Boundary Trees-Windbreakers [肯尼亚]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Paul Kahiga
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Deborah Niggli
Windbreaker
technologies_1738 - 肯尼亚
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
Gathenya Mwangi
Jomo Kenyatta University of Agriculture and Technology
PO Box: 62000-00200, Nairobi, Juja, Kenya
肯尼亚
SLM专业人员:
Home Patrick
Jomo Kenyatta University of Agriculture and Technology
PO Box: 62000-00200, Nairobi, Juja, Kenya
肯尼亚
SLM专业人员:
Chege Timothy
Jomo Kenyatta University of Agriculture and Technology
PO Box: 62000-00200, Nairobi, Juja, Kenya
肯尼亚
SLM专业人员:
Abamba Omwange
Jomo Kenyatta University of Agriculture and Technology
PO Box: 62000-00200, Nairobi, Juja, Kenya
肯尼亚
SLM专业人员:
Baobab Kimengich
Jomo Kenyatta University of Agriculture and Technology
PO Box: 62000-00200, Nairobi, Juja, Kenya
肯尼亚
SLM专业人员:
Wamuongo Jane
+254 729 054547
Kenya Agricultural Research Institute
Nairobi
肯尼亚
SLM专业人员:
Karanja Andrew
+254 729 054547
Kenya Agricultural Research Institute
Nairobi
肯尼亚
SLM专业人员:
Namirembe Sarah
+254 20 7224000
World Agroforestry Centre - ICRAF
United Nations Avenue, P. O. Box 30677, Nairobi, Kenya
肯尼亚
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Jomo Kenyatta University (Jomo Kenyatta University) - 肯尼亚有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
KARI Headquarters (KARI Headquarters) - 肯尼亚有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
International Centre for Research in Agroforestry (ICRAF) - 肯尼亚1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
18/09/2012
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.4 所述技术的可持续性声明
这里所描述的技术在土地退化方面是否存在问题,导致无法被认为是一种可持续的土地管理技术?:
否
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
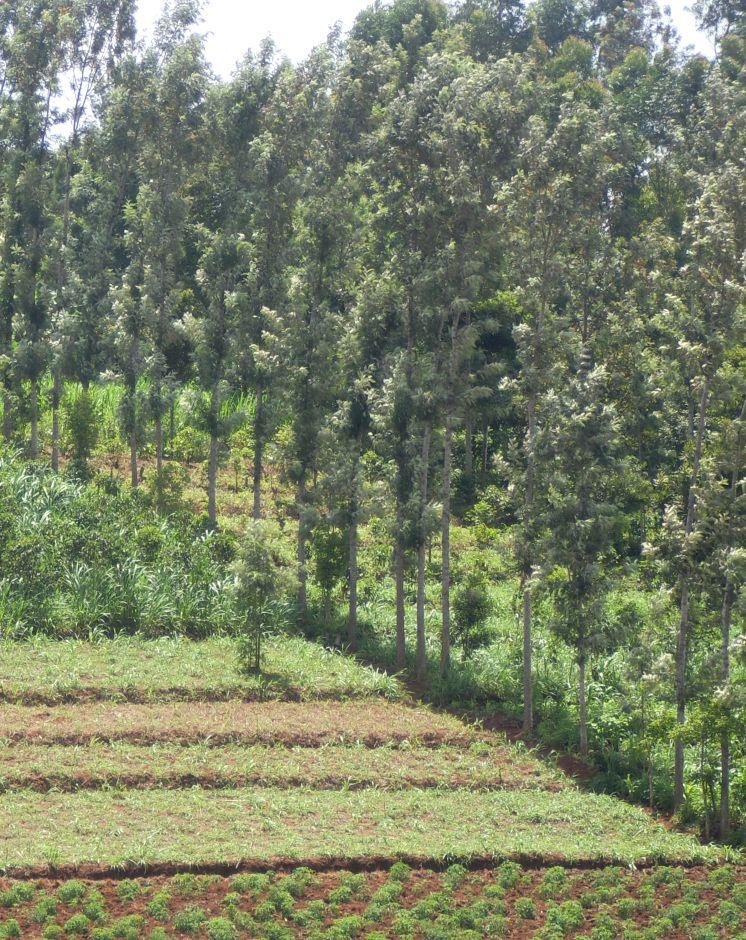
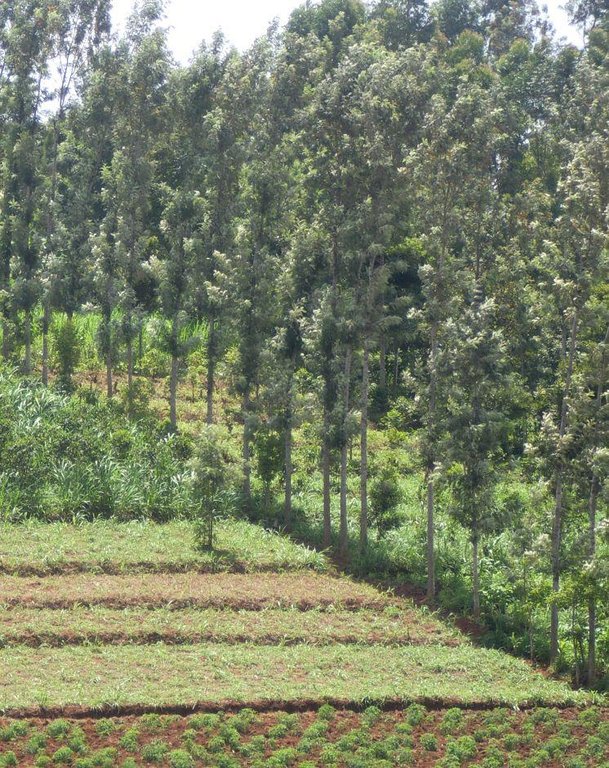
Windbreaks are narrow strips of trees, shrubs and/or grasses planted to protect fields, homes, canals, and other areas from the wind and blowing sand.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
Where wind is a major cause of soil erosion and moisture loss, windbreaks can make a significant contribution to sustainable production. They also be used to act as shelter-belts, a type of windbreak, are long, multiple rows of trees and shrubs, usually along sea coasts, to protect agricultural fields from inundation by tidal waves.
Purpose of the Technology: Windbreaks can make a significant contribution to sustainable production
Where wind is a major cause of soil erosion and moisture loss
It improves the microclimate in a given protected area by decreasing water evaporation from the soil and plants
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Trees ( mainly Grivelia robusta) are planted in rows. They are maintained by regular pruning from the tender age to old age. Also, regular replacement of old trees. The trees are closely planted, about 1m apart and a maximum height of about 10m. The trees are always planted along the edges of the fields to protect the effects of mainly wind and the tidal waves. Surveying of the planting lines should be done to ensure they are linear
Natural / human environment: The trees are used as boundaries, firewood, timber and fence posts, they should be environmental friendly.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
肯尼亚
区域/州/省:
Eastern Province
有关地点的进一步说明:
Mbeere South District
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 10-50年前
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过土地使用者的创新
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 改良生产
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
- 适应气候变化/极端天气及其影响
- 创造有益的经济影响
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

农田
- 一年一作
注释:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): There is a lot of wind erosion that leads to low land productivity.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Soil erosion of the top soil.
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Cropland: Ca: Annual cropping
如果由于技术的实施而导致土地用途发生变化,则在技术实施前说明土地利的用途。:
Cropland: Ca: Annual cropping
3.3 有关土地利用的更多信息
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 混合雨水灌溉
每年的生长季节数:
- 2
3.4 该技术所属的SLM组
- 防风林/防护林带
3.5 技术传播
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果该技术均匀地分布在一个区域上,请注明覆盖的大致区域。:
- 0.1-1 平方千米
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

植物措施
- V1:乔木和灌木覆盖层
注释:
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -along boundary
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤风蚀
- Et:表土流失
注释:
Main causes of degradation: wind storms / dust storms
Secondary causes of degradation: soil management, crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub), droughts, land tenure
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 防止土地退化
- 修复/恢复严重退化的土地
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
4.2 技术规范/技术图纸说明
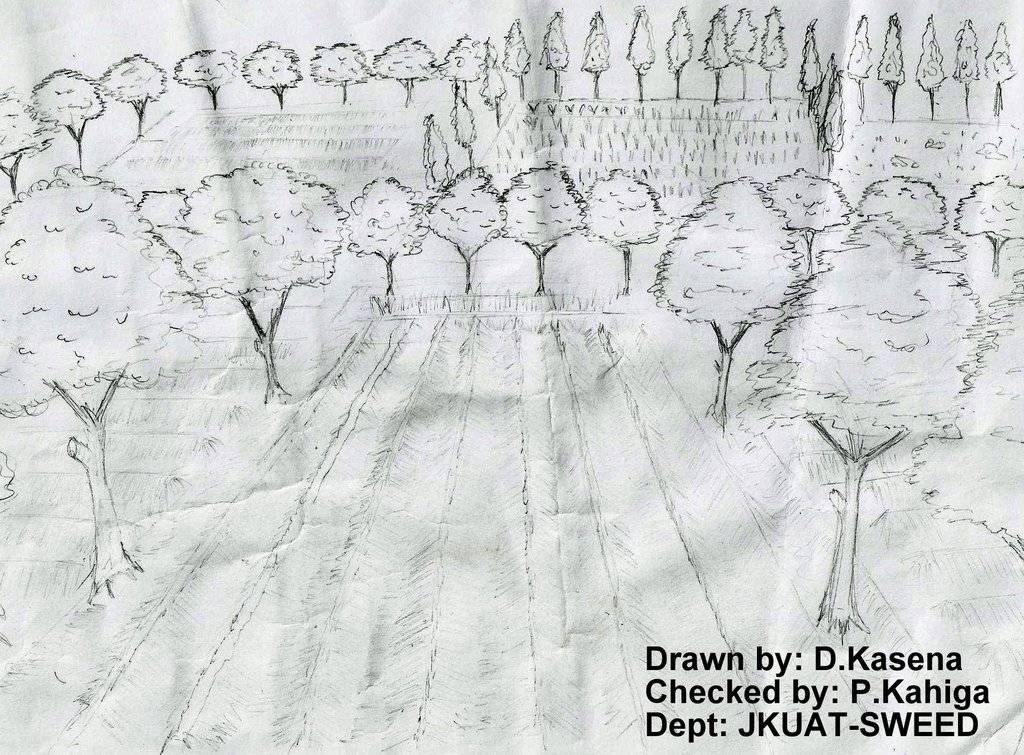
The technical drawing on the left hand shows boundary trees planted either along boundaries between farmers or between different portions of two crop stands. The spacing between the crops depend on the type of particular tree. The most common boundary trees used in Embu County is gravellia trees that have multiple uses (firewood, timber, animal feeds - leaves during the dry spells and mulch to some extent)
Location: Embu. Central Province
Date: 13.02.2013
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate (The technology does not require a lot of skills to demonstrate to the farmers. Just basic skills on spacing and vertical interval)
Technical knowledge required for land users: low (The basic skills of the farmer required to effect the technology)
Main technical functions: stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides), reduction in wind speed
Aligned: -contour
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Aligned: -along boundary
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 400
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 20
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 5
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.3
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.5
Trees/ shrubs species: Grivelia robusta
Grass species: Napier grass
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 5%%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is (see figure below): 5%%
4.3 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
KSh
注明美元与当地货币的汇率(如相关):1美元=:
85.0
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
4.70
4.4 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Establishing contours | 植物性的 | Each cropping season |
| 2. | Digging of holes | 植物性的 | Before the cropping season |
| 3. | Planting of trees | 植物性的 | After the digging of holes |
4.5 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Labour | ha | 1.0 | 470.0 | 470.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Tools | ha | 1.0 | 5.3 | 5.3 | 100.0 |
| 植物材料 | Seedlings | ha | 1.0 | 480.0 | 480.0 | 100.0 |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | Compost/manure | ha | 1.0 | 3.5 | 3.5 | 100.0 |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 958.8 | |||||
注释:
Duration of establishment phase: 24 month(s)
4.6 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Prunning | 农业学的 | Each cropping season |
| 2. | Pruning | 植物性的 | Onset of planting season |
4.7 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Labour | ha | 1.0 | 470.0 | 470.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 470.0 | |||||
4.8 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
If the land has a gentle sloping gradient, the trees need to be closely planted o reduce the effects of the winds and storms to the crops.
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
有关降雨的规范/注释:
The area receives relatively good amount of rainfall
农业气候带
- 半湿润
- 半干旱
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 中(1-3%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Soil texture: Medium (the soils are relatively friable)
Soil fertility: Medium (limited crops for productivity)
Topsoil organic matter: Medium (gently sloping lands)
Soil drainage/infiltration: Medium (the soils are relatively good drained)
Soil water storage capacity: Medium (soils have medium water holding capacity due to high intensities of sun rays)
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
> 50米
地表水的可用性:
中等
水质(未处理):
不良饮用水(需要处理)
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 低
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
生产系统的市场定位:
- 混合(生计/商业
非农收入:
- 收入的10-50%
相对财富水平:
- 平均水平
个人或集体:
- 个人/家庭
机械化水平:
- 手工作业
性别:
- 女人
- 男人
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Difference in the involvement of women and men: Men ensure establishment and women ensure good maintenance of the technology
Population density: > 500 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 1% - 2%
(Most people have avaragely living standards).
Off-farm income specification: There is increased production since the trees once grown big can be cut and provide timber
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者拥有或租用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 小规模的
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 个人,未命名
土地使用权:
- 个人
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
木材生产
产品多样性
土地管理
收入和成本
农业收入
社会文化影响
SLM/土地退化知识
冲突缓解
Improved livelihoods and human well-being
生态影响
生物多样性:植被、动物
栖息地多样性
减少气候和灾害风险
风速
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
风力搬运沉积物
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气象灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 局地风暴 | 好 |
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
积极
6.5 技术采用
注释:
There is a strong trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Reduce wind speed |
| They produce fruit, nuts, maple syrup, firewood, posts, poles and veneer |
| They provide nectar and pollen for bees |
| Wind breaks protect a variety of wind-sensitive crops |
| Acts as sound barriers and mitigate odors from neighboring properties |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| complicates equipment movement | Proper spacing to allow movement of equipment |
| Establishment and maintenance costs | The establishment and maintenance cost cant be equaled with the overall benefits |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Loss of space that could otherwise be utilized by food crops | Appropriate spacing even though the effect has less magnitude because it is established along the boundaries |
| Shading effects, effects on micro-climate and harbors pests. | Avoid very tall windbreaks which shades excessively and are susceptible to breakages. Use of appropriate chemicals for spraying the pests. |
| Competition for water and nutrients | Supplemental irrigation in times of droughts |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
- 实地考察、实地调查
- 与土地使用者的访谈
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块