Lolldaiga Hills Ranch: Rotational Grazing and Boma-Based Land Reclamation [肯尼亚]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Michael Herger
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Rima Mekdaschi Studer
technologies_2982 - 肯尼亚
- Lolldaiga Hills Ranch: Rotational Grazing and Boma-Based Land Reclamation : Sept. 3, 2018 (inactive)
- Lolldaiga Hills Ranch: Rotational Grazing and Boma-Based Land Reclamation: Sept. 4, 2019 (inactive)
- Lolldaiga Hills Ranch: Rotational Grazing and Boma-Based Land Reclamation: Nov. 2, 2021 (public)
- Lolldaiga Hills Ranch: Rotational Grazing and Boma-Based Land Reclamation : Feb. 22, 2018 (inactive)
- Lolldaiga Hills Ranch: Rotational Grazing and Boma-Based Land Reclamation : Feb. 1, 2018 (inactive)
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
关键资源人
土地使用者:
Tomlinson Lance
+254 (0) 72 288 78 82
office@lolldaiga.com
Lolldaiga Hills Ltd.
Lolldaiga Hills, Mukgodo District, Laikipia, Kenya P.O. Box 26, Nanyuki – 10400, Kenya
肯尼亚
1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
22/01/2017
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.4 所述技术的可持续性声明
这里所描述的技术在土地退化方面是否存在问题,导致无法被认为是一种可持续的土地管理技术?:
否
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
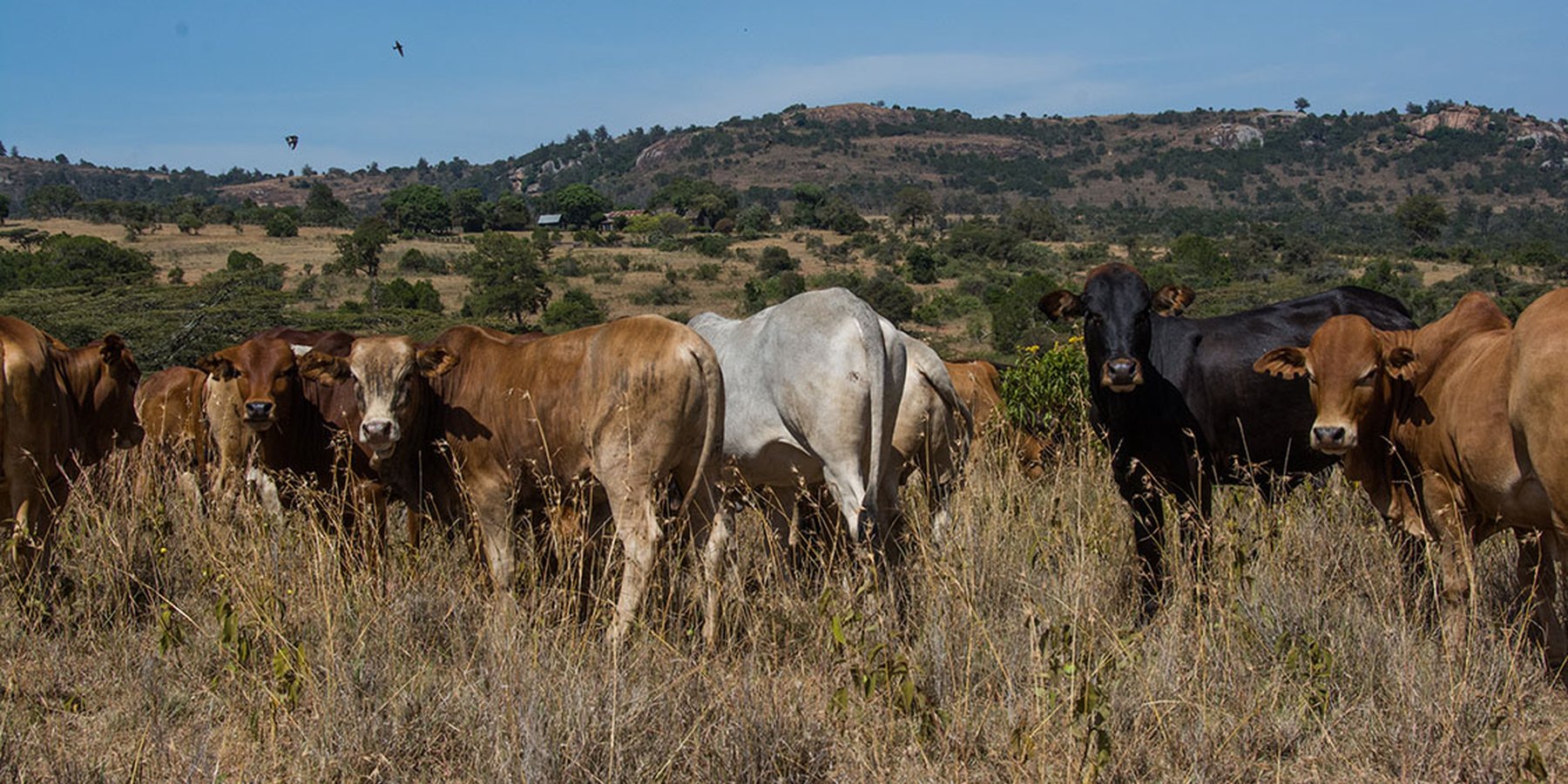
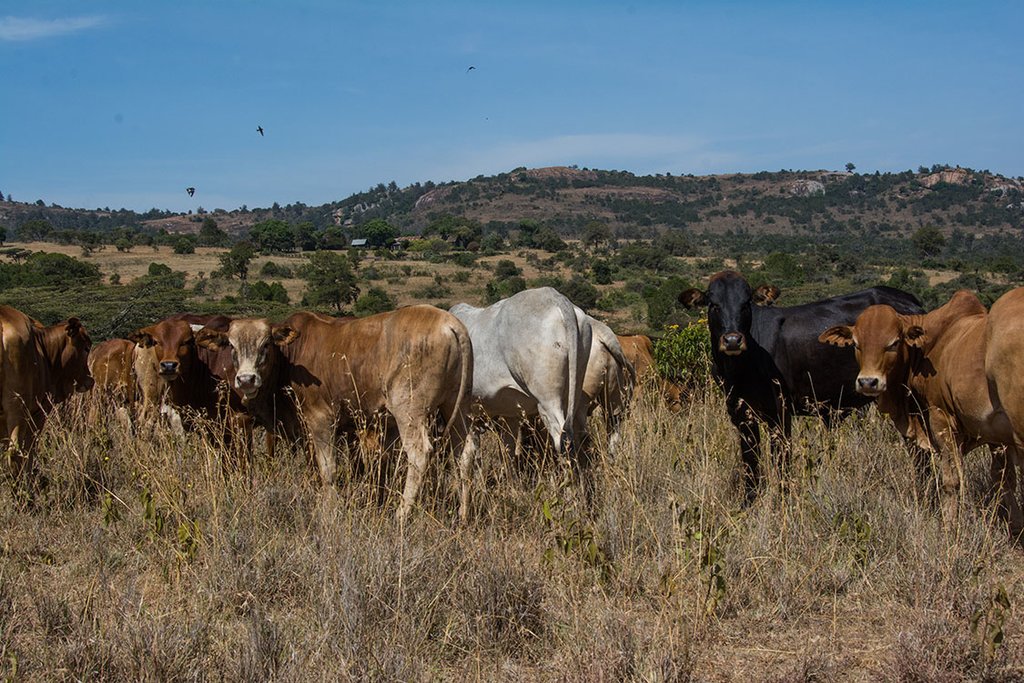
Lolldaiga Hills ranch is a private ranch and conservancy with livestock production and tourism. Rotational grazing is used to manage livestock on semi-arid lands with limited water resources. Bare land is recovered by a "Boma” technology – strategic corralling of animals overnight on degraded land.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
Livestock production on Lolldaiga Hills ranch is managed under an extensive grazing system for dairy, beef, sheep and camel production, with strategic fattening and selling, in harmony with conservation principles. The conservancy is dedicated to the sustainable conservation of critical habitat and wildlife. The ranch serves also as a training ground for the British Army.
Grazing is managed without fixed blocks. Grazing areas vary considerably, depending on rainfall and location within the farm. Similarly, grazing duration in one area also varies significantly (from two weeks to eight months). Starting after the long rains (April to May), livestock are moved gradually from north to south: movement only occurs when areas are completely grazed. They stay for about four months in the north and eight months in the south - due to better grass in the southern part. Some of the dry season grazing is land set aside for later use. They use, for instance, highland forests in the west where zebra and other livestock are largely absent. During the rains, grazing takes place on a much smaller area than during the dry season, where water can be a major challenge. Livestock are kept together, though steers/heifers/breeding cows/resting bulls are separated into different herds of 90-150 units per herd. But these are not tightly “bunched” as in other ranches in the area which apply “Holistic Management” principles, since bunching is not appropriate due to strong wind erosion. The closer livestock are aggregated, the more damage – that is dust generated - in dry areas. As is typical of private ranches in Laikipia, Lolldaiga supports some of the highest densities of wildlife in Kenya. The wild herbivore biomass density on private ranches is estimated by Georgiadis (2007) at 14 ha /TLU.
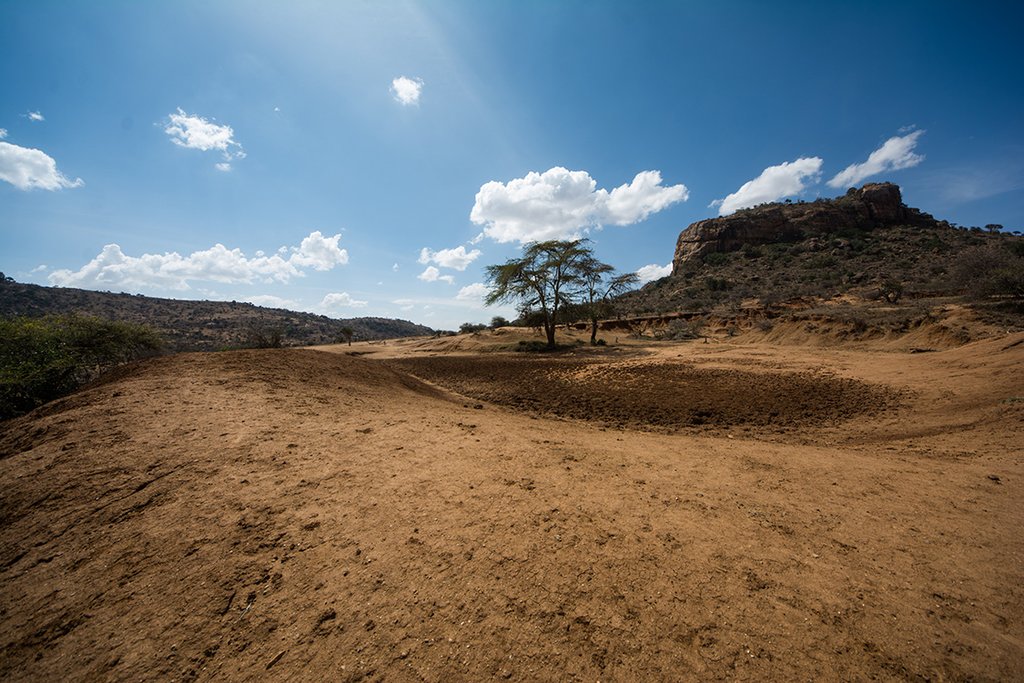
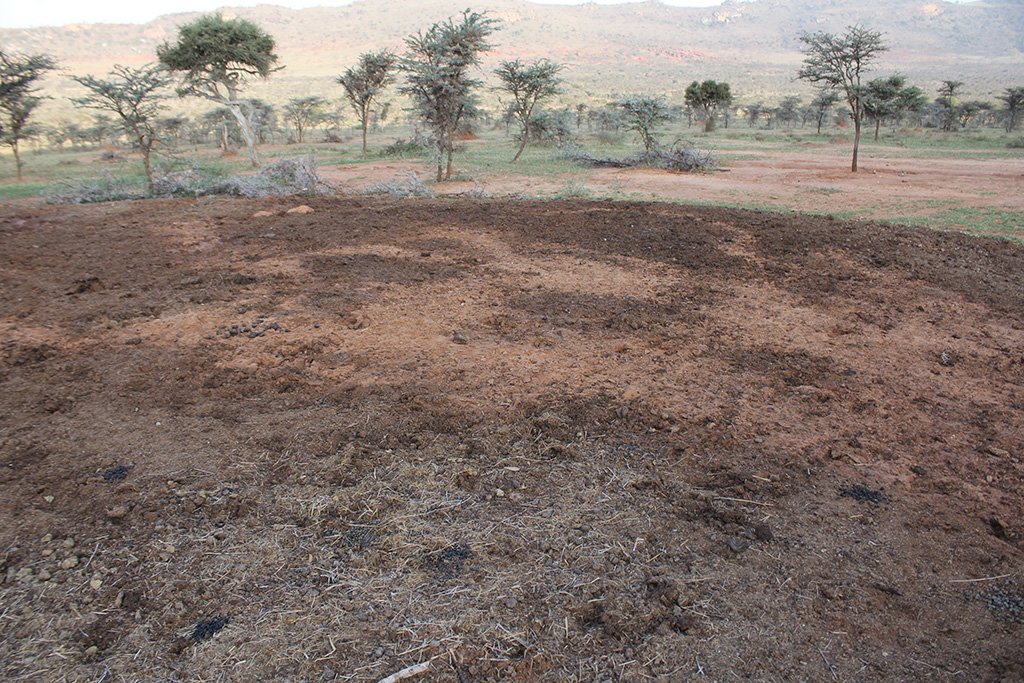
Whilst the livestock is moving, large bomas (corrals in Kiswahili) are constructed for the herds. Here, animals are closely together kept in protective enclosures overnight. Bomas are strategically sited on bare areas to recover the land through dung accumulation and breaking soil crusts by hooves. Currently, there are 20 bomas covering an area of 0.02 km2 (0.01% of their land). This can be taken to represent the area that can be restored each year. Boma sites are steadily but slightly shifted. On average, one boma is located on the same denuded patch for only one to two weeks during the dry season, and again for one week during the wet season.
In a single boma of 0.1 ha, 400 cows are corralled. Former bare patches with bomas have recovered well after just a few years. Results of a boma site comparison (see Herger 2018) have shown how bomas turn into ecological hotspots with a long-lasting effect. Amounts of soil organic carbon (SOC), as well as macro- and micronutrients in topsoil (especially) and subsoil of former boma sites were much higher than reference sites close-by. The chronology of former boma sites (1, 5, 9 years ago) also played a decisive role in soil parameters. Former boma sites from 5 and 9 years ago performed better than the most recent boma (1 year ago).
On the ranch, due to lack of rains, fodder supplements had to be purchased in 2016. However, it is usually water and not grazing that is the limiting factor on the rangeland.
Whereas cattle are sold to the leading meat producer "Farmer's Choice" (80% for domestic distribution, 20% for export to neighbouring countries and the Middle East), sheep are sold to East African Seafood (Nairobi) and camels to Somalis in town and local butcheries.
Lolldaiga also assists community grazing. The ranch helps neighbouring group ranches by allowing them access to their land for fattening purposes, but mostly as a grass bank during droughts (sometimes charging a small fee, sometimes none). During dry spells, they host on average 500-1000 livestock units from other communities. Along their fence informal (strictly "illegal") grazing of goats and sheep is tolerated.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
肯尼亚
区域/州/省:
Laikipia
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 10-50年前
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过土地使用者的创新
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 改良生产
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
- 保护生态系统
- 保持/提高生物多样性
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

牧场
粗放式放牧场:
- 经营牧场
主要动物种类及产品:
Livestock: Cattle, sheep, camels; Milk, wool, beef, camel meat, and lamb/ mutton. High-quality segment. Domestic (80%, Nairobi and hotels), international distribution (20%, neighbouring countries and the Middle East) Livestock: 3,920 TLU; Stocking rate: 5.1 ha/TLU Pressure on land including wildlife numbers (estimated by Georgiadis 2007): 3.7 ha/TLU Livestock numbers: 5,200 cattle, 1,800 sheep, 140 camels Sales: Cattle 20% sales, Sheep 15%, Camels 10%. Additional 1,000-2,000 livestock units from neighbouring community farms during droughts. Goats and sheep illegally grazing along the fence are tolerated. Wildlife: Giraffe, antelope/gazelle (e.g. gerenuk, impala, Thomson's gazelle), baboons, zebra, dikdik, hares, elephant and others. More wildlife than on group ranches. Wildlife herbivore biomass density (Georgiadis 2007) 14 ha/TLU

定居点、基础设施
- 定居点、建筑物
注释:
Few facilities for tourism.
Few farm houses.
3.3 有关土地利用的更多信息
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
每年的生长季节数:
- 2
具体说明:
Short rains in November and December. Long rains in April and May. Rains from (October) November to December are usually better in this area. Rainfalls with strong local variations and changing regimes.
牲畜密度(如相关):
Livestock: 3'920 TLU; Stocking rate: 5.1 ha/TLU, Pressure on land including wildlife numbers (estimated by Georgiadis 2007): 3.7 ha/TLU
3.4 该技术所属的SLM组
- 畜牧业和牧场管理
- 改良的地面/植被覆盖
3.5 技术传播
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果该技术均匀地分布在一个区域上,请注明覆盖的大致区域。:
- 100-1,000 平方千米
注释:
Lolldaiga has an area size of 200 km2. Similar technologies are also applied on other ranches (see the documentations for "Il Ngwesi", "Makurian", and "Borana")
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

管理措施
- M2:改变管理/强度级别
- M4:活动时间安排的重大变化
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀
- Wg:冲沟侵蚀/沟蚀

土壤风蚀
- Et:表土流失

物理性土壤退化
- Pc:压实
- Pk:熟化和结壳
- Pi:覆土

生物性退化
- Bc:植被覆盖的减少
- Bh:栖息地丧失
- Bq:数量/生物量减少
- Bs:质量和物种组成/多样性的下降
- Bl:土壤寿命损失
注释:
Across the grasslands and rangelands, an increase in bare land and bush has been a clear trend all over Laikipia for many years, both on community-owned lands and private ranches. Major identified ecological problems (partly) caused by livestock production are: bare ground, low contents of soil organic carbon and plant-available nutrients, soil erosion (sealing, crusting, rills and gullies, water flow patterns, sheet erosion, pedestals), poor soil properties, undesirable species, and (increasing) woody and invasive species. The current major problem on rangelands is the invasive species Opuntia stricta, which however only could spread that widely because of degraded land in the first place. The technology aims at improving vegetation cover of the land and thereby reducing further degradation and restoring degraded land. However, Lolldaiga is clearly not as much affected by degradation (compare Herger 2018).
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 减少土地退化
- 修复/恢复严重退化的土地
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
4.3 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
具体说明成本和投入是如何计算的:
- 每个技术单元
指定单位:
Only livestock production related: Herders, animals treatment
具体说明成本计算所用货币:
- 美元
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
4.5
4.6 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Herders, supervisors, watchmen etc | 管理 | |
| 2. | Animal treatments (vaccination, spraying, injections) | 农业学的 |
4.7 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Herders/employees | Person*days | 36000.0 | 4.5 | 162000.0 | |
| 其它 | Animals treatments | Per TLU | 3920.0 | 11.0 | 43120.0 | |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 205120.0 | |||||
注释:
Animal treatment costs are estimated according to other ranches in the area since figures for Lolldaiga are missing. Figures are not reconfirmed data.
4.8 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
Labor
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
指定年平均降雨量(若已知),单位为mm:
380.00
有关降雨的规范/注释:
Rainfall gauge Lolldaiga Northern gauge average from 2013-2016. Strong local (and temporal) variation, changing rainfall regimes.
注明所考虑的参考气象站名称:
Rainfall gauge Lolldaiga Northern Gate
农业气候带
- 半干旱
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 粗粒/轻(砂质)
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
土壤质地(地表以下> 20厘米):
- 粗粒/轻(砂质)
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 中(1-3%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
SOC 0.9-1.8 %
pH: 6.3
Clay: 9 %
Silt: 47 %
Sand: 44 %
More rangeland health data in Herger (2018)
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地表水的可用性:
中等
水质(未处理):
不良饮用水(需要处理)
水的盐度有问题吗?:
否
该区域正在发生洪水吗?:
否
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 高
栖息地多样性:
- 高
关于生物多样性的注释和进一步规范:
Grassed acacia bushland. Overall rather good vegetation coverage with some patches of bare ground. Especially in the northern part Lolldaiga is effected by the invasive species "Opuntia stricta". Dominant grasses: Pennisetum species, Eragrostis species, Cynadon species, Hyparrhenia species, Kelenger species. Dominant shrubs: Solyneum inconum, Lyceum europaeum, Barleria acuthodies, Grewia tembensis, Opuntia. Dominant trees: Acacia etbaica, Acacia drepanalobium, Acacia mellifera. Detailed list of all species (vegetation and wildlife) available (Herger 2018)
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
定栖或游牧:
- 定栖的
生产系统的市场定位:
- 商业/市场
非农收入:
- 收入的10-50%
相对财富水平:
- 非常丰富
个人或集体:
- 个人/家庭
机械化水平:
- 手工作业
性别:
- 男人
土地使用者的年龄:
- 中年人
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者拥有或租用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 大规模的
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 个人,有命名
土地使用权:
- 个人
用水权:
- 个人
注释:
Masai in the area have claimed that land leases of white settlers have expired and the land belongs to them. Government states the land belongs to the private ranchers, but the future development is unknown. There have already been conflicts and are likely to happen again. On the other hand, cooperation with group ranches has increased.
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.5 技术采用
- 单例/实验
如若可行,进行量化(住户数量和/或覆盖面积):
Similar practices, but different. Most ranches implement Holistic Management.
6.6 适应
最近是否对该技术进行了修改以适应不断变化的条件?:
否
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Ability to allow the land to recover |
| Drought resilience |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| The listed advantages from Lance Tomlinson, the land user, are shared by the compiler's view. Lolldaiga has moderate stocking rates and good management, resulting in an overall fairly good condition of the rangeland. However, there are some bare patches, invasive species, and erosion features, also because of the influence of the neighbouring group ranch “Makurian”. |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
- 实地考察、实地调查
6 field visits with included "rangeland health assessment" in different parts of Lolldaiga where I could see the condition of the land as well as several other visits of the area.
- 与土地使用者的访谈
Meetings with the grazing manager, general manager, owner of the ranch as well as with two resource people involved in the Lolldaiga Research programme.
- 与SLM专业人员/专家的访谈
Truman Young
Dan Rubenstein
Dino Martins
John Letai
Samali Letai
Peter Hetz
Dominic Maringa
Joseph Putunoi
Patrick Ekodere
- 根据报告和其他现有文档进行编译
Herger (2018)
Scientific papers, LWF reports etc.
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Herger, M.B. (2018). Environmental Impacts of Red Meat Production. MSc Thesis. University of Bern.
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
University of Bern
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Georgiadis, N.J., Olivero, I.N., Romanach, S.S. (2007). Savanna herbivore dynamics in a livestock-dominated landscape: I. Dependence on land use, rainfall, density, and time. Biology Conservation 137(3): 461-472.
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
Online
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块