Alternate Wetting and Drying [菲律宾]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Philippine Overview of Conservation Approaches and Technologies
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: David Streiff
technologies_1725 - 菲律宾
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
关键资源人
SLM专业人员:
Dinamling Djolly Ma
DA-BSWM
菲律宾
SLM专业人员:
Raquid Jemar G.
DA-BSWM
菲律宾
SLM专业人员:
Martinez Mamerto F.
DA-BSWM
SLM专业人员:
Pascual Kristine
Philrice
菲律宾
SLM专业人员:
Sibayan Evangeline B.
Philrice
菲律宾
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Bureau of Soils and Water Management (Bureau of Soils and Water Management) - 菲律宾有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Philippine Rice Research Institute (PhilRice) - 菲律宾1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
11/02/2016
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.5 请参阅有关SLM方法的问卷

Palayamanan: Climate Change Adaptation Strategy for Lowland Ecosystem [菲律宾]
Synergistic mix of farming ventures implemented by the farm family based on the existing environment and their resources to address food security, income instability, and sustainability.
- 编制者: Philippine Overview of Conservation Approaches and Technologies
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
Alternate Wetting and Drying is a water-use management technique wherein irrigation water input could be substantially reduced to as much as 35% without significantly affecting rice yields.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
It was observed that most of the farmer’s irrigation practice of continuously flooding their rice fields is wasteful and uneconomical. The imbalance amount of water, either in deficit or excess, might affect the development and productivity of the crops.
With this inefficient water use and coupled by the increasing frequency of drought, vulnerability to water scarcity is inevitable. Furthermore, it has been recognized that poor water management practices contributed to the process of land degradation. Hence, there is a need to practice proper water management in rice cultivation. As an integral part of the Palayamanan system, the Philippine Rice Research Institute (PhilRice) introduced a water saving technology to the farmers called Alternate Wetting and Drying (AWD).
The AWD modifies the irrigation scheduling and application and eventually the amount of water to be use in the field. Irrigation water is applied a few days after the disappearance of the ponded water in the so-called “observation well”. Hence, the field is alternately flooded and non-flooded.
Purpose of the Technology: The following are the purpose of this technology: (1)reducing water use for irrigation so that it can be used for other purposes, (2) reducing the use of irrigation water because there is less of it, and (3) reducing the use of irrigation water to reduce the cost. Emission of greenhouse gas (GHG) specifically on methane is reduced since this is caused by flooding of ricefields.
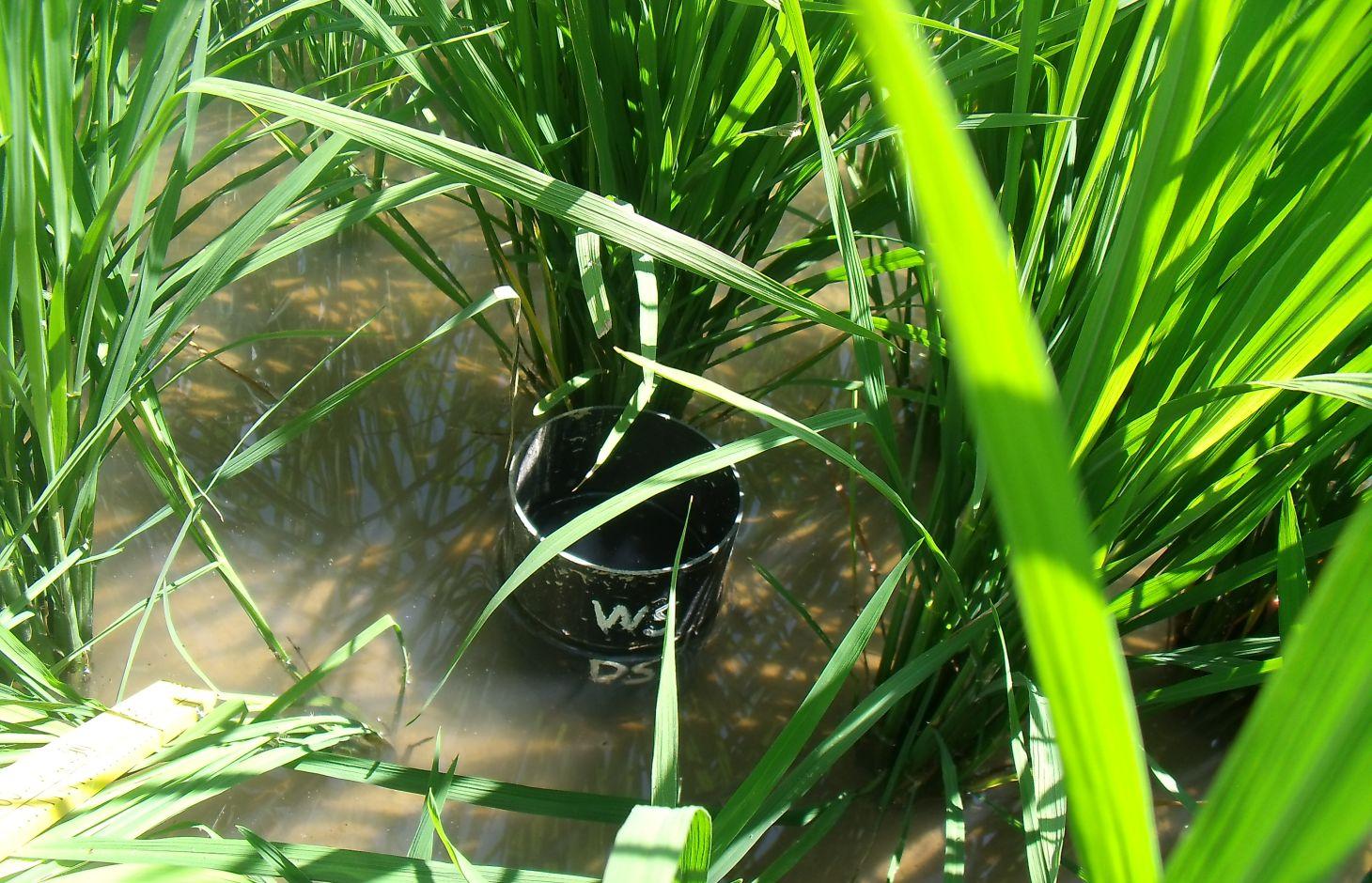
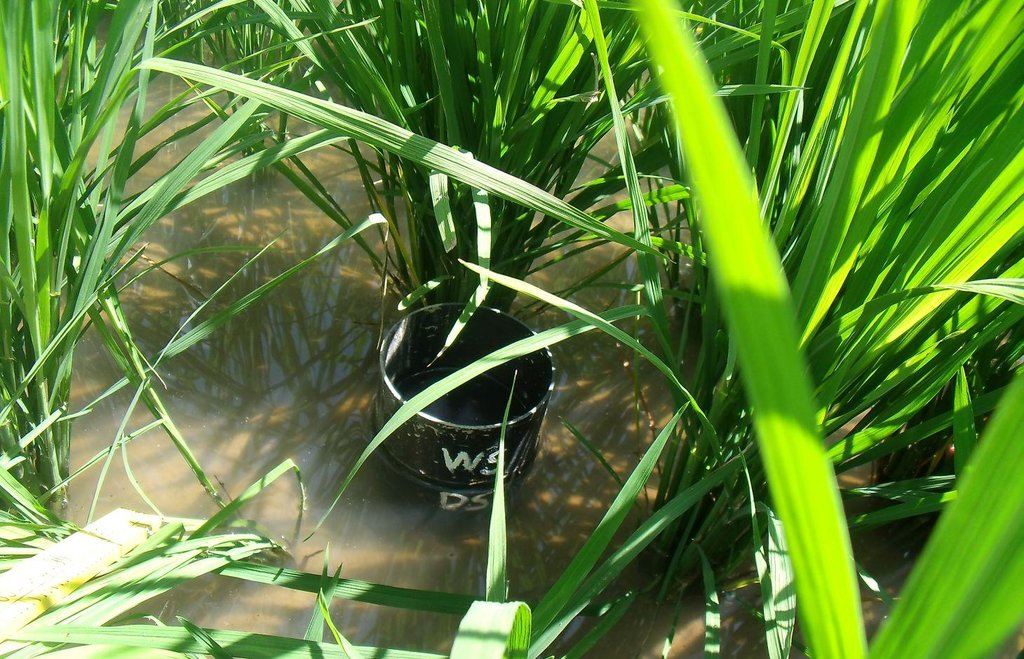
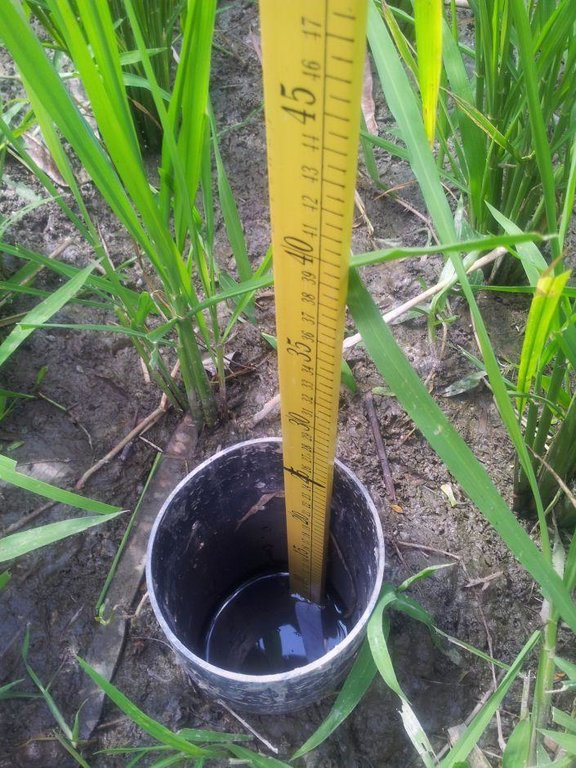
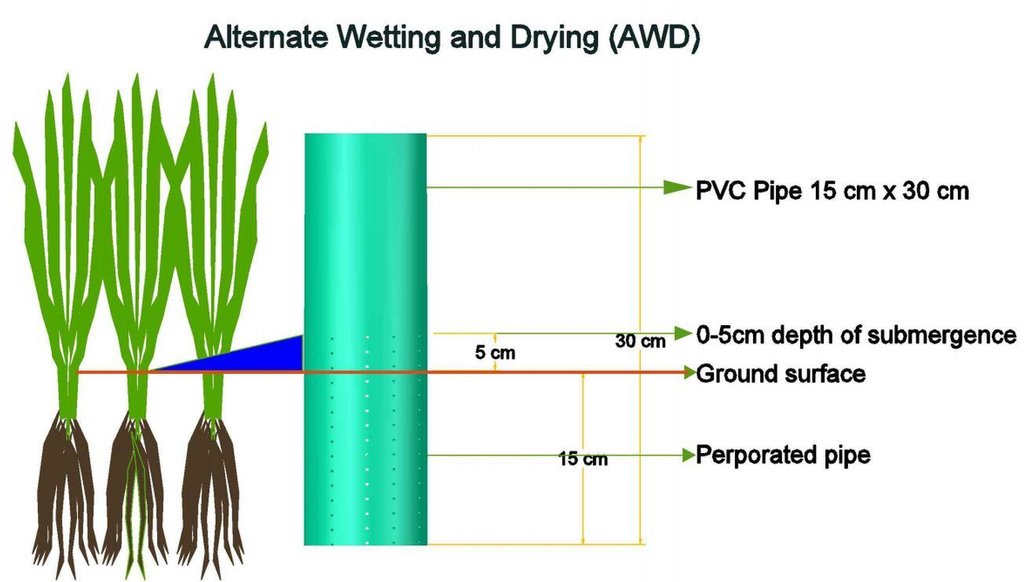
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Practical implementation of AWD is facilitated using a simple tool called a 'field water tube' as observation well, used in monitoring the water level in the field.It is made of a 25 cm long PVC pipe with a diameter of 10 to 15 cm. In some instances, bamboo can be used instead of the PVC pipe. The pipe is perforated with many holes on all sides to allow lateral movement of water in the root zone. It is installed into the soil by ensuring that 10 (dry season) or 5 (wet season) cm protrudes above the soil surface. Soil must be removed inside the tube so that the bottom is visible. During the first 21 to 30 days after direct seeding or transplanting, 2 to 3 cm of water is maintained to control weeds and to ensure that the crop has already
recovered from transplanting shock. AWD is imposed after 21 to 30 days where the water in the tube is monitored. Once the water inside the tube disappears, irrigation is applied to a water depth of 5 cm above soil surface. It is noted that during fertilizer application and flowering stage, sufficient water is maintained to avoid spikelet sterility. Terminal drainage from one to two weeks before the expected time of harvest is also done to promote uniform maturity of the crop and to facilitate easement of post-harvest operations in the field.
Natural / human environment: The area is under a humid climate experiencing wet and dry season with an annual average rainfall ranging from 1000-1500 mm per year. The technology was applied to irrigated rice field in flat and plain areas.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
菲律宾
区域/州/省:
San Nicolas, Dingras
有关地点的进一步说明:
Ilocos Norte
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 10-50年前
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过项目/外部干预
3. SLM技术的分类
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

农田
- 一年一作
主要农作物(经济作物及粮食作物):
major cash crop: rice
major food crop: rice
注释:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): lack of irrigation water
3.3 有关土地利用的更多信息
其它(比如洪水后):
- controlled flooding
注释:
The field is alternately flooded and non-flooded.
每年的生长季节数:
- 2
3.4 该技术所属的SLM组
- 灌溉管理(包括供水、排水)
3.5 技术传播
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果该技术均匀地分布在一个区域上,请注明覆盖的大致区域。:
- < 0.1 平方千米(10 公顷)
注释:
This is practiced in most of the "Palayamanan" sites in Ilocos Norte.
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

管理措施
- M4:活动时间安排的重大变化
- M7:其它
注释:
Main measures: management measures
Specification of other management measures: water use management
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

水质恶化
- Hs:地表水良变化
注释:
Main type of degradation addressed: Hs: change in quantity of surface water
Main causes of degradation: crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub), other human induced causes (specify) (water use management)
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 防止土地退化
注释:
Main goals: prevention of land degradation
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
4.2 技术规范/技术图纸说明
PVC pipe used for the technology.
Location: Ilocos Norte
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: more efficient water use
Major change in timing of activities: AWD modifies the irrigation scheduling and application
Other type of management: Water use management on irrigation water is applied a few days after the disappearance of ponded water in the field water tube.
4.3 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
具体说明成本计算所用货币:
- 美元
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
3.33
4.4 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Preparation of the PVC/bamboo pipes | 管理 | |
| 2. | Perforation with many holes on all sides of the PVC/bamboo pipe | 管理 |
4.5 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Perforation with many holes on all sides of the PVC/bamboo pipe | Person/day | 1.0 | 3.33 | 3.33 | 100.0 |
| 施工材料 | Preparation of the PVC/bamboo pipes | piece | 1.0 | 4.44 | 4.44 | |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 7.77 | |||||
4.6 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Installation of the PVC/bamboo pipe into the soil | 管理 |
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
农业气候带
- 潮湿的
Thermal climate class: tropics
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
说明该技术是否专门应用于:
- 不相关
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地表水的可用性:
好
水质(未处理):
良好饮用水
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 中等
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
生产系统的市场定位:
- 混合(生计/商业
非农收入:
- 低于全部收入的10%
相对财富水平:
- 平均水平
个人或集体:
- 团体/社区
机械化水平:
- 手工作业
- 畜力牵引
性别:
- 男人
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Market orientation: Rice produced are intended for market and food consumption for the family
Annual population growth: 1% - 2%; 1%
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者拥有或租用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 小规模的
注释:
Average area of land owned or leased by land users applying the Technology: < 0.5 ha, 0.5-1 ha and1-2 ha
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 个人,有命名
土地使用权:
- 租赁
- 个人
用水权:
- 社区(有组织)
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
水资源可用性和质量
灌溉用水需求
其它社会经济效应
weed growth during dry period
注释/具体说明:
seen as disadvantage
社会文化影响
冲突缓解
生态影响
水循环/径流
地表径流
多余水的排放
蒸发
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气候灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 干旱 | 好 |
水文灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 比较和缓的(河道)洪水 | 好 |
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
积极
6.5 技术采用
注释:
Comments on acceptance with external material support: No exact data is available to determine the numbers of land user who adopted the technology but most of the "Palayamanan" farmer partners in the irrigated areas adopted and practiced it.
Comments on spontaneous adoption: No exact data is available to determine the numbers of land user who adopted the technology but most of the "Palayamanan" farmer partners in the irrigated areas adopted and practiced it.
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Most of the land users practicing "Palayamanan" in the municipality and province of Ilocos Norte is adopting the technology.
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Positive outcome primarily in water savings without significant yield difference from the usual practice. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Simplicity of the technology's method. |
| AWD leads to firmer soil conditions at harvest, which is beneficial to operating machines in the field. |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Prone to weed growth during the period when the soil is dry. | Proper weed management |
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接

Palayamanan: Climate Change Adaptation Strategy for Lowland Ecosystem [菲律宾]
Synergistic mix of farming ventures implemented by the farm family based on the existing environment and their resources to address food security, income instability, and sustainability.
- 编制者: Philippine Overview of Conservation Approaches and Technologies
模块
无模块