Subsoiling [中国]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Zhanguo Bai
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
Shen Song
technologies_972 - 中国
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
SLM专业人员:
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
ISRIC World Soil Information (ISRIC World Soil Information) - 荷兰1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
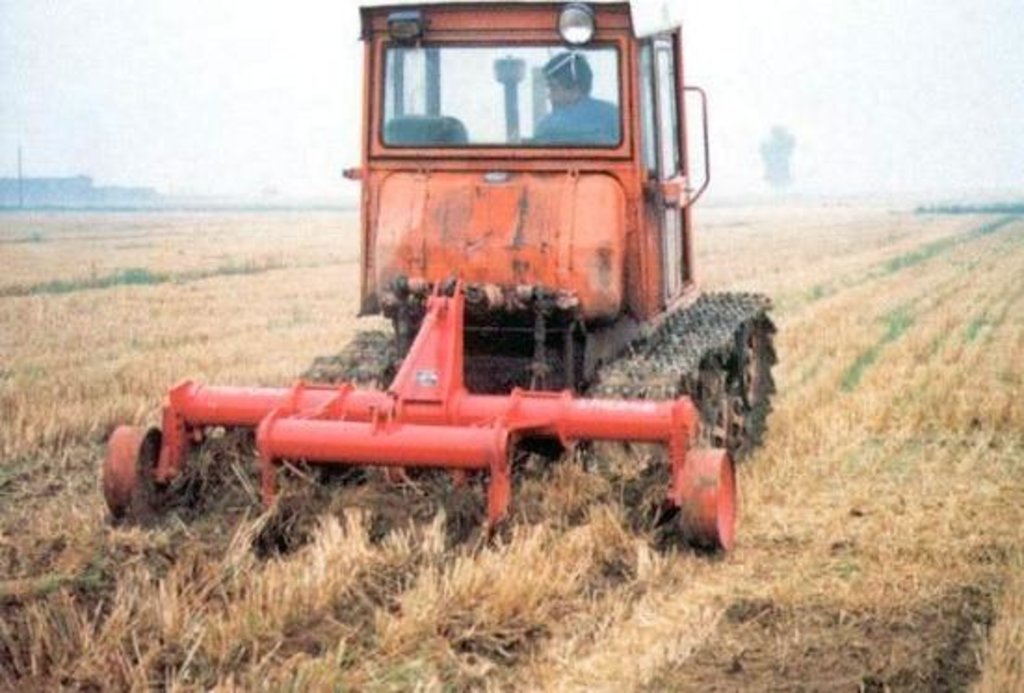
Subsoiling with mulching is cultivated using plough without disturbance of surface soils but loosing the subsoils.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
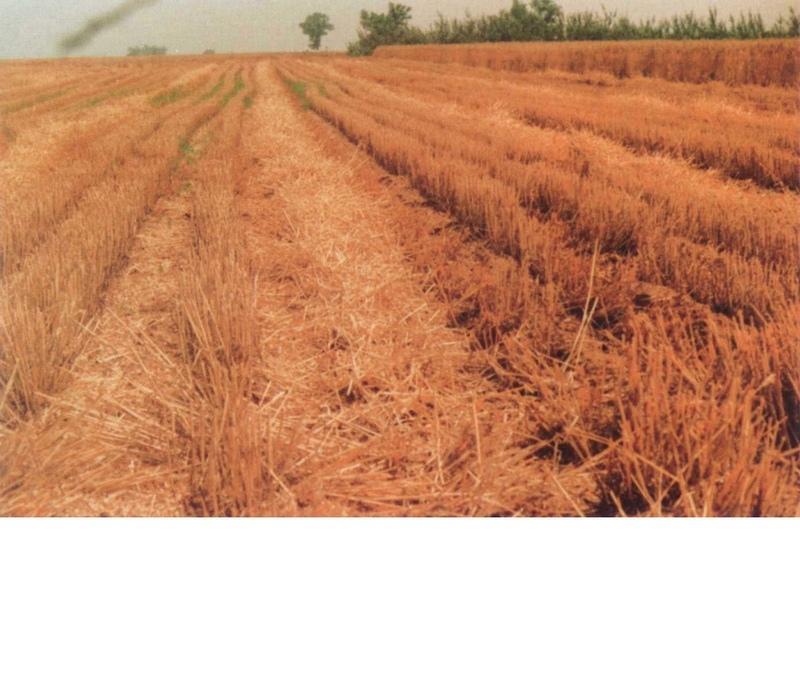
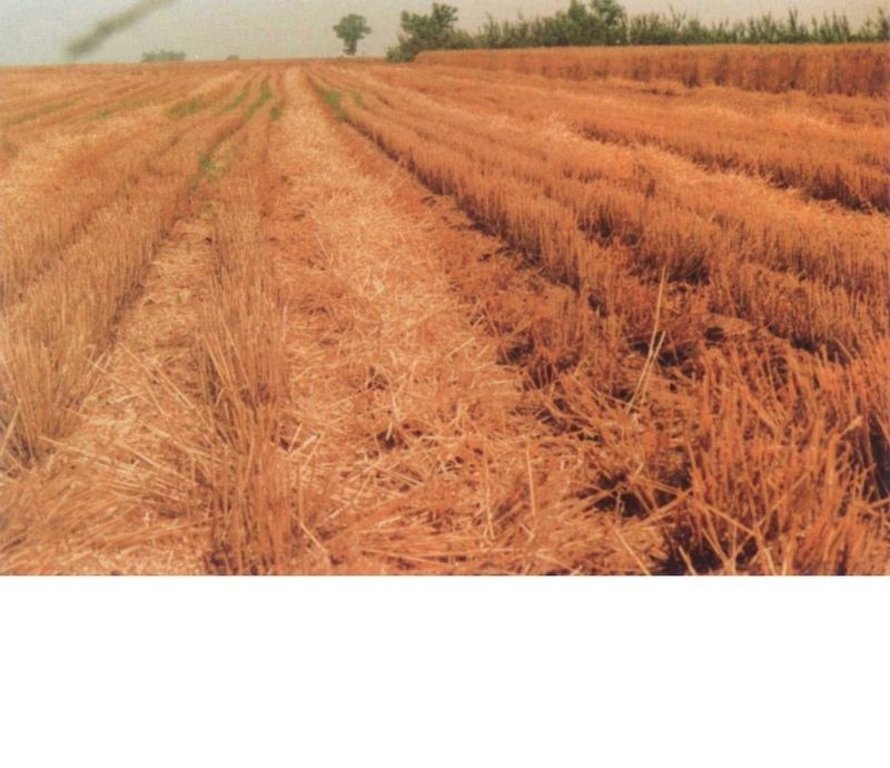
Subsoiling with mulching is one of the conservation tillage technology, it is to deep till to loose subsoils without disturbance of surface soils, it is combed with residuals coverage(straw). The purpose of the technology is to let all rainfall infiltrate in soil without runoff occur and incease soil moisture and organic matter content in order to raise yield.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
中国
区域/州/省:
Henan province
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果技术均匀分布在一个区域,则指定覆盖的区域(单位为平方千米):
2900.0
如果不知道精确的区域,请注明大致覆盖的区域:
- 1,000-10,000 平方千米
注释:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 2900 km2.
This technique has been successfully applied in the slope farmland, especially in the loess plateau and in the dry-semidry regions in the NW china. It is an ideal technology to let all precipitation in soils and decrease soil water loss in slope farmland.
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 不到10年前(最近)
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过项目/外部干预
注释(项目类型等):
USA, Canada
3. SLM技术的分类
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

农田
- 一年一作
年作 - 具体指明作物:
- 谷物类 - 玉米
- 谷类 - 小麦(冬季)
- 根/块茎作物 - 红薯、山药、芋头/椰子,其他
每年的生长季节数:
- 1
具体说明:
Longest growing period in days: 240Longest growing period from month to month: Oct - JunSecond longest growing period in days: 90Second longest growing period from month to month: Jul - Sep
注释:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Traditional tillage (multi-tillage) has made soil loose and easily being moved on the dry and semi-dry farmland. Subsoiling is a suitable way for slope cultivated land in keeping rainfall in soil with mulching that enhance content of soil organic matter and reducing wind erosion.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Practical and low input by using this technology, also easy to operate.
Type of cropping system and major crops comments: Winter wheat--corn/sweet potato--winter wheat
3.4 供水
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 最小的土壤扰动
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

农艺措施
- A3:土壤表面处理
注释:
Type of agronomic measures: mulching, minimum tillage
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀

化学性土壤退化
- Cn:肥力下降和有机质含量下降(非侵蚀所致)
注释:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content
Main causes of degradation: other natural causes (avalanches, volcanic eruptions, mud flows, highly susceptible natural resources, extreme topography, etc.) specify, traditional customs (multi-till)
Secondary causes of degradation: other human induced causes (specify) (agricultural causes), land tenure (land subdivision - National stratergy)
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 减少土地退化
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: improvement of ground cover, increase in organic matter, increase of infiltration, increase / maintain water stored in soil, water harvesting / increase water supply, water spreading, increase in soil fertility
Mulching
Material/ species: straw
Quantity/ density: entire
Remarks: leaving wheat straw when harvest
Minimum tillage
Material/ species: using subsoiling plough
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
具体说明成本计算所用货币:
- 美元
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
5.00
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
注释:
Duration of establishment phase: 96 month(s)
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Leaving straw | summer / twice |
| 2. | Subsoiling | summer / once |
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
注释:
At beginning much more input are tillage tools such as subsoiling plough, tractor etc.
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
subsoiling plough, tractor
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
指定年平均降雨量(若已知),单位为mm:
646.00
农业气候带
- 半干旱
- 干旱
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
说明该技术是否专门应用于:
- 不相关
关于地形的注释和进一步规范:
Landforms are also : valley floors and mountain slopes
Slopes can also be: hilly or steep
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
- 细粒/重质(粘土)
土壤质地(地表以下> 20厘米):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
- 细粒/重质(粘土)
表土有机质:
- 中(1-3%)
- 低(<1%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Soil depth on average: Also very shallow
Soil fertility: medium or low
Soil drainage / infiltration: good or medium
Soil water storage capacity: medium or low
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
非农收入:
- 低于全部收入的10%
相对财富水平:
- 平均水平
- 丰富
机械化水平:
- 畜力牵引
- 机械化/电动
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Population density: 100-200 persons/km2
Annual population growth: < 0.5%
20% of the land users are rich and own 80% of the land.
80% of the land users are average wealthy and own 20% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: Yield increase in about 20% compared to that SWC not be applied
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 州
- 社区/村庄
土地使用权:
- 租赁
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
生态影响
水循环/径流
地表径流
SLM之前的数量:
30
SLM之后的数量:
5
土壤
土壤流失
SLM之前的数量:
50
SLM之后的数量:
5
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
非常积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
非常积极
6.5 技术采用
- 11-50%
如若可行,进行量化(住户数量和/或覆盖面积):
1535 households (36 % of area)
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发的,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 0-10%
注释:
30% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
1500 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: estimates
5% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
35 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: estimates
There is a strong trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Those who applied the technology have gained great return from the SWC implementation and others try to adopt.
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
A road map from conventional to no-till farming. 2002.
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
World Bank
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Conservation agriculture. 2001.
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
FAO
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Report of ninth-Five plan project on Dryland Farming. Jan, 2002.
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
internal materials
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Introduction of Luoayng physicography. 2000.
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
unpublished reference
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
No-till farming for sustainable rural development. 2002.
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
World Bank
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块