Apocynum planting to protect and profit from saline soils in the Tarim River Basin, north-west China [中国]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Christian Rumbaur
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: David Streiff, Deborah Niggli, Rima Mekdaschi Studer
罗布红麻 and 罗布百麻 (Chinese)
technologies_1721 - 中国
- Apocynum planting to protect and profit from saline soils in the Tarim River Basin, north-west China: March 9, 2017 (inactive)
- Apocynum planting to protect and profit from saline soils in the Tarim River Basin, north-west China: April 4, 2018 (inactive)
- Apocynum planting to protect and profit from saline soils in the Tarim River Basin, north-west China: March 19, 2019 (public)
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
SLM专业人员:
Rouzi Ahmatjan
Catholic University Ingolstadt-Eichstaett
德国
SLM专业人员:
Thevs Niels
World Agroforestry Center, University of Central Asia
吉尔吉斯斯坦
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
Sustainable Management of River Oases along the Tarim River, China (SuMaRiO / GLUES)有助于对技术进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
Book project: Making sense of research for sustainable land management (GLUES)有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Catholic University Ingolstadt-Eichstaett (KU) - 德国有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
International Centre for Research in Agroforestry (ICRAF) - 肯尼亚1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
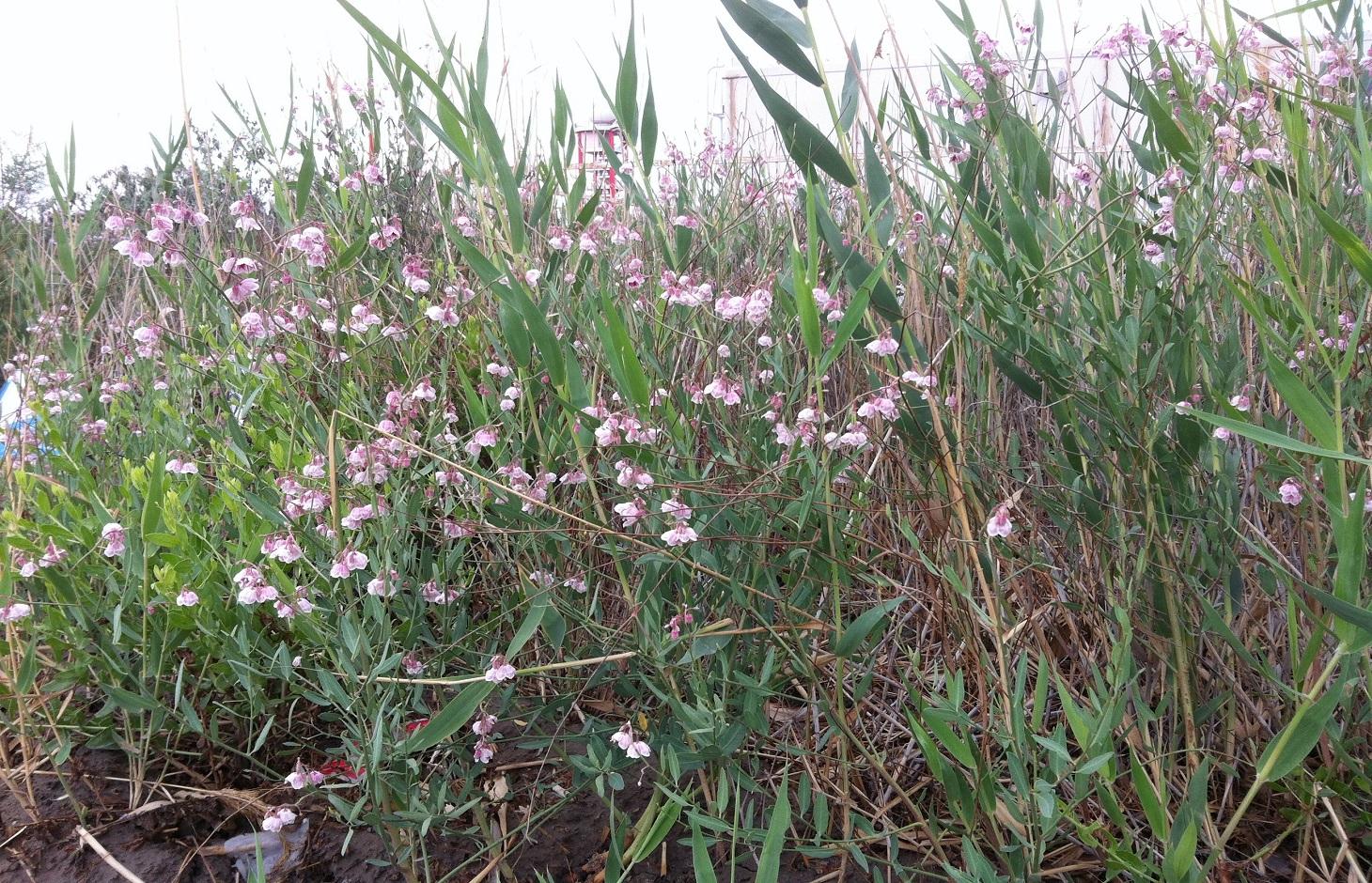
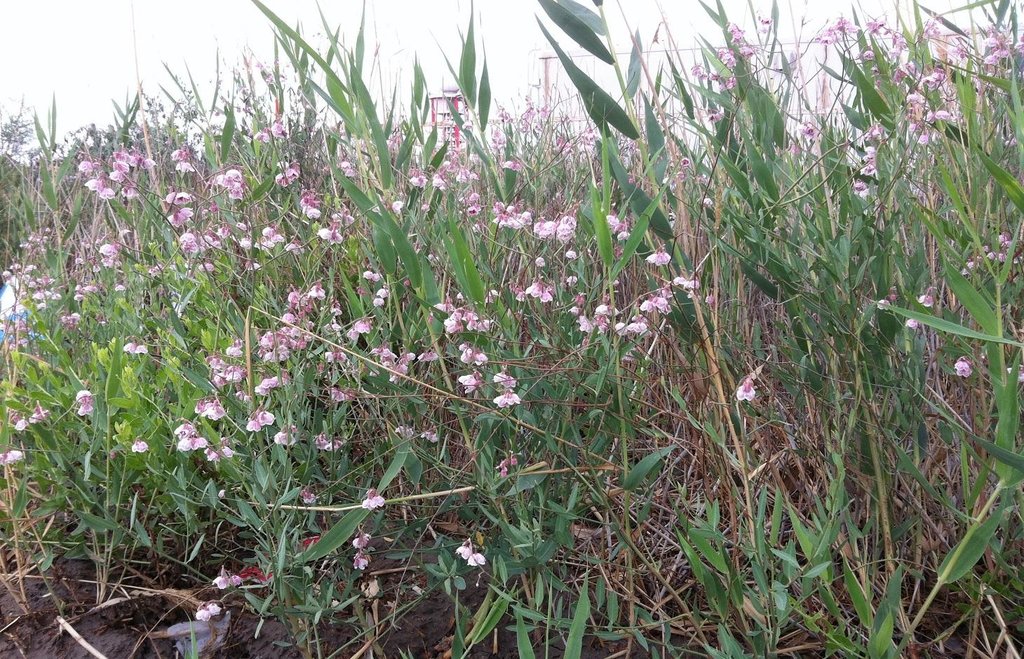
Plantation of Apocynum pictum and Apocynum venetum as protective and profitable indigenous plants - on soils made saline through irrigation of cotton without adequate drainage.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
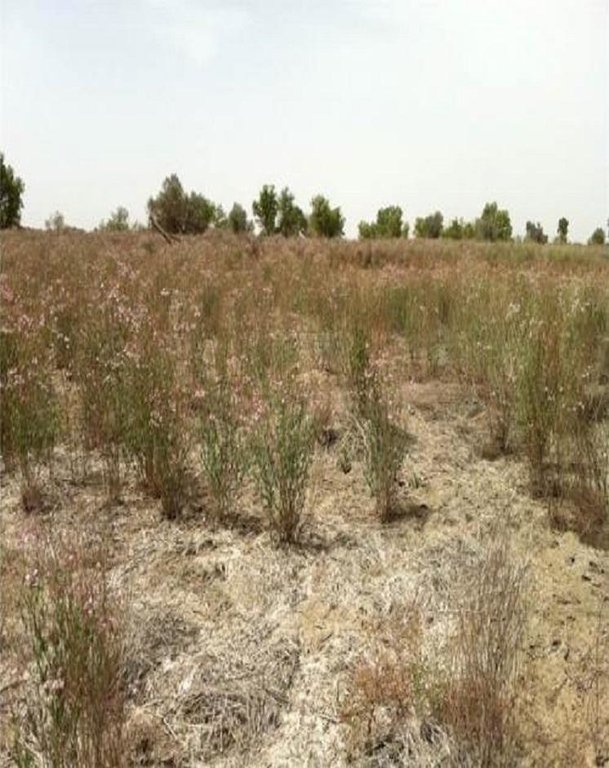
The natural ecosystems in north-west China, especially in Xinjiang Province, are dominated by steppes, semi-deserts and desert. Riparian forests along the Tarim River Basin have been reduced and degraded by the expansion of irrigated agriculture since the 1950s. The main crop planted is cotton. In the arid temperate cold desert climate, precipitation is very low and evaporation high. The only water source for the region is the Tarim River. Xinjiang is being promoted to become the main cotton production area of China, especially in the upper reaches of the Tarim River, and reservoirs with a large irrigation infrastructure have been established. Farmers water their fields with flood and drip irrigation. But most of the fields have no drainage system. With the high evaporation and the capillary rise of the shallow groundwater, salts dissolved in the water accumulate on the soil surface and in the soil. This salinization makes the fields unusable for cotton production and are abandoned as farmers move on. These barren saline soils are prone to wind erosion, as almost no plants can grow on them. Large-scale desertification is the result.
Purpose of the Technology: To halt desertification the barren saline soils need to be protected by vegetation to avoid soil loss by wind. But if this can be done through vegetation that yields an income then the advantage is double: a win-win situation. Apocynum venetum and Apocynum pictum are indigenous and both are drought and salt tolerant. They are phreatophytes: deep-rooted plants that tap groundwater or the soil layer just above the water table. A.venetum and A. pictum are rhizomatous perennials – and importantly they are cash crops too. Fibre from the stems are used to produce textiles, though the extraction process is time and labor consuming. The advantage of apocynum yarn is that it has antibacterial properties. The leaves and flowers are also sold and used to produce tea which is a Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) that reduces blood pressure. On a per hectare basis, the stem generates a potential income of US$ 3,650, the leaves US$ 1,995, and the flowers US$ 1,815: nevertheless the market for apocynum products is small. In Xinjiang most of the apocynum plantations are under commercial large-scale farmers. They have the capital to deal with the costly establishment of apocynum.
Natural / human environment: Fields on which apocynum is sown should have a groundwater level not deeper than 2m. Nevertheless the soil should be well-drained: best is a sandy loam. Waterlogged, calcareous, clayey soils are not suitable. Apocynum can withstand periods of water inundation; however, prolonged submergence or waterlogging inhibits its growth. The topsoil under apocynum is often saline, reaching salt contents of up to 20%. Apocynum can grow on sites with a pronounced surface salinization, as long as the subsoil and the groundwater are not strongly salinized. There are two methods of planting apocynum: by seed or by vegetative means. While irrigation helps establishment and good yields, this is at a much lower level than for cotton. In conclusion, A.venetum and A. pictum provide profitable options on saline soils, grow with minimal irrigation, and protect the land against wind erosion.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
中国
区域/州/省:
China / Xinjiang Province
有关地点的进一步说明:
Tarim River Basin
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果技术均匀分布在一个区域,则指定覆盖的区域(单位为平方千米):
6000.0
注释:
Boundary points of the Technology area: Location in China between 37°~46°N and 76°~104°E. Location in Tarim River Basin: 41°12'34.94"N and 84°19'28.19"E
In China the area of Apocynum vegetation, natural or artificial, amounts to 1,330,000 ha. One third to half of this area is located in Xinjiang, ie approximately 600,000 ha
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 50多年前(传统)
2.7 技术介绍
- naturally
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
- 创造有益的经济影响
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

农田
- 一年一作
- 多年一作(非木材)
- 乔木与灌木的种植
年作 - 具体指明作物:
- 纤维作物 - 棉花
- wheat
- Apocynum
每年的生长季节数:
- 1
具体说明:
Longest growing period in days: 220Longest growing period from month to month: March to October with irrigation
注释:
Apocynum venetum and Apocynum pictum
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Salinization, desertification, mismanagement of cotton monoculture, inadequate drainage under irrigation, abandonment of degraded land.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Water scarcity, salinization, land use rights.
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Cropland: Ct: Tree and shrub cropping
Constraints of wastelands / deserts / glaciers / swamps: salt crust on the top soil layer and high salt content in the soil
3.3 由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?
由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?:
- 是(请在技术实施前填写以下有关土地利用的问题)

农田
- 一年一作

不毛之地
具体说明:
Desertification: Wastelands, deserts, glaciers, swamps, recreation areas, etc
3.4 供水
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 混合雨水灌溉
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 防风林/防护林带
- 改良植物品种/动物品种
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

植物措施
- V1:乔木和灌木覆盖层

管理措施
- M1:改变土地使用类型
注释:
Main measures: vegetative measures, management measures
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -graded strips *<sup>3</sup>, scattered / dispersed
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤风蚀
- Et:表土流失

化学性土壤退化
- Cs:盐化/碱化

生物性退化
- Bc:植被覆盖的减少
- Bh:栖息地丧失
- Bq:数量/生物量减少
- Bs:质量和物种组成/多样性的下降
注释:
Main type of degradation addressed: Et: loss of topsoil, Cs: salinisation / alkalinisation, Bc: reduction of vegetation cover, Bh: loss of habitats, Bq: quantity / biomass decline, Bs: quality and species composition /diversity decline
Main causes of degradation: soil management (Most fields have no drainage -> Increase of groundwater -> salinisation of soils), crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (Cotton monocultures), wind storms / dust storms (Duststorms, blow ou tof topsoil), droughts (It is an arid climate), population pressure (doubling the population during the last thirty years), land tenure (land belongs to the state), education, access to knowledge and support services (poorer farmers have less access to extension services)
Secondary causes of degradation: discharges (point contamination of water) (Non-point source pollution and drainage water discharge from the fields), disturbance of water cycle (infiltration / runoff) (Most fields have no drainage -> Increase of groundwater -> salinisation of soils), floods (Floods are necessary for the region (riparian forests)), poverty / wealth (family farmers are poorer than city dwellers)
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 修复/恢复严重退化的土地
注释:
Main goals: rehabilitation / reclamation of denuded land
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
Apocynum planted in a levelled field with strips of 8 to 18 cm height and 30 to 40 cm width with 40 cm space between each strip
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate (for regeneration and multiplication)
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: improvement of ground cover, stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides), promotion of vegetation species and varieties (quality, eg palatable fodder)
Secondary technical functions: reduction in wind speed
Aligned: -graded strips
Vegetative material: C : perennial crops
Number of plants per (ha): 20,000
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 0
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.4
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.3 to 0.4
Scattered / dispersed
Vegetative material: C : perennial crops
Number of plants per (ha): 60,000 to 70,000
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.3
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.3
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.3
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.3
Gradient along the rows / strips: 0%
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
具体说明成本计算所用货币:
- 美元
如相关,注明美元与当地货币的汇率(例如1美元=79.9巴西雷亚尔):1美元=:
-0.42
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Manuring (3700 to 5000 kg/ha) and ploughing | Before sowing |
| 2. | Site establishment/ preparation | |
| 3. | Planting of seedlings/ root cuttings/ transplants | most suitable seeding time is mid April to May or transplantation |
| 4. | Irrigation at establishment (10000-12000 m3/ha) | After sowing |
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Site establishment/ preparation | ha | 2.0 | 18.7 | 37.4 | 100.0 |
| 植物材料 | Seeds | ha | 100.0 | 2.5 | 250.0 | |
| 植物材料 | Seedlings | ha | 100.0 | 6.18 | 618.0 | |
| 其它 | Manure | ha | 171.1 | 18.7 | 3199.57 | 100.0 |
| 其它 | Waterfee | - | 1.0 | 460.0 | 460.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 4564.97 | |||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | -10868.98 | |||||
注释:
Duration of establishment phase: 15 month(s)
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | irrigation and weeding labor | 6 times |
| 2. | Fertilizer | |
| 3. | Harvest labor | at harvest |
| 4. | Transport | after harvest |
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | irrigation and weeding labor | ha | 10.0 | 114.0 | 1140.0 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Harvest labor | ha | 1.0 | 359.0 | 359.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Transport | ton | 1.0 | 11.0 | 11.0 | 100.0 |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | Fertilizer (Phosporus) | kg | 150.0 | 4.12 | 618.0 | |
| 其它 | Waterfee | 1.0 | 2280.0 | 2280.0 | ||
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 4408.0 | |||||
| 技术维护总成本,美元 | -10495.24 | |||||
注释:
Machinery/ tools: hoe, shovel, tractor and plough
Costs were calculated for 2015, per hectare. Labour has become more expensive over the last few years. In the beginning (first two years) cultivation of apocynum is very labour and input intensive. After 1.5 to 2 years the plants can be harvested for the first time. The price for the products of apocynum (leafs and stems) are very high. Direct seeding as compared to vegetative propagation is the most labour-saving method to cultivate apocynum.
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
有关降雨的规范/注释:
Per year: 90 mm; Jan, Feb, Apr, May: 3 mm; Mar, Sept: 5mm; Jun: 33 mm; Jul: 18 mm; Oct: 0 mm; Dec: 8 mm
农业气候带
- 干旱
Thermal climate class: temperate. cold desert climate
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
说明该技术是否专门应用于:
- 不相关
关于地形的注释和进一步规范:
Altitudinal zone: Altitude between 800 and 1300 m
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 粗粒/轻(砂质)
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 低(<1%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Soil fertility: low - medium
Soil drainage / infiltration: medium
Soil water storage capacity: medium - high
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
5-50米
地表水的可用性:
好
水质(未处理):
不良饮用水(需要处理)
关于水质和水量的注释和进一步规范:
Ground water table also < 5 m: Apocynum is a phreatophyte. The most productive sites of Apocynum venetum are found on a groundwater not deeper than 3 m with salt contets between 1g/l and 10g/l.
Ground water table 5-50 m: Apocynum pictum is mainly found on groundwater levels of 4-6m below surface with a maximum groundwater depth of 8 m. Apocynum is restricted to groundwater levels not deeper than 4 m below surface.
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 中等
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
生产系统的市场定位:
- 商业/市场
非农收入:
- 低于全部收入的10%
相对财富水平:
- 丰富
- 非常丰富
个人或集体:
- 团体/社区
机械化水平:
- 手工作业
- 机械化/电动
性别:
- 男人
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Difference in the involvement of women and men: Man are doing the hard work in the fields, women do more the harvesting
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: > 4%; 7%
5% of the land users are very rich and own 10% of the land.
20% of the land users are rich and own 30% of the land.
40% of the land users are average wealthy and own 30% of the land.
30% of the land users are poor and own 20% of the land.
5% of the land users are poor and own 10% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: The plantation of Apocynum brings a high income to the farmers.
Level of mechanization manual labour: harvesting
Market orientation of production system commercial/ market: Apocynum is planted for fibre, tea and medicinal products
Level of mechanization mechanized/motorized: field preparation
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 中等规模的
注释:
< 0.5 ha: family farms
5-15 ha: state farms
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 州
土地使用权:
- 社区(有组织)
- 租赁
用水权:
- 社区(有组织)
- 租赁
注释:
All the land belongs to the state. Farmers have the right to use the land for 70 years.
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
木材生产
生产故障风险
产品多样性
生产区域
水资源可用性和质量
灌溉用水需求
收入和成本
农业投入费用
农业收入
收入来源的多样性
工作量
其它社会经济效应
market for apocynum fibre
market for TCM
社会文化影响
文化机会
娱乐机会
冲突缓解
Livelihoods and human well-being
生态影响
水循环/径流
水量
水质
多余水的排放
土壤
土壤水分
土壤覆盖层
土壤流失
土壤结壳/密封
土壤有机物/地下C
生物多样性:植被、动物
生物量/地上C
植物多样性
栖息地多样性
减少气候和灾害风险
风速
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
地下水/河流污染
风力搬运沉积物
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 增加或减少 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年温度 | 增加 | 未知 |
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气象灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 局地暴雨 | 好 |
| 局地风暴 | 好 |
气候灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 干旱 | 好 |
水文灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 比较和缓的(河道)洪水 | 不好 |
其他气候相关的后果
其他气候相关的后果
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 缩短生长期 | 未知 |
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
消极
长期回报:
非常积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
轻度消极
长期回报:
非常积极
注释:
In the beginning (first two years) the plantation of Apocynum is very labour and input intensive. After 1.5 to 2 yearsthe plants can be harvested for the first time. The price for the producst of Apocynum (leafs and stems) are very high.
6.5 技术采用
如若可行,进行量化(住户数量和/或覆盖面积):
No number on households
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发的,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 91-100%
注释:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: Most of the plantations are planted by large investing farmers. The farmers sell the products of Apocynum to the pharmaceutical companies for Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM)
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
Both species yield fibres and leaves for fiber production and the leaves for medicinal products or tea on considerable areas under the arid climate of Xinjiang Province, China, without intensive irrigation, because they use the groundwater as for example cotton. Furthermore, both species can withstand higher soil salinization levels than cotton. How can they be sustained / enhanced? The plantations can be enhanced by analyzing the water consumption and the water use efficiency to apply only as much water to the plants as they need Not decreasing the yields. |
|
Both species can provide an income to local people - fibre and leaves for medicinal products or tea - under conditions which are unfavorable to grow crops under irrigation. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Promote apocynum on saline wastelands and subsidize the establishment of the plantations. Explore further markets and promote the products. |
|
Through apocynum plantations wastelands are reclaimed. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Highlight the potential to reduce wind erosion and ‘dust bowls’. |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Difficult process to extract fibre from the stems. | New technology needs to be developed. |
| Small market. | New uses need to be explored to expand the market. |
| High investment in the beginning of the plantation. | Planting of apocynum should be subsidized. |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
N Thevs et al. (2012) Apocynum venetum L. and Apocynum pictum Schrenk (Apocynaceae) as multi-functional and multi-service plant species in Central Asia: a review on biology, ecology, and utilization.
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
Journal of Applied Botany and Food Quality 85, 159-167.
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块