Planting sunn hemp as green manure for soil improvement [泰国]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Bunjirtluk Jintaridth
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Rima Mekdaschi Studer, Pitayakon Limtong, William Critchley
Por Toeng
technologies_4336 - 泰国
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
关键资源人
SLM专业人员:
Poonkasaem Pisan
Land Development Department (Regional 1)
泰国
土地使用者:
Choen Eium Num Kung
Good Agricultural Practices group, Ban Klong Raban
泰国
土地使用者:
Soop-Peug Yupa
Good Agricultural Practices group, Ban Klong Raban
泰国
土地使用者:
Soop-Peug Yupin
Good Agricultural Practices group, Ban Klong Raban
泰国
1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.4 所述技术的可持续性声明
这里所描述的技术在土地退化方面是否存在问题,导致无法被认为是一种可持续的土地管理技术?:
否
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
Growing sunn hemp in rice paddy fields as a green manure increases organic matter, and generally improves and nourishes the soil.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
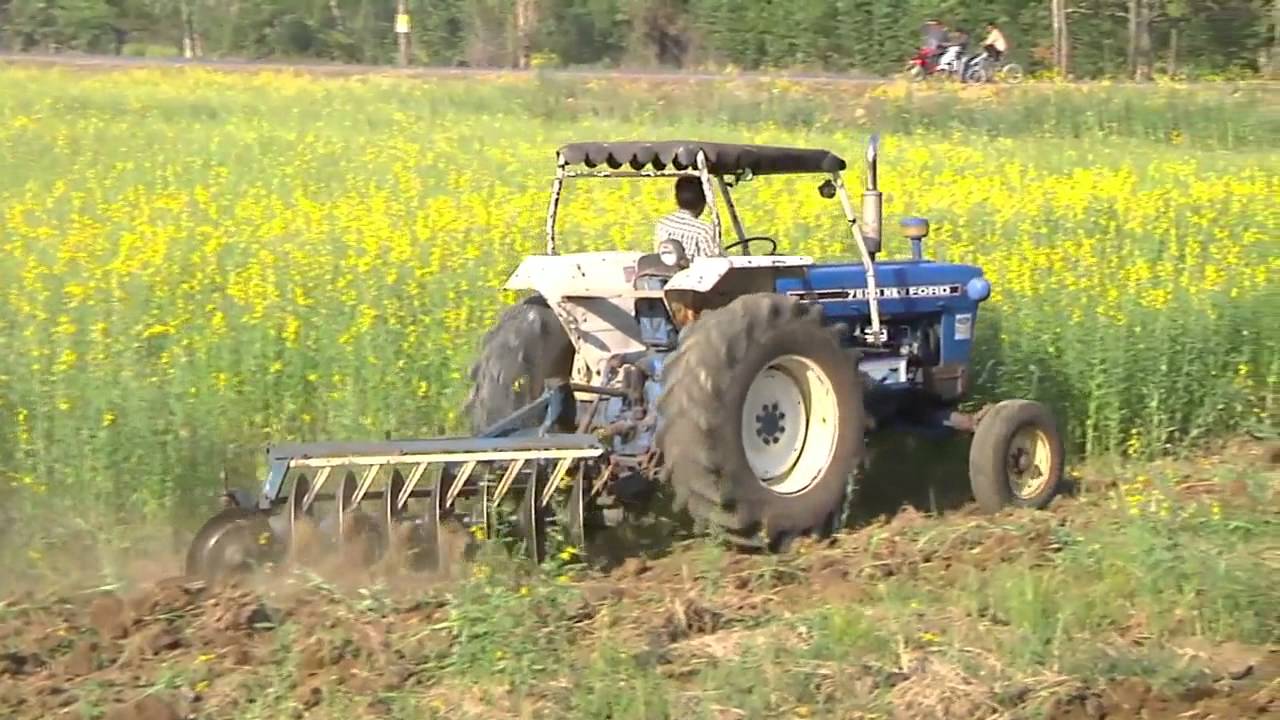
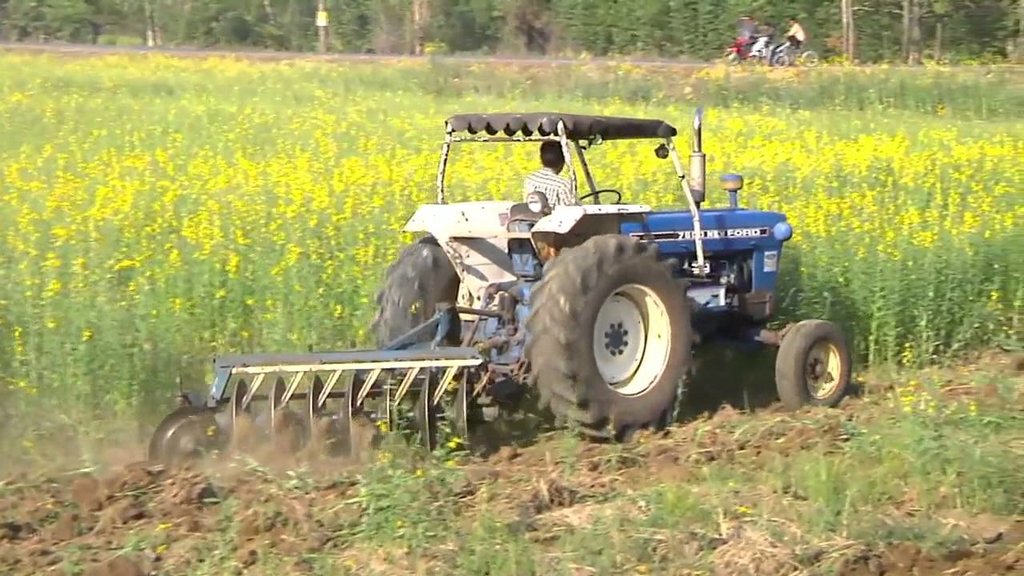
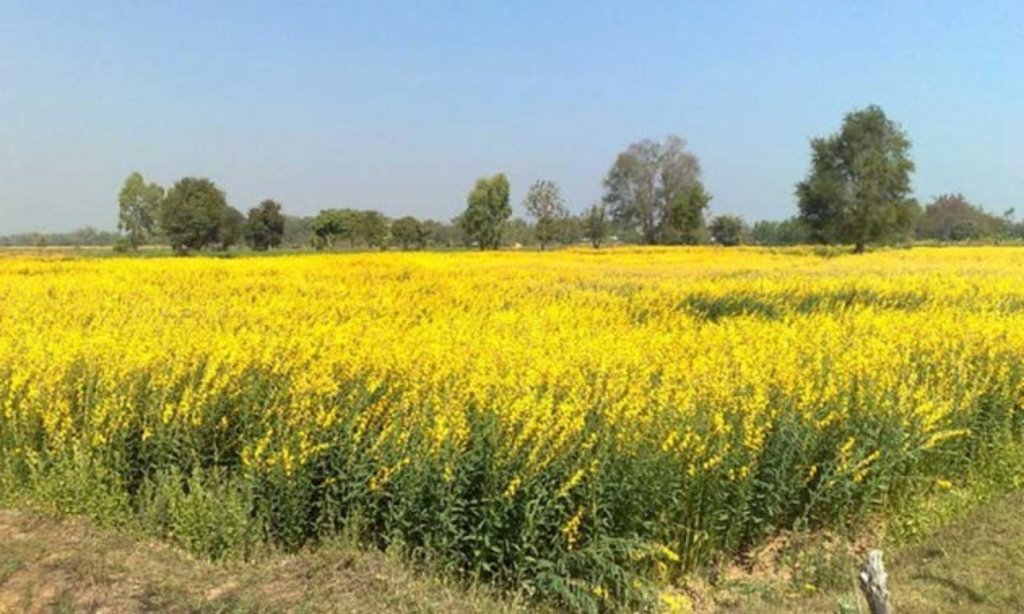
Planting sunn hemp (Crotalaria juncea) as green manure is an effective way to improve the fertility of the paddy fields in the irrigation zone of Chao Phraya River basin in the Central Plain of Thailand. Most farmers produce rice twice a year; some even grow 5 crops in 2 years. This is due to the fact that the water from the irrigation system is available also outside the rainy season. Continuous cropping without letting the land rest has a negative effect on the soil structure, because the soil has been prepared by small- to medium-sized machines, and preparation is done when there is moisture in the soil, leading to structural deterioration. As a result, its suitability for growing rice is reduced. In addition to this, the organic matter in the soil also decreases, resulting in low rice yields. Farmers solve the problem by increasing the amount of chemical fertilizers, but this increases costs. They therefore chose to grow sunn hemp instead which is a well known green manure - it is leguminous therefore it adds nitrogen to the soil and when it is ploughed in, and its bulky organic matter helps improve structure. At one stage, farmers experimented to know how to manage their paddy land by growing the sunn hemp as green manure crop appropriately. In the trial the land area being used was around one ha. Half of the land was under treatment Type 1 and the second half under Type 2.
Type 1 operation: Water was pumped into the paddy to moisten the soil. If a large amount of water was available, pumping would be done until the soil became well saturated or slightly flooded. The land would be left for a night. After that, the water was drained. On the following day, the sunn hemp seeds were sown.
Type 2 operation: The land was plowed at the start of the trial and the sunn hemp seeds were sown immediately. The sunn hemp plants were allowed to grow for 40-50 days or until the flowering was about 70-80%.
Then, the plots under both types were plowed over and were left idle for 15-30 days. Then, both plots were made muddy by plowing and harrowing for about 5-7 days; after that the rice seeds were sown.
Comparison between Type 1 and Type 2 showed they were not different in terms of production. However, Type 1 showed that some cash could be saved for plowing.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
泰国
区域/州/省:
Singburi province
有关地点的进一步说明:
50 Moo 3, Po ThaLae sub district, Bang-Rajan District,
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 适用于特定场所/集中在较小区域
技术现场是否位于永久保护区?:
否
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 10-50年前
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过土地使用者的创新
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 改良生产
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
- 保护生态系统
- 保持/提高生物多样性
- 创造有益的经济影响
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型
同一土地单元内混合使用的土地::
否

农田
- 一年一作
年作 - 具体指明作物:
- 谷类 - 水稻(湿地)
年作制度:
连作湿地稻
每年的生长季节数:
- 2
采用间作制度了吗?:
否
采用轮作制度了吗?:
是
如果是,请具体说明:
green manuring
3.3 由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?
由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?:
- 是(请在技术实施前填写以下有关土地利用的问题)
同一土地单元内混合使用的土地::
否

农田
- 一年一作
年作 - 具体指明作物:
- 谷类 - 水稻(湿地)
采用间作制度了吗?:
否
采用轮作制度了吗?:
否
3.4 供水
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 混合雨水灌溉
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 土壤肥力综合管理
- 家庭花园
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

农艺措施
- A1:植被和土壤覆盖层
- A2:有机质/土壤肥力
- A3:土壤表面处理
- A4:地表下处理
- A5:种子管理,改良品种
- A6:残株管理
A3:区分耕作制度:
A 3.2: Reduced tillage (> 30% soil cover)
A6:对残株管理作出具体说明:
A 6.3:收集
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

化学性土壤退化
- Cn:肥力下降和有机质含量下降(非侵蚀所致)
- Ca:酸化

生物性退化
- Bc:植被覆盖的减少
- Bl:土壤寿命损失
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 减少土地退化
- 修复/恢复严重退化的土地
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
作者:
Mr. Pisan Poonkasaem
日期:
30/12/2018
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
具体说明成本和投入是如何计算的:
- 每个技术区域
注明尺寸和面积单位:
4.45 ha
如果使用本地面积单位,注明转换系数为1公顷(例如1公顷=2.47英亩):1公顷=:
6.25 Rai
具体说明成本计算所用货币:
- 美元
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | After rice harvesting, prepare sunn hemp seed | March |
| 2. | Pumping water into the paddy field | March |
| 3. | Slightly flooding water out of land, then harvesting sunn hemp seeds | March |
| 4. | The land plots were plowed over after sunn hemp growth was 40-50 days | January - February |
| 5. | Sunn hemp plants were left idle for 15-30 days | February-March |
| 6. | Muddy rice field by plowing and harrowing for about 5-7 days | April-May |
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | seed harvesting | kg per ha | 320.0 | 0.02 | 6.4 | |
| 其它 | pumping water | rai | 10.0 | 30.0 | 300.0 | |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 306.4 | |||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 306.4 | |||||
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
指定年平均降雨量(若已知),单位为mm:
1100.00
有关降雨的规范/注释:
Rainy season is from May-October
注明所考虑的参考气象站名称:
Ministry of Meteorological
农业气候带
- 潮湿的
hot and humid
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
说明该技术是否专门应用于:
- 不相关
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 细粒/重质(粘土)
土壤质地(地表以下> 20厘米):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 中(1-3%)
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
5-50米
地表水的可用性:
好
水质(未处理):
仅供农业使用(灌溉)
水质请参考::
地表水
水的盐度有问题吗?:
否
该区域正在发生洪水吗?:
是
关于水质和水量的注释和进一步规范:
Soil was polluted by chemical agriculture during summer.
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 中等
栖息地多样性:
- 中等
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
定栖或游牧:
- 定栖的
生产系统的市场定位:
- 混合(生计/商业)
非农收入:
- > 收入的50%
相对财富水平:
- 平均水平
个人或集体:
- 个人/家庭
机械化水平:
- 机械化/电动
性别:
- 女人
土地使用者的年龄:
- 中年人
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Main crop is rice and surrounding by other crops such as vegetable and fruits.
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 中等规模的
注释:
Land owner is 60% and rent is 40%
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 个人,有命名
土地使用权:
- 个人
用水权:
- 社区(有组织)
土地使用权是否基于传统的法律制度?:
是
注释:
there is irrigation system
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
产品多样性
生产区域
土地管理
社会文化影响
食品安全/自给自足
健康状况
土地使用权/用水权
文化机会
注释/具体说明:
religion activities decrease
娱乐机会
注释/具体说明:
activities decrease
社区机构
SLM/土地退化知识
冲突缓解
注释/具体说明:
increase good relationship
社会经济弱势群体的情况
生态影响
水循环/径流
水量
水的回收/收集
多余水的排放
土壤
土壤水分
土壤覆盖层
土壤流失
土壤堆积
土壤压实
土壤有机物/地下C
生物多样性:植被、动物
植被覆盖
生物量/地上C
植物多样性
栖息地多样性
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
水资源可用性
旱季稳定可靠的水流
下游洪水
下游淤积
地下水/河流污染
缓冲/过滤能力
风力搬运沉积物
温室气体的影响
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 增加或减少 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 季雨量 | 冬季 | 增加 |
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
积极
6.5 技术采用
- 1-10%
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发的,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 0-10%
6.6 适应
最近是否对该技术进行了修改以适应不断变化的条件?:
否
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Government support for sunn hemp seeds to farmers every year. |
| Sunn hemp crops are easy to take care of and also growth rate is very good. |
| Sunn hemp crops are resisted to insects and diseases. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Rice production increases after sunn hemp was plowed over and was left idle for 15-30 days before sowing rice. |
| The flowering of sunn hemp is beautiful, therefore is attractive for tourists. |
| Sunn hemp crops are resisted to insects and diseases. |
| Sunn hemp crops reduce chemical fertilizer rate of application for rice. |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| There is a sunn hemp seeds support for farmers every year, however there are not enough summ hemp seeds. | Should have the good plan for sunn hemp seeds production. |
| Land preparation costs are increased | Support farmer's groups for decreasing costs of Land preparation, which may be in the agricultural cooperative system. |
| Some farmers are in a hurry to grow rice, so they do not use this technology. | Promoting and training for this technology |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Soil are low moisture in some areas, then sunn hemp can not grow well. | Coordinate with irrigation department to provide irrigation system. |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
- 实地考察、实地调查
10
- 与土地使用者的访谈
4
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Sunn hemp plowing and cooperating
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
Land Development Department
7.3 链接到网络上的相关信息
标题/说明:
Sunn hemp production
URL:
http:\\www.1ldd.go.th/WEB_PSD/prnew/2561/sr1-61/sr2.pdf
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块