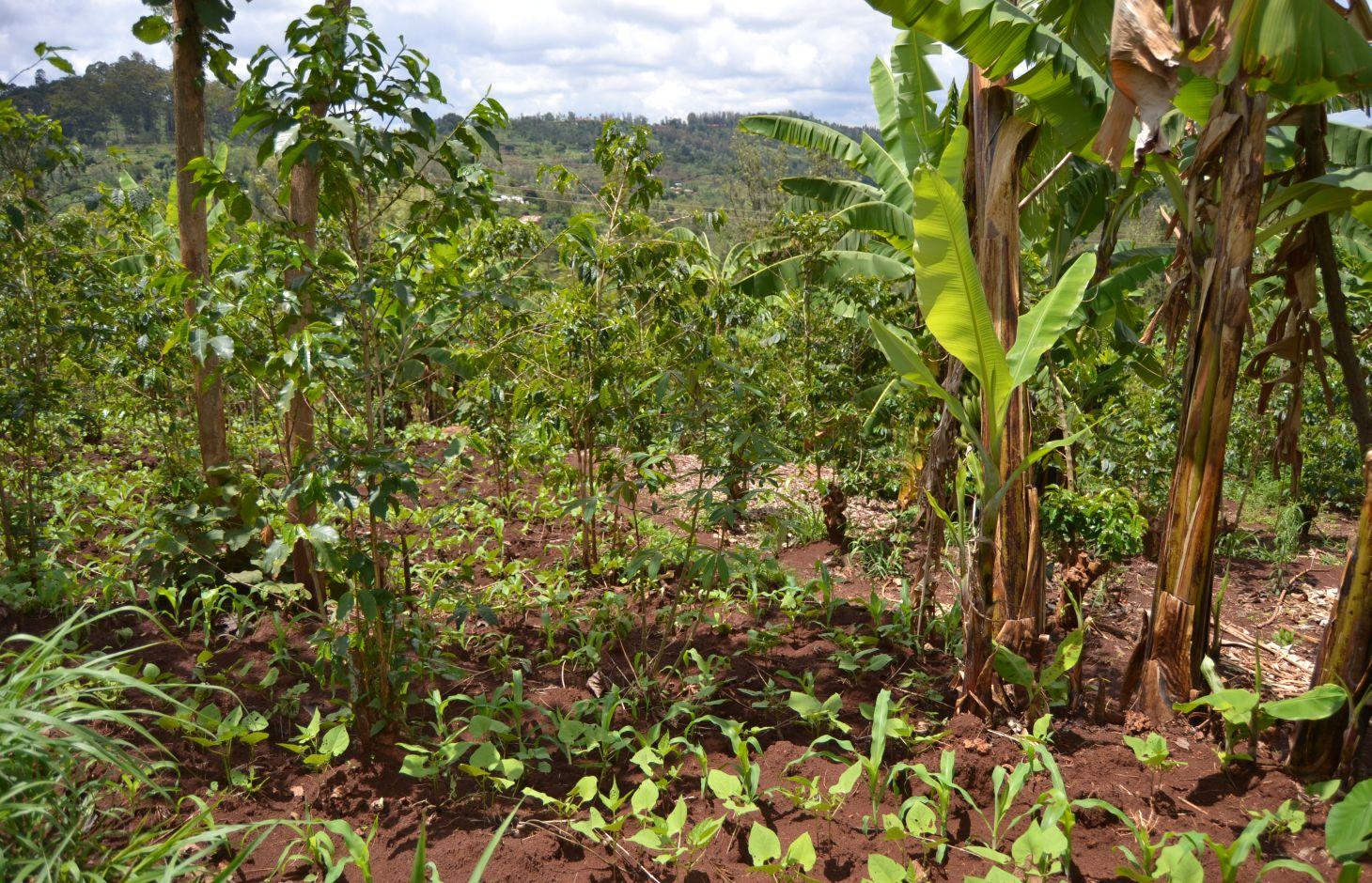
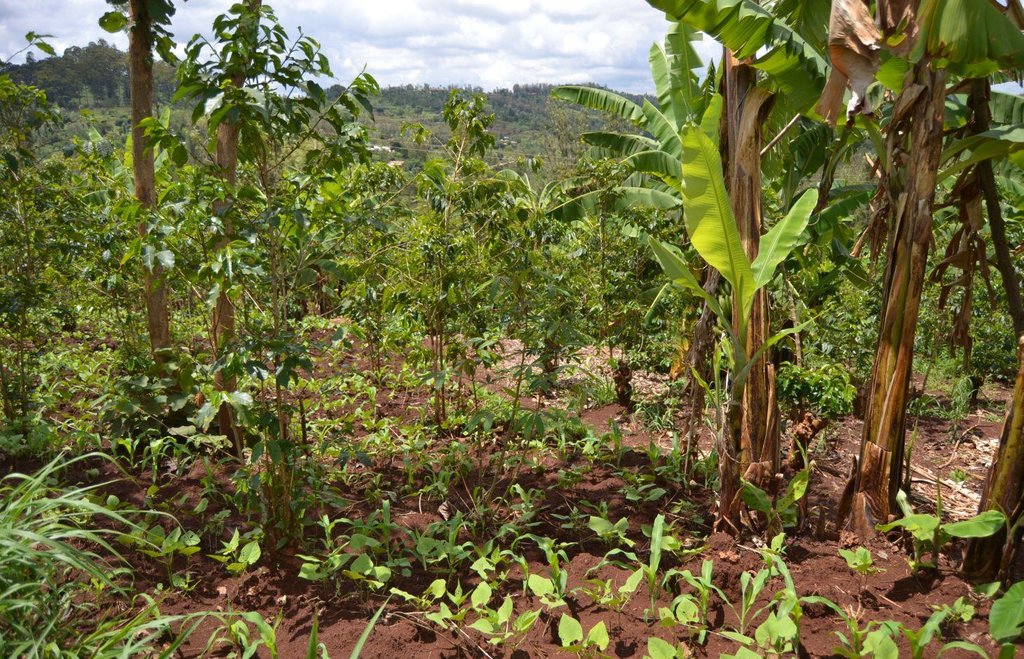
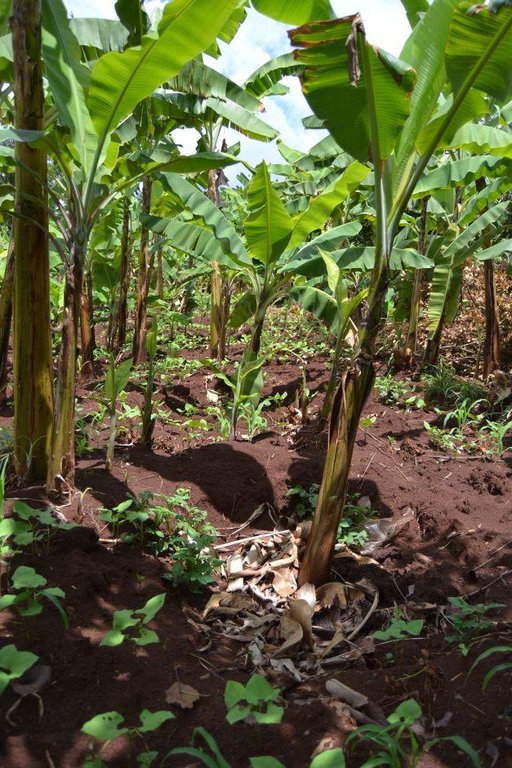
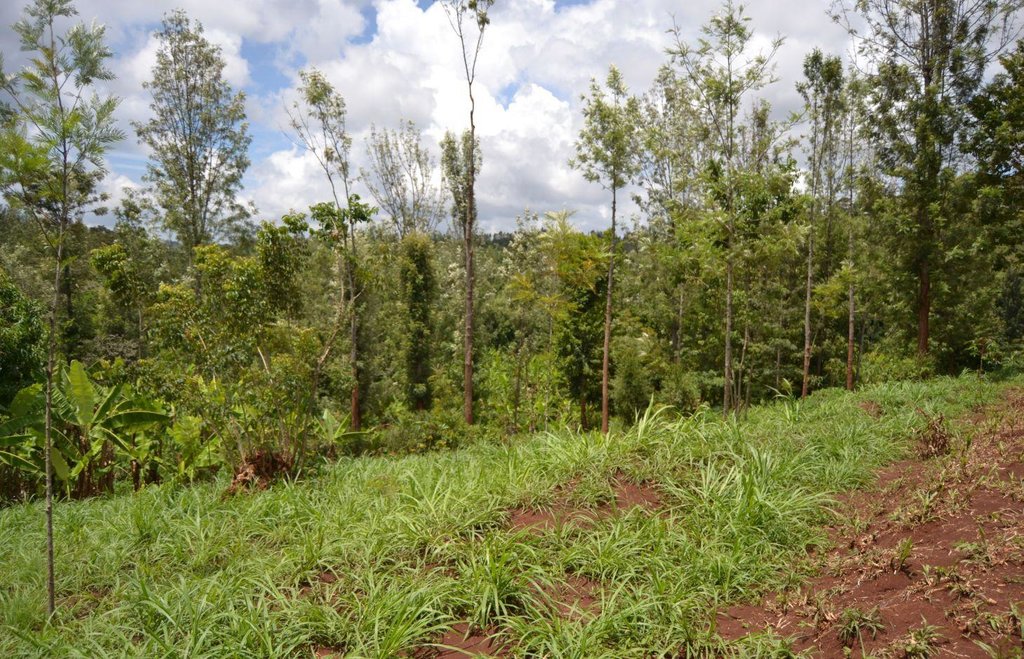
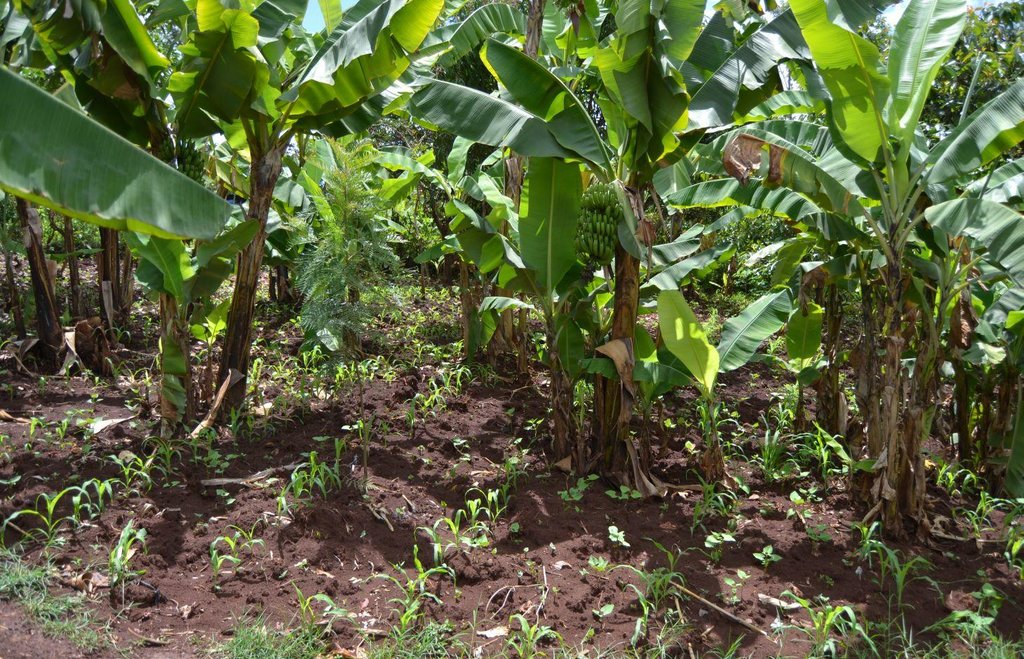
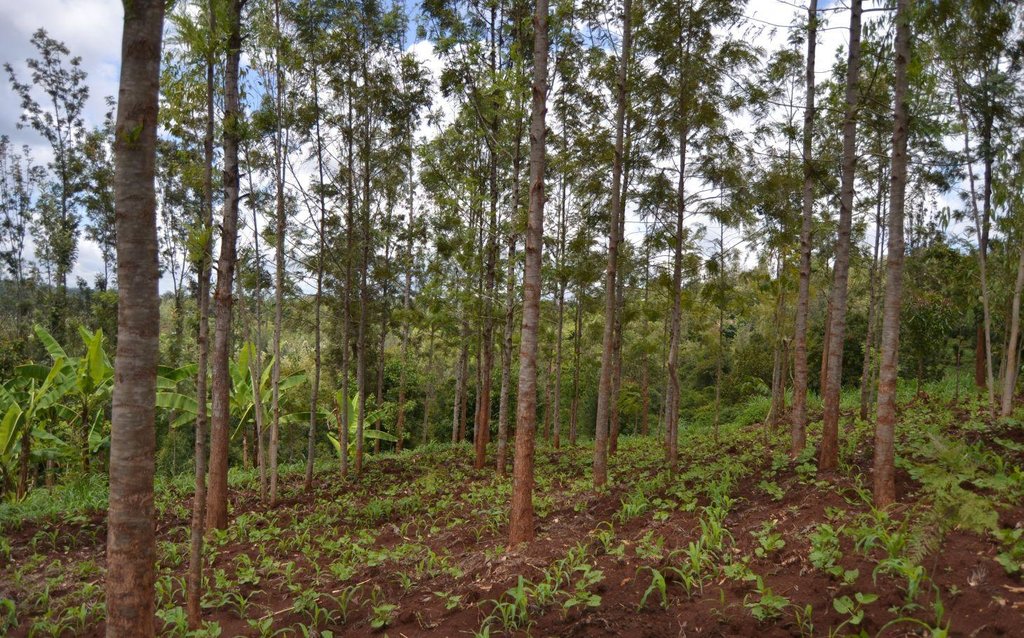
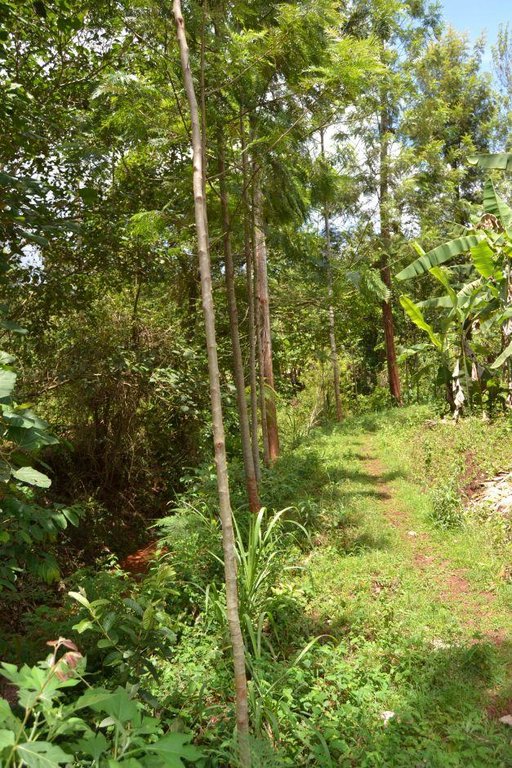
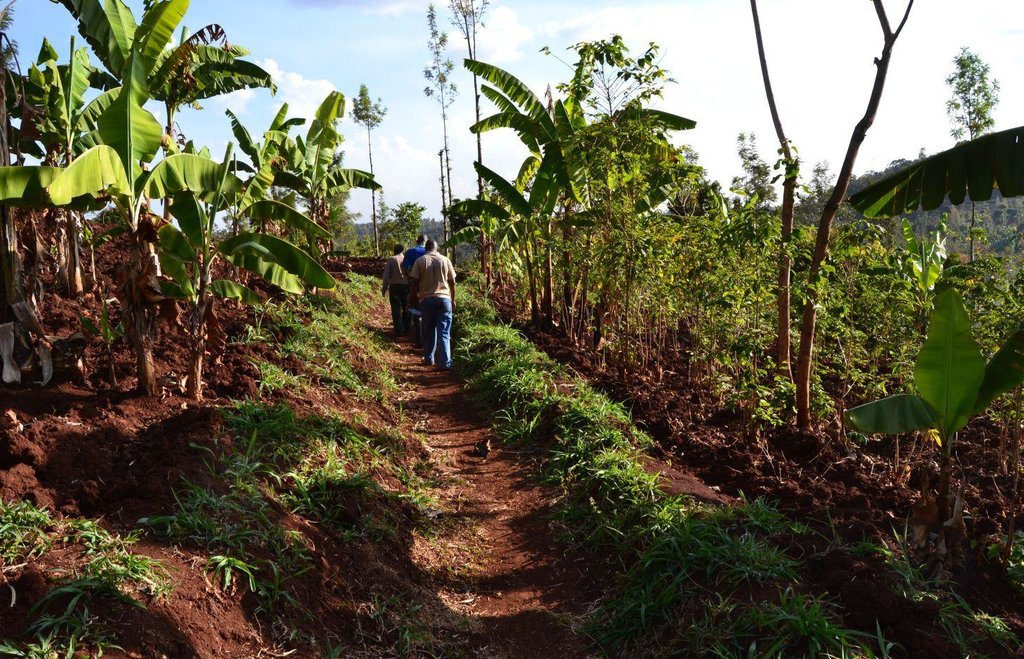
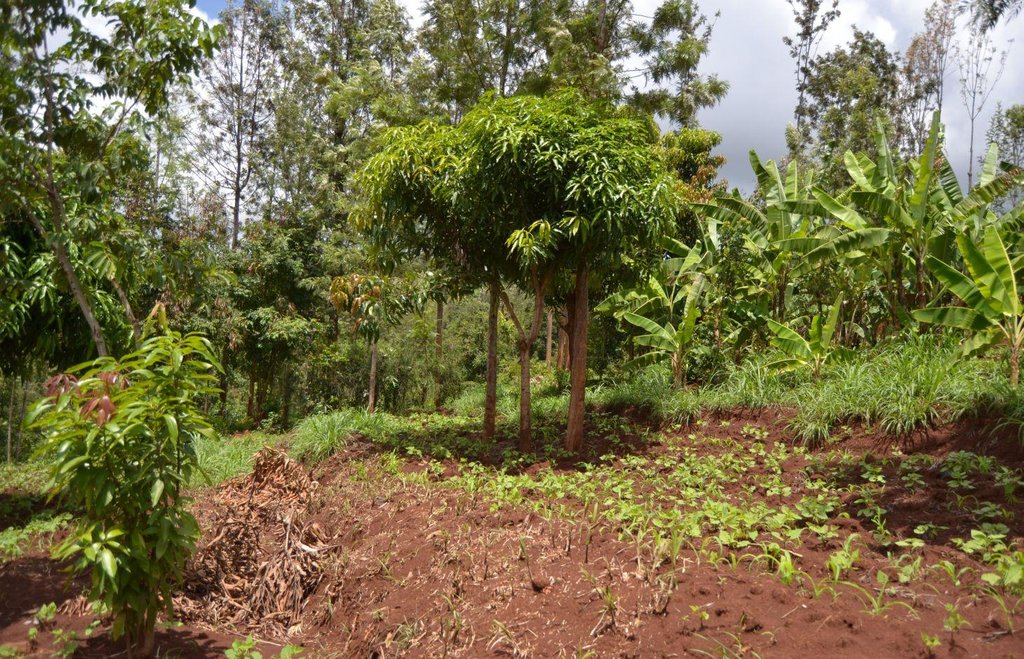
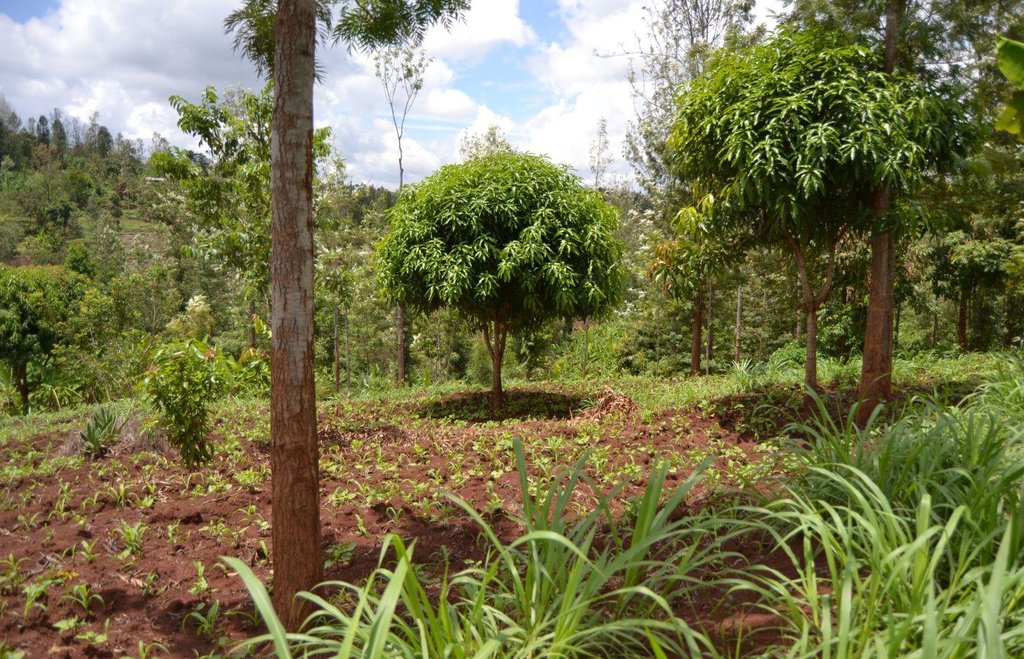
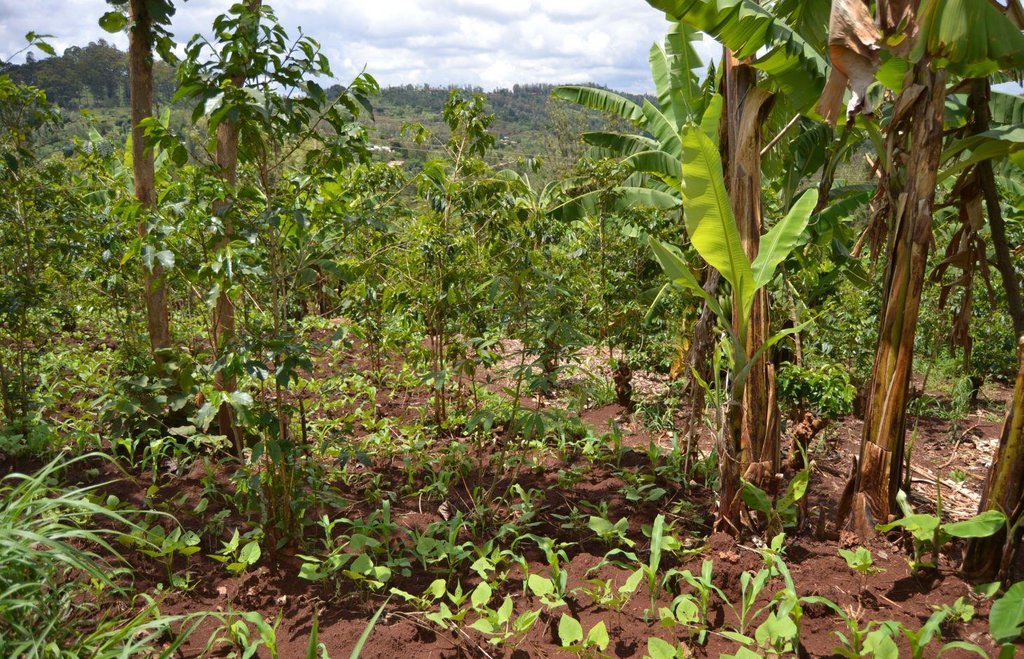
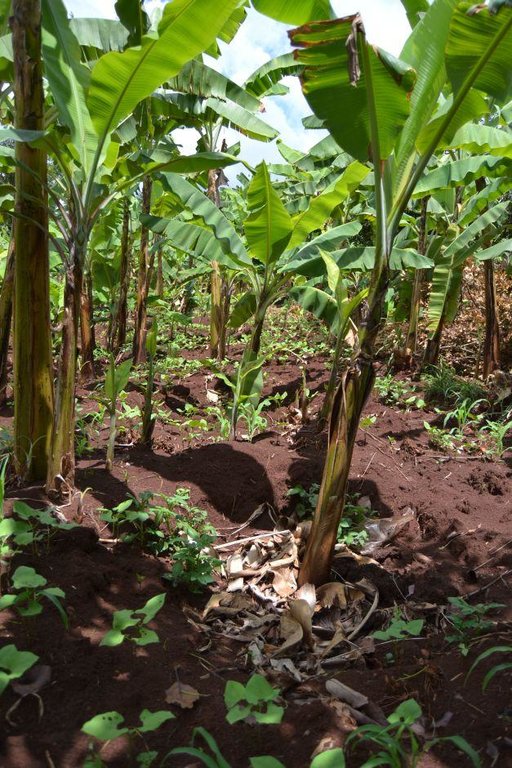
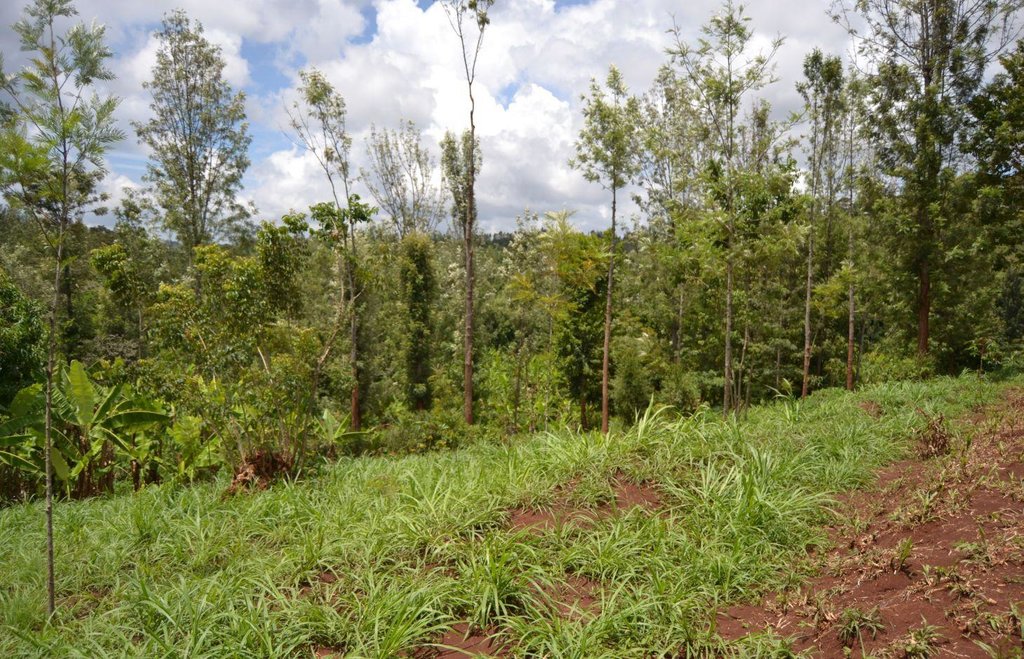
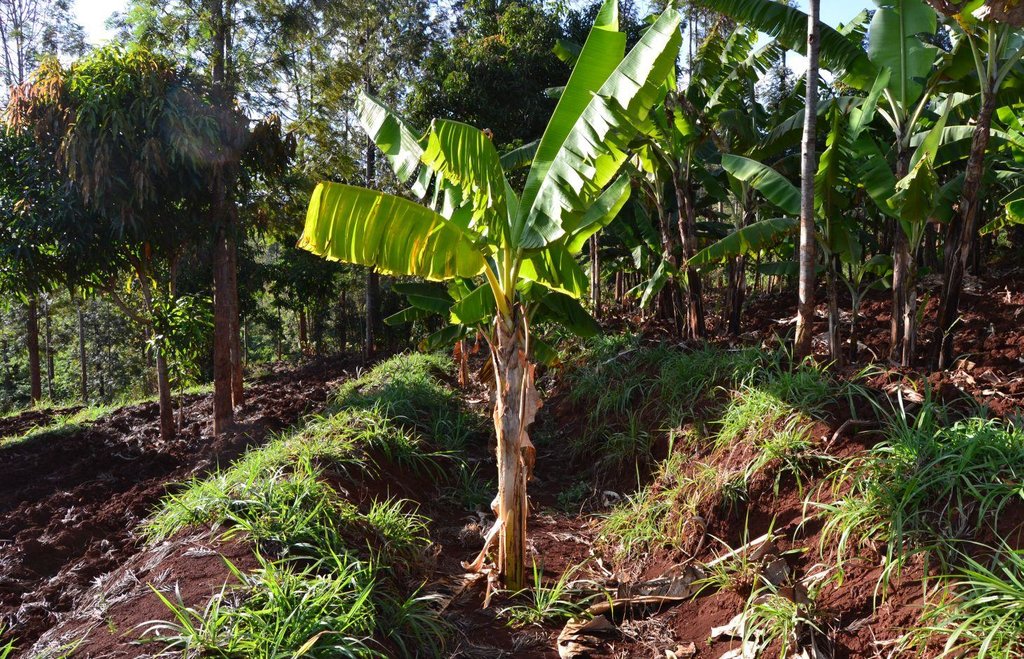
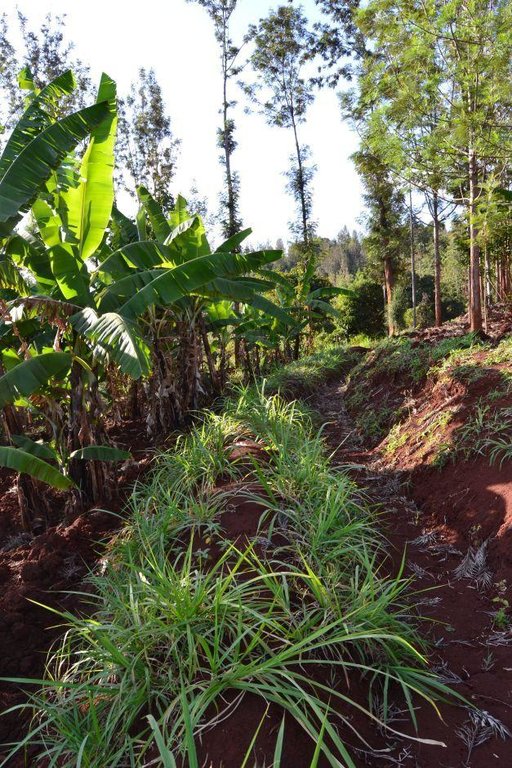
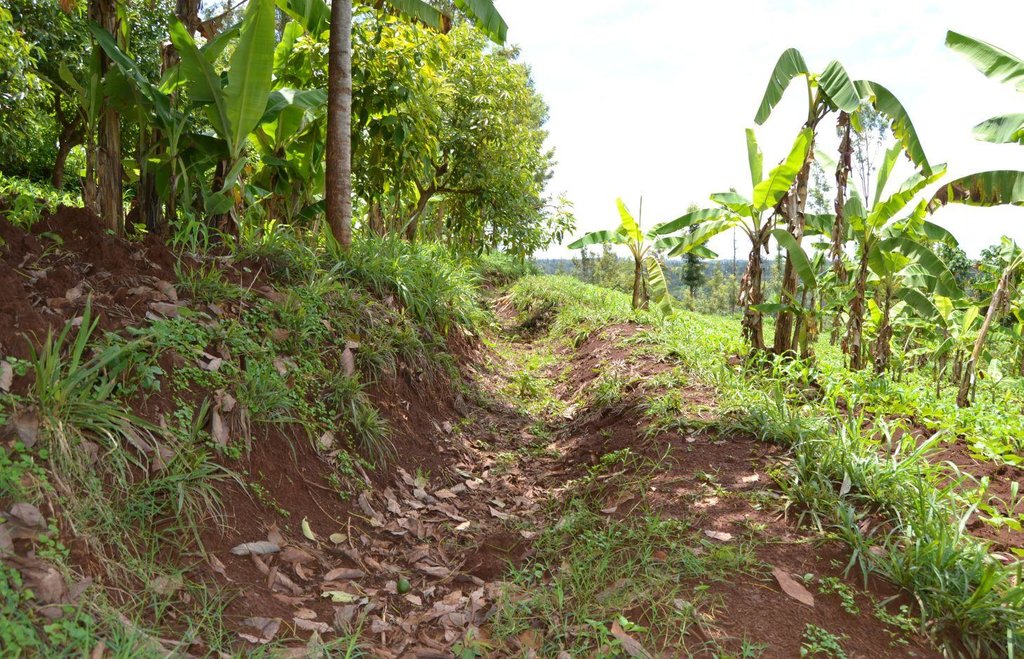
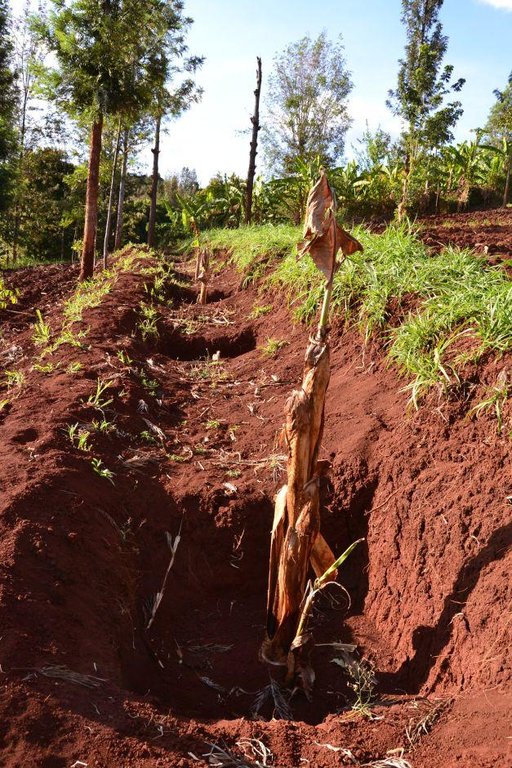
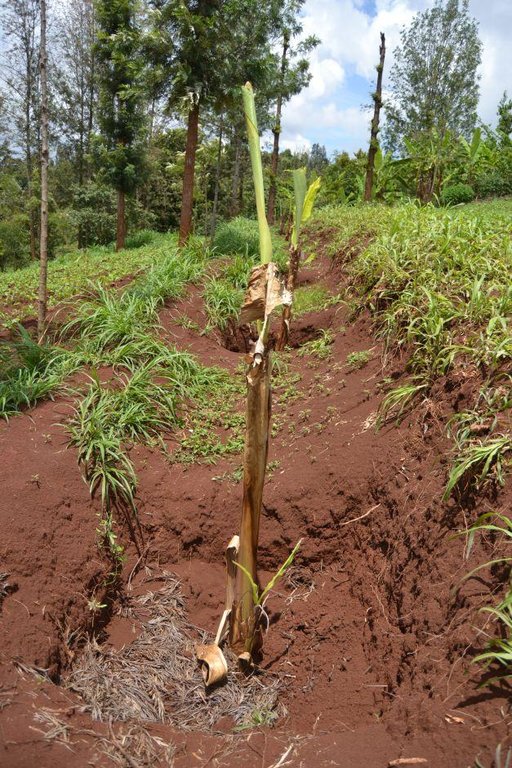
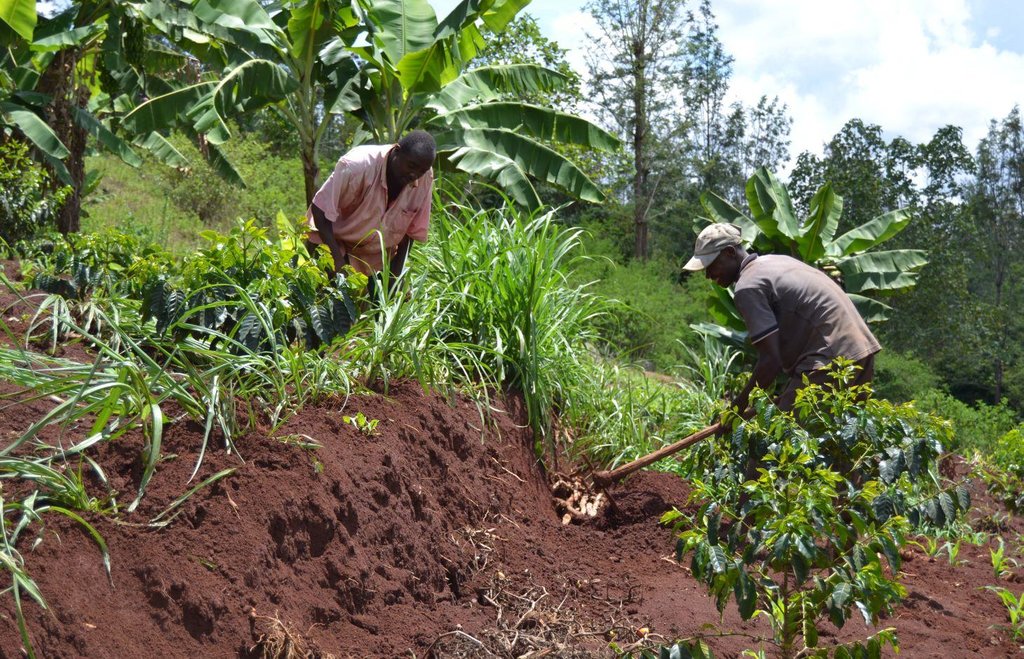
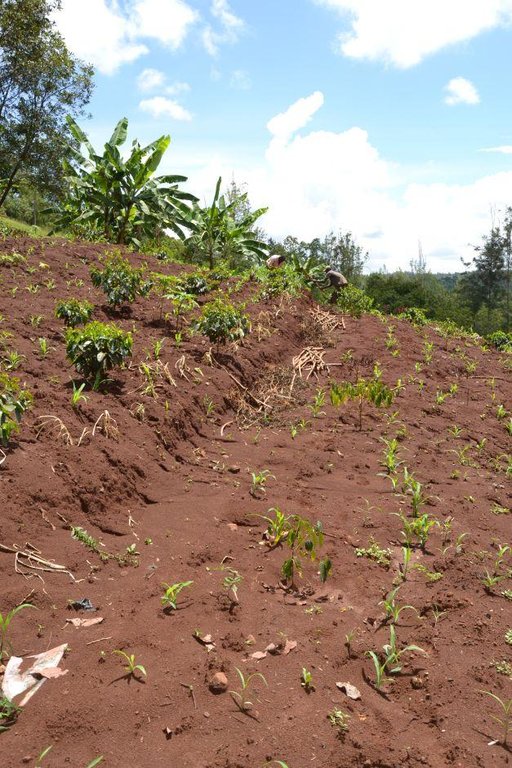
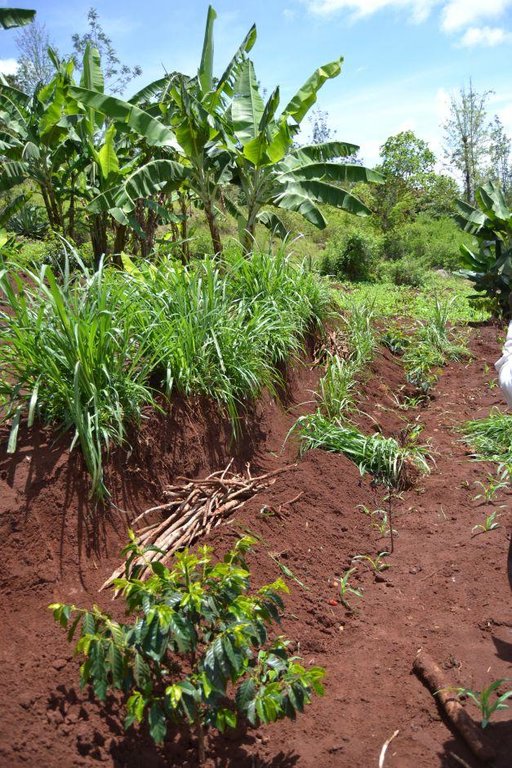
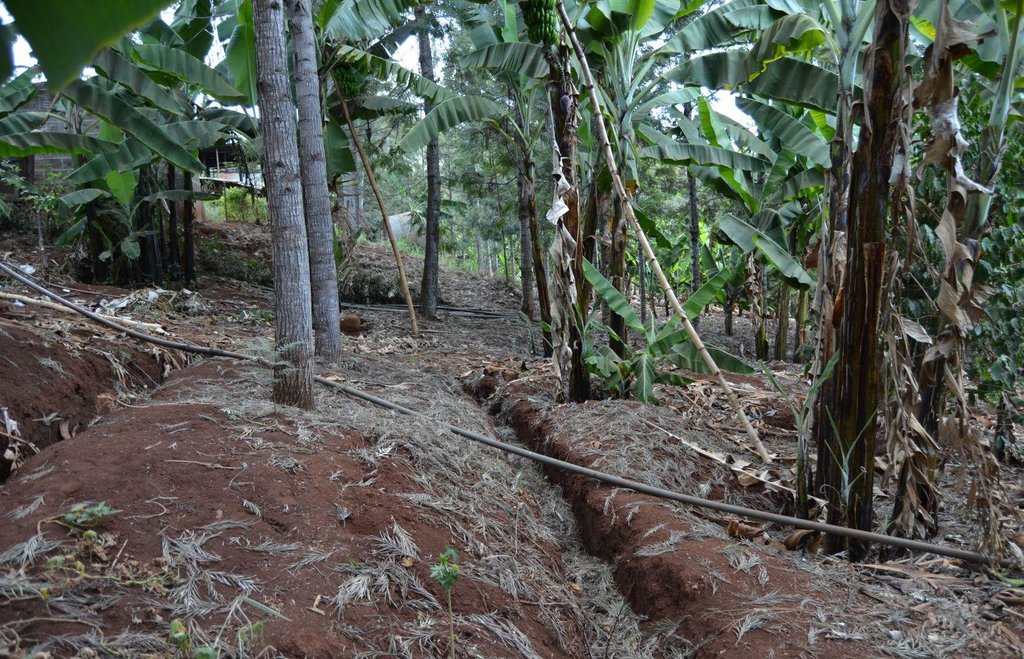
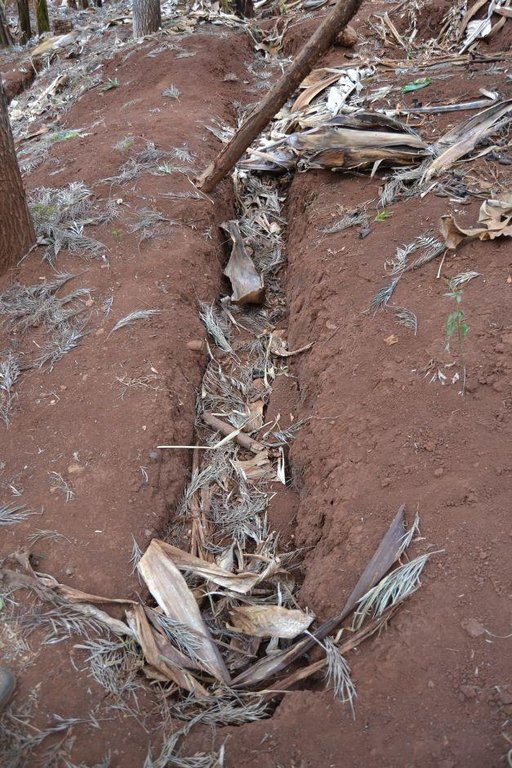
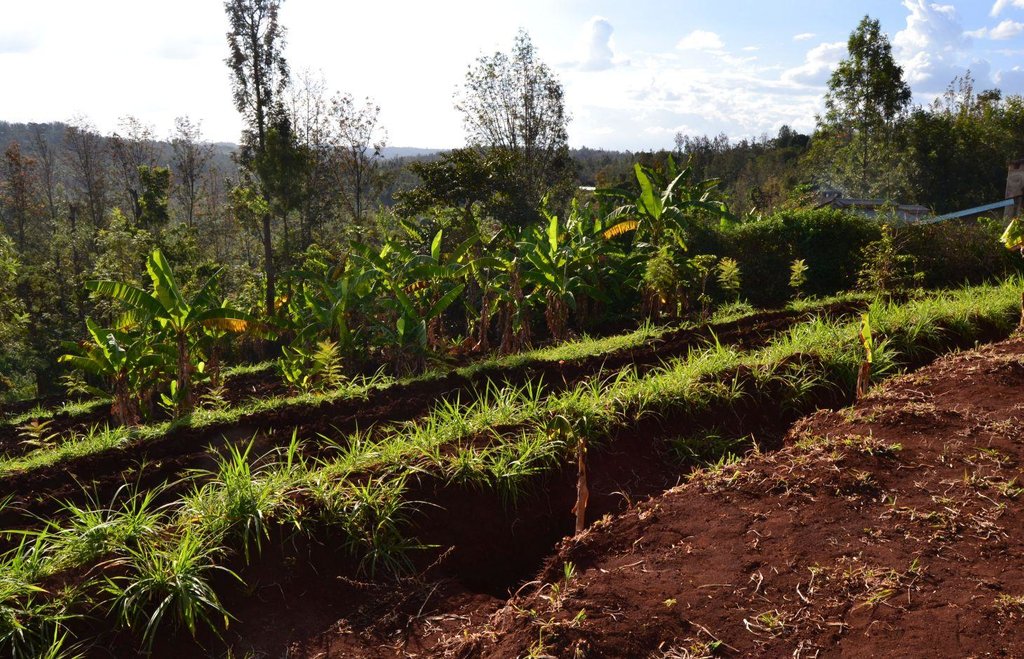
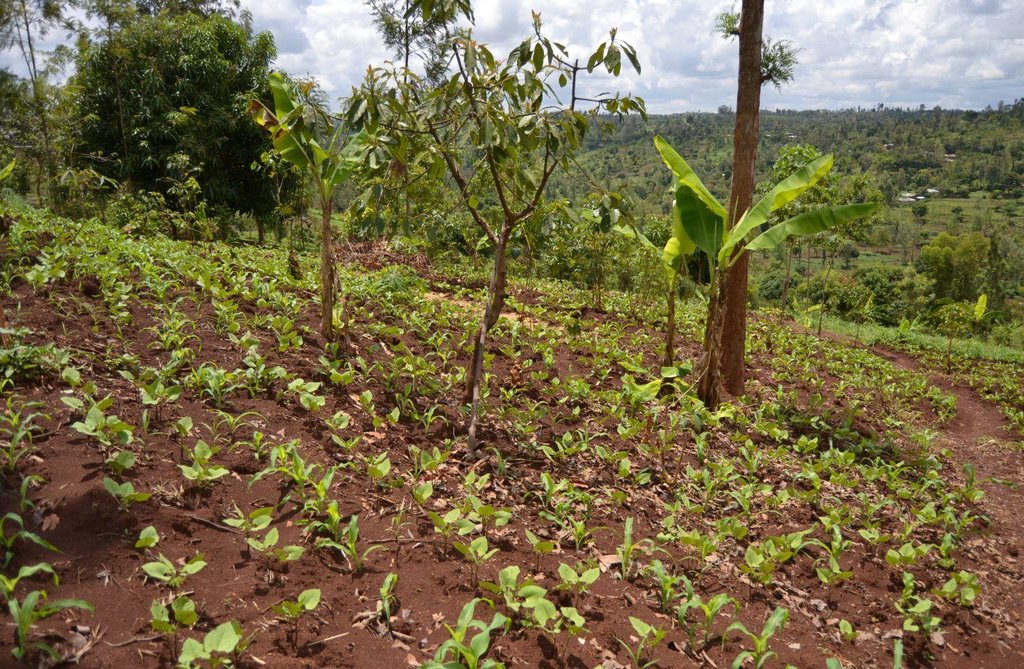
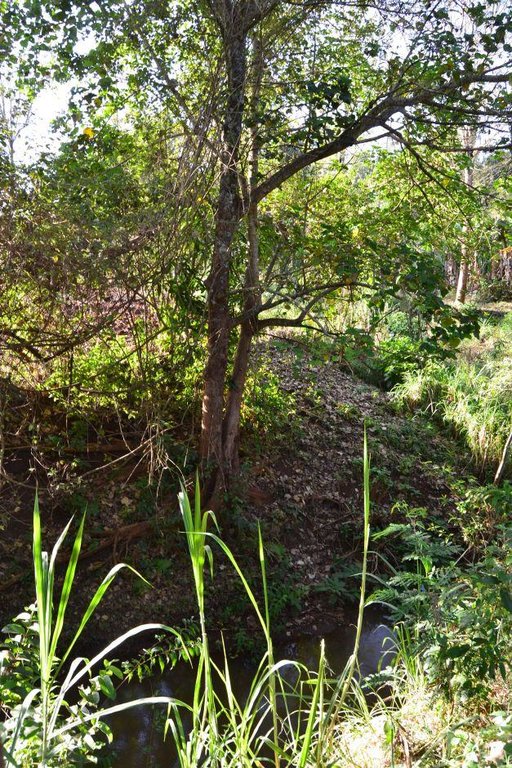
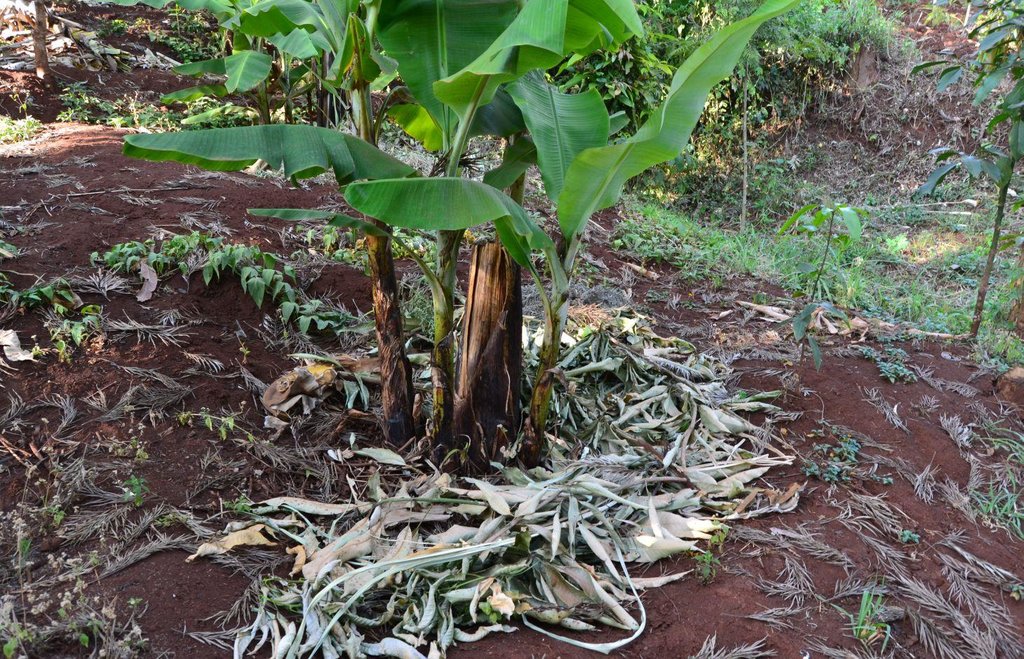
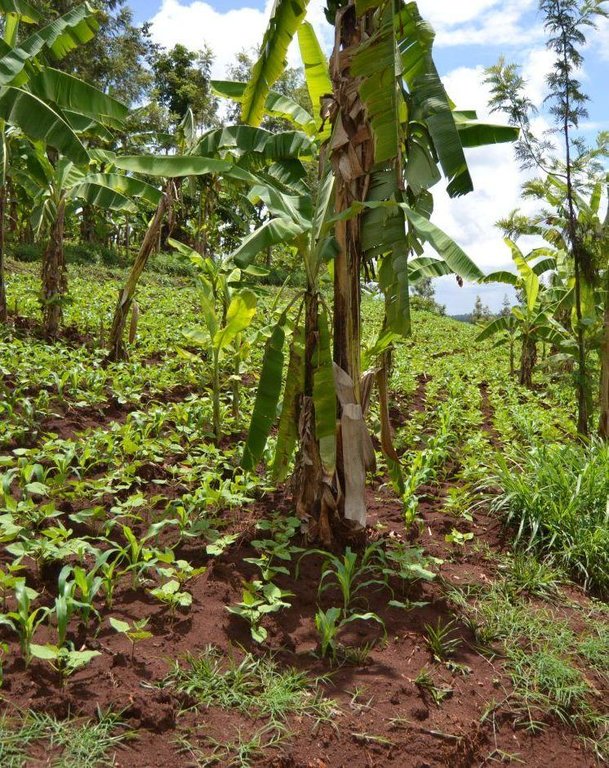
Agroforestry land use in bench terraces with cut-off and infiltration ditches and Napier grass strips. [肯尼亚]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Laura D'Aietti
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Alexandra Gavilano, Fabian Ottiger
technologies_1159 - 肯尼亚
- Agroforestry land use in bench terraces with cut-off and infiltration ditches and Napier grass strips.: Dec. 29, 2016 (inactive)
- Agroforestry land use in bench terraces with cut-off and infiltration ditches and Napier grass strips.: June 5, 2017 (inactive)
- Agroforestry land use in bench terraces with cut-off and infiltration ditches and Napier grass strips.: May 3, 2019 (public)
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
关键资源人
SLM专业人员:
F. K. Nyamu Jospeh
WRUA Sabasaba
肯尼亚
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) - 意大利1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
02/11/2012
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
A combination of agricultural (e.g. intercropping, mulching, minimum tillage), vegetative (e.g. Napier grass strips, trees planting) and structural (e.g. ditches, bench terracing) measures which aim to maximise the overall yield in a sustainable manner (e.g. reduction of soil erosion and increasing the soil quality).
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
The land of the farmer is of 3 acres: 2 acres to plant maize (Zea mays) intercropped with beans (Phaseolus vulgaris) in combination with several trees species: Mangoes, Avocadoes, Bananas, Grevillea and Makadamia and half acre for coffee plantation with Bananas and half with Napier grass production for fodder (to feed cows). To increase and fasten the grass growth, manure is applied twice a year, before the rainy season (around February and September), while mulching is practiced under Banana trees every season. Minimum tillage is applied to reduce soil disturbance and to increase water use efficiency by minimizing direct evaporation, increasing infiltration and water recharge (Liniger, 1991) especially during dry seasons, which results in better crop yields.
For timber production Grevillea trees are planted scattered overall the land and on the edge of the river for demarcation (environmental role in stabilizing the soil against erosive forces).
Concerning the structural measures, the farmer constructed has built 14 bench terraces, six of them were designed to plant cash crops (coffee); each terrace is characterized by a ditch to cut off the drainage and collect water and nutrients; they are also used as paths to facilitate transportation and farm operations. Ditches are both drainage and infiltration types and are excavated along the contour.
Purpose of the Technology: Beans and maize are cultivated for home consumption but partially (about 20%-4 bags of maize and half bag of beans) also for commercial purposes. Coffee is harvested twice a year, with a production of about 500 kg per season; the coffee is sold at 45 Kenyan Shillings (KSh) per kg (SL-28-arabica varieties). Indeed, the farmer is interested in cultivating the certified and improved variety called Ruiru 11 which is generally disease resistant, easy to maintain (less expensive) with a modest risk of pests (according to the farmer). Grevillea timber is sold twice a year, only trees of 1.5 feet in diameter (about 45 cm), at about 80 KSh per feet. Beside the commercial role of Grevillea, when sufficiently grown these trees lead to a reduction of the wind speed, protect the intercrops and provide mulching material to be used over banana trees. The deep roots of mature Grevillea are not in competition with the crops for soil and water, instead they enhance infiltration (Otengi, 2007). Makadamia will be used to produce cooking oil, while bananas, avocados and mangoes are fruits collected for the local markets. Napier grass is cultivated to stabilize the ditches and for fodder production.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: There is a high initial input (mainly labour) needed to create ditches and terraces and for planting crops is required. The vegetative and structural measures require a labour intensive management during the year, for example maintenance is necessary after each rainy season to repair ditches and to rebuild terraces (e.g. because of the accumulation of soil and organic matter in the pits and ditches). Concerning Napier grass, labour is employed regularly for weed control, to cut grass for fodder and every three seasons to replace and replant the grass because it becomes less productive. Concerning trees, in the Agroforestry systems, canopies of Mango and Avocado trees shade the soil reducing evapotranspiration and therefore improving soil water storage. On the other hand, regular pruning is needed when the shadow effect obstructs photosynthesis and therefore growth of the crops planted below (maize and beans). Pruning of branches is carried out also for firewood. Furthermore, a common practice is Grevillea root pruning to conserve soil moisture (Otengi, 2007) and to reduce competition for nutrients during the growing season. Indeed, the farmer explained how superficial roots may interfere with the Banana root system and to cut them he has created small trenches. Harvesting is carried out twice during the year for both cereals and coffee.
Natural / human environment: The area is characterized by rolling to hilly slopes, therefore it is exposed to erosion and land degradation. The combination of trees with mixed crops is adopted to maximise productivity and at the same time to prevent degradation by increasing the vegetative cover.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
肯尼亚
区域/州/省:
Kenya
有关地点的进一步说明:
Muthithi location-Kagurumo sublocation-Gatwamikwa village
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 50多年前(传统)
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 作为传统系统的一部分(> 50 年)
注释(项目类型等):
The technology has been started by the father of the farmer about 70 years ago. His initiative has been developed and improved over time thanks also to the support of the MoA extension officers.
3. SLM技术的分类
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

牧场
集约放牧/饲料生产:
- 收割和携带/零放牧
主要动物种类及产品:
Cut-and-carry/ zero grazing: fodder for 2 cows, from Napier grass

混合(作物/放牧/树木),包括农林
- 农林业
注释:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Soil erosion and nutrient leaching which could drain into the river (Fig. 17).
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): The most important limiting factor to the crop and fodder production remains water: not only related to the weather conditions (e.g. shorter and delayed rainy seasons) but due to the lack of a proper irrigation systems, to minimize the water losses and time. Furthermore, soil has been considered 'not good', because does not hold enough water due to the slope of the land.
如果由于技术的实施而导致土地用途发生变化,则在技术实施前说明土地利的用途。:
Agroforestry
3.3 有关土地利用的更多信息
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
每年的生长季节数:
- 2
具体说明:
Longest growing period in days: 122Longest growing period from month to month: from about March to JuneSecond longest growing period in days: 61Second longest growing period from month to month: from about October to November
牲畜密度(如相关):
< 1 LU/km2
3.5 技术传播
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果该技术均匀地分布在一个区域上,请注明覆盖的大致区域。:
- < 0.1 平方千米(10 公顷)
注释:
About 1.21 ha (3 acres).
The area accounts for the land owned and cultivated by the farmer. According to the interviewee from the Ministry of Agriculture, on average farmers in Saba Saba sub-catchment own 1 acre of land (Elemans, 2011).
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

农艺措施
- A1:植被和土壤覆盖层
- A2:有机质/土壤肥力
- A3:土壤表面处理

植物措施
- V1:乔木和灌木覆盖层
- V2:草和多年生草本植物

结构措施
- S1:阶地
- S4:平沟、坑
注释:
Type of agronomic measures: mulching, legume inter-planting, manure / compost / residues, minimum tillage
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -graded strips
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀

化学性土壤退化
- Cn:肥力下降和有机质含量下降(非侵蚀所致)

水质恶化
- Hp:地表水水质下降
注释:
Main causes of degradation: soil management (Poor soil management practices), deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (Poor vegetation cover, mainly herbaceous), disturbance of water cycle (infiltration / runoff) (Land use: cropland), other natural causes (avalanches, volcanic eruptions, mud flows, highly susceptible natural resources, extreme topography, etc.) specify (From gentle to hilly slope)
Secondary causes of degradation: Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts) (Especially during wet seasons: March-June and October-November)
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 防止土地退化
- 减少土地退化
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
4.2 技术规范/技术图纸说明
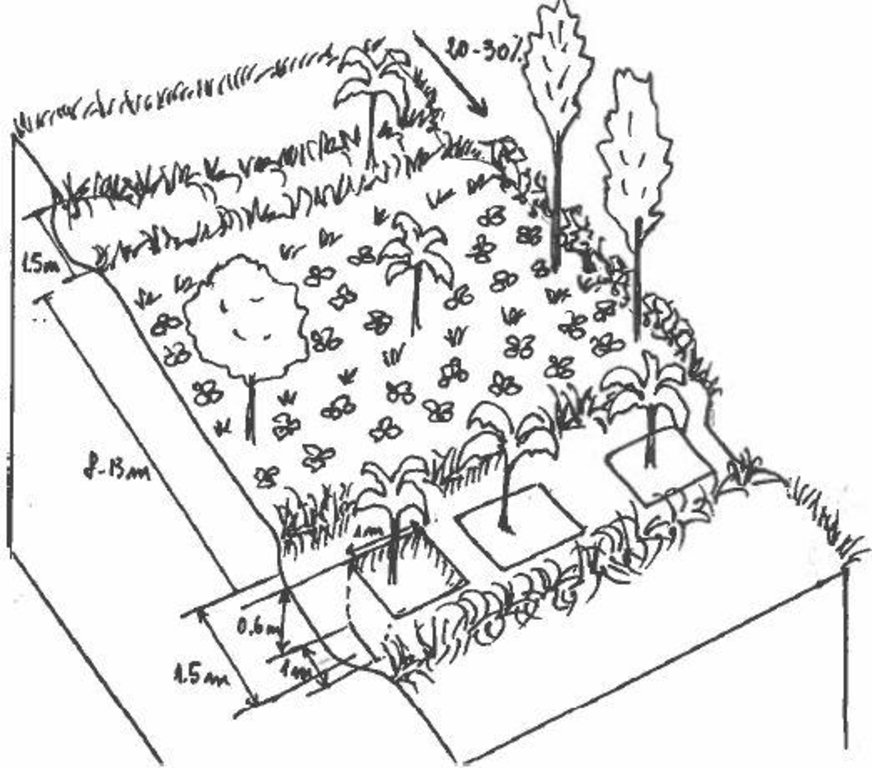
Detailed overview of the Agroforestry system in a bench terrace with infiltration (retention) and cut off (drainage) ditches. Along them, strips of Napier grass on both sides.
Location: Upper Saba saba river. Kagurumo in Muthithi location
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, reduction of slope angle, reduction of slope length, improvement of ground cover, increase in organic matter, increase of infiltration, increase / maintain water stored in soil, water harvesting / increase water supply, sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting
Secondary technical functions: improvement of topsoil structure (compaction), stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides), increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), improvement of water quality, buffering / filtering water, increase of biomass (quantity)
Mulching
Material/ species: Organic residues around Banana trees
Quantity/ density: undefined
Legume inter-planting
Quantity/ density: 3bags270kg
Manure / compost / residues
Material/ species: Manure from two cows
Quantity/ density: 8 tonnes
Remarks: for 1 year
Aligned: -graded strips
Vegetative material: G : grass
Number of plants per (ha): 400 grass per2lines strip
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): few cm
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 1
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.4
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.6-1
Scattered / dispersed
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs, F : fruit trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): about 80
Trees/ shrubs species: Grevillea, Coffee
Fruit trees / shrubs species: Persea americana, Musa sapientum, Mangifera indica, Macadamia tetraphylla
Grass species: Pennisetum pyramidalis (Napier grass or elephant grass)
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 20-25%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is (see figure below): 15%
Gradient along the rows / strips: 5-8%
Diversion ditch/ drainage
Vertical interval between structures (m): 1
Spacing between structures (m): 8-13
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.6-1
Retention/infiltration ditch/pit, sediment/sand trap
Vertical interval between structures (m): 1
Spacing between structures (m): 8-13
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.6-1
Terrace: forward sloping
Vertical interval between structures (m): 1
Spacing between structures (m): 12-15
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 5-8 (moderate) (Fig.4-7Annex3)%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is: 5%
Lateral gradient along the structure: 25-30%
4.3 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
Kenyan Schellings
注明美元与当地货币的汇率(如相关):1美元=:
85.9
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
2.00
4.4 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Digging holes and planting Coffee seedlings (20 KSh per plant) | 植物性的 | |
| 2. | Digging holes (1 feet ×1 feet) and planting trees (seedlings)- 4 days ×5 persons at Ksh 200.e.g. the main work consist of digging small pits for bananas (300 plants) | 植物性的 | |
| 3. | Establishment of the infiltration ditches and cutoff drains (total 5). 3p.d. (200 Ksh *3) each. | 结构性的 | Each season: during dry season |
| 4. | Establishment of the retention ditches with bench terraces (tot.8): 2 p.d., 250 Ksh per day | 结构性的 | Each season: during dry season |
| 5. | Purchase cows | 农业学的 |
注释:
Life span of the cows: Several years
4.5 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Digging holes and planting seedlings | person/day | 20.0 | 2.3 | 46.0 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Infiltration ditches | person/day | 1.0 | 1277.0 | 1277.0 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Establishment of the infiltration ditches and cutoff drains (total 5) | person/day | 15.0 | 2.333 | 35.0 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | stablishment of the retention ditches with bench terraces (tot.8) | person/day | 16.0 | 2.9375 | 47.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Cow | pieces | 2.0 | 349.0 | 698.0 | |
| 植物材料 | Seedlings Mango | pieces | 10.0 | 0.2 | 2.0 | 100.0 |
| 植物材料 | Coffee seedlings | pieces | 250.0 | 0.464 | 116.0 | 100.0 |
| 植物材料 | Seedlings Avocado | pieces | 12.0 | 0.25 | 3.0 | 100.0 |
| 植物材料 | Seedlings Macadamia | pieces | 8.0 | 0.25 | 2.0 | 100.0 |
| 植物材料 | Grevillea | pieces | 50.0 | 0.12 | 6.0 | 100.0 |
| 其它 | cows | animal | 2.0 | 349.0 | 698.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 2930.0 | |||||
注释:
Duration of establishment phase: 6 month(s)
4.6 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Minimum tillage and planting maize and beans | 农业学的 | 2 times in a year |
| 2. | Harvesting maize/beans (around Feb/March and Ag/Sept) | 农业学的 | 2 times in a year |
| 3. | Feeding cows on daily basis (normally 3 times a day): 200 Ksh is the price of 1 labour to feed the cows with lunch, for 6 days | 农业学的 | daily basis |
| 4. | Preparation and application of manure | 农业学的 | 2 times in a year |
| 5. | Digging planting holes and planting grass | 植物性的 | 2 times (because they get 'old') or 1 half year, depending on the conditions |
| 6. | Maintenance of the grass (weed control and cutting Napier grass/repairing and collecting fodder) | 植物性的 | Every season (March/Sept); cutting Napier: 2times in a season |
| 7. | Clearing the tree for selling timber (the price depends also of the use of the chainsaw (or saw) or not -(considering 4 trees at the time) - with machine operator | 植物性的 | When in need of cash (not regularly), not less than 5 years after planting |
| 8. | Prepare manure and feeding cows on daily basis (normally 3 times a day): 200 Ksh is the price of 1 labour to feed the cows with lunch, for 6 days (7200 for 6 months) | 植物性的 | Every season |
| 9. | Pruning branches/roots and let them dry for firewood- (considering 4 trees at the time) 3 persons days- 200Ksh | 植物性的 | Every 3 seasons (and when shortage of firewood) |
| 10. | Mulching | 植物性的 | Twice in the year on Bananas |
| 11. | Harvesting coffee | 植物性的 | Twice in the year |
| 12. | Distribute manure on Napier grass, also in the pits | 植物性的 | 2 times |
| 13. | Repairing the ditches and remove excess of soil/leaves accumulated during the rainy season | 结构性的 | After rains (every season) |
| 14. | Rebuilt repair terraces | 结构性的 | 3 times per year |
4.7 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Minimum tillage and planting maize and beans | person/days | 15.0 | 1.5333 | 23.0 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Harvesting maize/beans | person/days | 10.0 | 1.2 | 12.0 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Feeding cows and preparing the manure on daily basis | person/days | 312.0 | 0.166666 | 52.0 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Preparation and application of manure | person/days | 2.0 | 2.5 | 5.0 | 100.0 |
| 植物材料 | Seeds Maize | kg | 10.0 | 2.3 | 23.0 | 100.0 |
| 植物材料 | Seeds Beans | kg | 5.0 | 2.0 | 10.0 | 100.0 |
| 植物材料 | Seedlings grass | per trench | 200.0 | |||
| 其它 | Labour: Digging planting holes and planting grass | person/days | 5.0 | 1.8 | 9.0 | 100.0 |
| 其它 | Labour: Maintenance of the grass (weed control and cutting Napier grass/repairing and collecting fodder) | person/days | 3.0 | 1.66666 | 5.0 | 100.0 |
| 其它 | Labour: Clearing the tree for selling timber (the price depends also of the use of the chainsaw (or saw) or not -(considering 4 trees at the time) - with machine operator | person/days | 1.0 | 8.0 | 8.0 | 100.0 |
| 其它 | Labour: Repairing the ditches and remove excess of soil/leaves accumulated during the rainy season | person/days | 2.0 | 2.5 | 5.0 | 100.0 |
| 其它 | Labour: Rebuilt repair terraces | person/days | 5.0 | 1.8 | 9.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 161.0 | |||||
注释:
Machinery/ tools: panga, fork djembe, hoes, shovel, fork djembe, panga, saw, shovels, fork djembe
The costs has been computed during the period of the field visit and include all the costs for the establishment and the maintenance of the different measures (structural, agronomic and vegetative), for 3 acre of land.
4.8 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
In the farmer's opinion, the main constrains are the costs carried out to maintain the structural measures described. Water instead become the limiting environmental factor during dry season.
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
农业气候带
- 半湿润
Thermal climate class: subtropics. June, July and August
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 低(<1%)
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
> 50米
地表水的可用性:
中等
水质(未处理):
良好饮用水
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 中等
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
生产系统的市场定位:
- 生计(自给)
- 混合(生计/商业
非农收入:
- > 收入的50%
相对财富水平:
- 平均水平
个人或集体:
- 个人/家庭
机械化水平:
- 手工作业
性别:
- 女人
- 男人
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2% - 3%
Off-farm income specification: The farmer is rich because he owns 3 acre of land and livestock, assets (electricity) which are above the average standards of the community. No family food insecure issues during all year, and he was a teacher.
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者拥有或租用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 小规模的
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 个人,未命名
土地使用权:
- 个人
用水权:
- 自由进入(无组织)
注释:
Water use rights depend on the use: open access for drinking and domestic uses.
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
饲料生产
木材生产
收入和成本
农业投入费用
农业收入
社会文化影响
食品安全/自给自足
社会经济弱势群体的情况
生态影响
水循环/径流
地表径流
蒸发
土壤
土壤水分
土壤覆盖层
土壤流失
生物多样性:植被、动物
生物量/地上C
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
水资源可用性
下游淤积
缓冲/过滤能力
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 气候变化/极端天气的类型 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年温度 | 增加 | 未知 |
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气象灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 局地暴雨 | 好 |
| 局地风暴 | 好 |
气候灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 干旱 | 不好 |
水文灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 比较和缓的(河道)洪水 | 好 |
其他气候相关的后果
其他气候相关的后果
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 缩短生长期 | 未知 |
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
轻度消极
长期回报:
稍微积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
稍微积极
长期回报:
积极
6.5 技术采用
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发地采用该技术,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 0-10%
注释:
1% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
Agroforestry (dispersed trees on cropland) and intercropping: The technology is simple to adopt and provides a sustainable land management with a diversified source of income/ food supply. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Implementation could focus on the increase of species: Jaetzold et al. (1982) underlines the positive impacts of the use of biomass from Mucuna, Crotalaria, Tithonia, Calliandra and Leucanean hedges/trees for soil fertility improvements, increasing grain yields. Crop rotation and leaving crop residues on the ground could further help increasing the production. |
|
Napier grass has been used for different purposes: e.g. ditch stabilization, fodder production. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Other herbaceous vegetation could also be planted: e.g. Tithonia diversifolia (Mexican sunflower),an excellent green manure and medicinal plant. |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| The amount of work required to carry out all the activities is too much. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| The technologies in place require regular maintenance especially during rainy seasons. |
7. 参考和链接
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Jaetzold R., and Schmidt H., 1983. Farm Management Handbook of Kenya. Natural Conditions and Farm Management Information. Vol. 2.Part B: Central Kenya.
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
http://www2.gtz.de/dokumente/bib/07-1284.pdf
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Jaetzold R., Schmidt H., Hornetz B., Shisanya C., 1982. Farm Management Handbook of Kenya. Natural Conditions and Farm Management Information. West Kenya, Subpart A2. Nyanza Province.
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
http://www2.gtz.de/dokumente/bib/07-1284.pdf
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Liniger HP (1991). Water conservation for rainfall farming in the semi-arid Footzones northwest of Mt. Kenya (Laikipia highlands). Consequence on the water balance and the soil productivity. Laikipia/Mt. Kenya PaperD-3, Nairobi, Kenya & Bern, Switzerland.
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Ouma J. O., Murithi F. M., Mwangi W., Verguijl H., Gethi M., De Groote H., 2002. Adoption of maize seed and fertilizer technologies in Embu District, Kenya. KARI, CYMMIT.
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Otengi S. B. B., Stigter C. J., Ng'anga J. K. N. H. Liniger H. P., 2007. Soil moisture and its consequences under different management in a six year old hedged agroforestry demonstration plot in semi-arid Kenya, for two successive contrasting seasons. African Journal of Agricultural Research Vol. 2(3), pp. 089-104.
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Storey P. J., 2002. The conservation and improvement of sloping land. Volume 1: Practical understanding. Chapter 5: Improving the soil management.
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块