Road runoff management - Nyeri [肯尼亚]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: James Gatero Njuki
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
MRP - soil conservation pilot project
technologies_1094 - 肯尼亚
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Ministry of Agriculture and Livestock Development of Kenya (MoA) - 肯尼亚1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
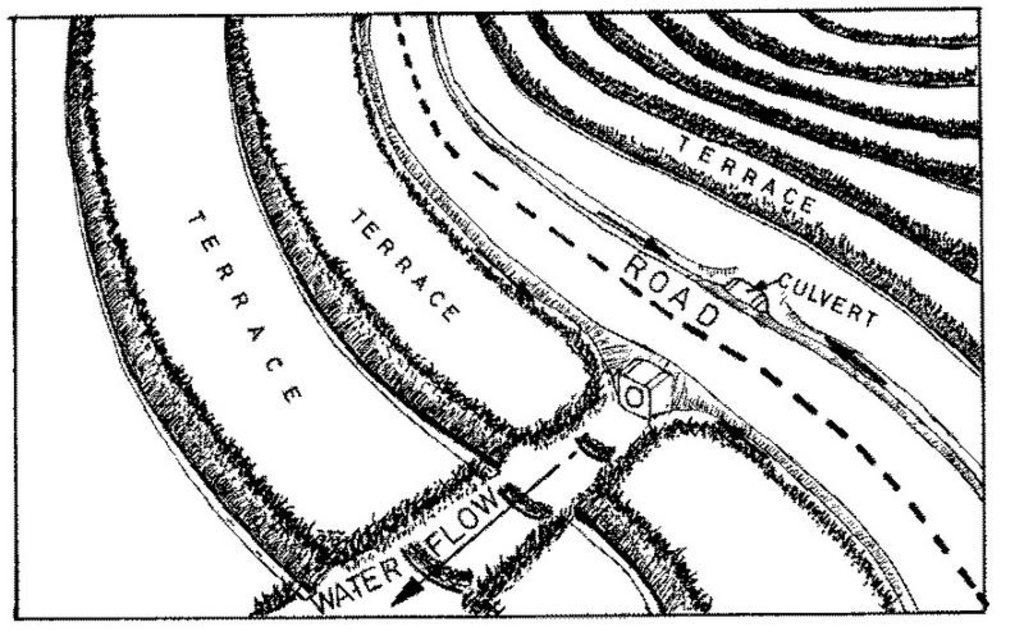
management of runoff water on the road and its environment to reduce land degradation
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
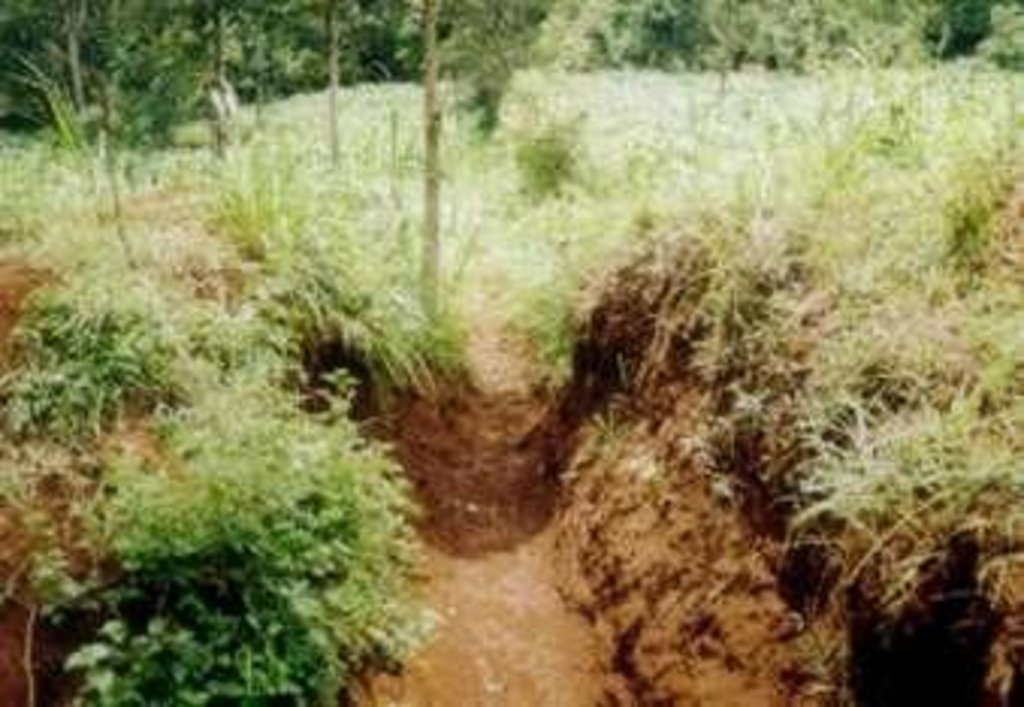
It encompasses agronomic, vegetative, structural and management aspects to minimise land degradation within the road catchment and its environment using participatory methods. The purpose of the technology was to improve on the managent of water from the road so that it does not cause degradation. Establishment and maintenance of the technology was done by the local community bordering the roads.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
肯尼亚
区域/州/省:
Central
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果不知道精确的区域,请注明大致覆盖的区域:
- < 0.1 平方千米(10 公顷)
注释:
the area covered depend on the area of the road. In total the technology was duplicated in roads totalling about 33 kilometres
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 不到10年前(最近)
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过土地使用者的创新
注释(项目类型等):
SWC specialists and land users
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

农田
- 一年一作
每年的生长季节数:
- 2
具体说明:
Longest growing period in days: 120Longest growing period from month to month: Mar - MaySecond longest growing period in days: 90Second longest growing period from month to month: Oct - Dec

定居点、基础设施
- 交通:公路、铁路
注释:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Declining soil fertility and soil erosion, land subdivision leading to small parcels of land
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Marketing/pricing of farm produce, high costs of inputs and lack of credit
Grazingland comments: stall feeding is the most common grazing system as there are no delienated portions for grazing , due to the small holdings
Type of grazing system comments: stall feeding is the most common grazing system as there are no delienated portions for grazing , due to the small holdings
3.4 供水
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 引水和排水
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

结构措施
- S4:平沟、坑
注释:
Main measures: structural measures
Secondary measures: agronomic measures, vegetative measures, management measures
Type of agronomic measures: contour ridging
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀
- Wg:冲沟侵蚀/沟蚀
- Wo:场外劣化效应

化学性土壤退化
- Cn:肥力下降和有机质含量下降(非侵蚀所致)
注释:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Wg: gully erosion / gullying, Wo: offsite degradation effects
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content
Main causes of degradation: other human induced causes (specify) (road surface & Agricultural causes), roads
Secondary causes of degradation: education, access to knowledge and support services (Lack of knowledge), Lack of enforcement of legislat./authority
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 减少土地退化
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
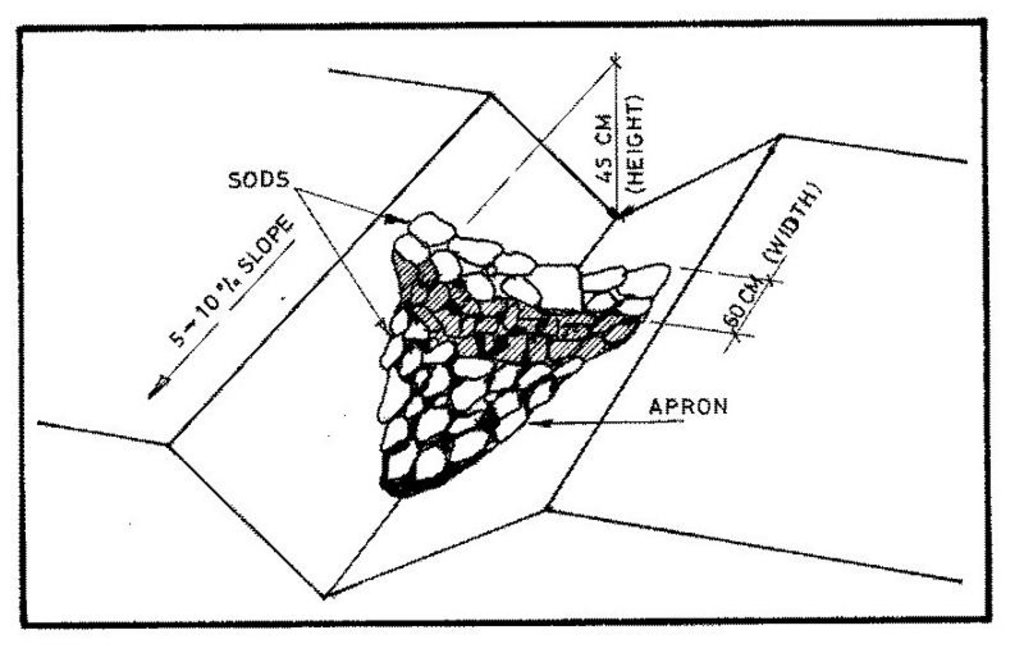
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Main technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap, control of concentrated runoff: impede / retard, control of concentrated runoff: drain / divert
Secondary technical functions: reduction of slope length, increase in organic matter, increase of infiltration
Grass species: napier grass
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 0.00%
Construction material (stone): for scour checks in the waterway
Construction material (wood): small posts for scour checks
Construction material (other): grass, brush wood, live vegetative material
Lateral gradient along the structure: 8%
Vegetation is used for stabilisation of structures.
Change of land use type: exclusion of land under waterway
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
Kenyan Shilling
如相关,注明美元与当地货币的汇率(例如1美元=79.9巴西雷亚尔):1美元=:
33.0
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
0.96
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | planting napier grass cuttings | after first rains |
| 2. | establish scour checks | on set of rains |
| 3. | excavation | dry spell |
| 4. | planting grass for stabilisation | on set of rains |
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
注释:
Duration of establishment phase: 24 month(s)
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | contour ridging | dry season / beginning of season |
| 2. | weeding | dry spell /once per season |
| 3. | desilting channel | dry season/each cropping season |
| 4. | gapping the grass | wet season/each cropping season |
| 5. | slashing grass in channel | wet season/each cropping season |
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
注释:
For the length of the waterway in metres. The length of the structure was kept constant
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
The general ground slope determines the cost of the structures and the distance of the safe discharge point from the road
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
农业气候带
- 潮湿的
- 半湿润
Thermal climate class: tropics
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
关于地形的注释和进一步规范:
Landforms: Also valley floors
Slopes on average: Also moderate
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 中(1-3%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Soil fertility is medium-high
Soil drainage / infiltration is good
Soil water storage capacity is medium-high
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
非农收入:
- 低于全部收入的10%
相对财富水平:
- 贫瘠
- 平均水平
机械化水平:
- 手工作业
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Population density: 200-500 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 3% - 4%
5% of the land users are rich and own 10% of the land.
50% of the land users are average wealthy and own 70% of the land.
25% of the land users are poor and own 15% of the land.
20% of the land users are poor and own 5% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: mainly from employment in the nearby urban areas
Level of mechanization: With hand tools
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 个人,有命名
土地使用权:
- 个人
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
生态影响
水循环/径流
地表径流
SLM之前的数量:
50
SLM之后的数量:
20
土壤
土壤流失
SLM之前的数量:
25
SLM之后的数量:
15
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
稍微积极
长期回报:
积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
稍微积极
长期回报:
中性/平衡
6.5 技术采用
- > 50%
如若可行,进行量化(住户数量和/或覆盖面积):
210 households in an area of 10 ha
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发的,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 0-10%
注释:
20% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
200 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: estimates
5% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
10 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: estimates
There is no trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: technology adoption not spontaneous because of dependency on material support from donor
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
farm management handbook of Kenya. 1983.
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
SWC branch, MoA, Nairobi
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
minor roads soil conservation project. Final report. 1992.
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
Ministry of Public Works. Nairobi.
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块