Level ditches in cropland [斯洛伐克]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Zuzana Studvova
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Fabian Ottiger, Alexandra Gavilano
Záchytné pásy na poľnohospodárskej pôde (Slovak language)
technologies_1666 - 斯洛伐克
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
Preventing and Remediating degradation of soils in Europe through Land Care (EU-RECARE )有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Slovak University of Technology (Slovak University of Technology) - 斯洛伐克1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.5 参考关于SLM方法(使用WOCAT记录的SLM方法)的调查问卷
The programme of landscape revitalization and integrated river … [斯洛伐克]
This approach is devoted to the implementation of 'The Landscape Revitalisation Programme and integrated river basins management of the Slovak Republic' in the Sobotište village.
- 编制者: Zuzana Studvova
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
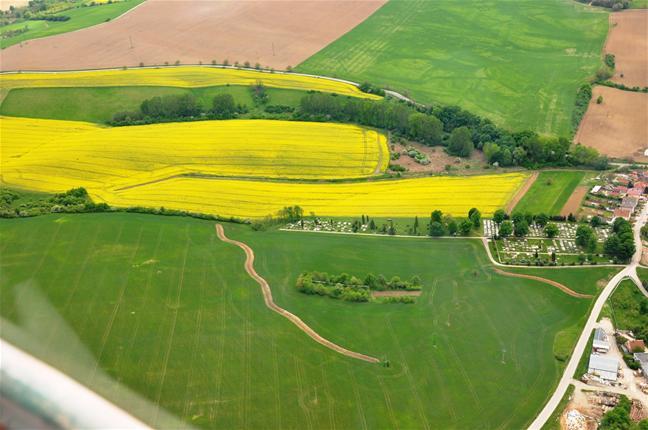
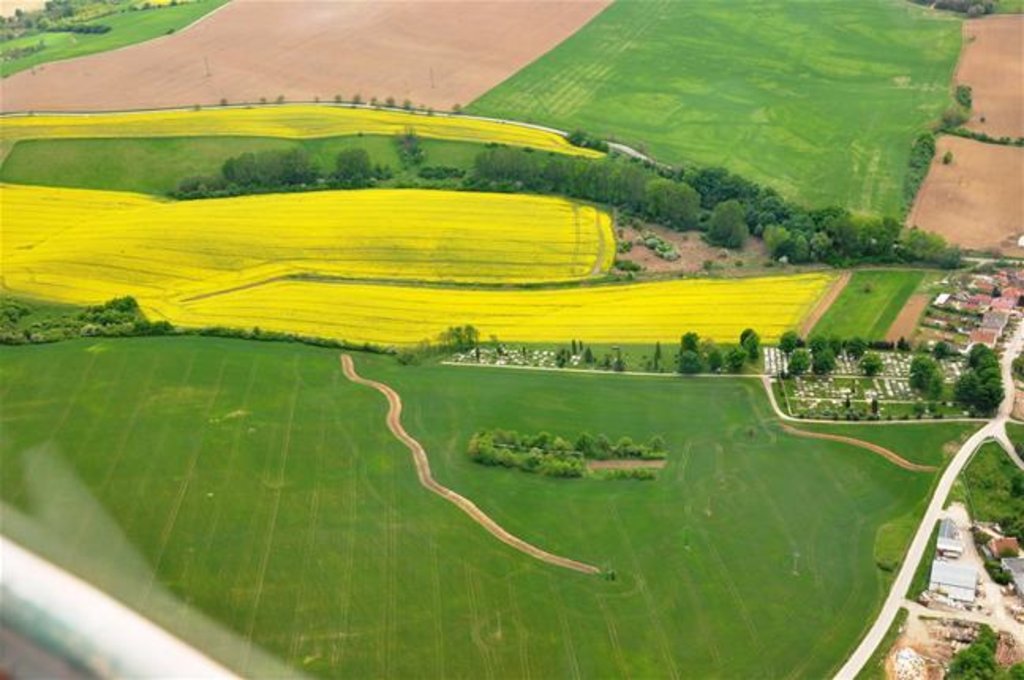
Conservation measures for eroded cropland. The technology contains level ditches of various lengths, which are digged along a contour.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
The structural measures are characterized as small technical structures to control and slow down surface runoff, created after extreme rainfall. The ditch is digged across the slope (along the contour) according to the terrain. Along the four of dithes there were also vegetative strips that should protect and retain rainfall.
Purpose of the Technology: Some damage has been observed on the farmland during storm rainfalls, long-lasting rainfalls, and periods of melting snow. The aim of the conservation measures is to eliminate hazards and damage to health and the economy, to improve the accumulation and infiltration of water into the soil, and to retard the surface runoff on the farmland.
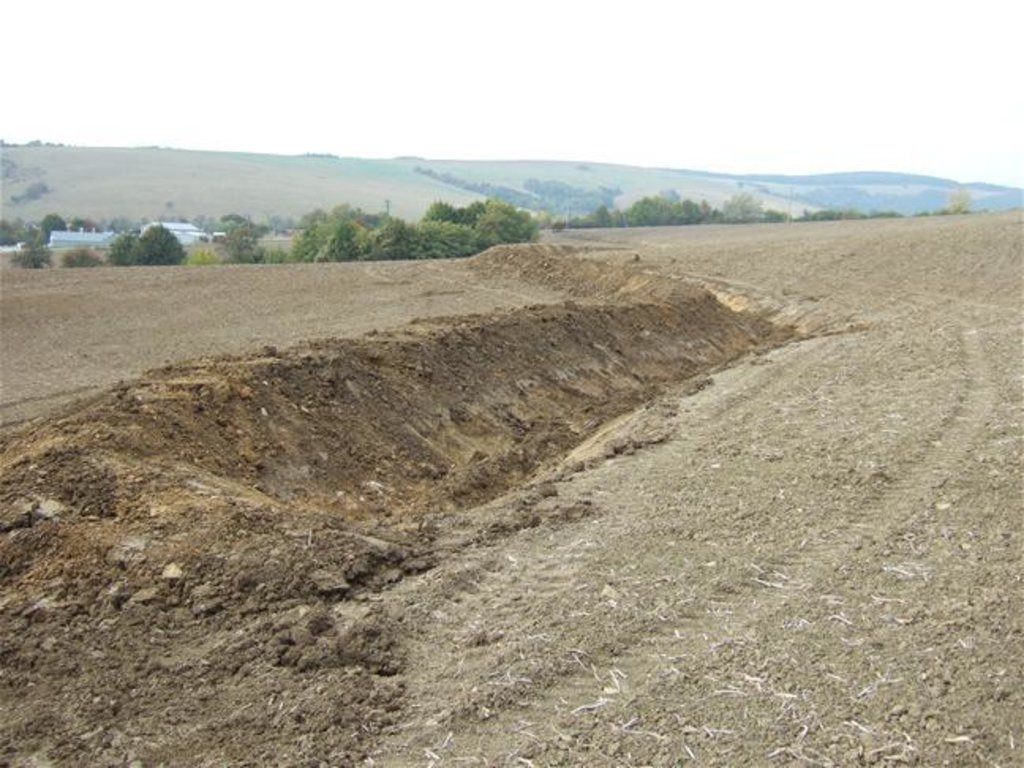
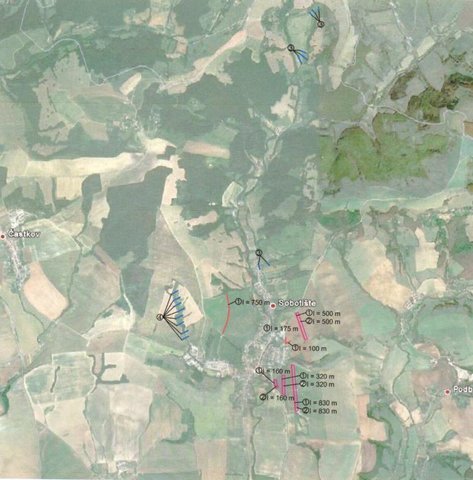
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: There are 7 ditches in the area (2842 m in total/ 23873 m3). In the locality of Padelky there are level ditches with lengths of 160 m + 320 m+ 830m = 1310 m; in the locality of Kubíny there are level ditches with lengths of 500 m + 100 m + 175 m = 775 m; in the locality of Šlachovec there is one ditch with the length of 750 m. The total water retention volume is 23873 m3. The ditches are in the shape of a trapezoid with a base width of 1 m, a height according to the terrain, and a slope of 1:1.5 while the digged soil is moved to the lower part of the ditch.
Natural / human environment: Sobotište is a village in the Teplica river basin; it is situated near the town of Senica in the Trnava region of western Slovakia. It is located in a valley at the foothills of the White Carpathians, which are part of the Carpathian Flysch Belt. The sedimentary flysh rocks are erodible, disintegrable, and sensitive to erosion.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
斯洛伐克
区域/州/省:
Slovakia
有关地点的进一步说明:
Sobotište
注释:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 12.4 km2.
Total area of the cropland cover is 12.37 km2 and the eroded area was estimated as 40 % (4.948 km2). This technology is used in the locality of Padelky and Kubina. Together 7 ditches were built. The area of the village 32.3 km2.
Map
×3. SLM技术的分类
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

农田
- 一年一作
年作 - 具体指明作物:
- 油料作物 - 向日葵、菜籽、其他
每年的生长季节数:
- 1
具体说明:
Longest growing period in days: 180Longest growing period from month to month: April to September
注释:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): The major problem is surface runoff that is formed by extreme rainfall whereby tillage, gully,or interrill erosion is forming.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): There are some soil threads connected with erosion probably due to agricultural practises and heavy mechanism that are visible e.g.: people had noticed a decrease of the hills peak that is tilled. Some problems with sediments occured after heavy rains, mud flowing directly to the city (cemetery, roads etc.) from the surrounding hills and fields.
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Cropland: Ca: Annual cropping
3.3 由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?
由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?:
- 是(请在技术实施前填写以下有关土地利用的问题)

农田
- 一年一作
3.4 供水
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 混合雨水灌溉
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 横坡措施
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

植物措施
- V2:草和多年生草本植物

结构措施
- S4:平沟、坑
注释:
Main measures: structural measures
Secondary measures: vegetative measures
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -contour
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀
- Wo:场外劣化效应
注释:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion
Main causes of degradation: Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts) (Slope in connection with heavy rainfall results in surface runoff that causes erosion and mud floods in the part of the city and nearby roads), other natural causes (avalanches, volcanic eruptions, mud flows, highly susceptible natural resources, extreme topography, etc.) specify (mud flows)
Secondary causes of degradation: soil management (tillage along the slopes, deep tillage), land tenure (Land belongs to private owners and there is often a problem to get permission to use their land for other purposes, or to built conservation measures. The process of land consolidation is too long.), governance / institutional (Legislation: The financial support from the state is mainly focused on flood protection for the main rivers.)
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 防止土地退化
- 减少土地退化
注释:
Main goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
Secondary goals: prevention of land degradation
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
There are 7 ditches in the area (2842 m in total/ 23873 m3). In the locality of Padelky there are level ditches with lengths of 160 m + 320 m+ 830m = 1310 m; in the locality of Kubíny there are level ditches with lengths of 500 m + 100 m + 175 m = 775 m; in the locality of Šlachovec there is one ditch with the length of 750 m. The total water retention volume is 23873 m3. The ditches are in the shape of a trapezoid with a base width of 1 m, a height according to the terrain, and a slope of 1:1.5 while the digged soil is moved to the lower part of the ditch.
Location: Sobotište. Myjava, Slovakia
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap
Secondary technical functions: reduction of slope length, sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting
Aligned: -contour
Vegetative material: O : other
Number of plants per (ha): -
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): -
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): -
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): -
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 40
Other species: Red clover, seeded along the ditch
Retention/infiltration ditch/pit, sediment/sand trap
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 1
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 1
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): various, 2842 m in total
Construction material (earth): The excavated earth is placed on the lower part and mechanically compacted to hold retained water.
Specification of dams/ pans/ ponds: Capacity 23873m3
Catchment area: 12 ham2
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
Eur
如相关,注明美元与当地货币的汇率(例如1美元=79.9巴西雷亚尔):1美元=:
0.88
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Digging of the ditch for 600 mm width | |
| 2. | Adjustment of the ditch´s embankment | |
| 3. | Digging of the ditch for 600-2000 mm width | |
| 4. | Digging of the ditch for over 2000 mm width | |
| 5. | expert guarantor and planner | |
| 6. | Transfer | |
| 7. | Vegetative strips next to the ditch in 40 m width. Red clover. | spring |
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Digging of the ditch for 600 mm width | m3 | 9.9 | 18.14 | 179.59 | |
| 劳动力 | Adjustment of the ditch´s embankment | m2 | 3861.0 | 0.82 | 3166.02 | |
| 劳动力 | Digging of the ditch for 600-2000 mm width | m2 | 5253.0 | 10.24 | 53790.72 | |
| 劳动力 | or Digging of the ditch for over 2000 mm width | m2 | 5253.0 | 1.26 | 6618.78 | |
| 植物材料 | Seeds for vegetative strips next to the ditch in 40 m width. Red clover. | kg | 704.0 | 8.15 | 5737.6 | |
| 其它 | expert guarantor and planner | person | 1.0 | 3062.61 | 3062.61 | |
| 其它 | Transfer | t | 58.655 | 46.11 | 2704.58 | |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 75259.9 | |||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 85522.61 | |||||
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
注释:
Together 7 ditches were built in the study area (1240 ha of cropland). The prices and costs were available as a summary for whole project, therefore the prices correspond for all 7 ditches together. Each of the ditches were slitly different (e.g., the length). The prices are valid for the year 2011. The prices are mostly given for m3 as a unit. (The prices were calculated with the 20% VAT)
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
The costs differ from project to project, it depends on the design, building company atc.
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
农业气候带
- 半湿润
Thermal climate class: temperate
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
关于地形的注释和进一步规范:
Slopes on average: Flat (59%), gentle, (23%) and moderate (9%)
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 粗粒/轻(砂质)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Soil depth on average: Moderately deep (75%), shallow (17%) and very shallow (5%)
Soil texture is coarse/light (34%), fine/heavy (12%) and medium (5%)
Soil fertiliy is medium
Top soil organic matter is unknown
Soil drainage/infiltration is good
Soil water storage capacity is unknown
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地表水的可用性:
过量
水质(未处理):
良好饮用水
关于水质和水量的注释和进一步规范:
Ground water table is unknown
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 中等
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
生产系统的市场定位:
- 混合(生计/商业)
- 商业/市场
相对财富水平:
- 平均水平
个人或集体:
- 团体/社区
机械化水平:
- 机械化/电动
性别:
- 女人
- 男人
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Difference in the involvement of women and men: no.
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: > 4%; 16%
Off-farm income specification: unknown
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 中等规模的
注释:
There are 485 permanently occupied dwellings (2001)
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 社区/村庄
土地使用权:
- 社区(有组织)
- 个人
用水权:
- 社区(有组织)
- 个人
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
社会文化影响
Improved livelihoods and human well-being
注释/具体说明:
The technology decreased risk of the mud flows that are capable of destroying homes, washing out roads, knocking down trees, and obstructing roadways.
生态影响
水循环/径流
地表径流
土壤
土壤覆盖层
土壤流失
其它生态影响
Risk of mud flood
Hazard towards averse events
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
对公共/私人基础设施的破坏
注释/具体说明:
Reduced risk of flooding and damage of the gardens and household.
Reduced the hazards and damage of the surrounding area by heavy rainfall events.
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 增加或减少 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年温度 | 增加 | 好 |
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气象灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 局地暴雨 | 不好 |
| 局地风暴 | 好 |
气候灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 干旱 | 好 |
水文灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 比较和缓的(河道)洪水 | 不好 |
其他气候相关的后果
其他气候相关的后果
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 缩短生长期 | 好 |
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
非常积极
长期回报:
积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
非常积极
长期回报:
积极
注释:
There were no maintanance required so far.
6.5 技术采用
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发的,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 0-10%
注释:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: The implementation of the technology was founded by the state (subsidy).
Comments on adoption trend: UNknown
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| The technology shows to be effective, however the rainfall events that have occured so far were not that extreme as before the implementation. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| The technology is easy to realize. There is no extra knowledge required. The mechanism used to implement the technology is easy to provide. |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| The land users are satisfied with effectivness of the technology. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| I don´t see any disadvantage or weekness of the technology. |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Project documentation, Hydrotechnológia Bratislava, s.r.o., April 2011
7.3 链接到网络上的相关信息
URL:
http://www.obecsobotiste.sk/Vodozadrzne-opatrenia.aspx
URL:
https://www.nku.gov.sk/documents/10157/19a2305b-d9c2-43a7-8262-743650db289b
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接

The programme of landscape revitalization and integrated river … [斯洛伐克]
This approach is devoted to the implementation of 'The Landscape Revitalisation Programme and integrated river basins management of the Slovak Republic' in the Sobotište village.
- 编制者: Zuzana Studvova
模块
无模块