Terracing for soil erosion protection [巴西]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Stefan Hohnwald
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Fabian Ottiger, Alexandra Gavilano
Terraços contra erosão
technologies_1275 - 巴西
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
SLM专业人员:
Schindewolf Marcus
Technische Universität Bergakademie Freiberg
德国
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Georg August Universität Göttingen (Georg August Universität Göttingen) - 德国有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Technische Universität Bergakademie Freiberg - 德国1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
Terracing of landscapes against soil erosion for soy, corn, cotton, and sugar cane production of large enterprises in Central Brazil
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
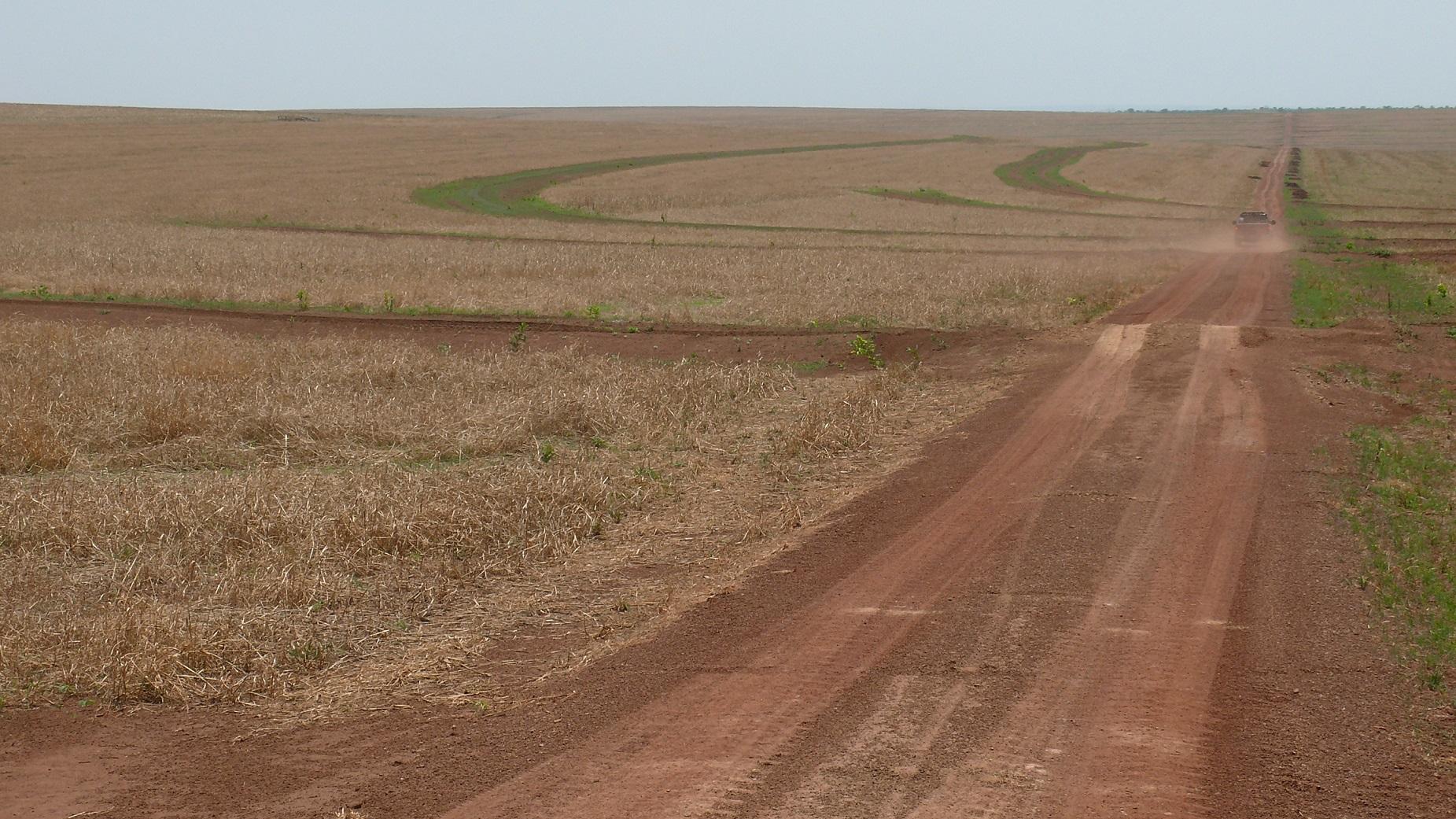
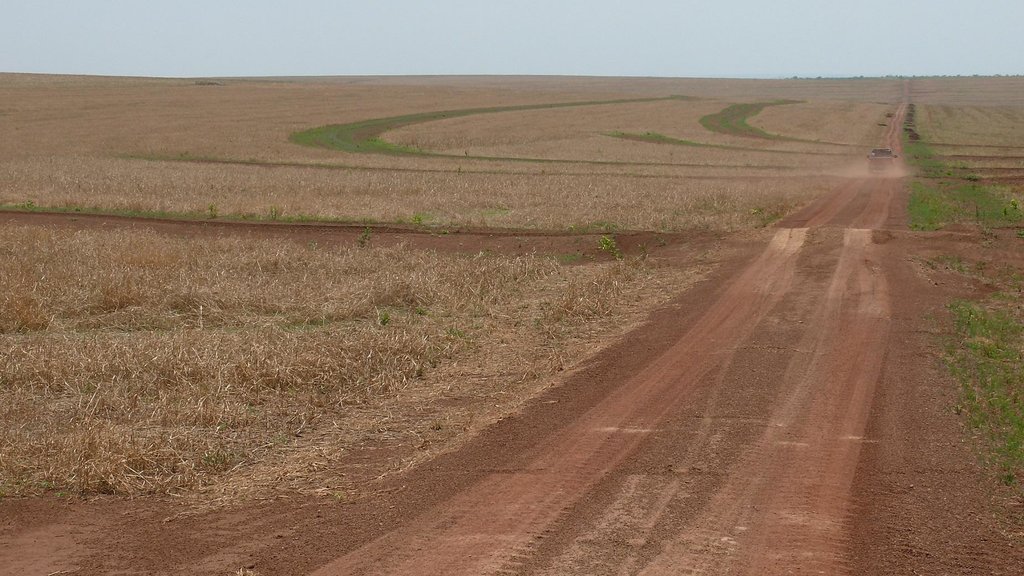
Medium to slightly inclined tablelands in the cerrados are protected by soil terraces against soil erosion, building kilometer long and up to 1m high terraces.
Purpose of the Technology: The purpose of the terraces is to protect the cotton, corn, and soy bean fields against top-soil losses due to heavy tropical rain events that occur during the starting rainy season. It is predicted and modeled for the future that heavy rain events will increase in the following decades.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: High-input machinery like tractors are used to install the terraces. These terraces have to be repaired and improved periodically, e.g. every 5 years.
Natural / human environment: The terraces are necessary because the potential natural vegetation, the cerrado forests that protected the soils before, have been converted to huge farmlands that are now directly exposed to heavy tropical rainfalls and soil erosion.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
巴西
区域/州/省:
Mato Grosso
有关地点的进一步说明:
Campo Verde, Primavera do Leste
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果不知道精确的区域,请注明大致覆盖的区域:
- > 10,000 平方千米
注释:
Boundary points of the Technology area: Cerrado biome of central Brazil.
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 10-50年前
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过土地使用者的创新
3. SLM技术的分类
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

农田
- 一年一作
- 多年一作(非木材)
年作 - 具体指明作物:
- 谷物类 - 玉米
- 纤维作物 - 棉花
- 豆科牧草和豆类 - 大豆
多年生(非木质)作物 - 指定作物:
- 甘蔗
每年的生长季节数:
- 2
具体说明:
Longest growing period in days: 6Longest growing period from month to month: corn/soySecond longest growing period in days: 3Second longest growing period from month to month: soy
注释:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): biodiversity loss, water pollution, soil erosion.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): climate change, market prices, erosion.
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Cropland: Ca: Annual cropping
3.3 由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?
由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?:
- 是(请在技术实施前填写以下有关土地利用的问题)

牧场
- Extensive grazing
3.4 供水
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 横坡措施
- terracing
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

农艺措施
- A3:土壤表面处理

植物措施
- V2:草和多年生草本植物

结构措施
- S1:阶地

管理措施
- M1:改变土地使用类型
注释:
Secondary measures: agronomic measures, vegetative measures, structural measures, management measures
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀
- Wg:冲沟侵蚀/沟蚀
- Wm:块体运动/滑坡

土壤风蚀
- Ed:风蚀风积
注释:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wg: gully erosion / gullying, Wm: mass movements / landslides, Ed: deflation and deposition
Main causes of degradation: change of seasonal rainfall, Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts)
Secondary causes of degradation: soil management, crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub), deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires), disturbance of water cycle (infiltration / runoff), change in temperature, wind storms / dust storms, floods, droughts, land tenure, labour availability, inputs and infrastructure: (roads, markets, distribution of water points, other, …), education, access to knowledge and support services, governance / institutional
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
注释:
Main goals: prevention of land degradation
Secondary goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation, rehabilitation / reclamation of denuded land
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
Terraces are planned at the desk and implemented by bull-dozers.
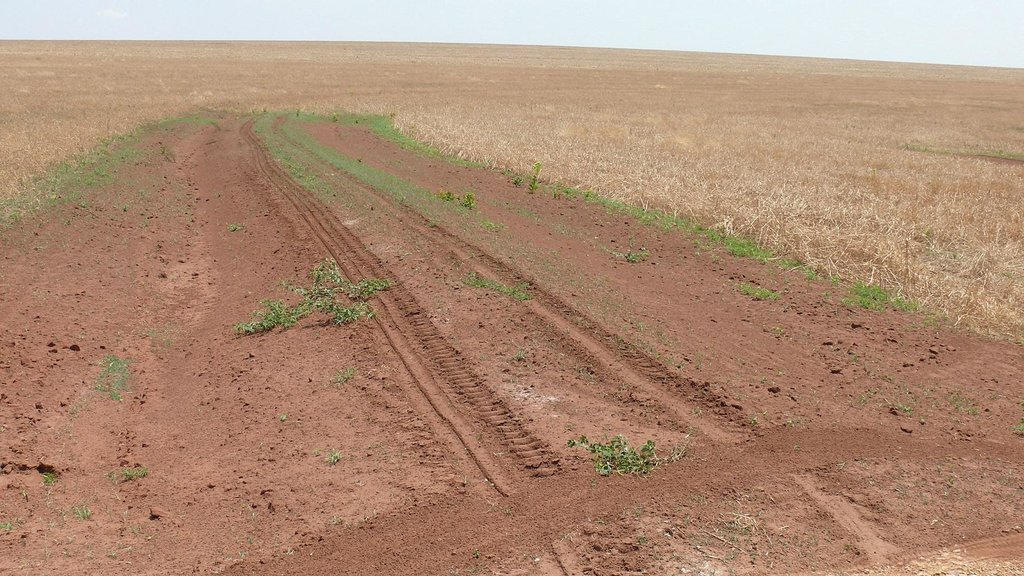
Close-up of a recently improved terrace of a slightly inclined corn field.
Location: Campo Verde. Mato Grosso
Date: 30.09.2011
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high (precision farming)
Technical knowledge required for land users: high (precision farming)
Main technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap, sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting
Secondary technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, control of concentrated runoff: impede / retard, control of concentrated runoff: drain / divert, reduction of slope angle, reduction of slope length, improvement of ground cover, increase of surface roughness, improvement of surface structure (crusting, sealing), improvement of topsoil structure (compaction), improvement of subsoil structure (hardpan), stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides), increase in organic matter, increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), increase of infiltration, increase / maintain water stored in soil, increase of groundwater level / recharge of groundwater, water harvesting / increase water supply, water spreading, improvement of water quality, buffering / filtering water, reduction in wind speed, increase of biomass (quantity), promotion of vegetation species and varieties (quality, eg palatable fodder), control of fires, reduction of dry material (fuel for wildfires), spatial arrangement and diversification of land use
Terrace: forward sloping
Vertical interval between structures (m): 5
Spacing between structures (m): 50
Terrace: bench level
Vertical interval between structures (m): 5
Spacing between structures (m): 50
Construction material (earth): 90%
Construction material (stone): 10%
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 3%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is: 2%
Lateral gradient along the structure: 1%
作者:
Hohnwald, Rotdornweg 9, 37120 Bovenden
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
Reais
如相关,注明美元与当地货币的汇率(例如1美元=79.9巴西雷亚尔):1美元=:
3.2
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
16.00
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Establishment | 3 |
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Labour | ha | 1.0 | 160.0 | 160.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Machine use | ha | 1.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 260.0 | |||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 81.25 | |||||
注释:
Duration of establishment phase: 1 month(s)
Life span of established technology: 5 years
Life span of repairs: 3 years
Number of parties sharing: 1
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | repairing | 3 |
| 2. | repairing | 1 |
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Labour | ha | 1.0 | 50.0 | 50.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Machine use | ha | 1.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 150.0 | |||||
| 技术维护总成本,美元 | 46.88 | |||||
注释:
Machinery/ tools: bulldozer
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
The costs are determined by labour time, gas costs, machinery maintenance
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
农业气候带
- 半湿润
Thermal climate class: tropics
Thermal climate class: subtropics
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
关于地形的注释和进一步规范:
Altitudinal zone: 501-1001 m a.s.l. (cerrado)
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 粗粒/轻(砂质)
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 中(1-3%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Soil fertility is low
Soil drainage/infiltration is good
Soil water storage capacity is medium
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
5-50米
地表水的可用性:
好
水质(未处理):
仅供农业使用(灌溉)
关于水质和水量的注释和进一步规范:
Availability of surface water: good, medium
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 高
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
生产系统的市场定位:
- 商业/市场
非农收入:
- 低于全部收入的10%
相对财富水平:
- 丰富
- 非常丰富
个人或集体:
- 个人/家庭
机械化水平:
- 机械化/电动
性别:
- 男人
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: < 10 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 1% - 2%
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 大规模的
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 个人,有命名
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
土地管理
社会文化影响
SLM/土地退化知识
冲突缓解
生态影响
水循环/径流
水量
地表径流
地下水位/含水层
土壤
土壤水分
土壤流失
减少气候和灾害风险
火灾风险
风速
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
旱季稳定可靠的水流
下游洪水
对邻近农田的破坏
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 增加或减少 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年温度 | 增加 | 好 |
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气象灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 局地暴雨 | 不好 |
| 局地风暴 | 不好 |
气候灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 干旱 | 好 |
水文灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 比较和缓的(河道)洪水 | 不好 |
其他气候相关的后果
其他气候相关的后果
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 缩短生长期 | 好 |
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
消极
长期回报:
稍微积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
轻度消极
长期回报:
中性/平衡
6.5 技术采用
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发的,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 91-100%
注释:
10% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
90% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Long-term soil conservation against prognosticated heavy rain fall with climate change. |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| In some cases the terraces are even exaggerated. |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块