Use of household ponds for garden irrigation and fish production. [柬埔寨]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Christoph Kaufmann
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Deborah Niggli, Alexandra Gavilano
ការប្រើប្រាស់ស្រះគ្រួសារសំរាប់ស្រោចស្រពច្បារដំណំានឹងការចឹញ្ចឹមត្រី (Khmer)
technologies_1627 - 柬埔寨
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
SLM专业人员:
Khun Lean Hak
SOFDEC/LAREC
柬埔寨
1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.4 所述技术的可持续性声明
这里所描述的技术在土地退化方面是否存在问题,导致无法被认为是一种可持续的土地管理技术?:
否
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
Ponds are used at household level to raise fish as well as to irrigate vegetable gardens and rice seedlings
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
Wet-season rice is the predominantly grown crop in the area, but some land users also grow other crops (e.g. sweet potatoes, pumpkins, or peanuts). However, if droughts occur or if the rainfall patterns are erratic, the production can be harmed. Furthermore, due to the lack of water, the land users usually leave their fields bare during the dry season. This results in an increase of wind erosion and in negative impacts on the soil biota due to its exposure to the sun.
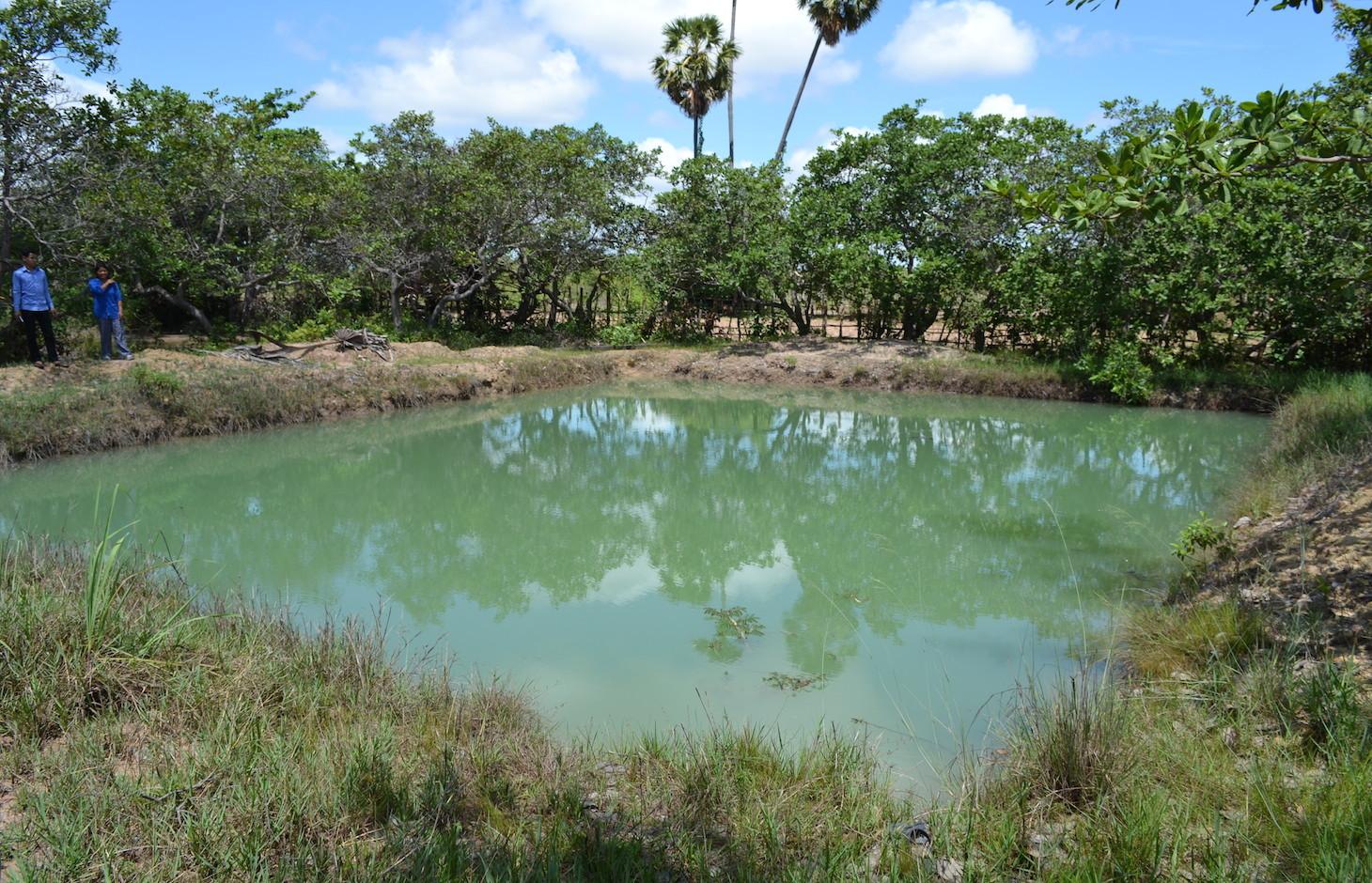
In order to tackle these challenges, ponds of 4 m depth (1 m deeper than the groundwater table during the dry season) are used at household level. By building ponds, some fields can be irrigated during the dry season, thus crops can be grown the whole year round. In this case study, sweet potatoes are the main cash crop grown on the irrigated fields during the dry season. The vines can be transplanted to the fields during the beginning of the rainy season, resulting in a better productivity of the crop. Peanuts and cucumbers are other cash crops grown on the irrigated fields.
Additionally, fish are introduced to the pond. These fish, which are caught during fishing for consumption in the flooded rice fields or nearby streams, increase the resilience of the land users: On one hand, they generate additional income and on the other hand, they allow the land users to eat fish the whole year round.
To build the ponds, the land users of this case study benefited from the road construction. The constructer needed soil, and offered to dig a pond for free if they could use the soil. They only dug 2 of the total 4 meters depth of the pond. The land users had to hire someone to dig deeper, as the groundwater level drops below 3 meters soil level during the dry season. The additional benefits from the pond, the fish are introduced as fingerlings when they are caught with the bigger fish. They are fed with termites (around 5 kg of termite nest each day) and with rice bran (1 kg every 3 days). As the pond is only 2 years old, the maintenance activities like digging out the mud did not have to be done yet.
The analysed area is flat (slope < 2%), tropic (dry and wet season), and the soils are mostly sandy or loamy. The soils contain little organic matter, the pH is sinking, the area has been deforested a long time ago and the groundwater table is rather high (1-2 m during the dry season, on the surface during wet season). and the groundwater table is rather high (3 m below soil level during the dry season, on the surface during the wet season).
Due to climate change, the rainfalls are more erratic, temperatures rise and droughts are more recurrent. Rice is the predominant crop grown in the area, since it serves as staple food (mix subsistence and commercial activities). Rice is often grown in monocultures and harvested once a year. Once the rice is harvested (dry season), some farmer release cattle to the paddy fields to eat the straw and weeds.
As an addition to rice, most land users grow vegetable and fruits in small home gardens (subsistence) and complement their income by producing handicrafts or through off farm income / remittances from family members working in other places. The increasing migration rate (the young generation leaves the villages to work in the cities, garment industry or abroad) results in a decrease of available labour force in the area which has detrimental effects on the agricultural activities. Furthermore, the civil war in the 1970s (Khmer Rouge) led to the loss of agricultural knowledge that different NGOs try to re-establish.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
柬埔寨
区域/州/省:
Kampong Chhnang
有关地点的进一步说明:
Roloer pha-er/Bantheay Preal/Tob Srauv (Village)
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果不知道精确的区域,请注明大致覆盖的区域:
- < 0.1 平方千米(10 公顷)
注释:
There are 4 ponds in the village. They are used to irrigate the rice seedlings if the rainy season starts with delay, or if there is a drought after the seeding. In the dry season they are used to irrigate vegetables. Total area of the irrigated fields is around 1 ha.
2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 不到10年前(最近)
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过土地使用者的创新
注释(项目类型等):
The pond was built in 2012 by the land user.
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 改良生产
- 创造有益的经济影响
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

农田
- 一年一作
- rice
每年的生长季节数:
- 1
具体说明:
Longest growing period in days: 210, Longest growing period from month to month: June to December

水道、水体、湿地
- 池塘、大坝
注释:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Low soil fertility, lack of water during the dry season, more recurrent droughts due to climate change, leaving the fields bare after the rice is harvested which results in higher erosion and in the loss of soil biota, predominance of rice monocultures, low technical knowledge of the land users about land conservation measures.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Droughts, especially in the early rainy season. Rice seedlings need a reliable source of water.
3.4 供水
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 混合雨水灌溉
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 灌溉管理(包括供水、排水)
- 地表水管理(泉、河、湖、海)
- 养蜂、养殖业、家禽业、养兔业、养蚕业等
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

结构措施
- S4:平沟、坑
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

生物性退化
- Bq:数量/生物量减少

水质恶化
- Ha:干旱化
注释:
Main causes of degradation: crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (Mainly annuals with high water demand are planted.)
Secondary causes of degradation: soil management (Ploughing of soil, lack of water retention.), change in temperature (More hot days, drying up the soil.), change of seasonal rainfall (Beginning of rain season is unpredictable.), droughts (.Especially detrimental in the beginning of the monsoon.), education, access to knowledge and support services (A lot of agricultural knowledge was lost during the Khmer Rouge Regime.)
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 防止土地退化
- 减少土地退化
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
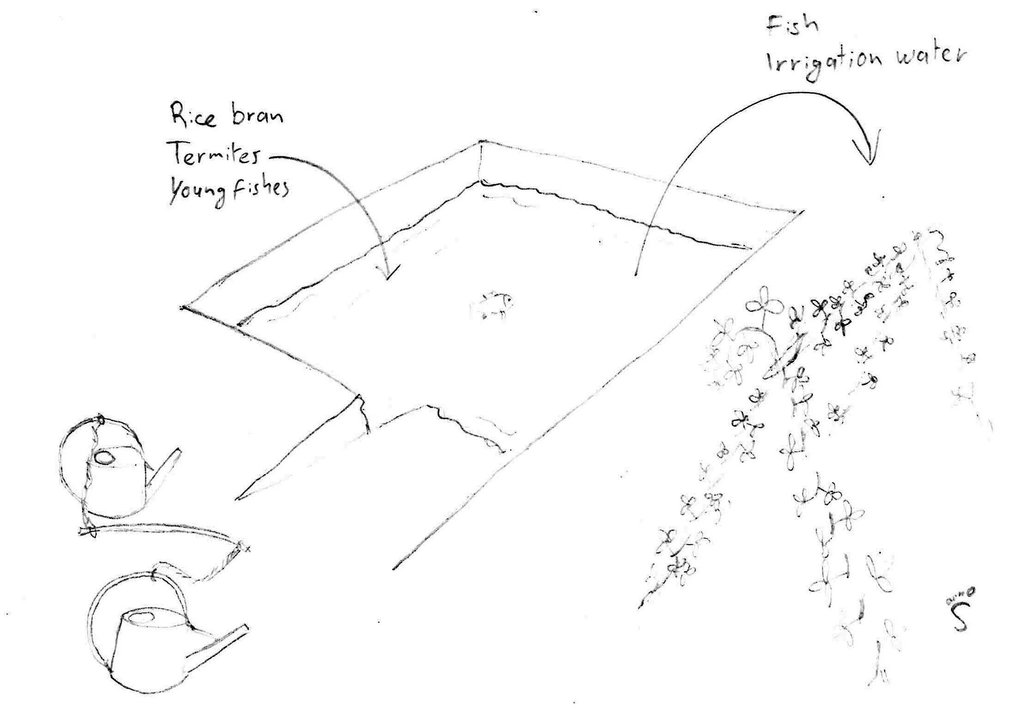
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
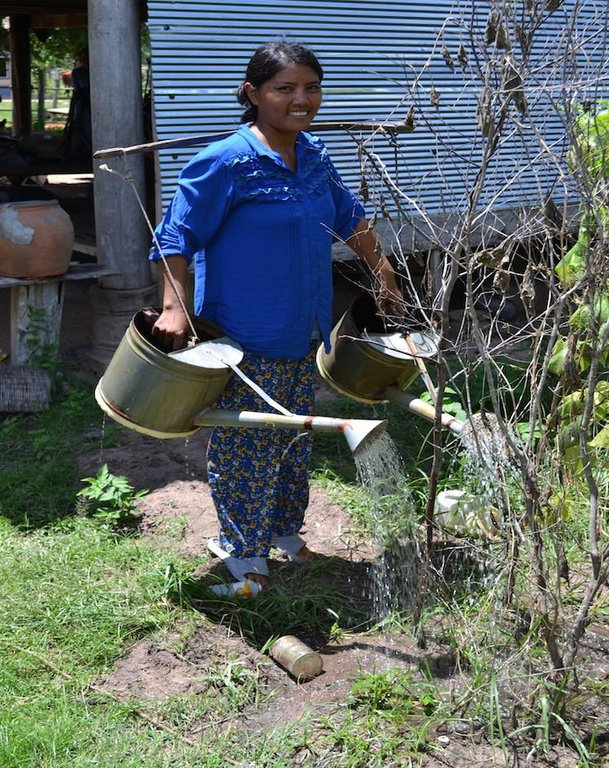
Pond used for irrigation as well as for fish production. In this case two watering cans are used, with a stick between them to transfer the weight to the shoulders.
Kampong Chhnang
Date: 2014
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: low (No field staff was involved.)
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: water harvesting / increase water supply
Dam/ pan/ pond
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 4
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 12
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 18
Specification of dams/ pans/ ponds: Capacity 800m3
Catchment area: ground waterm2
作者:
Stefan Graf, Switzerland
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
5.00
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Dig the first 2 m | Dry season |
| 2. | Dig the last 2 m | Dry season |
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 设备 | machine use | 1.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 50.0 | |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 100.0 | |||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 100.0 | |||||
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Catch and select fingerlings in the rice fields and canals. | Every year during wet season |
| 2. | Select fingerlings from catch in local streams to add in pond. | Every year during dry season. |
| 3. | Dig out the pond. Not yet done, as the pond is still new. | |
| 4. | Feed the fish with termites and rice bran. | Regularly. |
| 5. | Fertilize the pond | Yearly in the beginning of the wet season |
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | labour | 1.0 | 134.5 | 134.5 | 100.0 | |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 134.5 | |||||
| 技术维护总成本,美元 | 134.5 | |||||
注释:
Machinery/ tools: Fishing traps. 1 costs around 1.2 US$. Fishing net, around 6.5 US$. They had them anyway to catch fish for consumption.
The costs were calculated for one pond, as the area is not relevant.
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
The most expensive factor is the availability of an excavator to dig the pond.
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
有关降雨的规范/注释:
1486.45 mm (2013) in Kampong Chhnang
农业气候带
- 半湿润
Thermal climate class: tropics. 27-35°C
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 粗粒/轻(砂质)
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 中(1-3%)
- 低(<1%)
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
< 5米
地表水的可用性:
匮乏/没有
水质(未处理):
不良饮用水(需要处理)
关于水质和水量的注释和进一步规范:
Ground water table: during dry season
Availability of surface water: during dry season
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 中等
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
生产系统的市场定位:
- 混合(生计/商业)
非农收入:
- 收入的10-50%
相对财富水平:
- 平均水平
- 丰富
个人或集体:
- 个人/家庭
机械化水平:
- 手工作业
- 机械化/电动
性别:
- 女人
- 男人
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly Leaders / privileged
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 0.5% - 1%
Off-farm income specification: Handicraft, remittances, factory work
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 小规模的
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 社区/村庄
- 个人,未命名
土地使用权:
- 社区(有组织)
- 个人
用水权:
- 自由进入(无组织)
注释:
Land users have a title that is not recognized by the state.
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
畜牧生产
注释/具体说明:
Fish
生产故障风险
产品多样性
生产区域
收入和成本
农业收入
收入来源的多样性
社会文化影响
食品安全/自给自足
contribution to human well-being
注释/具体说明:
Ponds allow the land user to grow crops the whole year round. Furthermore, there are fish in the pond which provide a reliable source of food.
生态影响
水循环/径流
水量
土壤
土壤水分
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 增加或减少 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年温度 | 增加 | 好 |
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气象灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 局地暴雨 | 好 |
| 局地风暴 | 好 |
气候灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 干旱 | 好 |
水文灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 比较和缓的(河道)洪水 | 不好 |
其他气候相关的后果
其他气候相关的后果
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 缩短生长期 | 好 |
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
轻度消极
长期回报:
积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
积极
6.5 技术采用
- > 50%
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发的,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 0-10%
注释:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
The farmer from this case study got a kind of subsidy: For the construction of the nearby road, the builders needed soil. They offered to dig a pond if they could get the soil. They only dug 2 of the 4 meters of the pond debt, the farmer had to hire somebody to dig out the rest. The other land users who have implemented the ponds also collaborated with construction workers to dig the pond. The lack of money hinders most of the farmers to implement the technology.
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Water available in the dry season for cash crops. The rice fields can be used in the dry season instead of being left bare. |
| The rice seedlings can be irrigated during the early wet season in case of drought or erratic rainfall. |
| Diversification of diet and income: fish is available the whole year round. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| As parts of the rice fields are irrigated and planted during the dry season, there is less wind erosion and the soil is improving. |
| The fish feed (rice bran and termites) consists of local resources. |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| If flooded the fish can go away. | Nets need to be put around the pond in the wet season. This farmer already does this. |
| Fingerlings are difficult to find. | Find a fish breeder, or breed fish by themselves. Creating niches in the ponds for the offspring, where the bigger fish do not eat it, could do the breeding. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Fingerlings of different sizes and species are put into the pond. The bigger eat the smaller. | Fence off areas for bigger fish, and move the big fish there so they cannot catch the smaller. Or build structures where the smaller fish can hide. |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
- 实地考察、实地调查
- 与土地使用者的访谈
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
07/07/2014
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Konhel Pith, Local Agricultural Research and Extension Centre LAREC in Kampong Chhnang; khonhel@gmail.com
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块