Non-inversion shallow tillage on sandy soils in the Netherlands [荷兰]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: wijnand sukkel
- 编辑者: Marie Wesselink
- 审查者: Ursula Gaemperli, Gudrun Schwilch
Niet kerende, ondiepe grondbewerking op zandgronden in Nederland
technologies_2958 - 荷兰
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
Interactive Soil Quality assessment in Europe and China for Agricultural productivity and Environmental Resilience (EU-iSQAPER)有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Stichting Dienst Landbouwkundig Onderzoek, Wageningen University & Research Centre (DLO) - 荷兰1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
19/07/2017
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.4 所述技术的可持续性声明
这里所描述的技术在土地退化方面是否存在问题,导致无法被认为是一种可持续的土地管理技术?:
否
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
This technique can be applied in any crop rotation or soil. Tillage of the soils is done with special machines that do not turn over the soil (non-inversion), and the tillage depth can be more shallow than with conventional tillage (ploughing).
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
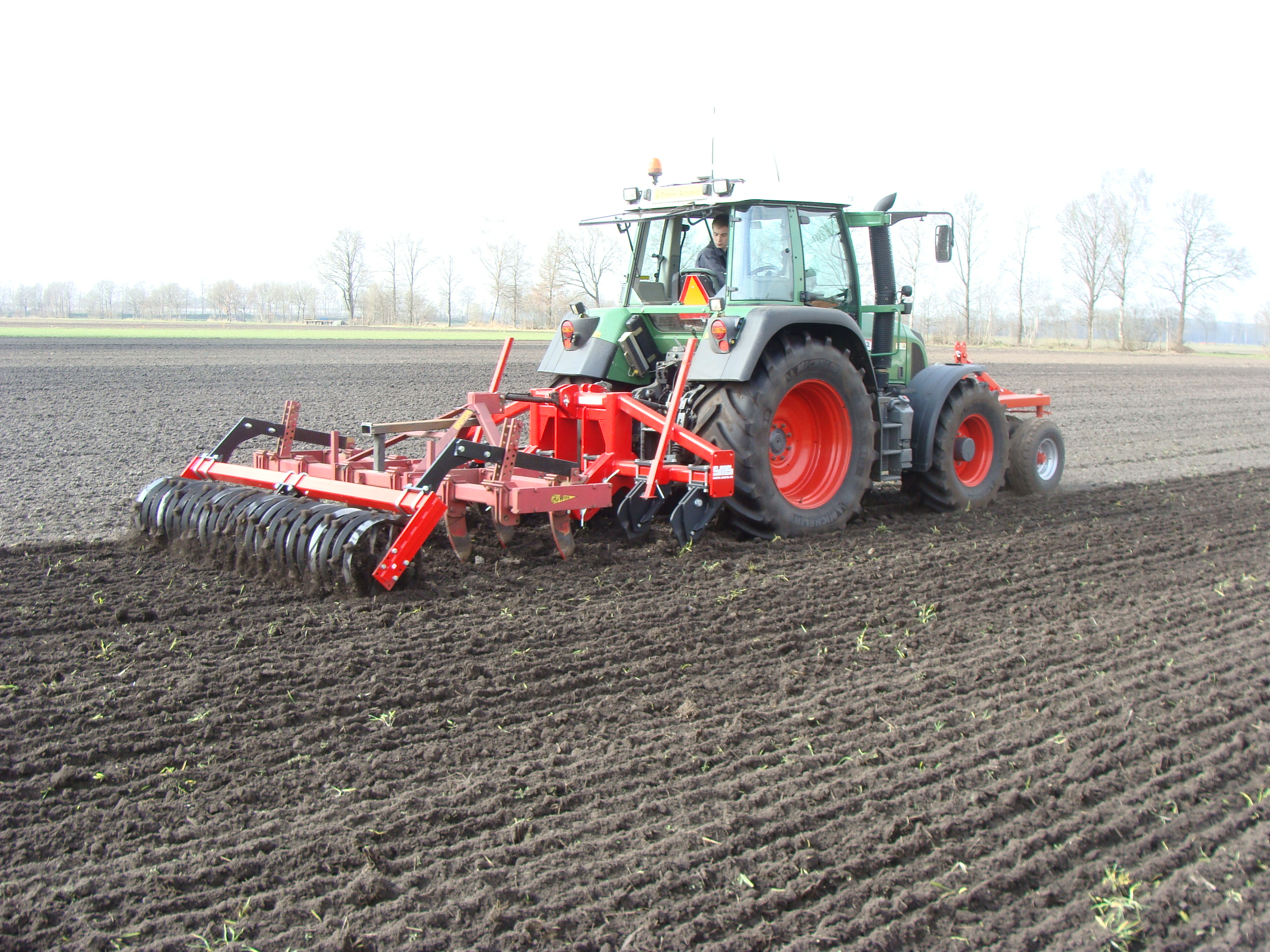
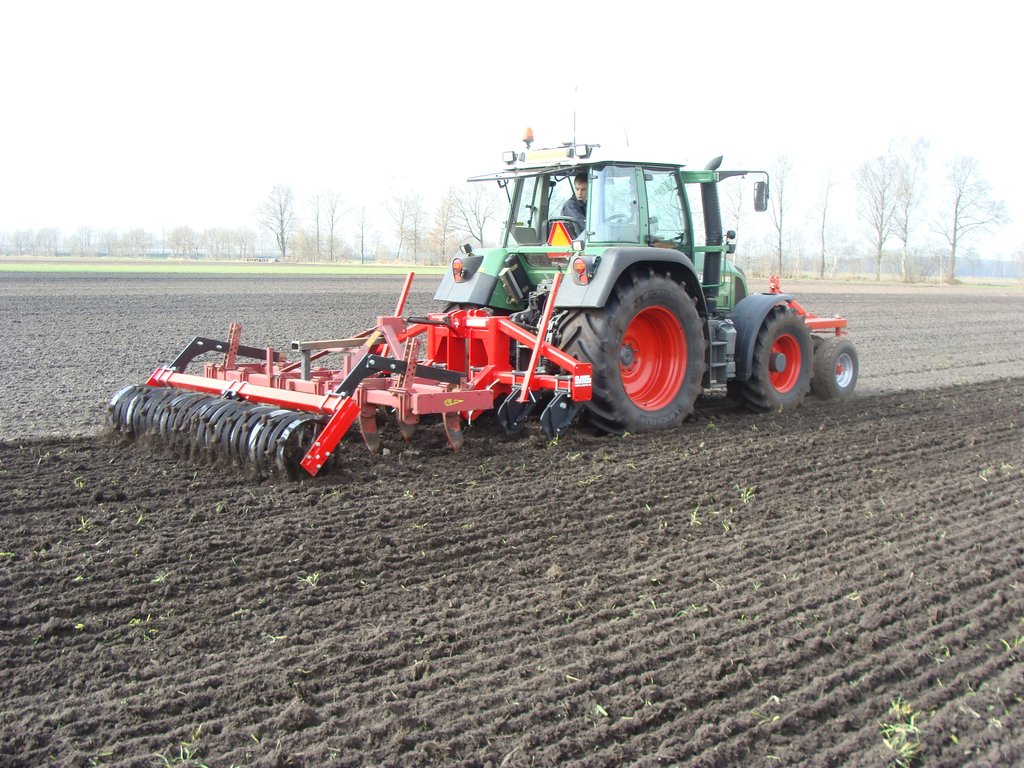
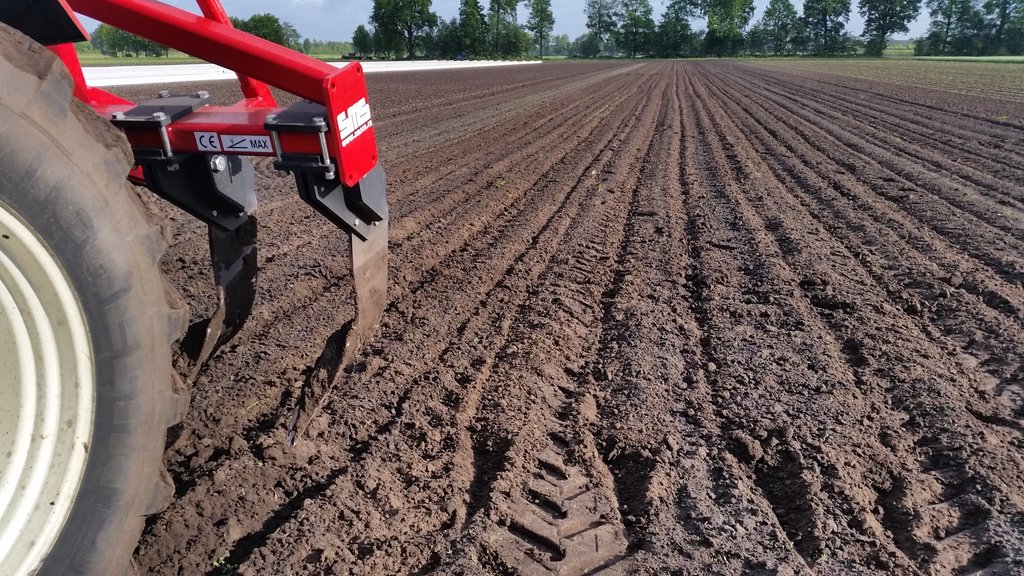
This technology is applied in Vredepeel (the Netherlands) on a sandy soil on arable fields. The technology is not by environment limited to these conditions, it could for example be applied on clay soils as well. It is applicable for various crop types. The main point of this technology is the specific machine that is used to do the tillage. The machine is called a rigid-tine cultivator. The machine can be purchased for a few thousand Euros, but in the Netherlands it is also possible to let a contractor do this tillage. The average tillage depth here is around 25 cm, dependent on the crops in the rotation. The purpose of the shallow non-inversion tillage is to keep the soil organic matter in the topsoil, and to disturb the soil as little as possible, which has as benefit that the organic matter levels in the topsoil can increase and soil life is maintained better. Overall, the soil structure in the topsoil will improve. This is also what the land users like about using the non-inversion tillage. The yields when using non-inversion tillage are similar to the yields of ploughed fields. The difficulty of this technology is the control of weeds, since the topsoil is not turned over, small weeds and seeds are not buried, and have a higher change to survive. This may make that more pesticide is used to control the weeds than when you plough the soil, therefore this tillage technique is less favorable amongst organic farmers. Also when grasses are a (large) part of the crop rotation non-inversion tillage might not be the best solution, since it is harder to destroy the grass when preparing the soil for the next crop.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
荷兰
区域/州/省:
de Peel
有关地点的进一步说明:
Vredepeel
Map
×2.6 实施日期
注明实施年份:
2012
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 在实验/研究期间
注释(项目类型等):
Research results over the last years have shown that ploughing might not always be the perfect solution as tillage technique. By experimenting it is now found that non-inversion tillage might as well do the job, and even improve soil quality on certain points.
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
- 保持/提高生物多样性
- 适应气候变化/极端天气及其影响
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

农田
- 一年一作
主要农作物(经济作物及粮食作物):
leek, silage maize, processing pea, carrot, spring barley, sugarbeet, potatoe
3.3 有关土地利用的更多信息
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 混合雨水灌溉
每年的生长季节数:
- 1
3.4 该技术所属的SLM组
- 最小的土壤扰动
3.5 技术传播
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果该技术均匀地分布在一个区域上,请注明覆盖的大致区域。:
- 100-1,000 平方千米
注释:
About a quarter of the landowners in the region uses this technique
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

农艺措施
- A3:土壤表面处理
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤风蚀
- Et:表土流失

化学性土壤退化
- Cn:肥力下降和有机质含量下降(非侵蚀所致)

物理性土壤退化
- Pc:压实

生物性退化
- Bl:土壤寿命损失
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 防止土地退化
- 减少土地退化
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
4.2 技术规范/技术图纸说明
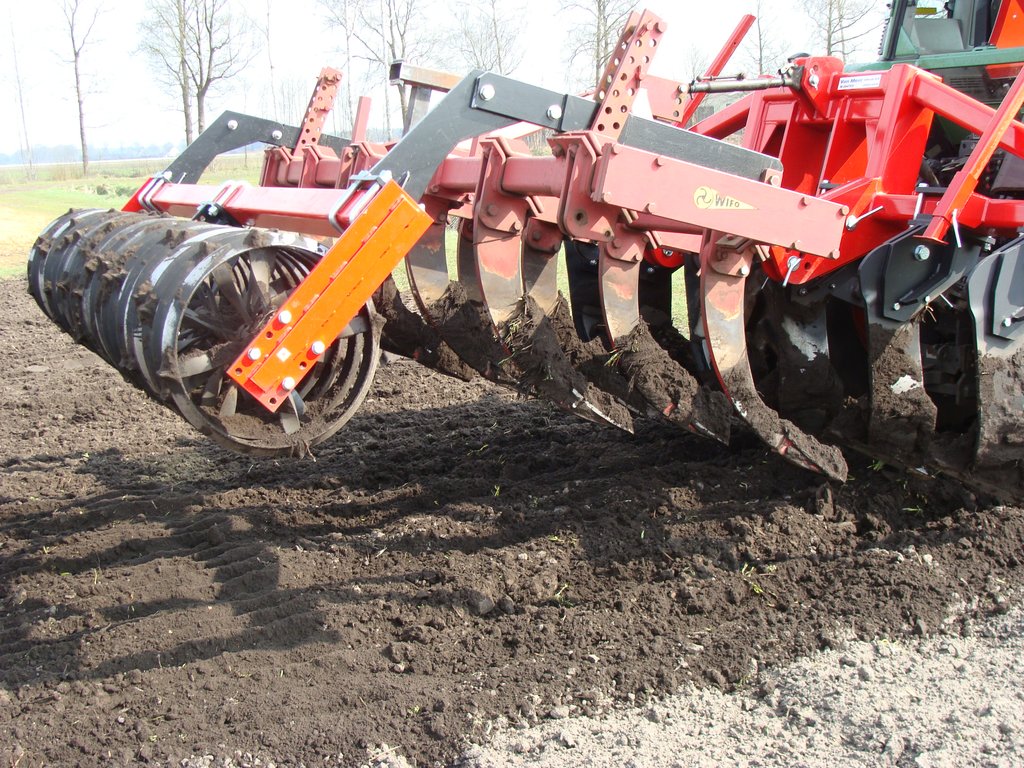
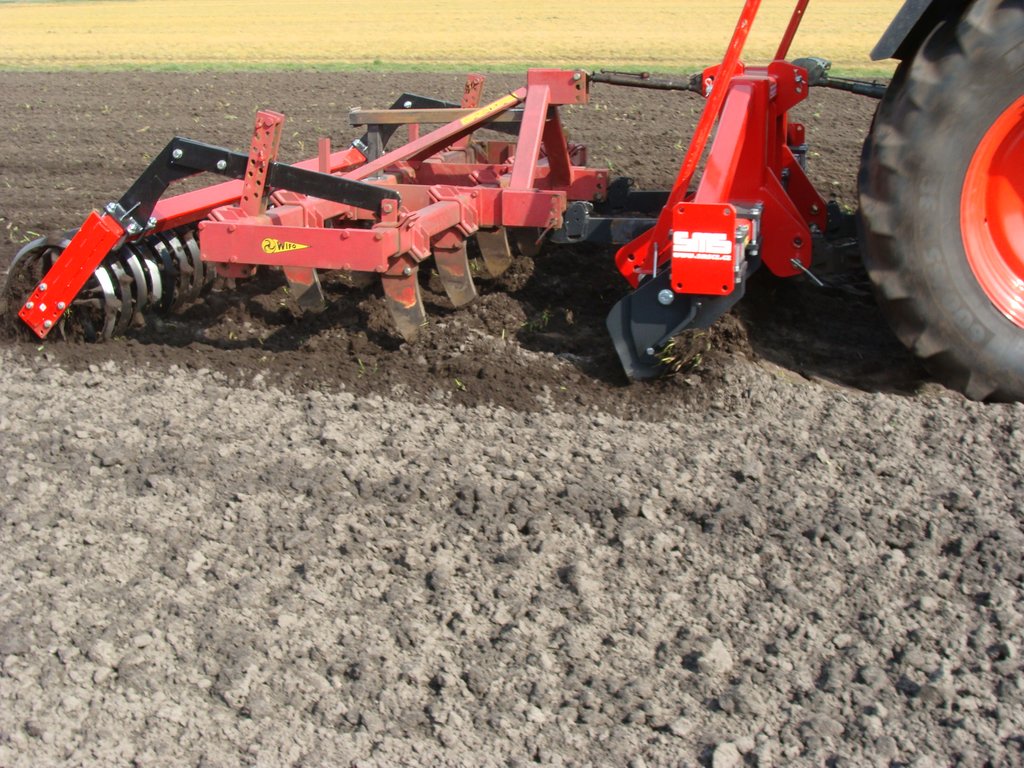
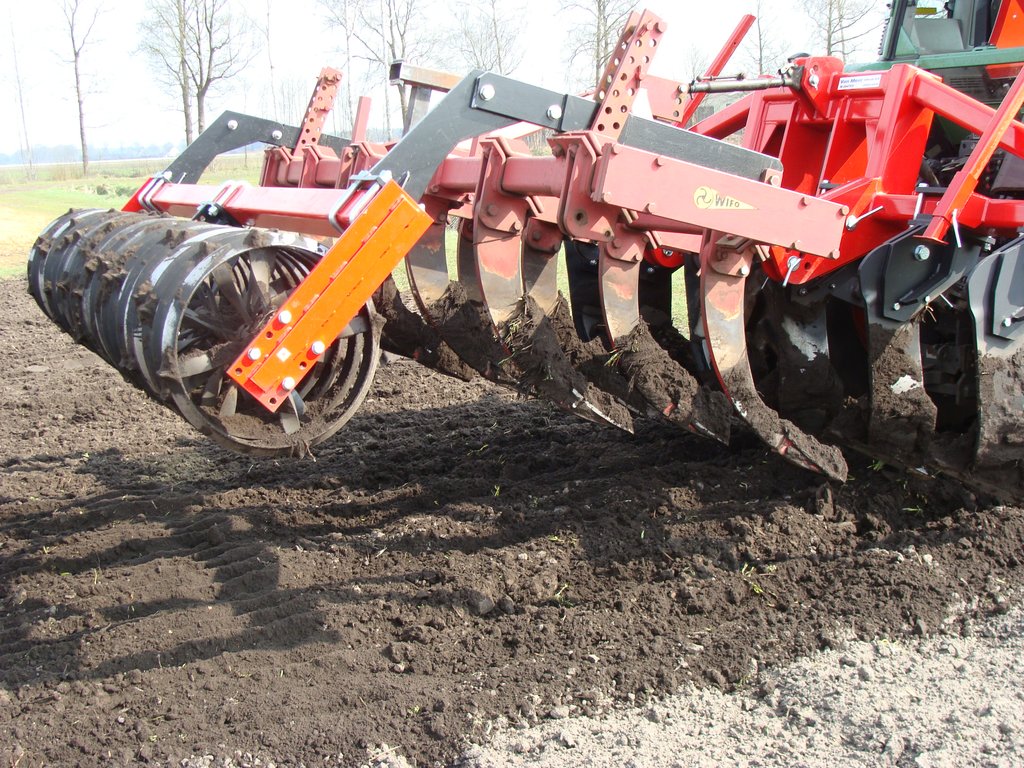
The pictures show the machine at work, and what the soil looks like once the soil has been worked.
The machine type is SMS HKK 300, with 6 pins that work in the soil. Dependent on the type of crop the soil is worked about 25 cm deep.
4.3 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
具体说明成本和投入是如何计算的:
- 每个技术区域
注明尺寸和面积单位:
hectare
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
Euro
注明美元与当地货币的汇率(如相关):1美元=:
0.87
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
160 euro
4.4 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | adapt tillage mechanisation | 农业学的 |
4.5 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 设备 | adapted tillage machine | piece | 1.0 | 2000.0 | 2000.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 2000.0 | |||||
4.6 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | destruction of cover crops after winter | 农业学的 | once per year |
| 2. | one additional tillage operation instead of ploughing | 农业学的 | once per year |
注释:
the described operations are the changes compared to conventional tillage which is ploughing
4.7 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
注释:
There are no additional costs for inputs compared to conventional tillage (ploughing in spring). There might be a minor reduction of fuel costs because the ploughing of a field takes more fuel, but on the other hand it is sometimes needed to cultivate the land an extra time, because you cannot destroy the winter crop/green manure at once. So in the end it will be around the same.
4.8 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
The investment costs for adapted machinery are the main factors affecting costs.
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
指定年平均降雨量(若已知),单位为mm:
850.00
注明所考虑的参考气象站名称:
volkel the Netherlands
农业气候带
- 半湿润
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
说明该技术是否专门应用于:
- 不相关
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 粗粒/轻(砂质)
土壤质地(地表以下> 20厘米):
- 粗粒/轻(砂质)
表土有机质:
- 高(>3%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
antroposol/gleyic podsol; sand to sandy loam with an organic matter content of approx 4%.
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
< 5米
地表水的可用性:
好
水质(未处理):
仅供农业使用(灌溉)
水的盐度有问题吗?:
否
该区域正在发生洪水吗?:
否
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 中等
栖息地多样性:
- 中等
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
定栖或游牧:
- 定栖的
生产系统的市场定位:
- 商业/市场
非农收入:
- 低于全部收入的10%
相对财富水平:
- 丰富
个人或集体:
- 个人/家庭
机械化水平:
- 机械化/电动
性别:
- 男人
土地使用者的年龄:
- 中年人
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者拥有或租用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 中等规模的
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 公司
土地使用权:
- 个人
用水权:
- 社区(有组织)
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
注释/具体说明:
The fields with non-inversion tillage and conventional ploughing are right next to each other, and with the same crops, no effects on crop production were found.
作物质量
注释/具体说明:
The fields with non-inversion tillage and conventional ploughing are right next to each other, and with the same crops, no effects on crop quality were found.
收入和成本
农业投入费用
注释/具体说明:
More shallow tillage needs less power from the machines, but on the other hand more tillage operations to destroy the crop .
生态影响
水循环/径流
地表径流
注释/具体说明:
Since the soil structure will improve, the infiltration capacity of the soil also improves.
土壤
土壤有机物/地下C
注释/具体说明:
Expectations are that soil organic matter content in the (top) soil will increase, but so far no significant results were found on that.
生物多样性:植被、动物
有益物种
注释/具体说明:
In general soil biodiversity increased, mainly fungal biomass and bacterial biomass.
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
有关影响评估的意见:
The technology is running too short still to measure impacts
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气象灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 局地暴雨 | 好 |
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
轻度消极
长期回报:
中性/平衡
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
中性/平衡
长期回报:
中性/平衡
6.5 技术采用
- 单例/实验
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发地采用该技术,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 90-100%
6.6 适应
最近是否对该技术进行了修改以适应不断变化的条件?:
否
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| The technology has been used for 5 years now. Yield were expected to decrease but did not. |
| There is a minor advantage in fuel costs, however this is compensated with additional labour needed. |
| Carbon stratification (higher content in the topsoil (0-15 cm)) was expected to change but did only minorly. |
| Water infiltration and topsoil protection is still expected to improve. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Higher soil biodiversity |
| On the long term increased carbon sequestration |
| Better top soil protection against acces of rainfall, improved infiltration and water holding capacity. Improved drought resistance |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| The change in tillage is effecting various other agronomic activities which need to be adapted. | building up of experience |
| There is a higher weed pressure | improved mechanical/chemical weed control. Maybe the weed pressure will stabilize the coming years |
| Problems with destroying cover crops | development of new techniques to destroy the cover crop |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| It takes a long period until effects are measurable, this makes it hard to convince farmers. | longt term monitoring |
| Very little practical experience with non inversion tillage in the Netherlands | communication and exchange experiences |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
- 实地考察、实地调查
On our experimental farm we have fields with non-inversion tillage, all the research data gathered there gives more information on this technology.
- 与土地使用者的访谈
the landowner, involved researcher and some of the landworkers were consulted.
- 根据报告和其他现有文档进行编译
As said, from our research farm much data is gathered, and reports/documentations are available
7.3 链接到网络上可用的相关信息
标题/说明:
website Beter Bodembeheer
URL:
www.beterbodembeheer.nl
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块