized efforts to work with communities in and near public forestlands with the intent to protect, rehabilitate, manage, conserve, and utilize the resources in partnership with the Local Government Units (LGUs) and other stakeholders.
- 编制者: Isabelita Austria
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
Growing of rattan is done by upland farmers as part of the Community-Based Forest Management (CBFM).
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
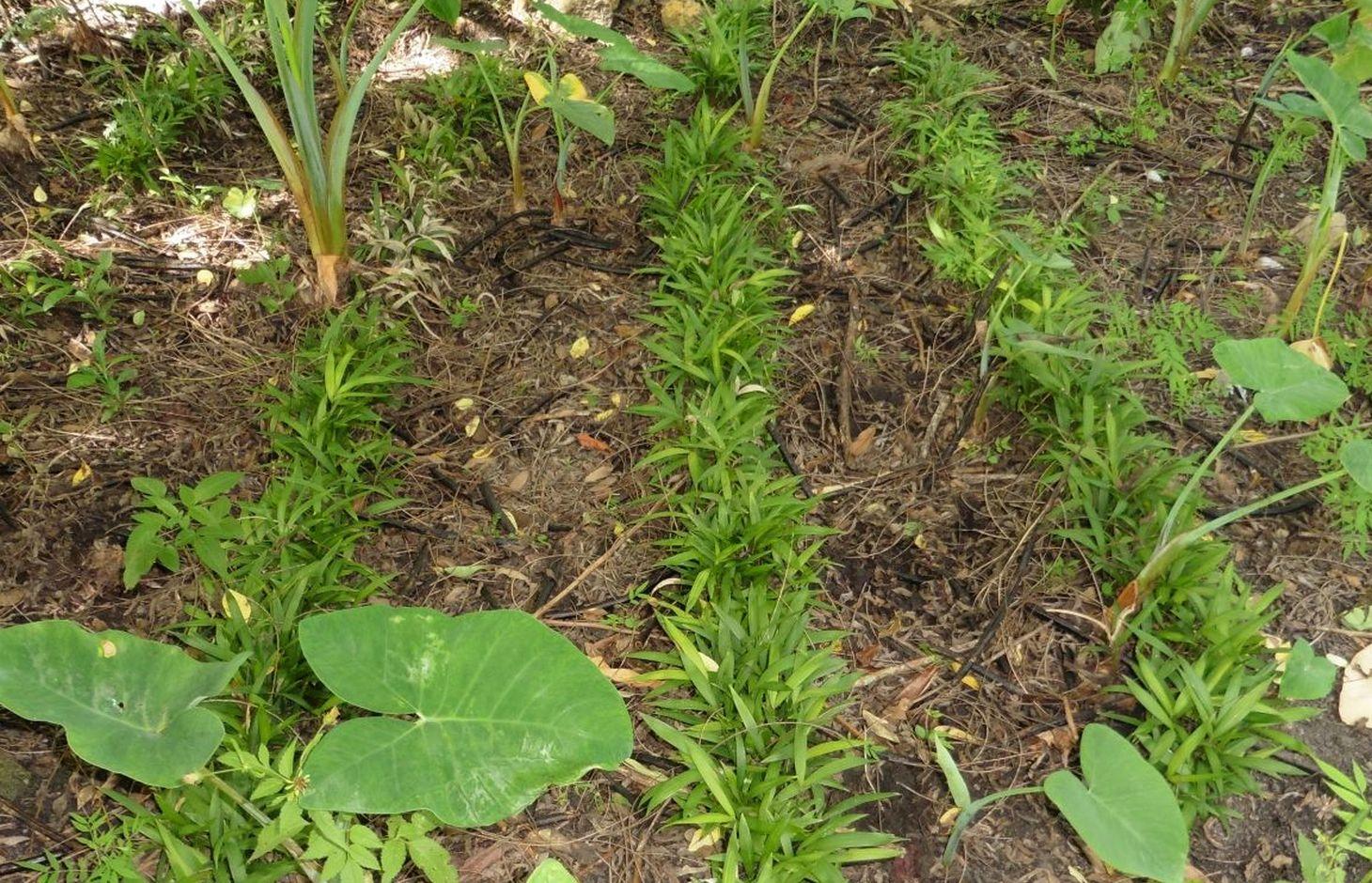
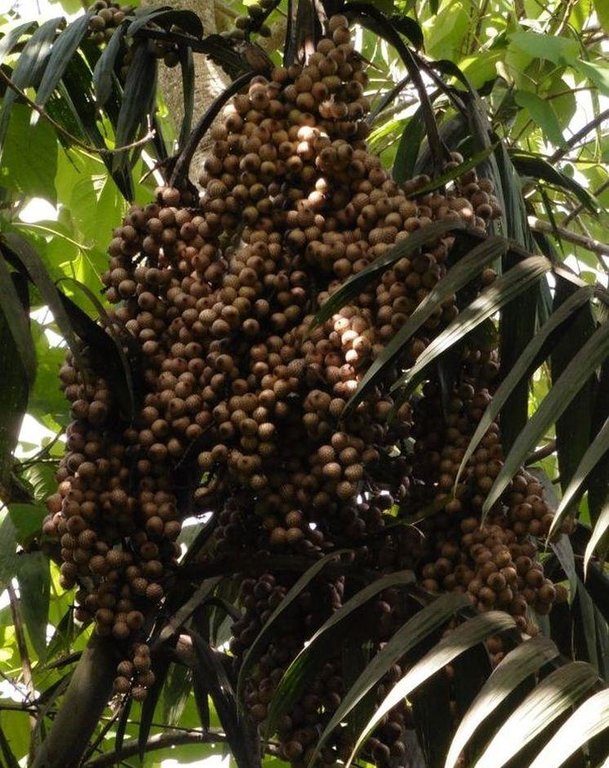
Littuko (Calamus manilensis) is a large rattan variety belonging to the climbing-palm family Arecaceae which is commonly found in the Cordillera, Caraballo, and Sierra Madre mountain ranges. It matures in seven years and bears 50 to 70 kilos of fruits each year. Its fruits are sweetish sour when ripe and are gathered around April to September.
Purpose of the Technology: The littuko provides green cover to the trees even in the dry months and in case of wildfire,they reinforce the forest's capacity to serve as firebreaks or greenbreaks. It also attract a lot of wildlife ranging from insects (bees, fire flies, and beetles) to birds, bats, and cloud rats. Forests with littuko become equipped with natural guards since the littuko's spines with sturdy thorns discourage people and stray animals to freely enter the forest area and disturb the ecosystem.Conservation of trees is also promoted on this technology.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: For the cultivation of littuko, the following procedures are done: (1) Before planting into a seedbed or polyethylene bags (plastic planting bag), the hilar cover of the littuko seed is gently scraped with the use of a sharp knife. Removing the hilar cover enables the tiny plant to easily break out of the seed. (2) The sprout is transplanted to the designated area under the host tree when it reaches six inches in height and with at least three leaves. The chosen host tree is where the littuko can cling on for support to prevent lodging or breakage of stems. (3) Within one to three years, ring weeding is done around the littuko plant. (4) Maintenance and inputs are needed after three years to ensure its growth.
Natural / human environment: Littuko grows underneath of growing trees in the natural forest. They grow best in rainforests and no cultivation is needed.The area is under a humid agro climate with an average annual rainfall of 2000-3000 mm per year. Land users have an average holding of 0.5-1 hectare for the forestlands or woodlands.Most of them are stewards of the forest through the Community Based Forest Management Agreement (CBFMA) for 25 years and renewable for another 25 years.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
菲律宾
区域/州/省:
Bayombong
有关地点的进一步说明:
Nueva Vizcaya
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 10-50年前
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过土地使用者的创新
注释(项目类型等):
In 1984, 100 littuko seeds were planted by the land users and 70% are male plants.
3. SLM技术的分类
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

森林/林地
(半天然)天然森林/林地:
- 选伐
- 非木材森林的利用
植树造林:
- 混交品种
产品和服务:
- 木材
- 其它森林产品
- 自然保持/保护
注释:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Logging, charcoal making and grazing since it was initially a grassland
Selective felling of (semi-) natural forests: Yes
Plantation forestry: Yes
Forest products and services: timber, other forest products / uses (honey, medical, etc.), nature conservation / protection
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Forests / woodlands: Fo: Other
如果由于技术的实施而导致土地用途发生变化,则在技术实施前说明土地利的用途。:
Grazing land: Ge: Extensive grazing land
3.3 有关土地利用的更多信息
每年的生长季节数:
- 1
具体说明:
Longest growing period from month to month: perennial
3.4 该技术所属的SLM组
- 天然和半天然森林管理
3.5 技术传播
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果该技术均匀地分布在一个区域上,请注明覆盖的大致区域。:
- 0.1-1 平方千米
注释:
The area for the propagation of rattan is part of the Community Based Forest Management (CBFM).
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

植物措施
- V5:其它
注释:
Main measures: vegetative measures
Specification of other vegetative measures: Involve the use of vines
Type of vegetative measures: scattered / dispersed
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀

化学性土壤退化
- Cn:肥力下降和有机质含量下降(非侵蚀所致)

物理性土壤退化
- Pc:压实

生物性退化
- Bc:植被覆盖的减少
- Bh:栖息地丧失
- Bq:数量/生物量减少
注释:
Main type of degradation addressed: Bc: reduction of vegetation cover, Bh: loss of habitats, Bq: quantity / biomass decline
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content, Pc: compaction
Main causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (Cutting of trees), land tenure (Insecurity (open access))
Secondary causes of degradation: crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (More on annual crops), overgrazing (Cattle raising), change in temperature, droughts, population pressure (Increase of population that leads to the increase of cutting of trees.)
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 修复/恢复严重退化的土地
注释:
Main goals: rehabilitation / reclamation of denuded land
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
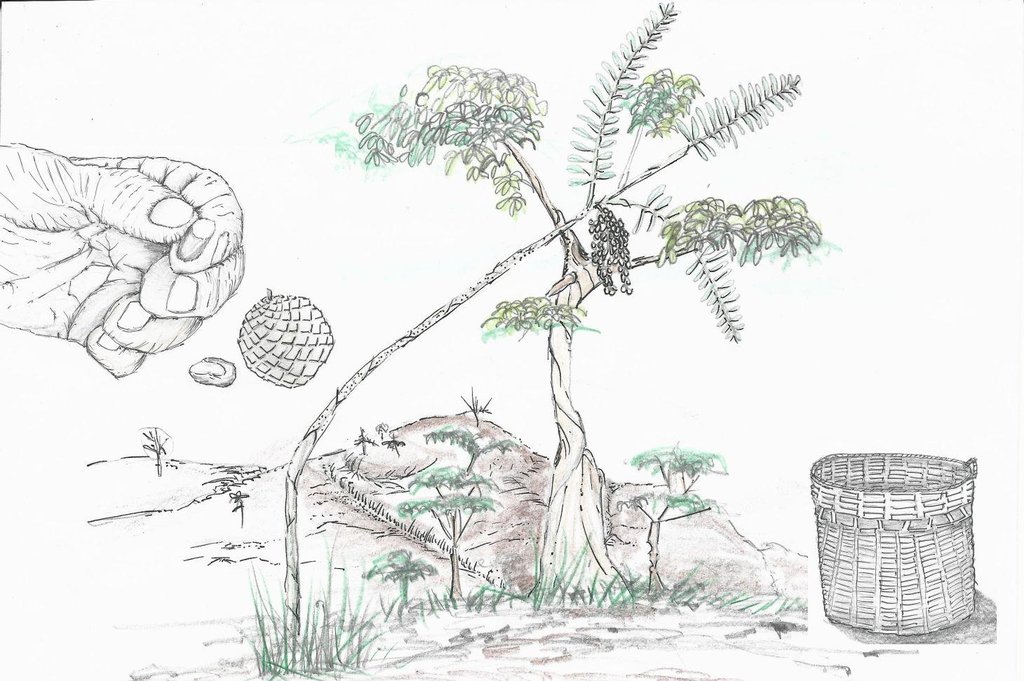
4.2 技术规范/技术图纸说明
Rattan vine planted in the forest with rattan made basket used in transporting littuko seeds in the market.On top is the scarification of the littuko seed to induce seed growth.
Location: Brgy. Buenavista. Bayombong, Nueva Vizcaya
Date: June 25,2015
Technical knowledge required for land users: high (Need skills in seed propagation and use of scarification of seeds.)
Main technical functions: promotion of vegetation species and varieties (quality, eg palatable fodder), Conservation of trees which serve as host or anchor trees
Secondary technical functions: control of raindrop splash, increase in organic matter, increase of biomass (quantity), Control weeds
Scattered / dispersed
Vegetative material: O : other
Number of plants per (ha): 1000
Other species: Vine (rattan)
4.3 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
Pesos
注明美元与当地货币的汇率(如相关):1美元=:
45.0
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
3.33
4.4 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Nursery establishment through seed bed | 植物性的 | Before the onset of rainy seasons |
| 2. | Transplanting | 植物性的 | After 8-12 months of seeding |
4.5 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Labour for nursery | Person/day | 1.0 | 3.3333 | 3.33 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Transplanting | Person/day | 1.0 | 3.3333 | 3.33 | 1000.0 |
| 植物材料 | Seedling | Seeds | 1000.0 | 0.22222 | 222.22 | 100.0 |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 228.88 | |||||
4.6 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Weeding | 植物性的 | Once a week for 2 years (maybe done once a month) |
| 2. | Harvesting | 植物性的 | After 5-8 years of planting |
4.7 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Weeding | Person/day | 2.0 | 3.333 | 6.67 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Harvesting | Person/day | 4.0 | 3.333 | 13.33 | 100.0 |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 20.0 | |||||
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
农业气候带
- 潮湿的
Thermal climate class: tropics
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
说明该技术是否专门应用于:
- 不相关
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 中(1-3%)
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
表面上
地表水的可用性:
好
水质(未处理):
良好饮用水
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 中等
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
生产系统的市场定位:
- 混合(生计/商业
非农收入:
- 低于全部收入的10%
相对财富水平:
- 贫瘠
- 平均水平
个人或集体:
- 个人/家庭
性别:
- 女人
- 男人
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
75% of the land users are average wealthy and own 75% of the land.
25% of the land users are poor and own 25% of the land.
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者拥有或租用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 小规模的
注释:
Just woodland, no crop or grazing land
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 州
土地使用权:
- 社区(有组织)
用水权:
- 社区(有组织)
注释:
CBFM Agreement, Certificate of Stewardship Contract of 10-25 years
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
木材生产
生产故障风险
水资源可用性和质量
饮用水的可用性
家畜用水的可用性
家畜用水的质量
收入和成本
农业收入
收入来源的多样性
其它社会经济效应
Difficulty to harvest
注释/具体说明:
Difficult to harvest since host tree is tall
社会文化影响
食品安全/自给自足
文化机会
社区机构
冲突缓解
Improved livelihood and human well-being
注释/具体说明:
The littuko fruits provide additional income to community based forest management implementer/participants.
生态影响
土壤
土壤有机物/地下C
生物多样性:植被、动物
植物多样性
有益物种
栖息地多样性
减少气候和灾害风险
碳和温室气体的排放
其它生态影响
Conservation of trees
注释/具体说明:
Conservation of trees is promoted because trees serve as hosts for the growing of rattan
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 气候变化/极端天气的类型 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年温度 | 增加 | 好 |
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气象灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 局地暴雨 | 好 |
气候灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 干旱 | 不好 |
水文灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 比较和缓的(河道)洪水 | 未知 |
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
稍微积极
长期回报:
非常积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
稍微积极
长期回报:
非常积极
6.5 技术采用
- 大于 50%
如若可行,进行量化(住户数量和/或覆盖面积):
200 households and 70 percent of land
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发地采用该技术,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 0-10%
注释:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
200 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
There is a strong trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Land users are adopting the technology since littuko seedlings nursery are established for the propagation of planting of rattan in the village and its neighboring area.
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
Littuko vine is multi-purpose. Its fruits are used for food consumption while its poles are used as handicrafts/furniture. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Provision of technical assistance in the development of product using rattan as the raw material. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
Littuko fruit is not perishable. It could be stored for a period of time under normal conditions. This could be used as condiments and ornaments. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Providing assistance in processing the littuko fruits such as creating jams, candies and others using the fruit. In this way, the marketability and market value of the product will be increased. |
| Low maintenance as a crop. Contributory to trees and it helps in the reduction of soil erosion. |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Difficult to harvest since the host tree is tall.It does not grow in open areas and does not stand alone. | Development of a tool that could be used in harvesting the fruit and planting of trees as pole stand to avoid lodging or breakage of littuko vine. |
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接

Community-Based Forest Management [菲律宾]
Community-Based Forest Management (CBFM) refers to the organized efforts to work with communities in and near public forestlands with the intent to protect, rehabilitate, manage, conserve, and utilize the resources in partnership with the Local Government Units (LGUs) and other stakeholders.
- 编制者: Isabelita Austria
模块
无模块