Ecological production of almonds and olives using green manure [西班牙]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Joris De Vente
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Fabian Ottiger, Deborah Niggli
Agricultura ecológica de almendros y olivos (Spanish)
technologies_1019 - 西班牙
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
SLM专业人员:
SLM专业人员:
López Carratala Jorge
+34.950.281045
carratala@cebas.csic.es
Consejo Superior de Investigaciones Científicas, Estación Experimental de Zonas Áridas (EEZA-CSIC)
General Segura 1, 04001; Almeria; Spain
西班牙
SLM专业人员:
Ibáñez Torres Ascensión
+34.968 36 66 87 / +34 699 65 36 16
ascension.ibanez@carm.es
Consejería de Agricultura y Agua Murcia (CARM)
30008 Murcia, Spain
西班牙
土地使用者:
Escamez Antonio
608 862 629 / 968 43 82 50
Alhagüeces. Zarzilla de Totana; Spain
西班牙
Inspector for ecological agriculture :
López Ros Elias
616 923918
eliaslopezros@gmail.com
西班牙
Responsible technician of ALIMER agricultural cooperation:
Lopez Pedro
(+34) 619189093
pd.lopez@alimer.es
ALIMER
Alimentos del Mediterráneo, S.Coop. Cmno. Villaespesa s/n Aptdo 217 30800 Lorca (Murcia)
西班牙
Technical agronomic engineer :
Cervantes Pujante Celestino
968 42 46 21
celestino.cervantes@coato.com
COATO S.Coop
Ctra. Mazarron Km. 2- COATO 30 850 Totana. Spain
西班牙
SLM专业人员:
Martinez-Mena Maria
mmena@cebas.csic.es
CEBAS-CSIC.
Campus Universitario de Espinardo. 30100, Murcia. Spain
西班牙
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
DESIRE (EU-DES!RE)有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
EEZA-CSIC (EEZA-CSIC) - 西班牙有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Consejería de Agricultura y Agua Murcia (CARM) - 西班牙有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Alimentos del mediterráneo (ALIMER) - 西班牙有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
COATO - 西班牙有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Centro de Edafología y Biología Aplicada del Segura (CEBAC-CSIC) - 西班牙1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
04/07/2011
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.5 请参阅有关SLM方法的问卷

Regional rural development programme [西班牙]
Regional development programme to protect natural resources and stimulate rural economies.
- 编制者: Joris De Vente
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
Ecological production of almonds and olives under dryland conditions using green manure to increase soil fertility, to protect against soil erosion and to obtain a high-value product.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
Ecological agriculture is a strictly controlled production system that does not use synthetic chemical products like fertilizers, insecticides or pesticides. Also genetically modified organisms and materials are not used. Green manure or low quantities of organic fertilizers, preferably from dung (sheep, goat, cow, chicken), are used to increase and maintain soil fertility. Green manure is provided by seeding a mixture of leguminous nitrogen-fixing species and cereals in autumn (October) and incorporating this into the soil with tillage in springtime (May). To optimize the fertilizer effect, there is still scientific discussion on the need for mowing the green manure and letting it dry for several days before it is ploughed into the soil. For this system, no ploughing is performed in winter, which reduces fuel use and emission of greenhouse gases. In addition to its fertilising effect, green manure provides a continuous surface cover during winter time protecting the soil from erosion. The products grown under this ecological system command a higher market price than those grown under conventional production schemes.
Purpose of the Technology: The aim of ecological agriculture is to protect biodiversity and the environment and maintain or improve soil fertility and reduce soil, water, and air pollution. Under ecological agriculture and by using green manure, soil cover, soil organic matter, and soil biological activity will increase, which positively affects soil structure, soil fertility and soil water infiltration capacity. This reduces the sensitivity of the soil to surface crusting and it reduces surface runoff and soil erosion by up to 60%. Workload and energy use are up to 50% lower than under conventional agriculture, and benefits may increase around 40% due to higher yields. Moreover, a higher market price of ecologically produced almonds and olives will lead to increased farm income. This better economic return discourages land abandonment of marginal lands with low productivities under conventional farming. Ecological almonds and olives production does not require special establishment activities or investments in specialized equipment.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Infestations by, for example, insects and caterpillars are treated twice yearly by degradable products based on copper salts (Oxicloruro, max 3‰ solution) and mineral oils in winter, or the spores and proteins produced by the bacteria Bacillus thuringiensis or based on natural pyrethrins (from the Chrysanthemum cinerariaefolium; max 1.5 l/ha) in springtime. In ecological agriculture, farmers are obliged to take advice and instructions regarding plague control and fertilizer use from technicians specialized in ecological agriculture.
Natural / human environment: Soils mostly have a shallow to medium depth (between 20-60 cm), and slopes are gentle to moderate (between 5 and 15%). The climate is semi-arid with a mean annual rainfall around 300 mm. Droughts, in summer, commonly last for more than 4-5 months. Annual potential evapotranspiration rates larger than 1000 mm are common. The production system is highly mechanised and market-oriented but depends strongly on agricultural subsidies. All cropland is privately owned.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
西班牙
区域/州/省:
Murcia
有关地点的进一步说明:
Guadalentin catchment
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 不到10年前(最近)
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过项目/外部干预
注释(项目类型等):
Ecological agriculture is strongly stimulated by regional government through subsidies in last 8 years.
3. SLM技术的分类
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

农田
- 乔木与灌木的种植
主要农作物(经济作物及粮食作物):
Major cash crop: Almonds and olives

混合(作物/放牧/树木),包括农林
- 农林业
注释:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): A lack of water availability seriously limits the production potential of the soil and results in a low vegetation/crop cover. The relatively high soil erosion rates cause various off-site related problems (i.e. flooding, reservoir siltation) and on-site problems (i.e. gully formation and reduced soil depth).
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): There is a lack of water for irrigation of crops limiting the crop types that can be planted as well as the crop yield of dryland farming.
Livestock is grazing on crop residues
3.3 有关土地利用的更多信息
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
每年的生长季节数:
- 1
具体说明:
Longest growing period in days: 220Longest growing period from month to month: Nov - Jun
3.4 该技术所属的SLM组
- 土壤肥力综合管理
3.5 技术传播
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果该技术均匀地分布在一个区域上,请注明覆盖的大致区域。:
- 10-100 平方千米
注释:
Ecological agriculture is rapidly increasing in the area and strongly stimulated by subsidies.
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

农艺措施
- A2:有机质/土壤肥力

管理措施
- M6:废物管理(回收、再利用或减少)
注释:
Main measures: agronomic measures
Secondary measures: management measures
Type of agronomic measures: green manure
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀
- Wo:场外劣化效应

化学性土壤退化
- Cn:肥力下降和有机质含量下降(非侵蚀所致)
- Cp:土壤污染

生物性退化
- Bl:土壤寿命损失
- Bp:害虫/疾病增加,捕食者减少

水质恶化
- Hp:地表水水质下降
- Hq:地下水水质下降
注释:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wo: offsite degradation effects, Cp: soil pollution, Hq: decline of groundwater quality
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content, Bl: loss of soil life, Bp: increase of pests / diseases, loss of predators, Hp: decline of surface water quality
Main causes of degradation: soil management (Excessive use of pesticides and herbicides), crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (Excessive use of pesticides and herbicides), education, access to knowledge and support services (lack of knowledge of off site effects for contamination)
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 防止土地退化
- 减少土地退化
注释:
Main goals: prevention of land degradation, mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
4.2 技术规范/技术图纸说明
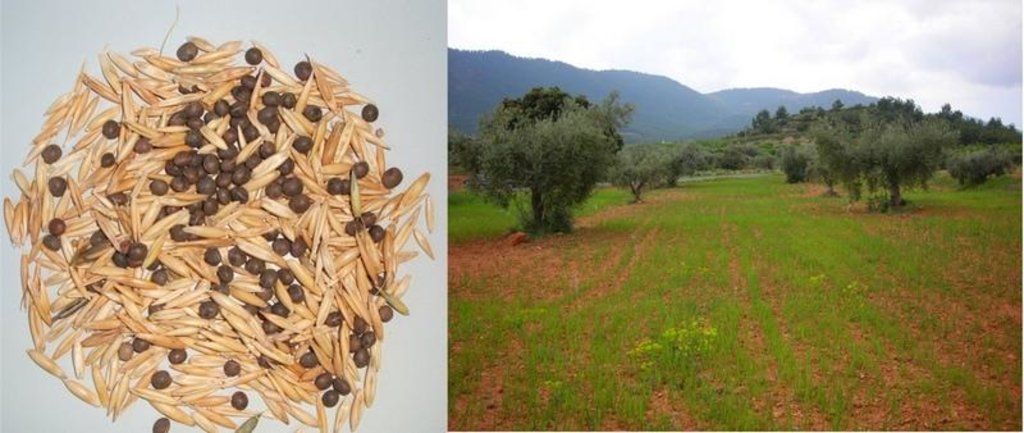
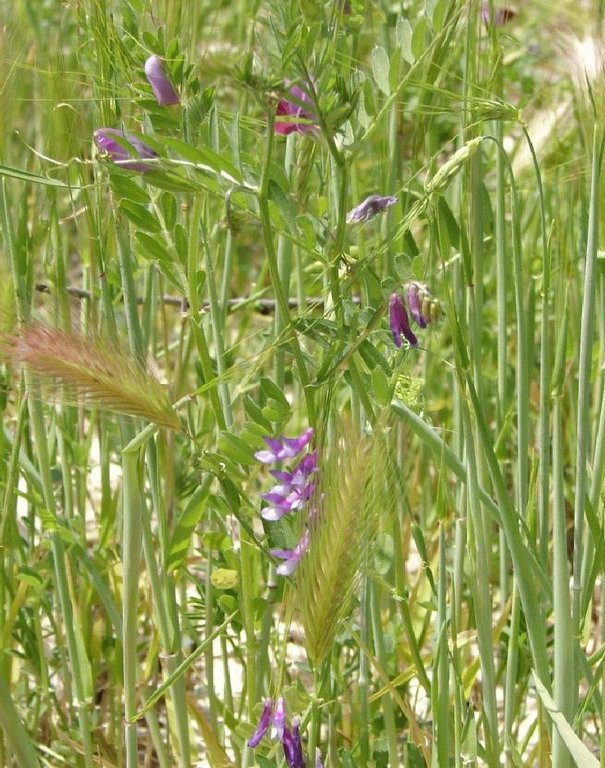
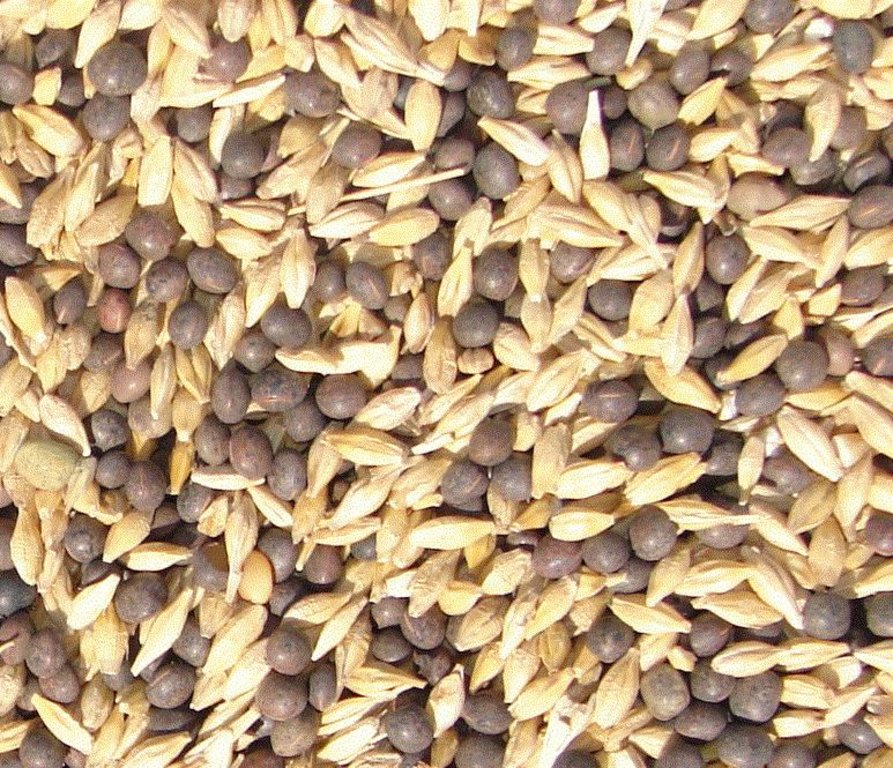
Mixture of barley and vetch (Vicia sativa) seeds used for seeding green manure.
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high (High level of knowledge of possibilities and limitations of fertilizer use and plague control is needed.)
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate (Moderate level of knowledge of fertilizer use and plague control.)
Main technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, improvement of ground cover, increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…)
Secondary technical functions: improvement of surface structure (crusting, sealing), improvement of topsoil structure (compaction), improvement of subsoil structure (hardpan), increase in organic matter, increase of infiltration, increase / maintain water stored in soil, improvement of water quality, buffering / filtering water
Green manure
Material/ species: seed
Quantity/ density: 195 kg/ha
Remarks: Mixture of Vicia (65kg) and Avena (130kg)
Other type of management: Ecological farming: Absence of chemical fertilizers, pesticides and herbicides
4.3 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
EURO
注明美元与当地货币的汇率(如相关):1美元=:
0.63
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
79.00
4.5 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
注释:
Duration of establishment phase: 1 month(s)
4.6 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | seeding green manure | 农业学的 | autumn (October) |
| 2. | ploughing green manure | 农业学的 | spring (May) |
| 3. | organic fertilizer of cow dung (optional) | 管理 | spring |
| 4. | ecological treatment against plagues days | 管理 | winter and april |
4.7 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Labour | ha | 1.0 | 25.0 | 25.0 | 37.0 |
| 设备 | Machine use | ha | 1.0 | 72.0 | 72.0 | 37.0 |
| 植物材料 | Seeds | ha | 1.0 | 96.0 | 96.0 | 37.0 |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | Fertilizer | ha | 1.0 | 79.0 | 79.0 | 37.0 |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | Biocides | ha | 1.0 | 159.0 | 159.0 | 37.0 |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 431.0 | |||||
注释:
Machinery/ tools: tractor with seeding machinery, tractor
Cow dung costs approximately US $350 per tonne and will therefore increase the costs significantly if applied. The costs are calculated assuming the application of green manure, ecological pesticides and organic fertilizer. However, many farmers decide not to use organic fertilizer because of their high costs. As part of the Rural Development Programme (QASPA01), ecological agriculture receives a subsidy of 476 US $ per ha during the first 3 years of production, after which the subsidy is reduced to 380 US $ per ha. Prices are for spring 2008.
4.8 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
Fuel price, ecological pesticides and organic fertilizer are the most determining factors affecting the costs.
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
有关降雨的规范/注释:
Dry period in summer during 3-4 months (June – August/September)
农业气候带
- 半干旱
Thermal climate class: subtropics
Thermal climate class: temperate. The higher parts are generally somewhat colder
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
说明该技术是否专门应用于:
- 不相关
关于地形的注释和进一步规范:
Landforms: plateau / plains, hill slopes, footslopes, valley floors
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
- 细粒/重质(粘土)
表土有机质:
- 中(1-3%)
- 低(<1%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Soil fertility is low
Soil drainage/infiltration is poor/none
Soil water storage capacity is medium
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
5-50米
地表水的可用性:
匮乏/没有
水质(未处理):
仅供农业使用(灌溉)
关于水质和水量的注释和进一步规范:
Ground water table: >50m (there is a lowering of groundwater table due to overexploitation for irrigation purposes)
Availability of surface water:S Poor/none. Sporadically there are flash floods during extreme rainfall events
Water quality (untreated): For agricultural use only (irrigation) (groundwater from aquifers)
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 低
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
生产系统的市场定位:
- 混合(生计/商业
- 商业/市场
非农收入:
- > 收入的50%
相对财富水平:
- 平均水平
个人或集体:
- 合作社
机械化水平:
- 机械化/电动
性别:
- 男人
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Difference in the involvement of women and men: Traditionally most agriculture is done by men in this region.
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 3% - 4%
15% of the land users are rich and own 20% of the land.
80% of the land users are average wealthy and own 75% of the land.
5% of the land users are poor and own 5% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: There is no difference in the ones who apply the technology and those who don’t. Most farmers do have an off-farm income for example from hunting, work in a factory, office or from animal farming (pigs, rabbits).
Market orienation: Commercial/market and mixed (subsistence and commercial) (some farmers are weekend or hobby farmers and not market oriented)
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者拥有或租用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 小规模的
注释:
There are few farmers with large properties within the study area (100-500ha)
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 个人,有命名
土地使用权:
- 个人
用水权:
- 个人
注释:
All cropland is privately owned. Water use is organised by permits to water extraction from aquifers on individual basis. Water rights are provided and controlled by the Water authority of the segura river basin (CHS).
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
收入和成本
农业投入费用
注释/具体说明:
Less fuel use for ploughing but plague control and cow dung can be costly during first years, but after 2-3 years costs are generally lower than under conventional farming because less pesticides are needed. Also use of organic fertilizer is expensive and requires subsidies
农业收入
注释/具体说明:
Depends on crop yield and market price.
工作量
社会文化影响
健康状况
文化机会
注释/具体说明:
Often farmers feel proud and satisfied of producing in a manner respectfull with the environment.
娱乐机会
注释/具体说明:
There is an added value of ecological agriculture for rural tourism activities
SLM/土地退化知识
Improved livelihoods and human well-being
注释/具体说明:
Farm income of most ecological farmers has increased due to higher market price, higher yield and subsidies
生态影响
水循环/径流
地表径流
土壤
土壤覆盖层
注释/具体说明:
Only with green manure
土壤流失
土壤结壳/密封
注释/具体说明:
Less tractor use
养分循环/补给
注释/具体说明:
Due to more biological activity
土壤有机物/地下C
生物多样性:植被、动物
植物多样性
动物多样性
有益物种
害虫/疾病控制
减少气候和灾害风险
碳和温室气体的排放
注释/具体说明:
The production process of conventional synthetic fertilizerss and pesticides is an important source of greenhouse gasses. There is also less tractor use.
其它生态影响
Carbon sequestration
注释/具体说明:
Under ecological agriculture more carbon is sequestred in the soil than under conventional farming
increased competition (water, sunlight, nutrients)
注释/具体说明:
Green manure potentially leads to competition for water. Therefore it is crucial to plough before competition become simportant in springtime.
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
下游淤积
地下水/河流污染
对邻近农田的破坏
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 气候变化/极端天气的类型 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年温度 | 增加 | 好 |
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气象灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 局地暴雨 | 好 |
| 局地风暴 | 好 |
气候灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 干旱 | 不好 |
水文灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 比较和缓的(河道)洪水 | 好 |
其他气候相关的后果
其他气候相关的后果
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 缩短生长期 | 好 |
注释:
The crop type is sensitive to changes in water availability under the semi arid conditions.
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
中性/平衡
长期回报:
中性/平衡
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
轻度消极
长期回报:
稍微积极
注释:
First years require some adaptation, but after 1-2 years the higher market price and crop yield will generate a slightly higher income.
6.5 技术采用
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发地采用该技术,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 0-10%
注释:
95% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: The majority is convinced by the subsidies provided for ecological agriculture
5% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: There is a limited number of farmers that started already before the existence of subsidies.
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Spontaneous, but strongly driven by available subsidies.
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
High quality products with a good market price are produced How can they be sustained / enhanced? Costs of pest control should fall |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
Ecological agriculture and green manure have a very positive effect on soil quality, biodiversity and reduction of runoff and erosion How can they be sustained / enhanced? Reduced costs related to pest control |
|
High quality products of ecological agriculture provide a good impression and an attractive product How can they be sustained / enhanced? Better marketing of eco-almond and olives |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Application of green manure is competition for water for the crop. | Plough away the green cover on time in spring before competition becomes important. Moreover, provide demonstrations on the effects of green manure on competition and crop productivity by additional nitrogen input. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Application of organic fertilizers and ecological pest control is relatively expensive and depend on subsidies especially in the first few years of implementation | Look for cheaper methods and combine possibly with other techniques such as reduced tillage to further reduce the costs. After several years, normally less pest control is required due to increased natural control and ecosystem integrity. |
7. 参考和链接
7.3 链接到网络上可用的相关信息
标题/说明:
Online shop for fertilizers and pesticides allowed in ecological agriculture.
URL:
http://www.ecotenda.net/info/
标题/说明:
Centro de Formación de la Asociación CAAE 2006 El cultivo del almendro en producción ecológica 15pp.
URL:
http://www.juntadeandalucia.es/agriculturaypesca/portal/www/portal/com/bin/portal/DGAEcologica/LA_DGAE/plancolumela3/almendro.pdf
标题/说明:
CARM 2008. Programa de Desarrollo Rural de la Región de Murcia 2007-2013 Tomo II. Calculo de primas de las medidas eje 2 208pp.
URL:
http://www.carm.es/neweb2/servlet/integra.servlets.ControlPublico?IDCONTENIDO=4689&IDTIPO=100&RASTRO=c431$m1219
标题/说明:
CARM 2008. Programa de Desarrollo Rural de la Región de Murcia 2007-2013 Tomo I. 508pp.
URL:
http://www.carm.es/neweb2/servlet/integra.servlets.ControlPublico?IDCONTENIDO=4689&IDTIPO=100&RASTRO=c431$m1219
标题/说明:
Regional advisory board on ecological agriculture:
URL:
http://www.caermurcia.com
标题/说明:
Greenpeace, 2007. El negocio del agua en la cuenca del Segura, Greenpeace.
URL:
www.greenpeace.es
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接

Regional rural development programme [西班牙]
Regional development programme to protect natural resources and stimulate rural economies.
- 编制者: Joris De Vente
模块
无模块