No-tillage [爱沙尼亚]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Endla Reintam
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Ursula Gaemperli, Gudrun Schwilch, Alexandra Gavilano
Otsekülv
technologies_3089 - 爱沙尼亚
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
土地使用者:
Tobreluts Toomas
Pirmastu OÜ
爱沙尼亚
researcher:
Penu Priit
Estonian Agricultural Research Centre
爱沙尼亚
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
Interactive Soil Quality assessment in Europe and China for Agricultural productivity and Environmental Resilience (EU-iSQAPER)1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.4 所述技术的可持续性声明
这里所描述的技术在土地退化方面是否存在问题,导致无法被认为是一种可持续的土地管理技术?:
否
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
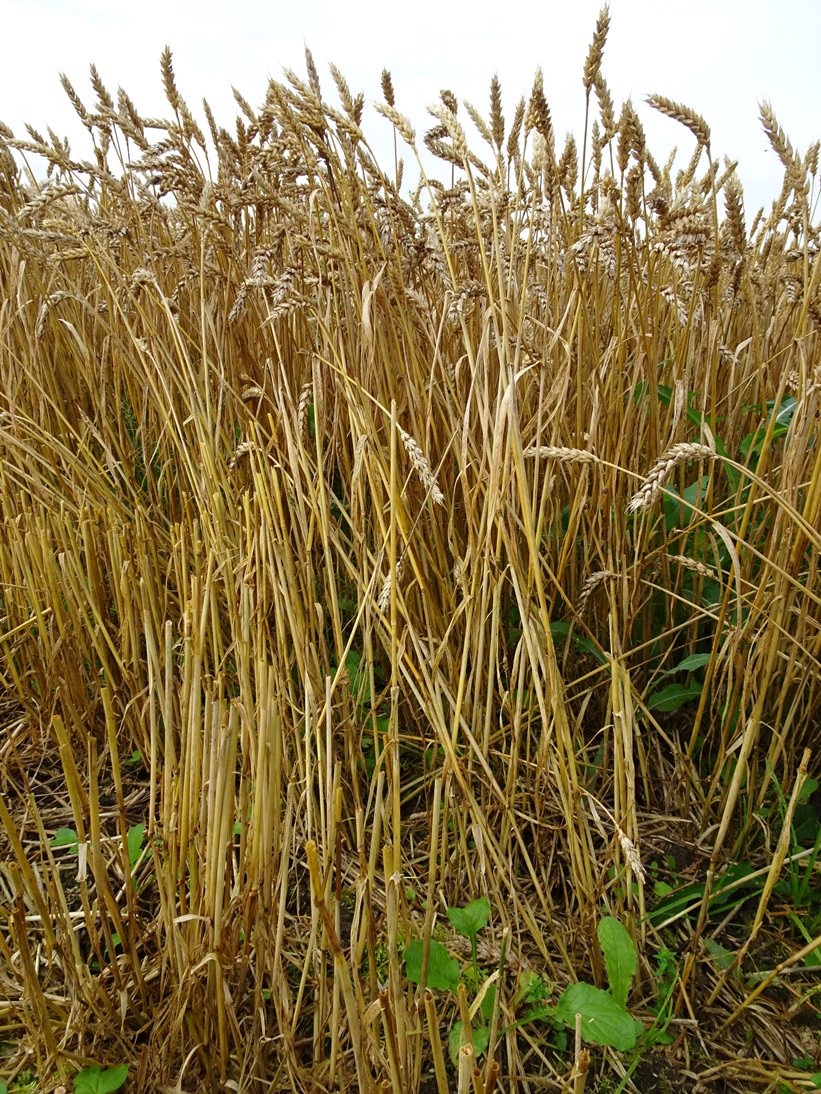
No-till farming (also called zero tillage or direct drilling) is a way of growing crops or pasture from year to year without disturbing the soil through tillage.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
The technology is applied in sub-humid climate with an average of 696 mm of precipitations per year, from which more comes from July to October and less in March and April. Average annual temperature is +4 C, length of the growing period is 180-195 days. The territory is mostly flat, the southern part is hilly with slopes of 6-10%. Average altitude from the sea level is 50 m. About half of the Estonian territory is above 50 m and half is below it. Soils are from very shallow (less than 0.1 m) in the north to very deep (> 120m ) in the south. Soil cover is very variable. In the agricultural area the soils are medium textured with low (< 1%) to high (>5%) organic matter in topsoil. Groundwater is near the surface in wet soils and deep in hilly areas. Biodiversity varies from high to low depending on soil and landscape. Market orientation of production system is mixed and off-farm income is less than 10%. Relative level of wealth is average from individual households to cooperatives. Soil management is mechanized. Land belongs to land users, but is leased also in case of bigger farms (over 100 ha).
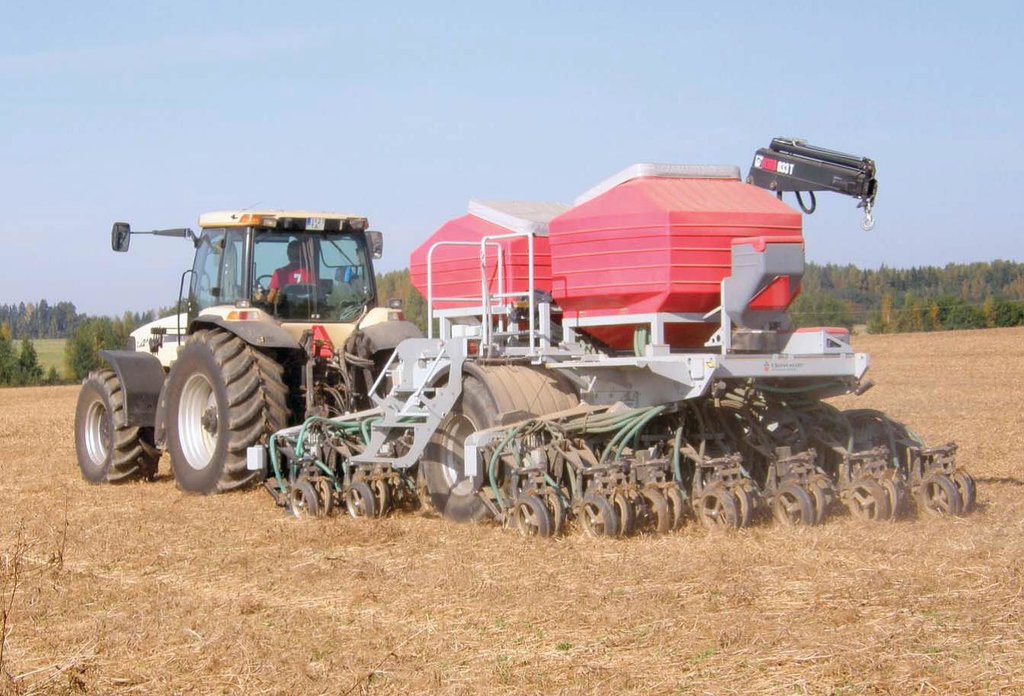
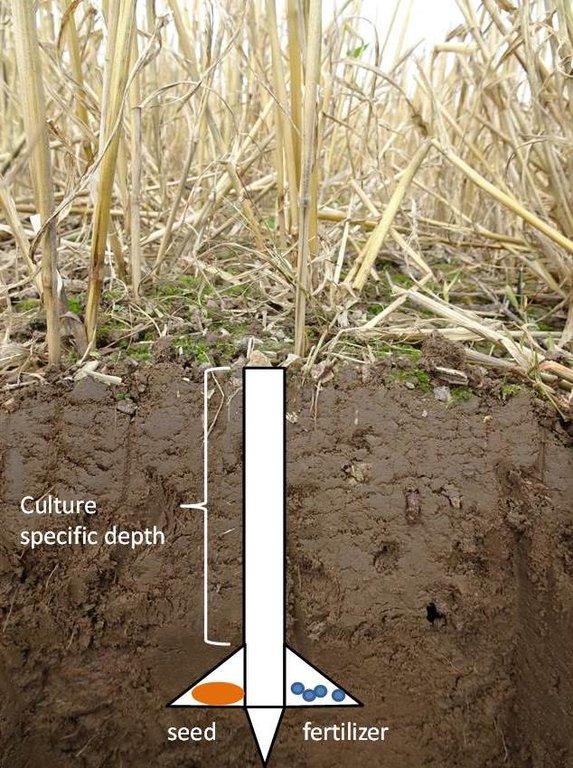
The purpose of the technology is to reduce soil disturbance and with that to reduce erosion and leaching, increase carbon storage, water infiltration and biological activity. Only 5-10% of the soil surface is disturbed during sowing. The drilling is made by special machinery and thus no-till farming requires specialized seeding equipment designed to plant seeds into undisturbed crop residues and soil. Drilling depth depends on the specific needs of the culture. If the straw remains on the field, it should be chopped to smaller pieces (25-40 mm). For direct seeding it is good if the previous culture was seeded with wider spacing, for example 25 cm and harvest height is 15-20 cm. New sowing will be done between previous crop rows. The highest investment to this technology is the new drilling machine. At the same time there is no need for special tillage machines. In order to help eliminate weed, pest and disease problems, crop rotations and pesticides are used. The system is not suitable for root crops. The no-till system is suitable for cereal based cropping systems as well as for renewing grasslands. The suitable crop rotation, for exampe, is: winter oilseed rape - winter wheat - pea (or bean) - winter wheat - spring barley undersown with red clover - red clover. The main benefit is the reduced working time, fuel costs and with that the lower net-cost of the product, but also the better soil structure. The adoption of the technology may increase weediness and pests and decrease the yield due to the preliminar soil compaction of upper 10-20 cm soil layer. If the soil surface of the field is not enough levelled out, the uniformity of the depth of the seedlings can suffer. There is also increased use of pesticides to control weeds, pests and diseases compared to minimum and conventional tillage. The technology is most suitable for medium-texture soils.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
爱沙尼亚
区域/州/省:
Tartu county, Põlva county
有关地点的进一步说明:
Tartu county, Meeri; Põlva county, Puuri
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果不知道精确的区域,请注明大致覆盖的区域:
- 1-10 平方千米
注释:
The total area of no-till in Estonia is ca 42 000 ha. On the farm near Tartu it is 1700 ha of land, of which 300 ha are grasslands. The farm near Põlva encompasses an area of 850 ha of which 330 ha are grasslands. The whole area of both farms is managed by no-tillage.
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 不到10年前(最近)
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过土地使用者的创新
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
- reduce tillage cost
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

农田
- 一年一作
年作 - 具体指明作物:
- 谷类 - 大麦
- 谷类 - 燕麦
- 谷类 - 黑麦
- wheat
每年的生长季节数:
- 1
具体说明:
One harvest of cereals.
3.3 由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?
由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?:
- 是(请在技术实施前填写以下有关土地利用的问题)

农田
- 一年一作
注释:
Before implementation of the no-tillage the conventional and/or reduced tillage was used.
3.4 供水
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 改良的地面/植被覆盖
- 最小的土壤扰动
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

农艺措施
- A3:土壤表面处理
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀

土壤风蚀
- Et:表土流失

化学性土壤退化
- Cn:肥力下降和有机质含量下降(非侵蚀所致)

物理性土壤退化
- Pc:压实
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 防止土地退化
- 减少土地退化
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
The agrotechnology in case of no-tillage depends on available equipments (drill). If the straw remains on the field, it should be chopped to smaller pieces of 25-40 mm. For direct seeding it is good if the previous culture was seeded with wider spacing, for example 25 cm. Harvest height is 15-20 cm. New seeding will be done between previous crop rows.
作者:
Endla Reintam
日期:
14/08/2017
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
具体说明成本和投入是如何计算的:
- 每个技术单元
指定单位:
per hectare
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
EUR
如相关,注明美元与当地货币的汇率(例如1美元=79.9巴西雷亚尔):1美元=:
1.18
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
36-40 EUR/day + taxes
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | New direct seeder |
注释:
If you are already active in agriculture, the investment is the new seeder. You also need to have machinery to spread fertilizers and pesticides.
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 设备 | Direct seeder (3m) | piece | 1.0 | 25000.0 | 25000.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 25000.0 | |||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 21186.44 | |||||
如果土地使用者负担的费用少于100%,请注明由谁负担其余费用:
It is possible to apply for an investment support up to 50% of the total price (governmental tool till the year 2020).
注释:
The cost of the direct seeder depends on the farmers prefererences regarding the technology. The cheapest direct seeder can be purchased for ca. 25 000 EUR. Better quality of a cross slot seeder that places seeds under the soil (technical drawing and picture) costs ca 200 000 EUR (working width 4.6 m).
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Sowing together with fertilization | before drilling (spring crops in spring (April), winter crops in autumn (August)) |
| 2. | Plant protection | in spring 2 weeks before sowing, herbicides, during growth period depending on the needs ca 3 times |
| 3. | Fertilization during growth period | For winter crops in spring after snowmelt in the beginning of growth, for spring crops in the beginning of intensive growth |
| 4. | Harvest and grain transport | At the end of season (end of July to beginning of September depending of the crop) |
| 5. | Drying of grain and soil tillage | after harvest |
注释:
The need of plant protection depends on the field conditions. Less pesticides are needed if proper crop rotation with break crops is established and weeds are thus suppressed.
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 设备 | Sowing with fertilization | times | 1.0 | 55.9 | 55.9 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Plant protection | times | 4.0 | 11.2 | 44.8 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Fertilization during growth period | times | 1.0 | 16.2 | 16.2 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Harvest and grain transport | times | 1.0 | 118.4 | 118.4 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Drying and after harvest activities | times | 1.0 | 132.1 | 132.1 | 100.0 |
| 植物材料 | seeds | kg | 200.0 | 0.28 | 56.0 | 100.0 |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | Ammonium nitrate (2x per season) | kg | 147.0 | 0.84 | 123.48 | 100.0 |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | Complex fertilizer (27 kg N, 40 kg P and 112 kg K per ha) (450 kg of fertilizer per ha) | kg | 179.0 | 0.74 | 132.46 | 100.0 |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | Herbicides (2 times) | times | 2.0 | 27.0 | 54.0 | 100.0 |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | Fungicides (1 time) | times | 1.0 | 33.2 | 33.2 | 100.0 |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | Insecticides (1 time) | times | 1.0 | 3.6 | 3.6 | 100.0 |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | Retartants | times | 1.0 | 14.0 | 14.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 784.14 | |||||
| 技术维护总成本,美元 | 664.53 | |||||
注释:
The labour costs are included to the machinery work costs. On average the labour cost for a driver is 15-18 EUR/ha.
The average machinery work costs to produce 6 t of winter wheat were 432 EUR/ha, 400 EUR/ha and 780 EUR/ha in conventional, minimum and no-tillage, respectively in 2016. Cost of production in this case was 137 EUR/t, 132 EUR/t and 128 EUR/t in conventional, minimum and no-tillage, respectively.
To produce the same amount of spring barley, the cost of machinery was 431 EUR/ha, 411 EUR/ha and 366 EUR/ha in conventional, minimum and no-tillage, respectively. Cost of production in this case was 123 EUR/t, 121 EUR/t and 114 EUR/t in conventional, minimum and no-tillage, respectively. It means that the cost of production is 8-11 EUR less than compared with plough based production.
Fuel cost is ca 50% less than in conventional plough based farming.
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
Fuel price, labour costs.
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
指定年平均降雨量(若已知),单位为mm:
696.00
有关降雨的规范/注释:
Average 696 mm, almost equally spread over the year, more from July to October, less in March and April.
注明所考虑的参考气象站名称:
Tartu Tõravere
农业气候带
- 半湿润
LGP 180-195 days
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
说明该技术是否专门应用于:
- 凸形情况
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
土壤质地(地表以下> 20厘米):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 中(1-3%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Soil type: sandy loam Stagnic Luvisol; N 0.12%, Corg 1.15%; C:N 9.97, P 4.35 mg/100g, K 10.19mg/100g, Ca 49.61mg/100g, Mg 12.19mg/100g, pH 6.0
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
5-50米
地表水的可用性:
好
水质(未处理):
良好饮用水
水的盐度有问题吗?:
否
该区域正在发生洪水吗?:
否
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 中等
栖息地多样性:
- 中等
关于生物多样性的注释和进一步规范:
Soil biodiversity is higher compared to conventional tillage.
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
定栖或游牧:
- 定栖的
生产系统的市场定位:
- 混合(生计/商业)
非农收入:
- 低于全部收入的10%
相对财富水平:
- 平均水平
个人或集体:
- 个人/家庭
- 合作社
机械化水平:
- 机械化/电动
性别:
- 女人
- 男人
土地使用者的年龄:
- 青年人
- 中年人
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 中等规模的
注释:
The farm near Tatu owns 1700 ha of land, of which 300 ha are grasslands. The farm near Põlva encompasses a total of 850 ha of which 330 ha are grasslands. All soils of both farms are managed by no-tillage.
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 州
- 个人,有命名
土地使用权:
- 租赁
- 个人
用水权:
- 自由进入(无组织)
- 个人
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
注释/具体说明:
In different years the crop production may be higher than by ploughing, but another year lower. There has been decrease of spring barley yield by 0.1 t/ha. Winter wheat yield has been ca 1.4 t/ha higher than by ploughing.
作物质量
注释/具体说明:
No statistically significant difference has been found. However, winter wheat 1000 grain weight was reported 39.6 g by no-tillage and 38.5 g by ploughing.
土地管理
注释/具体说明:
No need for soil tillage. Instead of several machinery to till the soil, one compact sowing machine is needed.
收入和成本
农业投入费用
注释/具体说明:
Less cost for fuel because 50% less fuel is needed compared with ploughing.
农业收入
注释/具体说明:
Even if the yield is a little bit lower or the same as with ploughing, the unit cost to produce barley or winter wheat is 8-11 EUR less than with ploughing.
工作量
注释/具体说明:
No time to be spent for tillage. Even extra spreading of pesticides takes less time than ploughing and other tillage operations.
社会文化影响
食品安全/自给自足
注释/具体说明:
Unit cost of the production is lower and thus it is possible to sell production cheaper.
SLM/土地退化知识
注释/具体说明:
If land was eroded before and soil was on the road, everybody can see the differences after establishment of the grasslands. It is not so severe in case of peatlands, however, less tractors will stuck in to the mud on rainy period.
生态影响
水循环/径流
水的回收/收集
注释/具体说明:
Residues remaining on the soil surface help to catch more snow during the winter.
地表径流
注释/具体说明:
Plant residues protect soil surface structure from raindrop effects, allowing water to infiltrate quicker in the soil.
多余水的排放
注释/具体说明:
Undisturbed soil pore structure allows water quicker to drain in the deeper soil layers. Water permeability of long-term no-till soil is 2 times higher than under conventional management.
蒸发
注释/具体说明:
Residues on the soil surface do not allow quick evaporation, protecting soil surface.
土壤
土壤水分
注释/具体说明:
Soil moisture content was 3% higher than by ploughing, but not significantly.
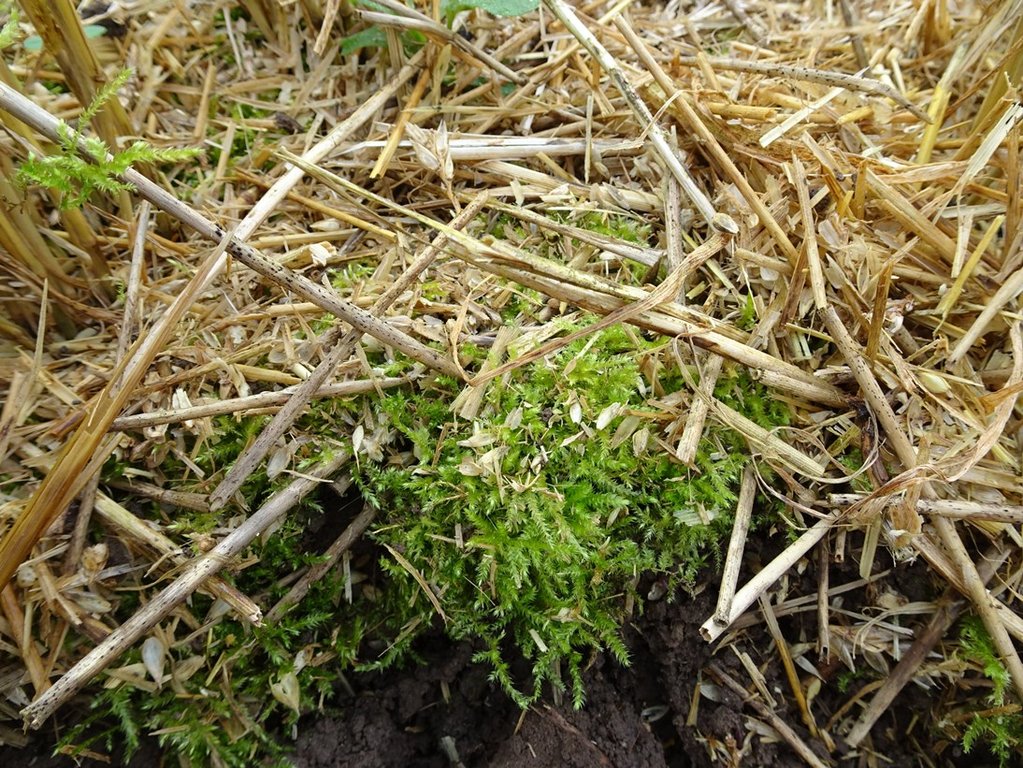
土壤覆盖层
SLM之前的数量:
0
SLM之后的数量:
100%
注释/具体说明:
The soil is covered by plants or by plant residues during the whole year.
土壤流失
注释/具体说明:
Residues and plant cover stop both wind and water erosion.
土壤堆积
注释/具体说明:
Reduced decomposition of organic matter increases organic carbon content by 0.1-0.2%.
土壤结壳/密封
注释/具体说明:
No crust after applying no-tillage as plant residues protect the soil surface.
土壤压实
注释/具体说明:
Increased from the top (by 0.04 g/cm3) but decreased deeper in the soil by 0.08 g/cm3) compared to the ploughing. No plough pan. Soil penetration resistance was 1 MPa lower between 20-40 cm under no-tillage compared to ploughing.
养分循环/补给
注释/具体说明:
Due to the decreased decomposition of organic matter and the increase of organic carbon, more nitrogen remains in the soil.
土壤有机物/地下C
注释/具体说明:
It was found that there was slight increase of organic carbon (Corg) by 0.1-0.2% in upper 5 cm of soil compared to ploughing.
生物多样性:植被、动物
植被覆盖
注释/具体说明:
Plant/residue cover is during the whole year.
生物量/地上C
注释/具体说明:
As there is no tillage, all residues remain on the soil surface.
植物多样性
注释/具体说明:
Due to the need of changes in crop rotation, more diverse rotations instead of monoculture to suppress weeds. Weeds diversity might increase and change due to the reduced tillage intensity.
动物多样性
注释/具体说明:
More spiders, beetles, ants compared with ploughing.
有益物种
SLM之前的数量:
2 species of earthworms
SLM之后的数量:
3-4 species of earthworms
注释/具体说明:
More earthworm species and higher abundance compared with ploughing.
栖息地多样性
注释/具体说明:
No-till areas create different pattern to the landscape.
害虫/疾病控制
注释/具体说明:
Some diseases and pests are surpressed, but there is increase of slugs and snails.
减少气候和灾害风险
碳和温室气体的排放
注释/具体说明:
Due to the reduced use of fuels for tillage, less greenhouse gases will be released. 0.05 kg/ha less greenhouse gases per kg yield is reported by no-tillage compared to ploughing.
火灾风险
注释/具体说明:
Dry plant residues are a high risk in spring.
微气候
注释/具体说明:
Due to the residue cover the soil temperature and water content fluctuations are smaller.
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
缓冲/过滤能力
注释/具体说明:
Due to the higher amount of organic matter, the nutrients and water holding capacity is higher.
风力搬运沉积物
注释/具体说明:
No wind erosion after applying no-tillage.
对邻近农田的破坏
注释/具体说明:
No sediments from the field to the neighbours fields.
对公共/私人基础设施的破坏
注释/具体说明:
In case of erosion, no soil is carried by water or wind to the ditches and on the roads.
温室气体的影响
注释/具体说明:
Due to the reduced use of fuels for tillage, less greenhouse gases will be released. 0.05 kg/ha less greenhouse gases per kg yield is reported by no-tillage compared to ploughing.
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 增加或减少 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年温度 | 增加 | 未知 | |
| 季节性温度 | 冬季 | 增加 | 未知 |
| 季节性温度 | 春季 | 增加 | 未知 |
| 年降雨量 | 增加 | 未知 | |
| 季雨量 | 冬季 | 增加 | 未知 |
| 季雨量 | 秋季 | 增加 | 未知 |
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气象灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 局地暴雨 | 未知 |
| 局地雷暴 | 未知 |
| 局地雹灾 | 未知 |
| 局地雪暴 | 未知 |
| 局地风暴 | 未知 |
气候灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 寒潮 | 未知 |
| 极端冬季条件 | 未知 |
| 陆地火灾 | 不好 |
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
轻度消极
长期回报:
积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
积极
6.5 技术采用
- 1-10%
如若可行,进行量化(住户数量和/或覆盖面积):
7% from agricultural land
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发的,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 51-90%
注释:
It is possible to get investment support from the governmental agricultural tools up to 50% from the total cost of equipment.
6.6 适应
最近是否对该技术进行了修改以适应不断变化的条件?:
否
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Decreases work load and time, also fuel consumption, increases income. |
| Increases soil biological activity, soil organic matter content, better structure and infiltration, decreases erosion. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Decrease of soil organic carbon decomposition, decrease of erosion, increase of soil biological activity. |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| High preliminary investment (seeder), increase of weediness and pests, | Investment support, better crop rotation. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Higher use of pesticides and therefore risk to soil and water pollution. | Suggestion of changes in crop rotation, cover crops. |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
- 实地考察、实地调查
2 during the iSQAPER project, more than 5 in total with other projects
- 与土地使用者的访谈
2, more than 5 in total with other projects
- 根据报告和其他现有文档进行编译
6
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
04/06/2017
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Minimeeritud harimine ja otsekülv. 2017. P. Viil. Eesti Taimekasvatuse Instituut. ISBN 978-9949-9742-2-1
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
ISBN 978-9949-9742-2-1
7.3 链接到网络上的相关信息
标题/说明:
Kattetulu arvestused taime- ja loomakasvatuses 2016. Koost: Marju Aamisepp, Helle Persitski. Maamajanduse infokeskus. 2017.
URL:
http://www.maainfo.ee/data/trykis/kattetulu/KATTETULU2016.pdf
标题/说明:
Statistics Estonia
URL:
https://www.stat.ee/en
标题/说明:
Erinevate viljelusmeetodite ( sh. otsekülv) rakendusteaduslik kompleksuuring. Riikliku programmi “Põllumajanduslikud rakendusuuringud ja arendustegevus aastatel 2009–2014” projekti lõpparuanne. 2015. Eesti Taimekasvatuse Instituut, Eesti Maaülikool, Põllumajandusuuringute keskus.
URL:
http://www.pikk.ee/upload/files/Erinevad_viljelusviisid_pikk_aruanne.pdf
标题/说明:
Minimeeritud harimine ja otsekülv. 2017. P. Viil. Eesti Taimekasvatuse Instituut.
URL:
http://taim.etki.ee/taim/public/pdf/Trukised/Otseklv-minimeeritud-mullaharimine.pdf
标题/说明:
Eesti maaelu arengukava 2014-2020 4. ja 5. prioriteedi meetmete ja 3. prioriteedi loomade heaolu meetme püsihindamisaruanne 2015. aasta kohta ja Lisad 1-30
URL:
http://pmk.agri.ee/mak/avaleht/
标题/说明:
Eesti tuleviku kliimastsenaariumid aastani 2100
URL:
https://www.envir.ee/sites/default/files/kliimastsenaariumid_kaur_aruanne_ver190815.pdf
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块