Vetiver Hedge Barrier along Seashore and River bank [中国]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Ursula Gaemperli
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
vetiver hedge barrier in huo garden
technologies_961 - 中国
- Vetiver Hedge Barrier along Seashore and River bank: March 6, 2017 (inactive)
- Vetiver Hedge Barrier along Seashore and River bank: March 21, 2017 (inactive)
- Vetiver Hedge Barrier along Seashore and River bank: March 23, 2017 (inactive)
- Vetiver Hedge Barrier along Seashore and River bank: Sept. 4, 2019 (public)
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
21/11/1997
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
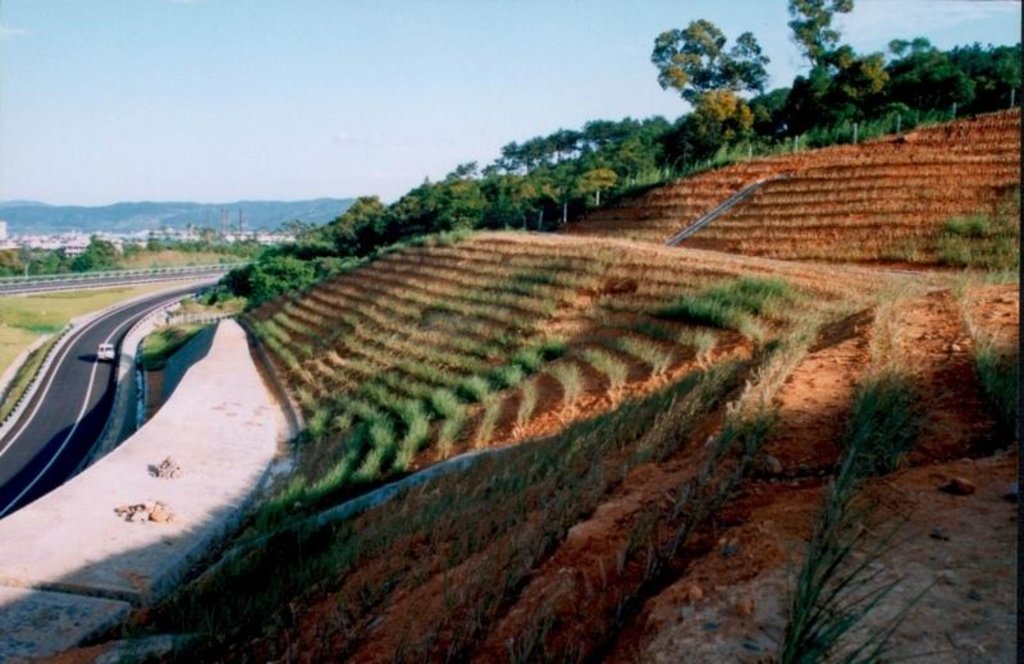
Uprightness to the main windward, planting Vetiver hedge as barriers to prevent wind erosion.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
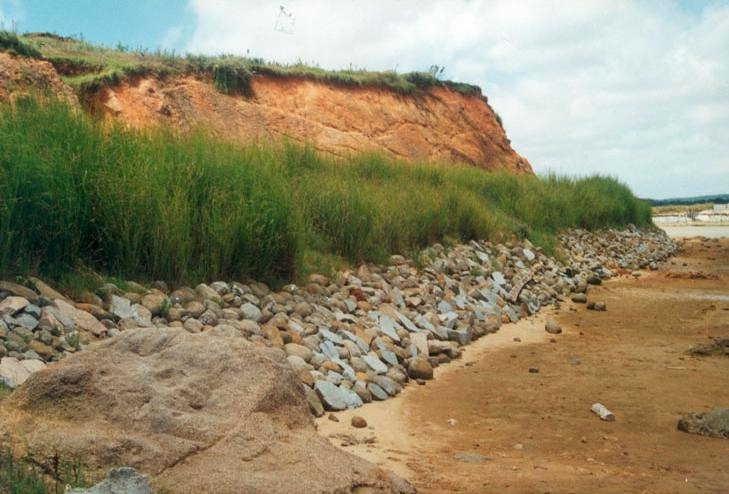
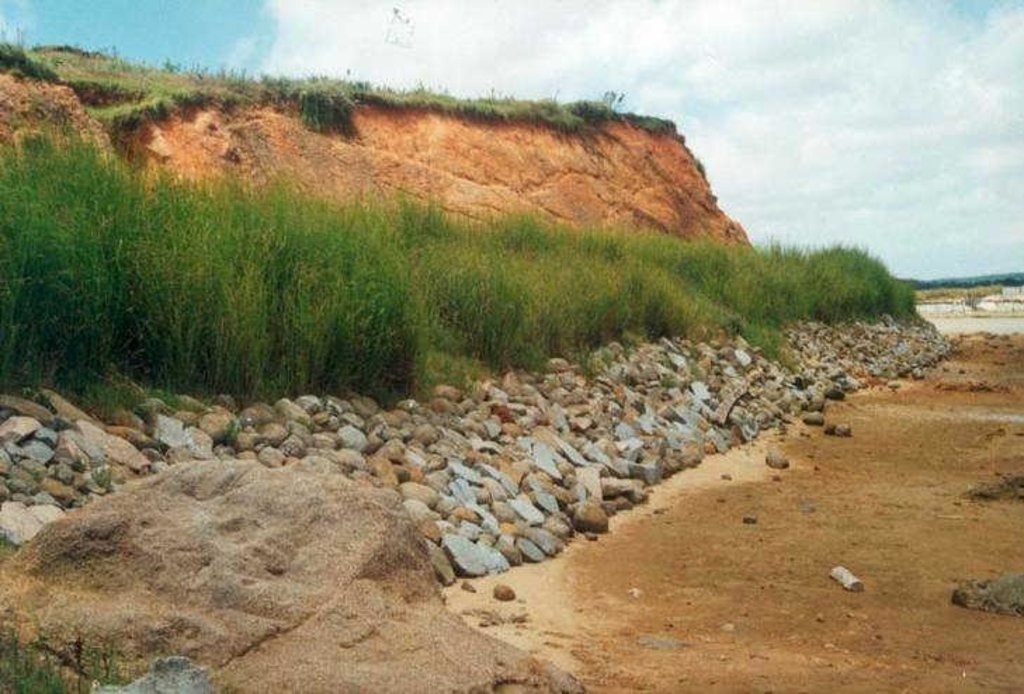
This technology is to use a good SWC vegetable --- Vetiver to form permanent hedge barrier. The barrier is upright to the main windward or along the river & dike bank. It is pruned 1-2 times after 2 months of planting. It can grow at about 1.5 m high within one year. Vetiver is a perennial plant, and has a strong fibrous roots, which can stretch 3 m beneath soils. It breeds by root & cane, and has strong adaptability. Vetiver is hygrophobe and can endure poor and saline-alkali soil. It is regarded as a saved money & low in labor input but with good benefits. This SWC technology is worth to be applied extensively.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
中国
区域/州/省:
Fujian
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 不到10年前(最近)
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过项目/外部干预
注释(项目类型等):
From India.
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

农田
- 一年一作
主要农作物(经济作物及粮食作物):
Rice-peanut-sweat potato etc.
注释:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Serious wind erosion damages crops and cultivated land along the seashore.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Crops were often damaged and crop yield is decreasing gradually.
Type of cropping system and major crops comments: Rice-peanut-sweat potato etc.
3.3 有关土地利用的更多信息
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
注释:
Water supply also full irrigation
每年的生长季节数:
- 1
具体说明:
Longest growing period in days: 365Longest growing period from month to month: Jan - Dec
3.4 该技术所属的SLM组
- 地表水管理(泉、河、湖、海)
3.5 技术传播
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果该技术均匀地分布在一个区域上,请注明覆盖的大致区域。:
- 0.1-1 平方千米
注释:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.5 m2.
The SWC area is about 0.5 sqkm.
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

植物措施
- V1:乔木和灌木覆盖层
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤风蚀
- Et:表土流失

化学性土壤退化
- Cn:肥力下降和有机质含量下降(非侵蚀所致)

水质恶化
- Ha:干旱化
注释:
Main type of degradation addressed: Et: loss of topsoil
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content, Ha: aridification
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.2 技术规范/技术图纸说明
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: low
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: Wind-break
Secondary technical functions: improvement of ground cover, increase in organic matter, increase of infiltration, increase / maintain water stored in soil, water harvesting / increase water supply, Increase in soil fertility
Mulching
Material/ species: Vetiver
Quantity/ density: 10000
Remarks: alignment
Grass species: Vetiver
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 30.00%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is (see figure below): 20.00%
Gradient along the rows / strips: 50.00%
4.3 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
具体说明成本计算所用货币:
- 美元
注明美元与当地货币的汇率(如相关):1美元=:
8.3
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
3.61
4.4 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | treating material | 植物性的 | mid-March |
| 2. | soil preparation | 植物性的 | early March |
| 3. | planting | 植物性的 | mid-March |
| 4. | water | 植物性的 | planting day |
4.5 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
注释:
Duration of establishment phase: 24 month(s)
4.6 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | pruning | 植物性的 | mid-May / |
| 2. | pruning | 植物性的 | early June / |
| 3. | applying fertilizer | 植物性的 | later May / |
4.7 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
注释:
Areas of vetiver cover.
4.8 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
seeds and labor.
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
指定年平均降雨量(若已知),单位为mm:
1182.00
农业气候带
- 潮湿的
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
说明该技术是否专门应用于:
- 不相关
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 粗粒/轻(砂质)
表土有机质:
- 低(<1%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Soil fertility: very low
Soil drainage / infiltration: good
Soil water storage capacity: very low
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
非农收入:
- 低于全部收入的10%
相对财富水平:
- 平均水平
机械化水平:
- 手工作业
- 畜力牵引
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Population density: 200-500 persons/km2
Annual population growth: < 0.5%
30% of the land users are average wealthy and own 20% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: This is an experimental project with small area so that not many persons involved in it.
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 社区/村庄
- 个人,有命名
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
生态影响
水循环/径流
地表径流
SLM之前的数量:
60
SLM之后的数量:
35
土壤
土壤流失
SLM之前的数量:
4.5
SLM之后的数量:
2
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
中性/平衡
长期回报:
非常积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
非常积极
6.5 技术采用
- 大于 50%
如若可行,进行量化(住户数量和/或覆盖面积):
100 households and 100% of the area
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发地采用该技术,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 50-90%
注释:
50% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
30 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: estimates
50% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
30 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: estimates
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Climate here is quite suitable for vetiver growing and it is easy to plant with low input and high output.
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块