Kanda [阿富汗]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Aqila Haidery
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Alexandra Gavilano
Kanda
technologies_1659 - 阿富汗
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
SLM专业人员:
SLM专业人员:
SLM专业人员:
SLM专业人员:
Sediqi Ali Ahmad
Helvetas Swiss Intercooperation
阿富汗
SLM专业人员:
Sthapit Keshar
Helvetas Swiss Intercooperation
阿富汗
SLM专业人员:
Arbab Ziauddin
Sourakhak Watershed Committee, Kahmard
阿富汗
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
HELVETAS (Swiss Intercooperation)1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
A traditional underground water tank carved out of rocks to collect rainfall and snow water and reduce evaporation losses.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
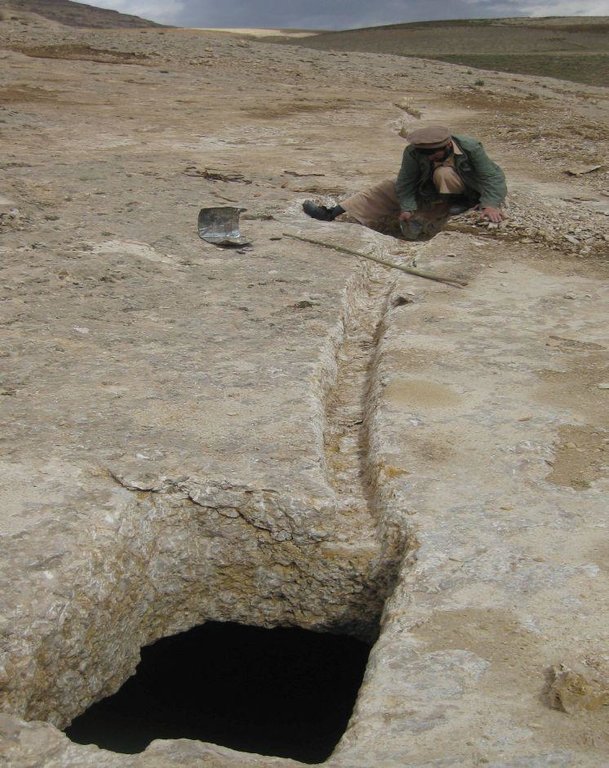
Kanda is an indigenous technology for collecting rain and snow melt. The technology comprises an underground tank carved out of rock (limestone), channels to convey the runoff into the underground tank or kanda and a rocky catchment from where runoff is collected. Kanda technology is applied in Afghanistan in many places, particularly in areas which experience scarcity of water for human beings, livestock and irrigation.
Purpose of the Technology: Due to high evaporation rates and low precipitation, harvesting runoff in open tanks is not an efficient way of water harvesting. HELVETAS Swiss Intercooperation is implementing community based watershed management projects in Kahmard district of Bamyan province (Afghanistan) since 2008 with financial support from the International Swiss Re Award for sustainable watershed management (2009) and the Swiss Agency for Development and Cooperation (SDC). One of the activities for sustainable watershed management is plantation of fruit and non-fruit trees in the selected watersheds (upland areas) which were used for grazing and extraction of vegetation for domestic use. Due to water scarcity in the upland areas, irrigation of the planted saplings becomes very difficult and water has to be transported on donkey from far locations. To overcome this constraint, Kanda was identified as the most potent technology for harvesting runoff and snow melt.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: For constructing Kandas, Kanda makers from Dara-e Suf district in Samangan province had to employed as there are no experts in Kahmard. Based on feasibility studies, eight kandas have been constructed including 4 kandas in Sourakhak wa-tershed and 4 in Baqa Kushta watershed. The size of each kanda is 6 m length, 6 m in width and 3 m in height. To convey the runoff into the tank, 10-20 m long graded channels were carved out of the rocks. The establishment cost of one Kan-da was approximately US$ 7163. Kanda making requires special skills, especially when it is carved out of rocks. A kanda maker has sound understanding of the area’s geology, and this wisdom is gained through learning by doing and ances-tors.. In Kahmard, 2-3 experts worked for 4-5 months for one Kanda.
Natural / human environment: In 2012, due to sufficient rains, 2 Kandas which did not have leakage problems in Sourakhak watershed got full with runoff water, which was then used for irrigating 6500 saplings seven times during the year. Kahmard district has a semi-arid cli-mate. Some years are dry with rainfall of about 190 mm. Considering this context, it becomes very necessary to tap rainwater, especially in the rainfed uplands, and use it for irrigating saplings or for livestock.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
阿富汗
区域/州/省:
Bamyan
有关地点的进一步说明:
Kahmard
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 适用于特定场所/集中在较小区域
注释:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.005 km2.
2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 50多年前(传统)
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过项目/外部干预
注释(项目类型等):
Kanda technology is an age old water harvesting traditional technology.
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- access to water
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

牧场
粗放式放牧:
- 半游牧畜牧业
集约放牧/饲料生产:
- 改良牧场
动物类型:
- 山羊
- 绵羊
注释:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Scarcity of water in the upland makes plantation activities and livestock productivity difficult. Carrying water from far places for irrigating plants is an expensive activity.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Degraded upland watershed resulting severe flash flood.
Forest products and services: timber, fuelwood, fruits and nuts, grazing / browsing, nature conservation / protection, protection against natural hazards
Other forest products and services: flash flood
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Grazing land: Gi: Intensive grazing/ fodder production
Longest growing period in days: 90; Longest growing period from month to month: March-July
3.3 由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?

牧场
- Extensive grazing
3.4 供水
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 集水
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

结构措施
- S11:其它
注释:
Specification of other structural measures: Under ground cistern
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀

生物性退化
- Bc:植被覆盖的减少
注释:
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion
Main causes of degradation: over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use (Bush collection for fire wood), overgrazing (By sheep and goets), droughts (Natural climate phenomenon), land tenure (Common land without good management), poverty / wealth, governance / institutional (Lack of organizationals for organization for supporting management of common resources.)
Secondary causes of degradation: crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (Rainfed agriculture), Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts) (Change in climate patterns), population pressure (Fast increasing population which depands on natural resources for livelihoods), war and conflicts (Leading to uncontrolled cutting down of trees and shrubes)
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 修复/恢复严重退化的土地
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
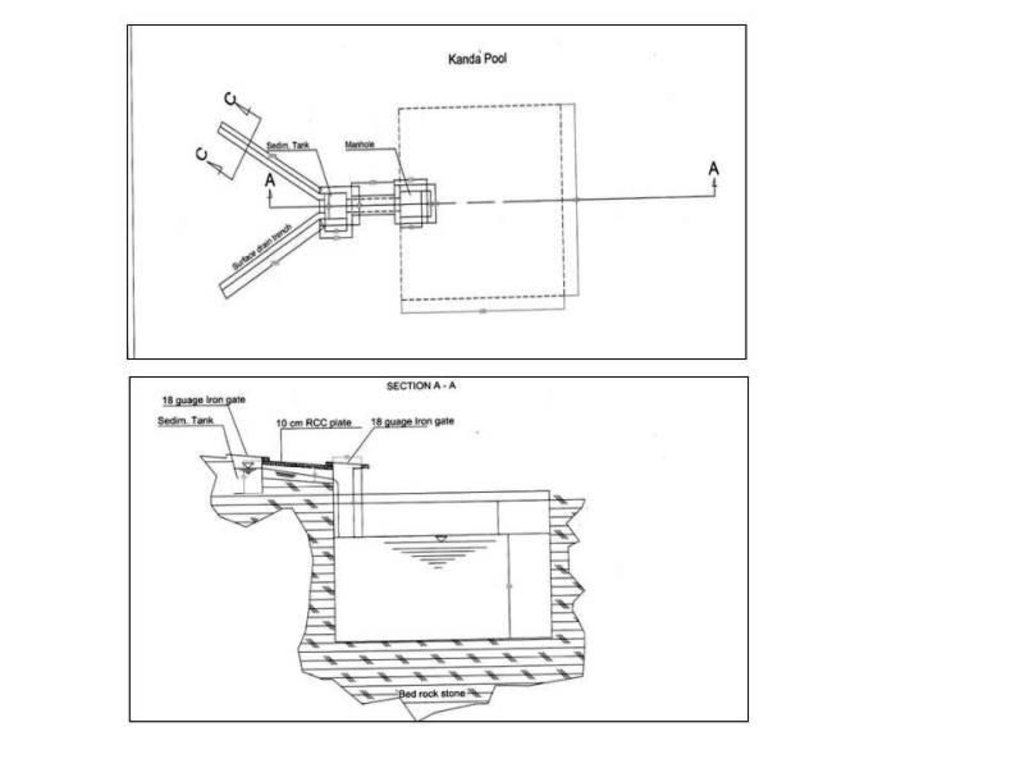
Technical drawing of a Kanda constructed at Baqa Kushta watershed in Kahmard district (Bamyan province).
Size of one Kanda tank:
Length:6m
Width :6m
Height:3m
108 cu.m water can be stored in one Kanda.
Location: Baqa Koshta watershed. Kahmard
Date: 24/03/2013
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high
Technical knowledge required for land users: high
Main technical functions: control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap, water harvesting / increase water supply, Reduction in evaporation and seepage losses
Secondary technical functions: improvement of ground cover
Structural measure: cistern(from rock)
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 3
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 6
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 6
Construction material (other): Constructed from rock
作者:
Helvetas Swiss Intercooperatio, Kabul Afghanistan
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
具体说明成本计算所用货币:
- 美元
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
5
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Labour | kanda | 1.0 | 5640.0 | 5640.0 | 15.0 |
| 设备 | Equipement | kanda | 1.0 | 458.0 | 458.0 | |
| 施工材料 | Materials | kanda | 1.0 | 1065.0 | 1065.0 | 8.0 |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 7163.0 | |||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 7163.0 | |||||
注释:
Duration of establishment phase: 0 month(s)
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Cleaning of the canals and Kanda | once/year |
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Cleaning of the canals and Kanda | persons/day/kanda | 2.0 | 5.0 | 10.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 10.0 | |||||
| 技术维护总成本,美元 | 10.0 | |||||
注释:
The kanda is for water collection which runoff and snow melt. The usage of water for sapling irrigation because there is upland and no water resources.
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
农业气候带
Thermal climate class: temperate
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 粗粒/轻(砂质)
表土有机质:
- 低(<1%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Soil depth on average: Because there is fully of rocks.
Soil texture: Mostly rocky
Topsoil organic matter: Because there is erosion
Soil fertility is low (Loss by wind and water erosion)
Soil drainage / infiltration is poor because there is fully of rock
Soil water storage capacity because of rocky catchment
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
> 50米
地表水的可用性:
匮乏/没有
水质(未处理):
仅供农业使用(灌溉)
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 低
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
生产系统的市场定位:
- 混合(生计/商业)
非农收入:
- 收入的10-50%
相对财富水平:
- 贫瘠
- 平均水平
个人或集体:
- 团体/社区
机械化水平:
- 手工作业
性别:
- 男人
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Difference in the involvement of women and men: Because there is to much workload
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2% - 3%
10% of the land users are rich.
40% of the land users are average wealthy.
50% of the land users are poor.
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 小规模的
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 州
土地使用权:
- 社区(有组织)
用水权:
- 社区(有组织)
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
生产故障风险
水资源可用性和质量
饮用水的可用性
饮用水的质量
收入和成本
工作量
其它社会经济效应
expense for construction
社会文化影响
SLM/土地退化知识
livelihood and human well-being
注释/具体说明:
Increased availability of water for small scale irrigation such as trees, sapling and livestock and increase successful afforestation in dry land areas which in the longer term will lead to increased income, fuel wood and timber for land user and greener watersheds
aesthetic value due to greener watershed
生态影响
水循环/径流
水的回收/收集
地表径流
注释/具体说明:
due to water harvesting
其它生态影响
sediments due to excavation of rocks
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
下游洪水
对公共/私人基础设施的破坏
Contributes to flash flood risk reduction by supporting regreening effort
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 增加或减少 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年温度 | 增加 | 好 |
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气象灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 局地暴雨 | 好 |
| 局地风暴 | 好 |
气候灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 干旱 | 好 |
水文灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 比较和缓的(河道)洪水 | 好 |
其他气候相关的后果
其他气候相关的后果
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 缩短生长期 | 好 |
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
非常积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
非常积极
长期回报:
非常积极
注释:
This technology is very positive and useful for land users and collected the water for irrigation and livestock.
6.5 技术采用
注释:
Comments on acceptance with external material support: It is an indigenous technology applied in many other districts of Afghanistan in Dara-e Suf and Ruy-i Doab districts of Samangan province by several families either collectively or privately without external support. In Dare-e Suf are not constructed inside of rocks but in soil.
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
The technology supports plantation activities in sites which are far from perennial water sources How can they be sustained / enhanced? The collected water should be used efficiently during irrigation by combining with conservation measures like mulching, drip or pitcher irrigation |
|
As the kanda catchment is rocky, infiltration losses are minimized and most of the surface runoff is harvested How can they be sustained / enhanced? The channel must be constructed properly so that all runoff is trapped and conveyed to the Kanda. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
An indigenous multipurpose technology How can they be sustained / enhanced? Kanda size can be improved if the catchment area and precipitation amount are considered. This also depends on availability of long-term rainfall data. |
|
Requires minimum maintenance when constructed properly How can they be sustained / enhanced? Kanda, conveyance canals, sediment pits and catchment areas should be cleaned. If any leakages occur in the tank, they should be sealed. |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Due to a lack of geological and hydro-meteorological information, it is not possible to prepare precise and cost-effective kanda proposals | Make best use of traditional wisdom, install hydro-met stations if possible and make adjustments based on regular monitoring. |
| If the kanda and sediment trap tanks are not cleaned regularly and the kanda opening is not covered, sedimentation can be problem leading to reduced Kanda capacity and also animals could fall | Cleaning and maintenance works must be carried out by the local people every year before spring rains. The openings must be covered. |
| Due to availability of water, there can be grazing pressure near the Kanda | Watershed committee members and guards should ensure that the site is protected from over grazing. Construct Kandas outside the selected watershed for livestock purposes. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Establishment cost is high if the catchment is rocky | Needs external support during the establishment phase |
| Lack of kanda makers in some districts like Kahmard | Get kanda makers from other districts and build capacities of interested local people. |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
7.3 链接到网络上的相关信息
URL:
www.wocat.net(Online Technology Database)
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块