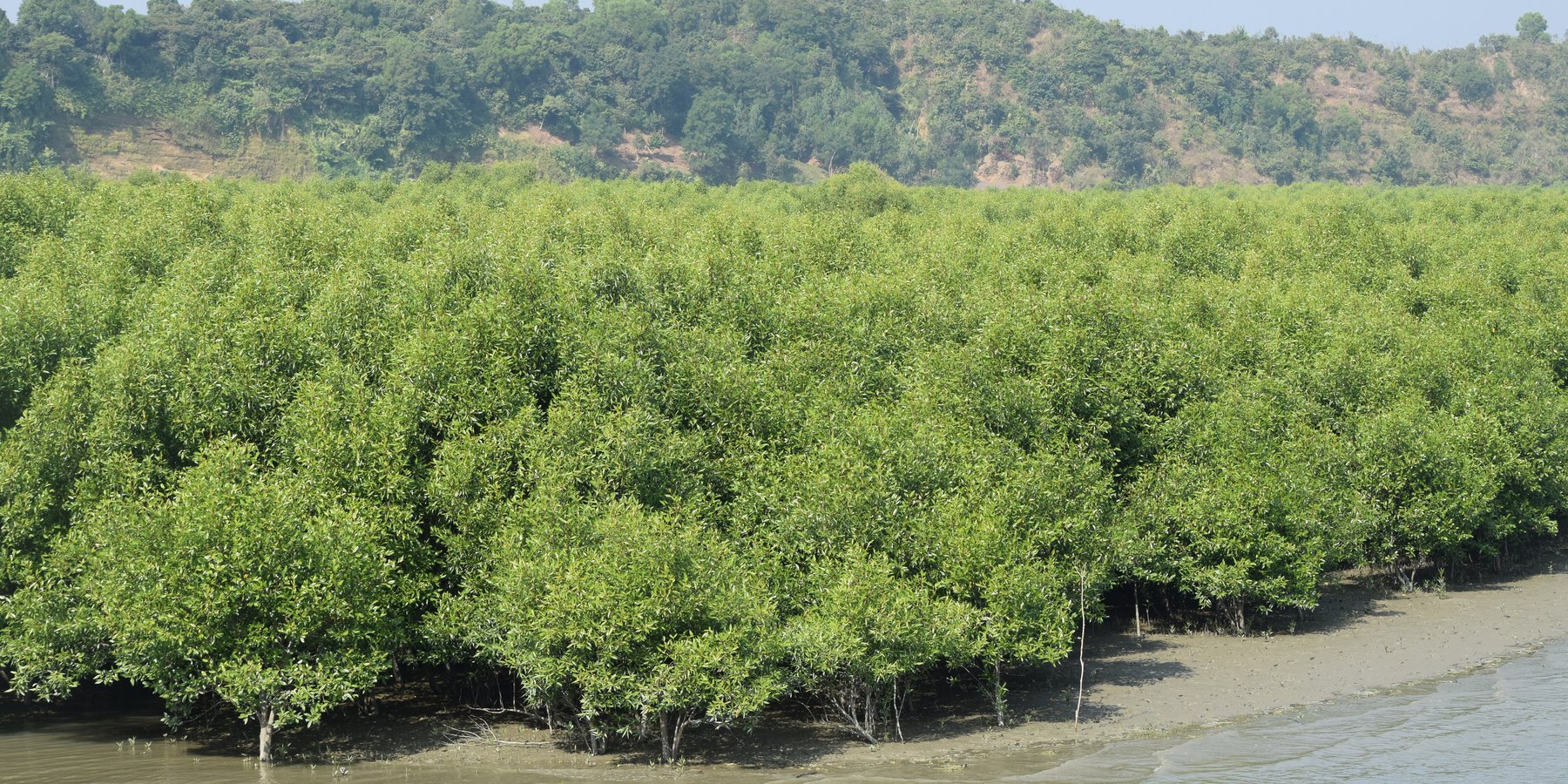
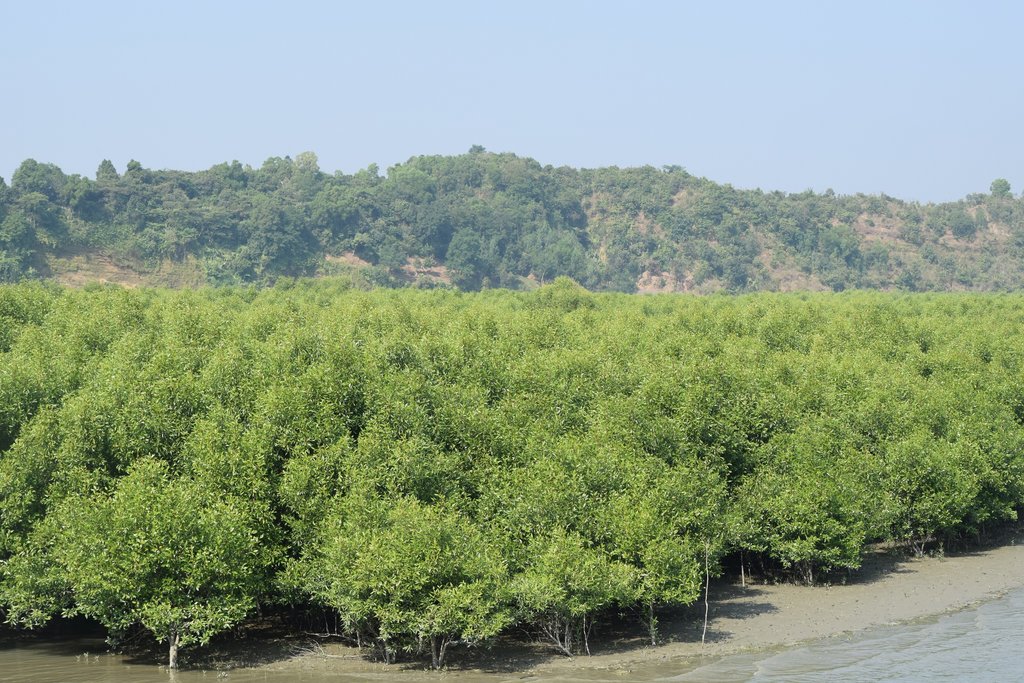
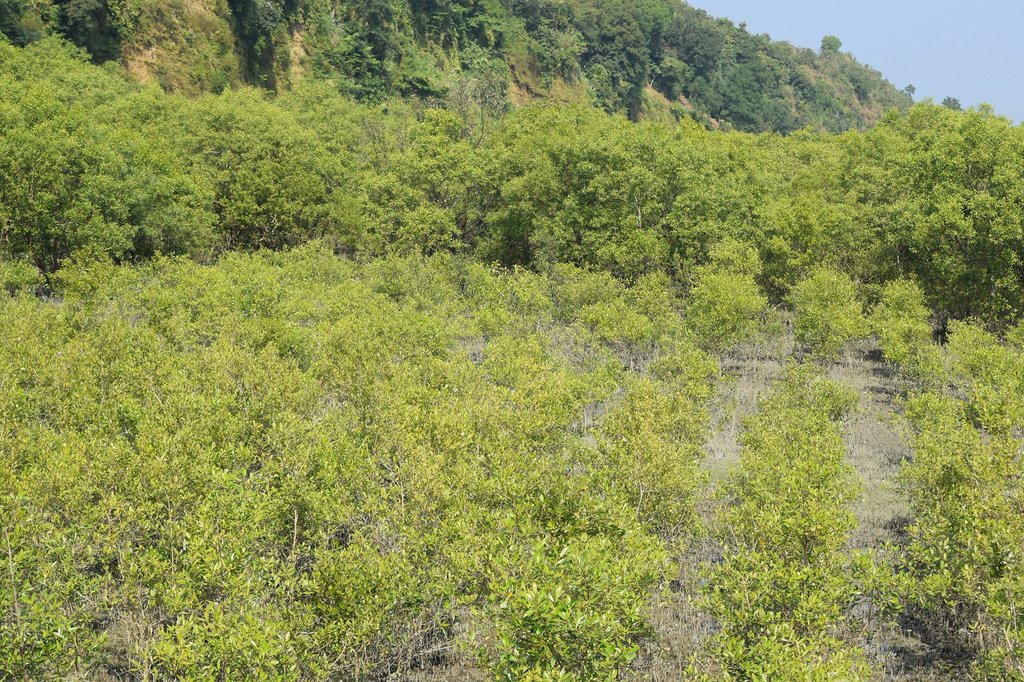
Afforestation with mangrove plants to protect land degradation [孟加拉国]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Fazlay Arafat
- 编辑者: Mutasim Billah, Md. Arfanuzzaman
- 审查者: Nicole Harari, Rima Mekdaschi Studer, Ursula Gaemperli
Upokuliyio Bonayon
technologies_4300 - 孟加拉国
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
关键资源人
土地使用者:
Hossain Md. Kamal
Bangladesh Forest Department
孟加拉国
土地使用者:
Hussain Md. Jobair
Bangladesh Forest Department
孟加拉国
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
Decision Support for Mainstreaming and Scaling out Sustainable Land Management (GEF-FAO / DS-SLM)有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
FAO Bangladesh (FAO Bangladesh) - 孟加拉国有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Bangladesh Forest Department (Bangladesh Forest Department) - 孟加拉国1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.4 所述技术的可持续性声明
这里所描述的技术在土地退化方面是否存在问题,导致无法被认为是一种可持续的土地管理技术?:
否
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
Mangrove afforestation in newly accreted land along cooastal regions accelerates the process of land stabilization, creates new forest resources, and enriches biodiversity.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
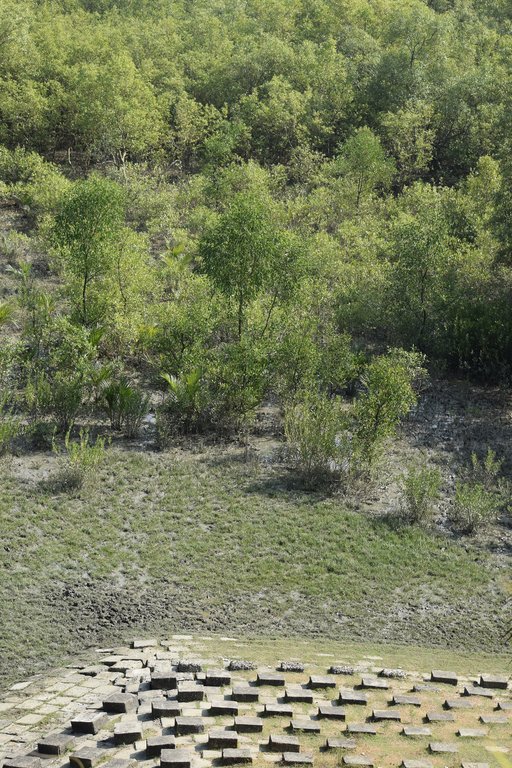
Maheshkhali is the only hilly island of Bangladesh and situated in northwest of Cox’s Bazar. This island has become a tourist destination for its mangrove plantation and ancient Adinath Temple situated at the hilltop. Historically the island had suffered from coastal erosion and structural measures like building blocks along the coast were implemented in some places to protect the Adinath hill from erosion. The Maheshkhali channel have deposited sediments in the near-shore zone and formed mud banks along the coast. This newly accreted land and other lands were used for mangrove plantations, which stabilized the land and provided protection against coastal erosion, storm damage, flooding, and siltation of adjacent seagrass beds. Mangrove plantations can provide a long-term and cost-effective solution to coastal erosion while at the same time improving the landscape aesthetically and increasing ecological habitats. Before the mangroves were planted, the existing shrub and tree vegetation along the coastline of Maheshkhali was scattered. The barren and exposed coastline is now converted to a green shelter-belt and protecting the soil. Bangladesh Forest Department is the land user and the mangrove plantation was carried out with the support from World Bank through "Forest Resource Management Plan (FRMP)" project in 1997. Later, some new plantation also carried out in 2016 on newly accreted land through "Climate Resilient Participatory Afforestation and Reforestation Project (CRPARP).
The mangrove plant species Baen (Avicennia officinalis) was used to create the plantation. Salinity in coastal regions increased as consequence of global warming and Avicennia officinalis is among the most salt tolerant species that prefer clay soil. The young tree forms a low, dense bushy crown. When it matures, it forms a columnar tree up to 15 m and may grow up to 30 m. The spreading root system of the plant also provides stability in shifting substrates. When planting mangroves, site selection and proper nursery management is crucial. Geo-morphological changes in coastal areas can be rapid and unpredictable, making it difficult to identify suitable sites correctly. Accreted land with grasses and crab burrows indicating a stable site, ideal for planting. The experience of field staff is a key factor in identifying suitable sites. Nursery management is carried out by forest department. Seed collection, site clearing, leveling and fencing, drainage arrangement, bed preparation, making overhead shed, poly-bag preparation, potting seeds, manuring, irrigation and weed control are the major activities of nursery management. Proper care of seedlings needs to be ensured while transporting from nursery to plantation site thorough boat. Gunny bags can be used to carry the seedlings while transporting. The spacing between each plant was 1.5m x 1.5m and 4444 seedlings/ha were planted in the visited site. Compost fertilizer was used both in nursery and while planting in pit. After planting, each seedling was tied up with a bamboo stick for support and to prevent from washing away in tides. The plantation activities were carried out by the staff of forest department. As mangrove afforestation is carried out in unstable environments, there is always a risk of losing some plantation during the time it takes for trees to reach maturity.
Coastal afforestation accelerates the process of land stabilization, and by creating new forest land it enriches biodiversity and natural resources. It also protects the lives and property of the coastal population against cyclones and tidal surges. The plantation develops suitable habitats for wildlife, fish and other estuarine and marine fauna. It produces timber for fuelwood and industrial uses. However, the local community people can only collect fuelwood and other non-timber forest products like honey, crabs and fishes from this plantation site. The mangrove plantation increased the aesthetic beauty of the area and also create employment opportunities for remote rural communities through eco-tourism.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
孟加拉国
区域/州/省:
Chittagong division
有关地点的进一步说明:
Moheskhali, Cox's Bazar
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果不知道精确的区域,请注明大致覆盖的区域:
- 1-10 平方千米
技术现场是否位于永久保护区?:
否
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 10-50年前
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过项目/外部干预
注释(项目类型等):
Plantation was carried out from the support of World Bank project "Forest Resource Management Plan (FRMP) project in 1997" and "Climate Resilient Participatory Afforestation and Reforestation Project (CRPARP) in 2016"
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
- 降低灾害风险
- 创造有益的经济影响
- 创造有益的社会影响
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型
同一土地单元内混合使用的土地::
否

森林/林地
- 植树造林
植树造林:说明树种的起源和组成:
- 单一栽培的本地品种
- Mangrove plantation
- Avicennia officinalis
以上的树木是落叶树还是常绿树?:
- 常绿
产品和服务:
- 木材
- 薪材
- 水果和坚果
- 其它森林产品
- 自然保持/保护
- 娱乐/旅游
- 自然灾害防护
注释:
Due to the establishment of mangrove plantation, the degraded land is now covered with vegetation and protected from land degradation
3.3 由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?
由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?:
- 是(请在技术实施前填写以下有关土地利用的问题)
同一土地单元内混合使用的土地::
否

水道、水体、湿地
- fellow accreted land
主要产品/服务:
Fish and crabs
注释:
The areas were inundated regularly by the tide and physical barriers were imposed to protect the land from degradation
3.4 供水
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 森林种植管理
- 防风林/防护林带
- 减少基于生态系统的灾害风险
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

植物措施
- V1:乔木和灌木覆盖层
注释:
Plantation of mangrove species in newly accreted land to stabilize the soil to protect from land degradation
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wc:海岸侵蚀
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 减少土地退化
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
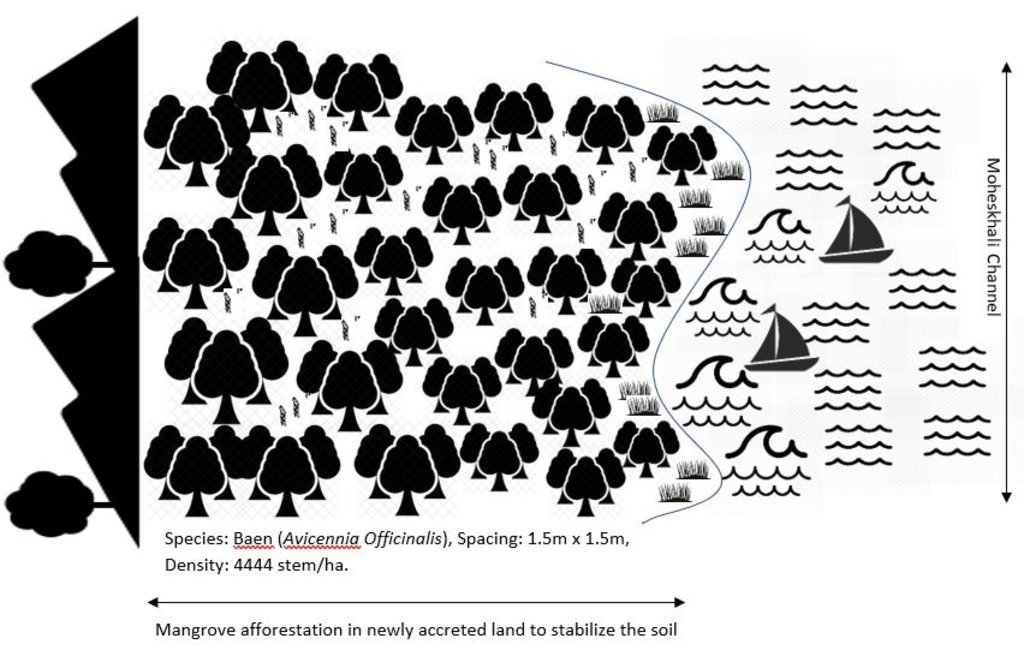
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
Planted species: Baen (Avicennia officinalis)
Soil condition: Accreted land with grasses indicated a stable site and suitable for planting Baen plant.
Spacing: 1.5m X 1.5m
Density: 4444 stem/ha.
Vacancy filling: 3 consecutive years after plantation
作者:
Md. Fazlay Arafat
日期:
21/04/2019
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
具体说明成本和投入是如何计算的:
- 每个技术区域
注明尺寸和面积单位:
1 ha
如果使用本地面积单位,注明转换系数为1公顷(例如1公顷=2.47英亩):1公顷=:
2.47 acres
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
BDT
如相关,注明美元与当地货币的汇率(例如1美元=79.9巴西雷亚尔):1美元=:
84.0
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
BDT 500
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Nursery preparation (seed collection, site clearing, leveling and fencing, drainage arrangement, bed preparation, making overhead shed, poly-bag preparation, potting seeds, manuring, irrigation, weed control) | March-April |
| 2. | Survey plantation site and prepare site map | August |
| 3. | Transportation of seedlings | September-October |
| 4. | Plantation | September-October |
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Nursery preparation (seed collection, site clearing, leveling and fencing, drainage arrangement, bed preparation, making overhead shed, poly-bag preparation, potting seeds, manuring, irrigation, weed control) | person-days | 20.0 | 500.0 | 10000.0 | |
| 劳动力 | Plantation site survey | person-days | 1.0 | 500.0 | 500.0 | |
| 劳动力 | Transportation of seedlings | person-days | 4.0 | 500.0 | 2000.0 | |
| 劳动力 | Plantation | person-days | 10.0 | 500.0 | 5000.0 | |
| 设备 | Boat rent for seedlings transportation | lump-sum | 1.0 | 2500.0 | 2500.0 | |
| 设备 | Poly bags | pieces | 4500.0 | 1.0 | 4500.0 | |
| 设备 | Rope for tying up seedlings with bamboo stick | lump-sum | 1.0 | 1500.0 | 1500.0 | |
| 设备 | Gunny bags (to carry seedlings to the plantation pit) | lump-sum | 1.0 | 400.0 | 400.0 | |
| 植物材料 | Bamboo sticks to support seedlings | pieces | 4500.0 | 2.0 | 9000.0 | |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | Compost fertilizer (to apply in pit) | kg | 50.0 | 10.0 | 500.0 | |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 35900.0 | |||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 427.38 | |||||
注释:
Bangladesh Forest Department is the land user and the costs was borne from the project "Forest Resource Management Plan (FRMP)"
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | 1 year old plantation replanting nursery 40% ( 2 bed/ha) | March-April |
| 2. | 2 year old plantation replanting nursery 30% ( 2 bed/ha) | March-April |
| 3. | 3 year old plantation- replanting nursery 20% (1 bed/Ha.) | March-April |
| 4. | 1 year old plantation- replanting (VF) 40% (1777 seedling/Ha.) | September-October |
| 5. | 2 year old plantation- replanting (VF) 30% (1333 seedling/Ha.) | September-October |
| 6. | 3 year old plantation- replanting (VF) 20% (888 seedling/Ha.) | September-October |
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Nursery work | person-day | 18.0 | 500.0 | 9000.0 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Replanting work | person-day | 10.0 | 500.0 | 5000.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Boat rent for seedlings transportation | Lump-sum | 1.0 | 6000.0 | 6000.0 | 100.0 |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | Compost fertilizer | kg | 25.0 | 10.0 | 250.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 20250.0 | |||||
| 技术维护总成本,美元 | 241.07 | |||||
注释:
Bangladesh Forest Department is the land user and borne the maintenance cost of the technology
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
Labor cost
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
指定年平均降雨量(若已知),单位为mm:
3700.00
注明所考虑的参考气象站名称:
Cox's Bazar
农业气候带
- 潮湿的
Mean annual temperature is 25.6 °C
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
说明该技术是否专门应用于:
- 不相关
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 细粒/重质(粘土)
土壤质地(地表以下> 20厘米):
- 细粒/重质(粘土)
表土有机质:
- 中(1-3%)
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
5-50米
地表水的可用性:
过量
水质(未处理):
不可用
水质请参考::
地表水
水的盐度有问题吗?:
是
具体说明:
Due to regular tidal inundation the soil become saline and only support to grow mangrove plant species
该区域正在发生洪水吗?:
是
规律性:
偶然
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 中等
栖息地多样性:
- 低
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
定栖或游牧:
- 定栖的
生产系统的市场定位:
- 混合(生计/商业)
非农收入:
- 低于全部收入的10%
相对财富水平:
- 贫瘠
个人或集体:
- 员工(公司、政府)
机械化水平:
- 手工作业
性别:
- 女人
- 男人
土地使用者的年龄:
- 青年人
- 中年人
- 老年人
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 中等规模的
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 州
土地使用权:
- 自由进入(无组织)
用水权:
- 自由进入(无组织)
土地使用权是否基于传统的法律制度?:
否
具体说明:
Land use rights based on forest management type
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
木材生产
森林/林地质量
非木材林业生产
注释/具体说明:
Honey, fish and crab production increased
生产故障风险
产品多样性
注释/具体说明:
The mangrove plantation support production of timber, fuel wood, crabs, fruits for wildlife, honey, etc.
生产区域
土地管理
收入和成本
收入来源的多样性
注释/具体说明:
Promote alternate income through ecotourism
社会文化影响
文化机会
注释/具体说明:
The mangrove plantation saved one ancient temple (Adinath Mondir) of Hindu religion from destruction by land degradation.
娱乐机会
注释/具体说明:
The mangrove forest now become a tourist place
SLM/土地退化知识
注释/具体说明:
Forest department now replicating the practice in other degraded areas
生态影响
水循环/径流
地表径流
注释/具体说明:
surface runoff decreased due to canopy coverage and accretion of sediments in plantation site
土壤
土壤堆积
注释/具体说明:
soil accumulation increased as the plantation promote soil accretion during tides
养分循环/补给
土壤有机物/地下C
生物多样性:植被、动物
植被覆盖
生物量/地上C
动物多样性
注释/具体说明:
the plantation site support habitats for birds and crabs
有益物种
注释/具体说明:
Honey bee and various birds living here and add benefits in pollination and pest control
栖息地多样性
注释/具体说明:
The plantation develops suitable habitats for wildlife and fish
减少气候和灾害风险
洪水影响
滑坡/泥石流
注释/具体说明:
The plantation protect the debris flows of Adinath hill from washed away in water. The Adinath hill is on the edge of coast and now protected from bank erosion.
飓风、暴雨的影响
碳和温室气体的排放
风速
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
缓冲/过滤能力
注释/具体说明:
The plantation act as a buffer to reduce the saline water flow of high tide towards terrestrial land
温室气体的影响
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 增加或减少 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年温度 | 增加 | 好 | |
| 季雨量 | 湿季/雨季 | 增加 | 好 |
| 其他渐变气候 | water salinity in coastal areas due to global warming | 增加 | 好 |
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气象灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 热带风暴 | 适度 |
| 局地雷暴 | 好 |
水文灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 风暴潮/沿海洪水 | 好 |
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
消极
长期回报:
积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
消极
长期回报:
积极
6.5 技术采用
- 1-10%
注释:
Forest Department is the land user here
6.6 适应
最近是否对该技术进行了修改以适应不断变化的条件?:
否
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Protect the lives and property of the coastal population against cyclones and tidal surges. |
| Conserve and stabilize newly accreted lands and protect from land degradation |
| Produce fuel wood for local people |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Develop ecotourism facility for local communities |
| Develop suitable habitats for wildlife, fish and other estuarine and marine fauna |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Vulnerable to natural calamities specially in initial stage | Proper management and vacancy filling |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Risk of low production due to unstable environment for plantation | Proper monitoring and management of plantation |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
- 实地考察、实地调查
number of field visits: 02
- 与土地使用者的访谈
number of informants: 04
- 与SLM专业人员/专家的访谈
number of informants:02
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
16/01/2019
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Macintosh, D.J., Mahindapala, R., Markopoulos, M. (eds) (2012). Sharing Lessons on Mangrove Restoration. Bangkok, Thailand: Mangroves for the Future and Gland, Switzerland: IUCN. ISBN: 978-2-8317-1558-2
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
www.mangrovesforthefuture.org
7.3 链接到网络上的相关信息
标题/说明:
Mangroves for the Future
URL:
www.mangrovesforthefuture.org
7.4 一般注释
The WOCAT questionnaire covers all the aspect of this technology
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块