Vermiculture [尼加拉瓜]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Ramén Ernesto Caceres Ordonez
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Deborah Niggli, Alexandra Gavilano
Lombricultura
technologies_1022 - 尼加拉瓜
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
SLM专业人员:
Gómez Martínez Julio César
De ENITEL
尼加拉瓜
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
Book project: where the land is greener - Case Studies and Analysis of Soil and Water Conservation Initiatives Worldwide (where the land is greener)1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.4 所述技术的可持续性声明
这里所描述的技术在土地退化方面是否存在问题,导致无法被认为是一种可持续的土地管理技术?:
否
1.5 参考关于SLM方法(使用WOCAT记录的SLM方法)的调查问卷

Productive development and food security programme [尼加拉瓜]
An integrated programme-based approach promoting participatory testing and extension of various SWC technologies, as well as providing institutional support.
- 编制者: Philippe Zahner
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
Continuous breeding of earthworms in boxes for production of high quality organic compost.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
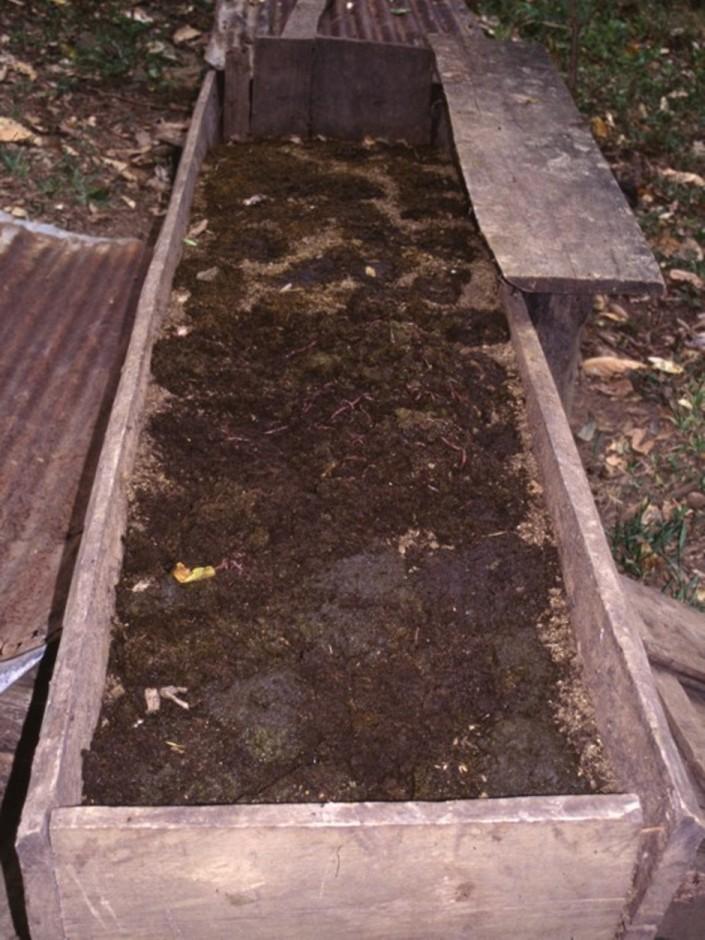
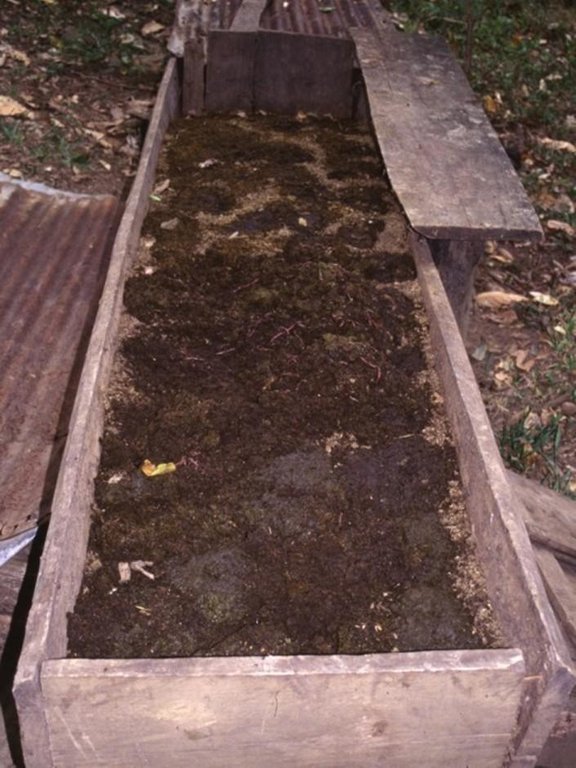
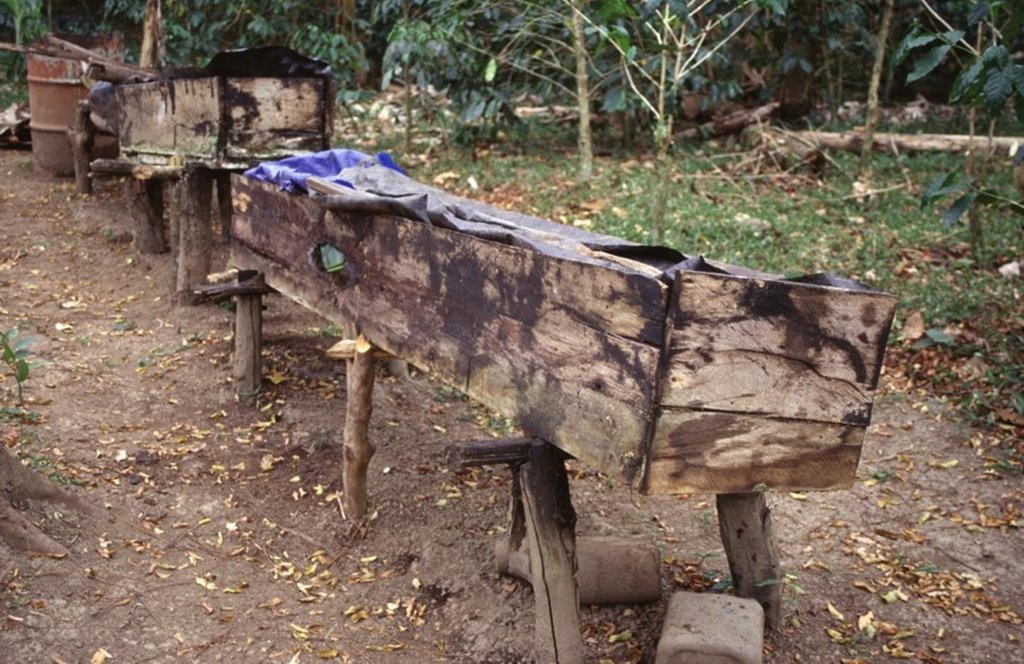
Vermiculture is a simple and cheap way to produce a continuous supply of organic compost of high quality. Eisenia foetida, the Red Californian earthworm (also called ‘the red wiggler’) is ideal for vermiculture since it is adapted to a wide range of environmental conditions. Under culture, the worms are kept under shade, in long wooden boxes filled with earth, cattle manure and an absorbent material (eg straw). The box is covered by sheet metal (or wood, thick plastic sheeting, or banana leaves) to protect the worms against UV radiation and birds/chickens, and also to maintain a favourably humid microclimate. Fresh cattle manure is a perfect food for the worms, but rotten coffee pulp can also be fed. Chopped crop residues (eg cowpeas, leucaena leaves or other legumes) may be added.
The compost produced by the earthworms has a dark colour, no smell and a loose and spongy structure. It is a high value, high quality product which is very rich in nutrients, and in a form that makes them readily available to vegetation. The content of a full box can be harvested every 3-4 months, and is used for crops -mainly coffee and vegetables, but also maize and beans. It is very effective in increasing soil fertility and thus crop production. It also improves soil structure, infiltration and water storage capacity.
The compost can either be applied directly to coffee, mixing it with an equal amount of earth and applying 1 kg to each plant. Alternatively it can be sprayed: for preparation of liquid fertilizer 50 kg compost are mixed with 50 litres of water and left to soak for 5 days. The concentrated solution produced is mixed with water at a ratio of 1 to10 and applied to the crop using a knapsack sprayer. The earthworms reach their reproductive age after three months and live for many years. In perfect conditions an earthworm produces up to 1,500 offspring per year. Thanks to their rapid reproduction, new cultures can easily be established, or earthworm stocks can be sold according to the farmer’s needs. A certain amount
of earthworm compost is kept back and being used instead of fresh earth to reinitiate the whole process, or to start new cultures.
The area is characterised by humid climate, steep slopes and low soil fertility. Farmers are mainly smallholders with individual properties. Earthworm culture does not depend closely on the external environment, but it is essential to maintain favourable conditions inside the box - namely continuous feeding and wetting. That’s why it is usually recommended to keep cultures near the house and the home-garden. Ants, the main enemy of earthworms, can be controlled standing the boxes on poles in cans filled with water.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
尼加拉瓜
区域/州/省:
Matagalpa
有关地点的进一步说明:
Matiguas, Pancasán
注释:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 5 m2.
Map
×2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过项目/外部干预
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 保持/提高生物多样性
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

农田
- 一年一作
- 多年一作(非木材)
每年的生长季节数:
- 1
具体说明:
Longest growing period in days: 300, Longest growing period from month to month: May untill February
注释:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion):
- low crop yields due to soil fertility decline
- water and wind erosion
- small landholdings
3.4 供水
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 土壤肥力综合管理
- 养蜂、养殖业、家禽业、养兔业、养蚕业等
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

农艺措施
- A4:地表下处理
注释:
Type of agronomic measures: manure / compost / residues
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

化学性土壤退化
- Cn:肥力下降和有机质含量下降(非侵蚀所致)
注释:
Main causes of degradation: soil management, deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires), overgrazing (on a single cattle farm), poverty / wealth (lack of capital)
Secondary causes of degradation: over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use, other natural causes (avalanches, volcanic eruptions, mud flows, highly susceptible natural resources, extreme topography, etc.) specify (impacts of hurricane Mitch), governance / institutional (lack of strenght of law and authorities), inter-generational subdivision of land
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 减少土地退化
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
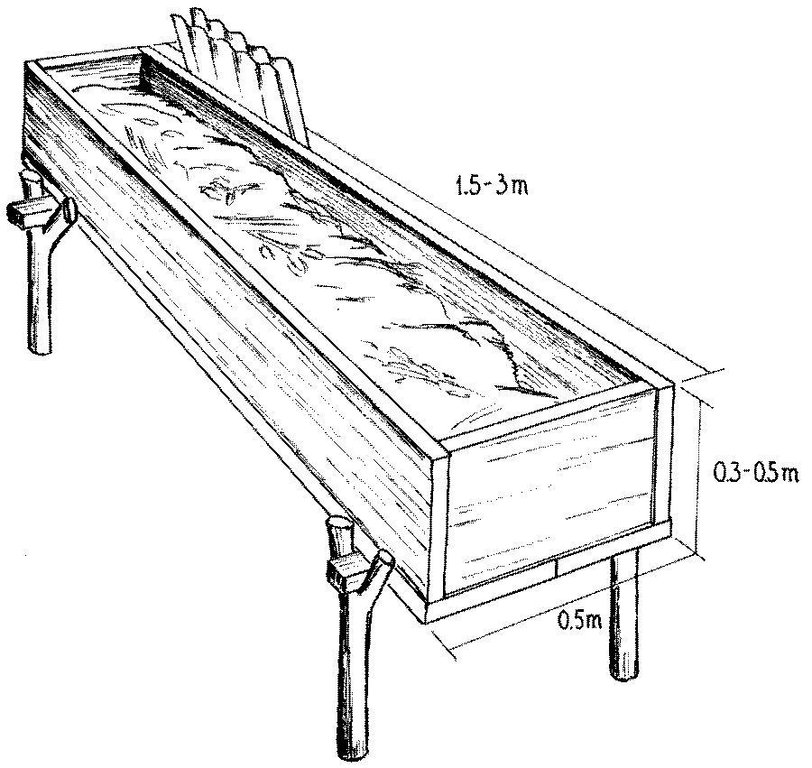
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
Detailed view of wooden box for compost production by earthworms. Cover (corrugated iron or alternative) is important to protect worms from light, from birds and other natural enemies, and to maintain moisture in the box.
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: increase of surface roughness, improvement of topsoil structure (compaction), increase in organic matter, increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…)
Secondary technical functions: increase of infiltration
Manure / compost / residues
Material/ species: compost
作者:
Mats Gurtner
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | labour | ha | 1.0 | 6.0 | 6.0 | 100.0 |
| 施工材料 | wood | ha | 1.0 | 50.0 | 50.0 | 100.0 |
| 施工材料 | Sheet metal, plastic | ha | 1.0 | 6.0 | 6.0 | 100.0 |
| 其它 | earthworms (kg) | ha | 1.0 | 60.0 | 60.0 | |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 122.0 | |||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 122.0 | |||||
注释:
Duration of establishment phase: 0.07 month(s)
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | 1. Feeding: add another layer of cattle manure(1 kg earthworms eat 1 kg manure per day). | no specific timing for maintenance / every 3–5 days |
| 2. | 2. Maintain humidity at 80%, water frequently in dry season, maintaintemperature between 15–30°C: do not exceed 42°C. | no specific timing for maintenance / frequently in dry season |
| 3. | 3.The worms migrate into the fresh manure. After 2–3 days take out thesieve and gather the ready, worm free compost. | no specific timing for maintenance / every 3–4 months |
| 4. | 4. Apply compost to the crops (1 kg/coffee plant, see description). | no specific timing for maintenance / every 3–4 months |
| 5. | 6. Possible improvement: add lime to raise pH to a optimum level of 7.0. | no specific timing for maintenance / |
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | labour | ha | 1.0 | 60.0 | 60.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 60.0 | |||||
| 技术维护总成本,美元 | 60.0 | |||||
注释:
Machinery/ tools: hammer, nails, buckets/wheelbarrow, shovel, possibly water hose, hammer, nails, buckets/wheelbarrow, shovel, possibly water hose
60% of the land users have their own cattle, others get manure free from their neighbours. The cattle manure has no commercial price in the region - there is no market for it. The inputs and costs are estimated for the production of approx. 4,000 kg of worm compost, which is enough for one hectare of coffee per year (note figures from India for vermiculture suggest higher input-output ratios: in other words less output for the same amount of input).
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
农业气候带
- 潮湿的
- 半湿润
Thermal climate class: tropics
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 细粒/重质(粘土)
表土有机质:
- 低(<1%)
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
生产系统的市场定位:
- 生计(自给)
- 混合(生计/商业)
非农收入:
- 低于全部收入的10%
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Off-farm income specification: nearly all land users are fully occupied with agricultural activities, very few are involved in commerce or are employed
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 个人,未命名
- 个人,有命名
土地使用权:
- 租赁
- 个人
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
饲料生产
饲料质量
收入和成本
农业收入
社会文化影响
冲突缓解
生态影响
土壤
土壤水分
注释/具体说明:
through improvement of soil water storage capacity
生物多样性:植被、动物
害虫/疾病控制
注释/具体说明:
the compost attracts pests like ants, chickens, moles
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
地下水/河流污染
注释/具体说明:
lower inputs of chemical fertilizers
6.5 技术采用
注释:
88 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
6 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology. As ADDAC (the Association for Agricultural Community Development and Diversification) has a permanent and longterm presence in the approach area, most interested farmers are directly involved in the programme activities: this explains the fact that only 5% of the technology users (6 people) took up earthworm culture without incentives (see approach).
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Additional economic income through commercialization of earthworm stocks |
| Health: clean products without chemical treatment. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Continuous and increasing production of organic and very effective compost with high nutrient content (replacing chemical fertilizers) |
|
Appropriate for different crops (though in different forms – direct application or spraying). |
| Simple and cheap technology; low labour input |
| Increased crop yields |
| Earthworm culture is becoming an integrated part of the production system, especially for land users who have cows. |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Requires permanent access to water | A close fitting and secure box cover, as well as placement of the box in the shade reduces loss of humidity. Roof-top rainwater collection helps to get over dry periods. |
| Requires continuous availability of manure to feed worms. | Improve the construction of the boxes (close holes and cover the box tightly). |
| Attracts natural enemies like ants, chickens, moles, flies; needs protection |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
- 实地考察、实地调查
- 与土地使用者的访谈
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
01/02/2004
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
PASOLAC. Guía Técnica de Conservación de Suelos y Agua.. 2000.
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
PASOLAC, Managua
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Ferruzzi C. Manual de Lombricultura. Ediciones Mundi-Prensa. Madrid, Spain. 1986.
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Castillo H . La lombricultura. in Altertec. Alternativas de Mejoramiento de Suelos.Proceso de Capacitación para Profesionales. Modulo II. Altertec, Ciudad de Guatemala. 1994.
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接

Productive development and food security programme [尼加拉瓜]
An integrated programme-based approach promoting participatory testing and extension of various SWC technologies, as well as providing institutional support.
- 编制者: Philippe Zahner
模块
无模块