Gravity type inverted tyre structure [南非]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Mirjam Staehli
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
Swaartekrag tipe omgedopte bande struktuur (Afrikaans)
technologies_1374 - 南非
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
关键资源人
SLM专业人员:
Du Toit Boeta P.
Marico Bushveld Soil Conservation Committee, South Africa
南非
SLM专业人员:
Meiring C. H.
Marico Bushveld Soil Conservation Committee, South Africa
南非
1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.5 参考关于SLM方法(使用WOCAT记录的SLM方法)的调查问卷
Community driven Protection of the Molatedi Dam Catchment … [南非]
Development and capacity building in participating communities through the implementation of measures to prevent topsoil losses through erosion in the Molatedi dam catchment area.
- 编制者: Philippe Zahner
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
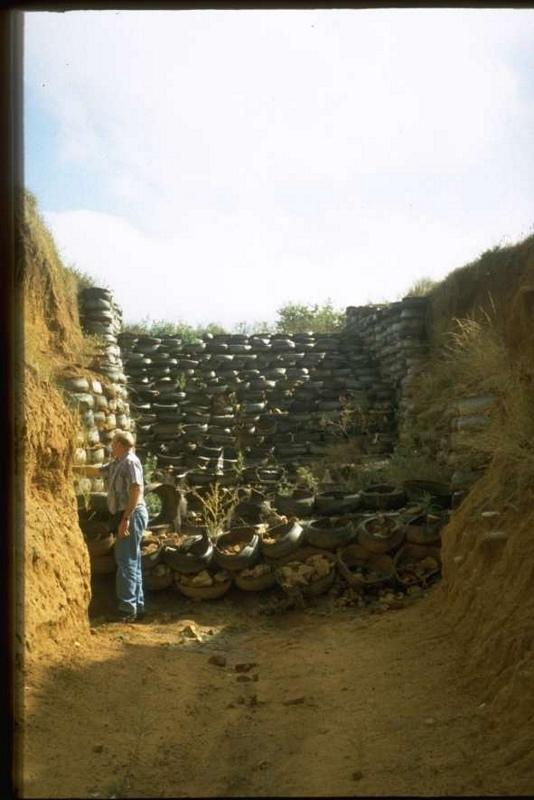
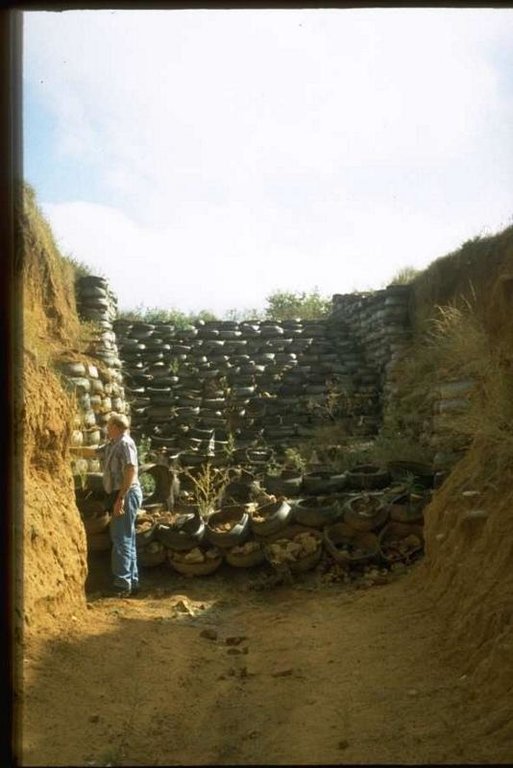
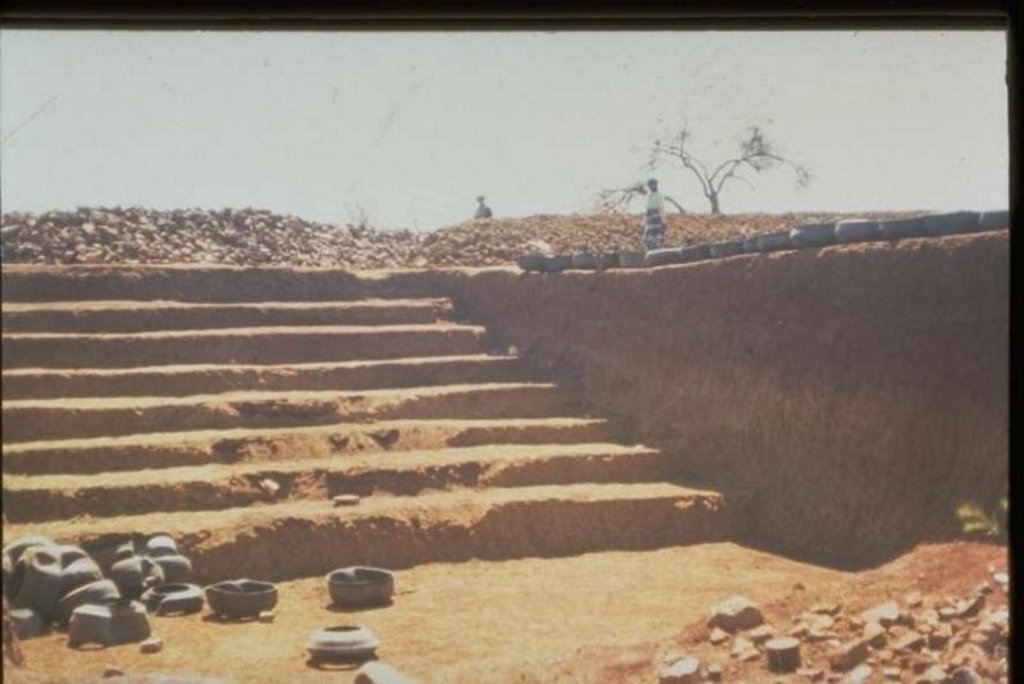
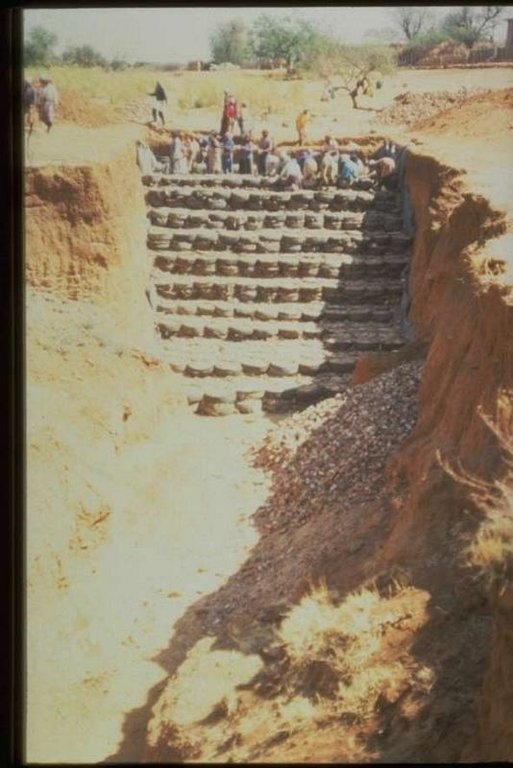
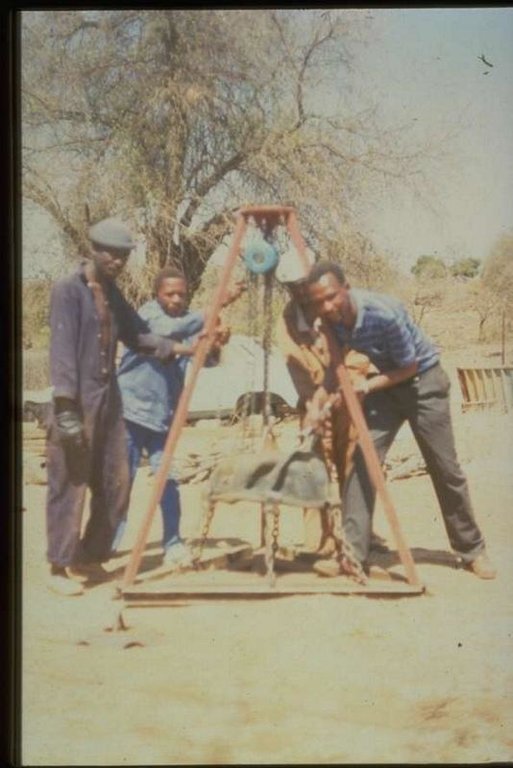
Stabilising of gully erosion by means of gravity type inverted tyre structures filled with stone.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
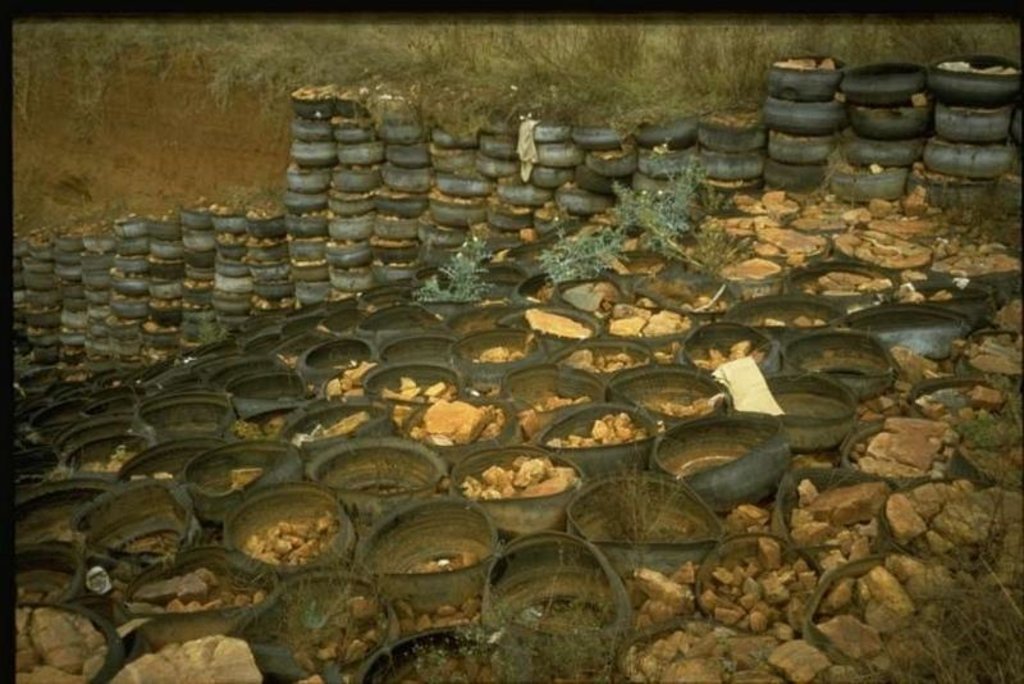
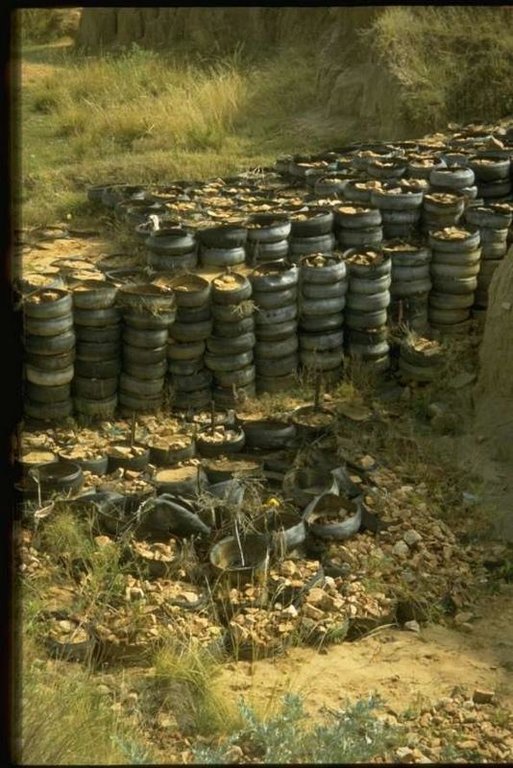
Gravity type inverted tyre structure is bound together with wire and filled with stone.
The valley floor gully head drop is protected to prevent further erosion. Survey planning and design are important for the construction of the structure.
Maintenance includes prevention of leakage alongside the structure. The walls to prevent the erosion of soil are filled in. Ensure that the top layer stones are not washed away.
The structure is situated in a semi-arid area which is highly degraded through overgrazing.
Due to the location of the structure, further erosion was stopped that would have endangered some of the homesteads.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
南非
区域/州/省:
North West Province
有关地点的进一步说明:
Marico District
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果技术均匀分布在一个区域,则指定覆盖的区域(单位为平方千米):
12.0
注释:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 12 km2.
Same technology was also applied in the Molatedi tribal village (70 km away in the same catchment area)
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 不到10年前(最近)
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过项目/外部干预
注释(项目类型等):
Developed by technician department Resource Conservation and farmer from local conservation committee.
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

牧场
注释:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Lack of landuse planning. Overgrazing. Overpopulation.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Lack of grazing land, frequent occurrence of droughts.
Constraints of infrastructure network (roads, railways, pipe lines, power lines): Not planning for access roads in the village
Number of growing seasons per year: 1
Longest growing period in days: 240; Longest growing period from month to month: Sep - Apr
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 横坡措施
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

结构措施
- S1:阶地
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀
- Wg:冲沟侵蚀/沟蚀
注释:
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion
Main causes of degradation: overgrazing, droughts, education, access to knowledge and support services (Lack of knowledge - Lack of training & awareness)
Secondary causes of degradation: over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use, other human induced causes (specify) (Agricultural causes - Lack of extension and planning), land tenure (Land subdivision - Only if someone own land (commercial farmers)), poverty / wealth (Lack of employment), Lack of enforcement of legislat./authority (Regarding natural resources)
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 防止土地退化
- 减少土地退化
注释:
Secondary goals: prevention of land degradation
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
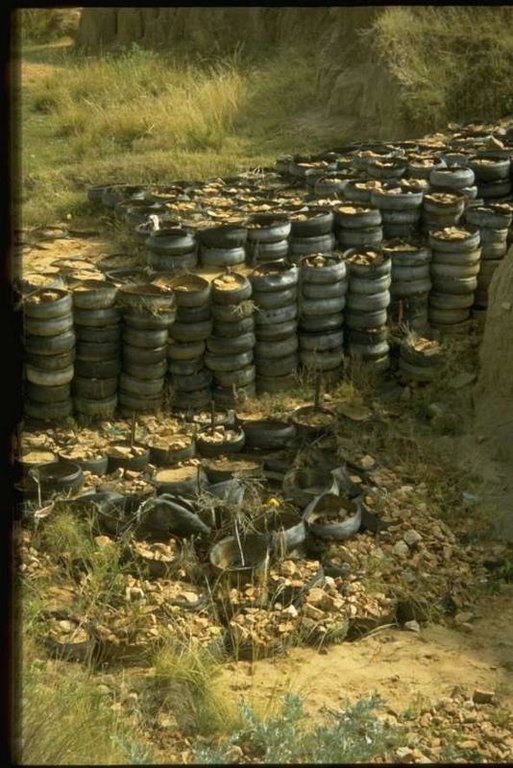
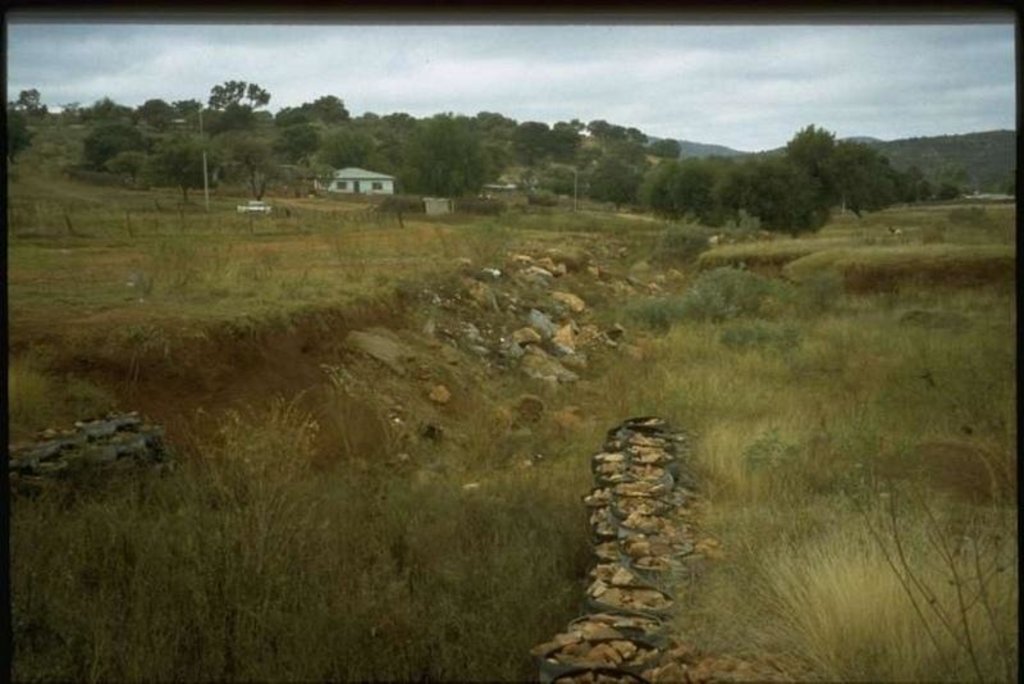
further downstream another tyre construction trapping the silt, behind the structure silting up and vegetation is well growing
North West
Date: April 1999
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard
Structural measure: Gully head drop structure
Construction material (earth): wire iron posts, plastic material, geotextilemembranes (bidim-kaymat) -water permeable soil exclude
Lateral gradient along the structure: 50%
作者:
Mirjam Staehli, Switzerland
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
Rand
如相关,注明美元与当地货币的汇率(例如1美元=79.9巴西雷亚尔):1美元=:
6.0
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
1.50
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Labour | ha | 1.0 | 9400.0 | 9400.0 | |
| 设备 | Tools | ha | 1.0 | 600.0 | 600.0 | |
| 设备 | Tyre averting tool machine | ha | 1.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | |
| 施工材料 | Geotextile membrane | ha | 1.0 | 2000.0 | 2000.0 | |
| 施工材料 | Wire 2mm (rolls a 50kg) | ha | 1.0 | 330.0 | 330.0 | |
| 施工材料 | Fully galvanised iron | ha | 1.0 | 50.0 | 50.0 | |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 12480.0 | |||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 2080.0 | |||||
注释:
Duration of establishment phase: 0 month(s)
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
注释:
The complete structure.
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
Labour - very low productivity. Transportation of tyres. Tying wire must be cut economically according to need otherwise huge waste take place.
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
有关降雨的规范/注释:
Thunderstorms, heavy rainfall
农业气候带
- 半干旱
Summer rainfall
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
说明该技术是否专门应用于:
- 凹陷情况
关于地形的注释和进一步规范:
Soil fertility is low
Soil drainage / infiltration is good
Soil water storage capacity is medium
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 低(<1%)
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
非农收入:
- > 收入的50%
相对财富水平:
- 贫瘠
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Population density: 100-200 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 3% - 4%
and own 100% of the land (Communal land belongs to the tribe).
Off-farm income specification: State pensions- head of family work elsewhere.
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 社区/村庄
土地使用权:
- 自由进入(无组织)
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
收入和成本
收入来源的多样性
注释/具体说明:
short term job creation
社会文化影响
社区机构
SLM/土地退化知识
生态影响
土壤
土壤流失
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
下游洪水
下游淤积
spending on consumer goods in shops in area
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
中性/平衡
长期回报:
积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
积极
6.5 技术采用
- 11-50%
如若可行,进行量化(住户数量和/或覆盖面积):
20 percent of the area
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发的,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 0-10%
注释:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
100 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: estimates
There is no trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Labour intensive, job creation |
| Received training |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Low cost material |
| Labour intensive can be utilized without machinery |
| Mostly unskilled labour can be used. |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Storm water walls are in the way of motor vehicles, travelling in the village | Plan roads properly - construct alternative road around wall. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Costly if manual labour is unproductive | Maintain high productivity. Train workers, work smart, contract work |
| Transport cost of tyres is a big factor. | Utilize tyres from nearby areas. Utilizes big transport trucks with big loading capacity. |
| Need machine to invert tyres | Tool well and practically constructed - operators trained. |
| Must technically be well planned and constructed. | Use skilled technician for planning and to assist workers during construction. |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接

Community driven Protection of the Molatedi Dam Catchment … [南非]
Development and capacity building in participating communities through the implementation of measures to prevent topsoil losses through erosion in the Molatedi dam catchment area.
- 编制者: Philippe Zahner
模块
无模块