Improved Kibanja cropping system [坦桑尼亚联合共和国]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Jasson Rwazo
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
Ekibanja ekiine emikolele emirungi (Haya/Nyambo)
technologies_1183 - 坦桑尼亚联合共和国
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
Government:
SLM专业人员:
Government:
Makung'uto Iddi
Missenyi District Council
坦桑尼亚联合共和国
Government:
Kagaruki Anna Grace
Missenyi District Council
坦桑尼亚联合共和国
Government:
Subira John
Missenyi District Council
坦桑尼亚联合共和国
SLM专业人员:
Kaihura Fidelis
Kagera TAMP
坦桑尼亚联合共和国
Government:
Kitundu Elizabeth
Missenyi District Council
坦桑尼亚联合共和国
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
The Transboundary Agro-ecosystem Management Project for the Kagera River Basin (GEF-FAO / Kagera TAMP )有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) - 意大利有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Missenyi District Council (Missenyi District Council) - 坦桑尼亚联合共和国1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.5 参考关于SLM方法(使用WOCAT记录的SLM方法)的调查问卷

Integrated farm knowledge adoption [坦桑尼亚联合共和国]
The way and means through which a performing farmers adopt and use a combination of indigenous and scientific to maximaze production.
- 编制者: Jasson Rwazo
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
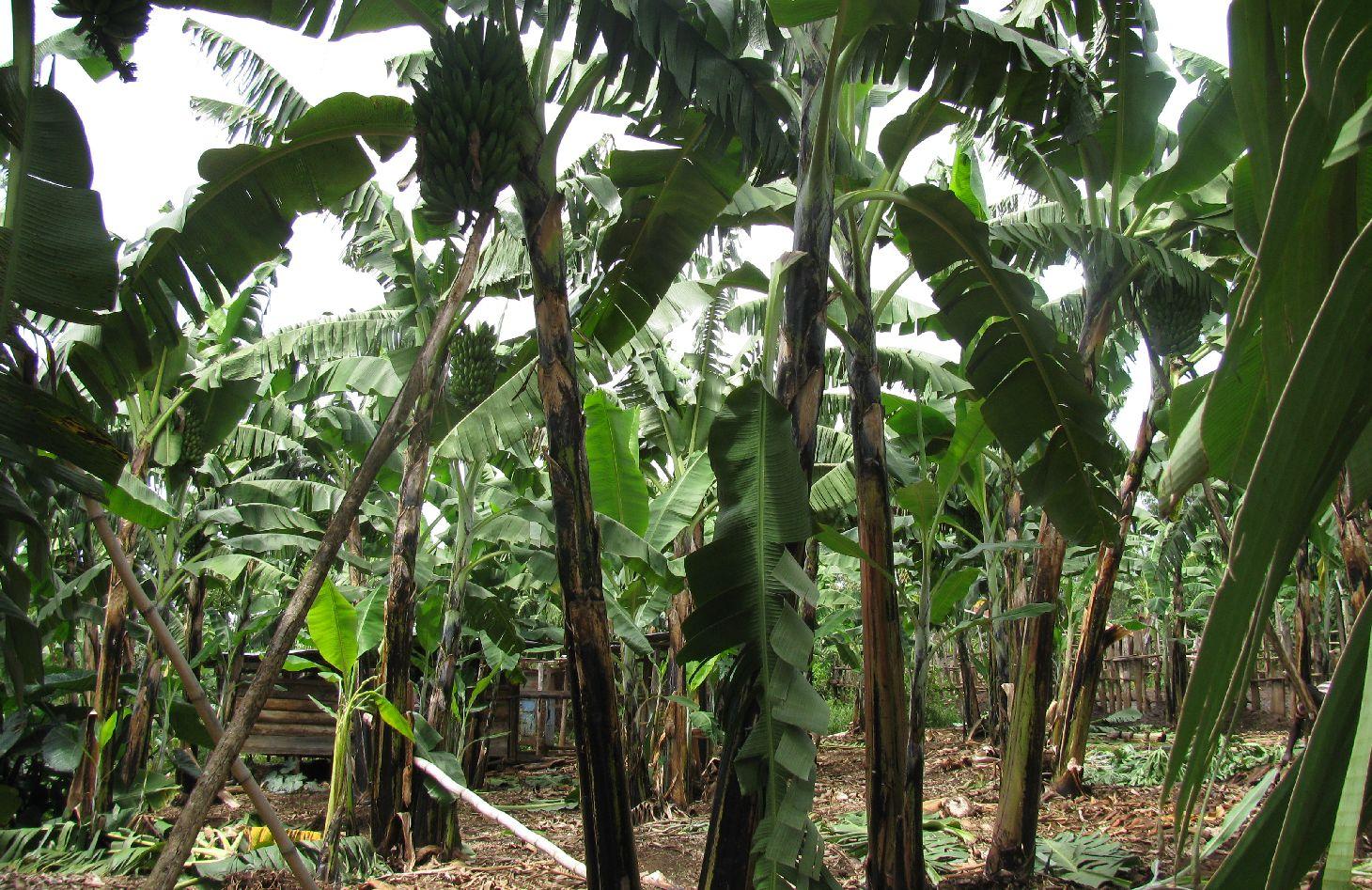
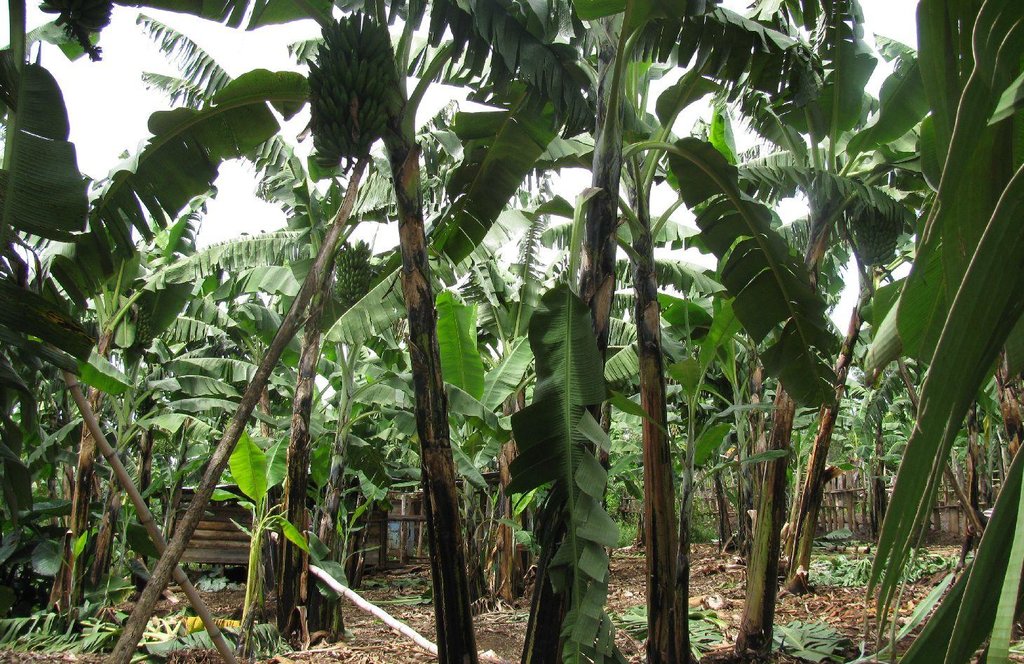
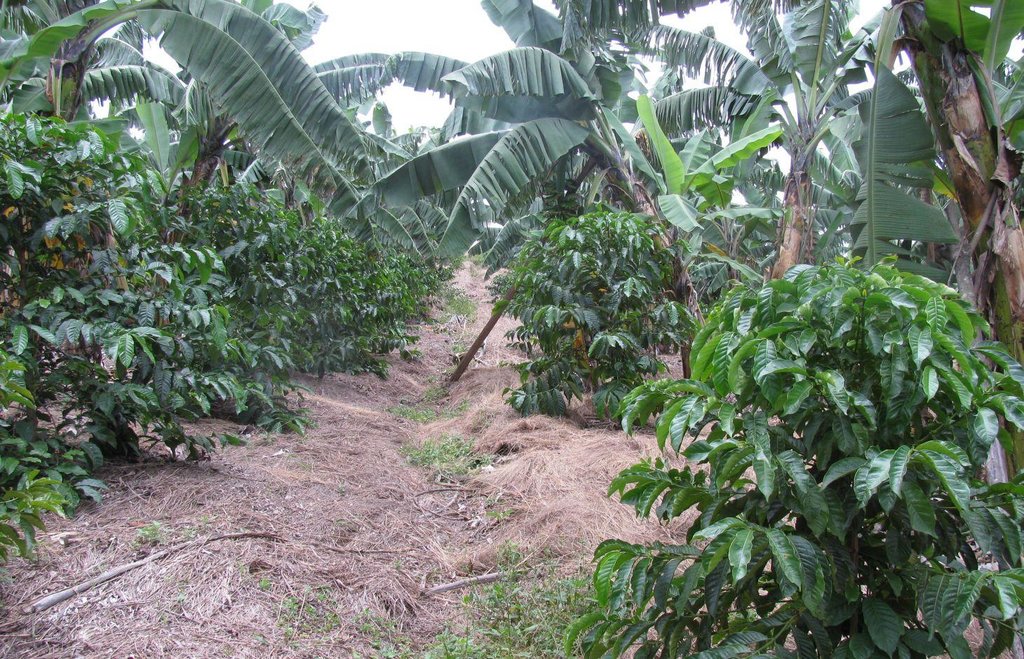
This is a traditional banana and coffee complex cropping system interplanted with annual crops, trees,shrubs, vegetables and other diverse plants of social economic importance.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
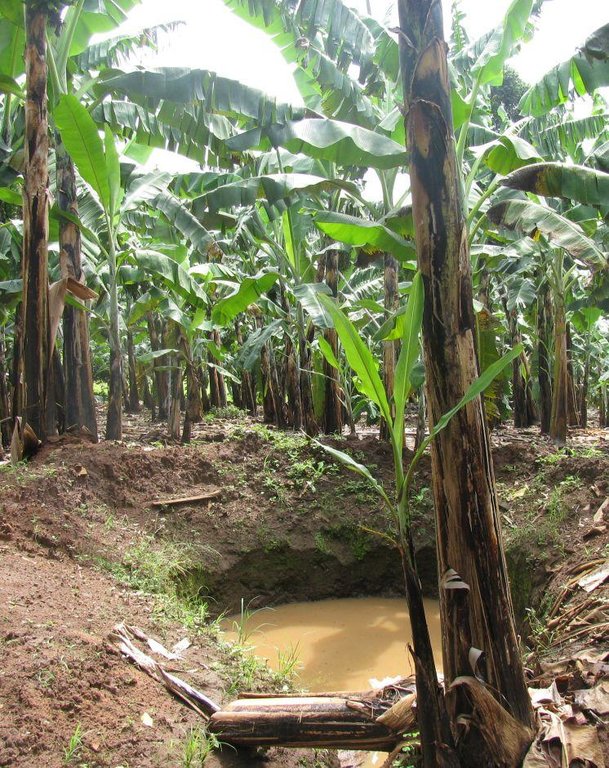
Improved traditional multi-cropping system that combines banana and coffee as main crops planted in a specific spacing to optimize plant stands. Banana and coffee are intercropped with; 1. annuals crops: Maize, beans, yams, coco-yams;2. Vegetables: Lycoperscum esculentum, Amaranthus spp, Cucumis communis and Solanum aethopium ;3. Shrubs of social economic value. Trees (e.g Maesopsis eminii, Makhcamia lutea, Ricinus comunis, Ficus thorninghii) and shrubs (Dracaena usambarensis) are planted on the farm edge. These serve as live fence, wind breaker, source of timber, fuel wood, medicine and protect the field against erosion. To optimize farm production, application of 15cm thick mulch ( grass mulch and banana prunnings), farmyard or compost manure and interplanting with soil fertility and/or soil moisture improvement trees are ensured. With problems of climate change, water harvesting ditches and trenches are constructed. Water harvesting ditches are constructed to collect water from micro catchments like roads or homestead. Sustainability of the Improved Kibanja system has always been assured through crop/livestock integration approaches.The cropping system is typical in high rainfall areas along foot slopes, valley bottoms or hilltops preferably on fertile and deep soils.
Purpose of the Technology: The purpose is improve soil fertility,moisture, controlling soil erosion (wind and water) and suppressing weeds in order to improve the production banana, coffee and other inter planted crops.
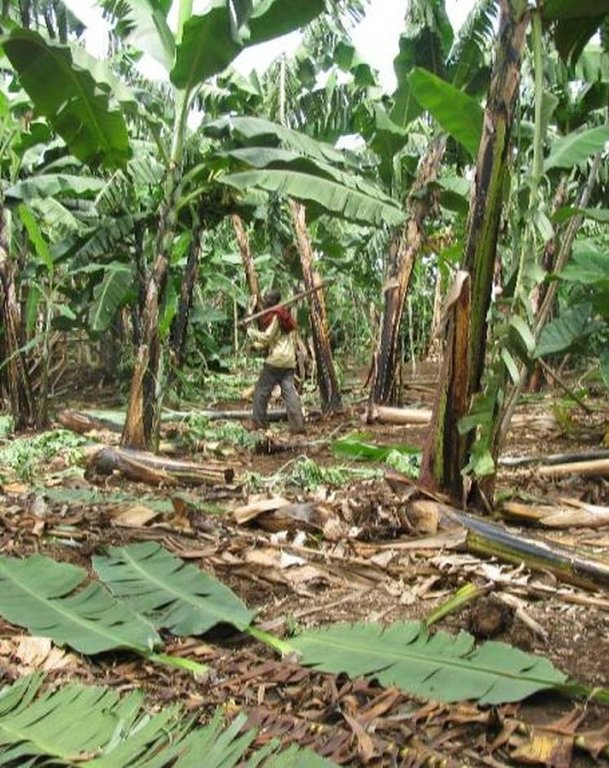
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Establishment activities: 1. Land clearing and preparation: Slashing, uprooting tree stumps, ploughing and pitting 60cm x 90cm banana hole and 60cm x 60cm coffee (Mid June to August) using simple farm implements; 2.Farm Yard Manure application: 60 Kg per banana holes and 36 Kg per coffee hole (August to early September); 2. Planting: 308 banana suckers at 3.6m x 8m spacing, 830 coffee seedlings at 3m x 8m spacing in alternating row, edge row trees seedling at 10m spacing and 15cm spacing for shrubs e.g. Dracaena usambarensis (September to November);4. Excavation of water retention structure ( after planting mainly in Novermber). Full establishment of Improved Kibanja cropping system can be attained in three years.
Maintenance activities:1. Weeding:Done two times per year (mid January to February / July to augost) before planting annual crops; 2.FYM enrichment: Every after 3 years; iii. banana dethrashing and desuckering ,topping mulch, coffee pruning and harvesting (Immediately after weeding); 4. Other maintenence activities: Disease control (nematode, banana weevils, Banana Xanthamonas Wilt) and Propping (using pole to support banana plant with heavy bunches against wind); 5.Inputs: Labour, farmyard manure, propping poles, mulch; 6. Simple farm implements:Hand hoe,machete and wheel barrow.
Natural / human environment: The technology is implemented in mixed land use type under sub humid condition receiving 1000-1500mm of rains per year. A combination of soil and water improvement measures (FYM application, Mulching, water retention ditches and live fencing) complement each other to minimize risk of crop failure and hence improve production. The slope is gentle to moderate , soil depth is moderate and soil texture loam. Simple hand tools are traditional used,Land ownership is individual not titled. Application of this technology determined by high establishment and maintenence cost.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
坦桑尼亚联合共和国
区域/州/省:
Tanzania
有关地点的进一步说明:
Missenyi District, Kyazi Village
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果不知道精确的区域,请注明大致覆盖的区域:
- < 0.1 平方千米(10 公顷)
注释:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.062 km2.
2ha approximately
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 不到10年前(最近)
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过项目/外部干预
注释(项目类型等):
Improved traditional land use system: The use of combination of measures in Improved Kibanja Cropping system in Kagera has been existing for more than 100 year ago.
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 改良生产
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
- improve soil fertility
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型
同一土地单元内混合使用的土地::
是
具体说明混合土地使用(作物/放牧/树木):
- 农牧业(包括农牧结合)

农田
- 一年一作
- 多年一作(非木材)
- 乔木与灌木的种植
- Ficus thoninji,Markhamia lutea,Maesopesis eminii
年作 - 具体指明作物:
- 豆科牧草和豆类 - 豆子
- Lycoperscum esculentum, Amaranthus spp, Cucumis communis and Solanum aethopium
多年生(非木质)作物 - 指定作物:
- 香蕉/芭蕉/蕉麻
乔木和灌木种植 - 指定作物:
- 鳄梨
- Orange, Paw paw, Maesopsis eminii, Makhcamia lutea, Ricinus comunis, Ficus thorninghii, Dracaena usambarensis
每年的生长季节数:
- 2
具体说明:
Longest growing period in days: 120; Longest growing period from month to month: Short rains (September to December); Second longest growing period in days: 65; Second longest growing period from month to month: Long rains (March to June)
采用间作制度了吗?:
是
如果是,说明哪些作物是间作的:
banana, coffee

森林/林地
产品和服务:
- 木材
- 薪材
- 其它森林产品
注释:
Livestock density (if relevant):
1-10 LU /km2
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Soil nutrient loss, decline of soil moisture and soil erosion by wind and fast water runoff.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Reduced crop production, loss of indigenous medicinal plants, reduced water water quatity in natural water sources.
Type of cropping system and major crops comments: Due to mixed farming and agroforestry there is high nutrient cycling resulting in high productivity
3.4 供水
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 农业林学
- 防风林/防护林带
- 集水
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

农艺措施
- A2:有机质/土壤肥力

植物措施
- V1:乔木和灌木覆盖层
- V2:草和多年生草本植物

结构措施
- S4:平沟、坑

管理措施
- M3:根据自然和人文环境进行布局
注释:
Secondary measures: management measures
Type of agronomic measures: mixed cropping / intercropping, retaining more vegetation cover, mulching, manure / compost / residues, minimum tillage, pits
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -against wind, aligned: -along boundary, aligned: -linear
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀

化学性土壤退化
- Cn:肥力下降和有机质含量下降(非侵蚀所致)

生物性退化
- Bc:植被覆盖的减少
注释:
Main causes of degradation: soil management (Cultivation along the slope and overcultivation), crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (Cultivation of season crop without reprenishing of soil nutrients), change of seasonal rainfall (Fractuation in rain season), droughts, population pressure, education, access to knowledge and support services
Secondary causes of degradation: Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts), land tenure, poverty / wealth, inputs and infrastructure: (roads, markets, distribution of water points, other, …)
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 防止土地退化
- 减少土地退化
注释:
Secondary goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
Location: Kyazi Village. Missenyi District, Kagera Region, Tanzania
Date: 2012.08.28
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate (The technology requires moderate technical knowledge for adoption)
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate (The technology requires moderate technical knowledge for adoption)
Main technical functions: control of raindrop splash, control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap, improvement of ground cover, increase in organic matter
Secondary technical functions: increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), increase of infiltration, water harvesting / increase water supply, reduction in wind speed, increase of biomass (quantity)
Mixed cropping / intercropping
Material/ species: Banana
Quantity/ density: 304
Remarks: 3.6 m by 8m
Retaining more vegetation cover
Material/ species: Beans
Remarks: Random
Mulching
Material/ species: Grass mulch, banana(Prooning) trashes mulch
Quantity/ density: 10000
Remarks: Spreading the mulch
Material/ species: Coffee
Quantity/ density: 830
Remarks: 3m by 8m
Manure / compost / residues
Material/ species: Farmyard manure, farm residure,
Quantity/ density: 40 tone
Remarks: Spreading on the pit
Minimum tillage
Material/ species: Hand hoe,matechette
Pits
Material/ species: Hand hoe,matechette
Aligned: -against wind
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 277
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): Random
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): Random
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): Random
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 6
Aligned: -along boundary
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 100000
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.01
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.01
Aligned: -linear
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 100000
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.01
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.01
Trees/ shrubs species: Maeesopsis Eminii, Dracaena usambalensis,Erythrina abysinica
Fruit trees / shrubs species: Pawpaw, Orange, Avocado
Perennial crops species: Banana, Coffee, Vanilla
Other species: Carisa edulis (shrubs)
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 6.3%
Gradient along the rows / strips: 6.3%
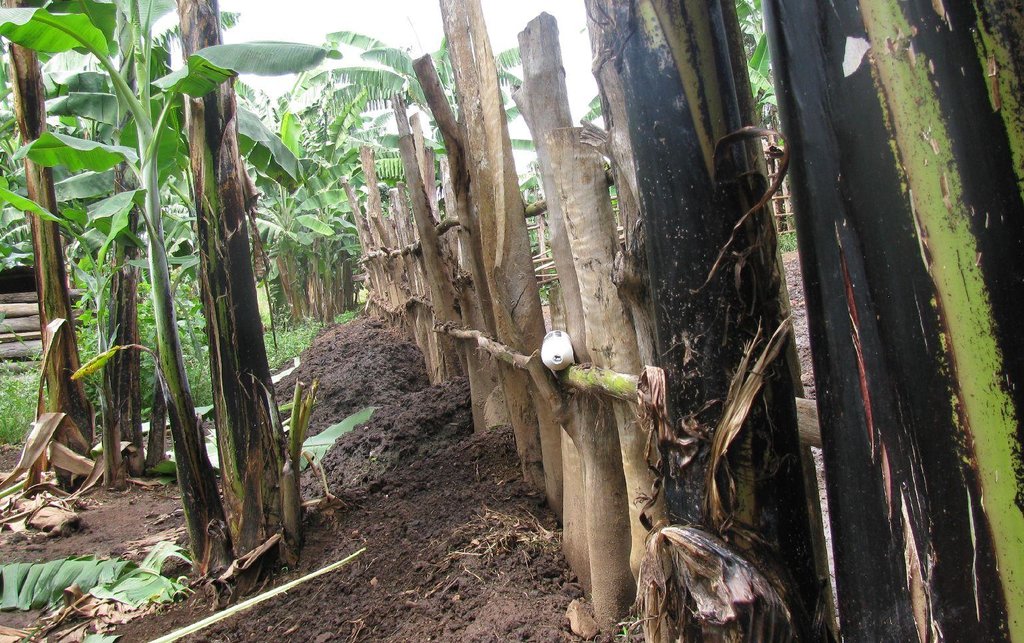
Diversion ditch/ drainage
Vertical interval between structures (m): 0.4
Spacing between structures (m): 6
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.3
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.3
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 3
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.15
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.15
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 3
Waterway
Vertical interval between structures (m): 0.4
Spacing between structures (m): 6
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.75
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 1.5
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 2
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.3
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.4
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 5
Retention/infiltration ditch/pit, sediment/sand trap
Vertical interval between structures (m): 0.4
Spacing between structures (m): 6
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.75
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 1.5
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 2
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.3
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.4
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 5
Construction material (earth): 2.25 m3 of earth material used per ditch
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 6%
Lateral gradient along the structure: 8%
Specification of dams/ pans/ ponds: Capacity 10m3
Catchment area: 1.6Ham2
For water harvesting: the ratio between the area where the harvested water is applied and the total area from which water is collected is: 1:3.5
作者:
Jasson Rwazo, P.O.BOX 38 Misseny Tanzania, rjrwazo@gmail.com
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
具体说明成本计算所用货币:
- 美元
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
1
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Land clearing and preparation:Slashing,uprooting tree stumps, ploughing and pitting | June to August |
| 2. | Availing and applying 54 tone Farm Yard | August to early September |
| 3. | Planting: 308 banana suckers 830 coffee and tree edge low tree seedlings | From September |
| 4. | Construction of water harvesting ditches | Once year |
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Land clearing | persons/day | 202.0 | 1.18316 | 239.0 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Construction of water harvesting ditches | persons/day | 4.0 | 0.937 | 3.75 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Tools | ha | 1.0 | 61.56 | 61.56 | 100.0 |
| 植物材料 | Seedlings | pieces | 1138.0 | 0.0468 | 53.26 | 100.0 |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | Manure | tons | 54.0 | 34.7222 | 1875.0 | |
| 其它 | Cuttings | ha | 1.0 | 2234.6 | 2234.6 | 100.0 |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 4467.17 | |||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 4467.17 | |||||
注释:
Duration of establishment phase: 36 month(s)
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Topping grass mulch | 3 times per year |
| 2. | Farm yard manure enrichment | 2 times per year |
| 3. | Removal of sediments and debris in water retention ditches. | Every year |
| 4. | To replacement propping Poles | Every 1.5 year |
| 5. | To corve transportation cost | Manure |
| 6. | Replacement of propping pole and live hedges | Every 1.5 year |
| 7. | Removal of sediments and debris in water retention ditches | Once per year |
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Topping grass mulch | persons/day | 10.0 | 4.101 | 41.01 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Applying FYM | persons/day | 10.0 | 3.906 | 39.06 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Removal of sediments | persons/day | 4.0 | 0.9375 | 3.75 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | To replacement propping Poles | persons/day/ha | 10.0 | 3.906 | 39.06 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Tools | per ha | 4.0 | 1.875 | 7.5 | 100.0 |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | Farm yard manure | tons | 20.833 | 46.8 | 974.98 | 100.0 |
| 施工材料 | Wood | pieces/ha | 600.0 | 0.625 | 375.0 | 100.0 |
| 其它 | Mulching material | bundle | 300.0 | 1.875 | 562.5 | 100.0 |
| 其它 | Transportation | trips | 19.0 | 61.673 | 1171.79 | 100.0 |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 3214.65 | |||||
| 技术维护总成本,美元 | 3214.65 | |||||
注释:
Machinery/ tools: Machetes, Mattocks, Hand hoe, spade, wheel barrow, Machete,Hand hoes, spade, Hand hoe,Machete, Spade
Cost assesment completed in June 2012
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
Manure is most determinate factor high transportation cost especially during establishment
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
有关降雨的规范/注释:
Avarage rainfall 1200mm, Bimode rainfall, 5 month dry season
农业气候带
- 半湿润
Thermal climate class: tropics. Annual temperature 23C
Length of growing period 120 -300 days
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
说明该技术是否专门应用于:
- 凹陷情况
关于地形的注释和进一步规范:
Altitudinal zonation: 1270m a.s.l
Slopes on average: Movement of soil due to erosion, exposure of parent rock on some part of the farm
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 中(1-3%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Soil depth on average: Shallow on the hill slope and moderately deep on the valley bottom, also deep sometimes
Soil texture (topsoil): Sandy loam
Topsoil organic matter: Due to the high use of organic manure (farm yard manure) and mulch
Soil fertility is medium
Soil drainage / infiltration is medium due to the high use of organic manure (farm yard manure), mulch, good aeration
Soil water storage capacity is medium due to the high use of organic manure (farm yard manure) and mulch
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
> 50米
地表水的可用性:
中等
水质(未处理):
不良饮用水(需要处理)
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 中等
关于生物多样性的注释和进一步规范:
Different species of soil micro organisms and plant species
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
生产系统的市场定位:
- 混合(生计/商业)
非农收入:
- 低于全部收入的10%
相对财富水平:
- 平均水平
个人或集体:
- 个人/家庭
机械化水平:
- 手工作业
性别:
- 女人
- 男人
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Difference in the involvement of women and men: The land inheritance is mainly dominated by male, women mostly use the land for production of understory crops such as beans; banana and coffee production is dominated by men
Population density: > 500 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2% - 3%; 3%
5% of the land users are very rich and own 30% of the land (Own 2.5-5 acre land, car, 10-20 catlle,brick wall house).
15% of the land users are rich and own 20% of the land (Own 1-2.5 acre of land,2-5 cattle, brick wall house).
60% of the land users are average wealthy and own 35% of the land (Own 0.5-1 acre of land,2-3 goats,mud wall house with corrugarated iron roof).
15% of the land users are poor and own 10% of the land (Own 0-0.5 acre of land, no livestock, mud house withgrass roofing).
5% of the land users are poor and own 5% of the land (Does not own land or own less than 0.5 acre of land, work as casual labour).
Off-farm income specification: 90% of land users income depends on on- income
Market orientation of production system: Mainly for substence for commecial
Level of mechanization: Using hand tools
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 个人,未命名
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
SLM之前的数量:
50
SLM之后的数量:
300
注释/具体说明:
Bunch of banana with 70 kg each
生产故障风险
产品多样性
注释/具体说明:
Depend mainly on banana sell
土地管理
收入和成本
农业投入费用
SLM之前的数量:
1875 $
SLM之后的数量:
1406 $
农业收入
SLM之前的数量:
6250
SLM之后的数量:
25000
注释/具体说明:
Annual income in dollar
收入来源的多样性
注释/具体说明:
Solery depend on farm
工作量
注释/具体说明:
Reduced weeding, but technology is labour intensive.
社会文化影响
食品安全/自给自足
SLM之前的数量:
1000
SLM之后的数量:
4000
注释/具体说明:
Increase in bunch of banana produde annually
健康状况
SLM之前的数量:
5
SLM之后的数量:
2
注释/具体说明:
Frequency of attedndence to hospital due to edequate food supply
娱乐机会
SLM/土地退化知识
注释/具体说明:
Adoption by neighbouring farmers
生态影响
水循环/径流
水的回收/收集
SLM之前的数量:
0
SLM之后的数量:
10
注释/具体说明:
Due to water harvesting dithchers along the foot path in the farm
地表径流
注释/具体说明:
Due to the use of mulch and corver crops
蒸发
注释/具体说明:
Due to corver crop and mulch
土壤
土壤水分
注释/具体说明:
Use of banana trash mulch and other corver crops
土壤覆盖层
养分循环/补给
生物多样性:植被、动物
生物量/地上C
减少气候和灾害风险
碳和温室气体的排放
火灾风险
注释/具体说明:
Due to mulching material
风速
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
水资源可用性
对邻近农田的破坏
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 增加或减少 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年温度 | 增加 | 好 |
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气象灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 局地暴雨 | 好 |
| 局地风暴 | 好 |
气候灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 干旱 | 好 |
水文灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 比较和缓的(河道)洪水 | 不好 |
其他气候相关的后果
其他气候相关的后果
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 缩短生长期 | 好 |
注释:
Use drainage trenches
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
稍微积极
长期回报:
非常积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
非常积极
注释:
Depending on regular application of manure and mulch plus good management of the farm
6.5 技术采用
- > 50%
如若可行,进行量化(住户数量和/或覆盖面积):
317 households (70 percent of all land users in the area)
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发的,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 91-100%
注释:
317 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Limited with high labour and input cost (Manure)
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
Increased house hold food security and income How can they be sustained / enhanced? Schedule regular maintenance activities |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
Soil moisture conservation How can they be sustained / enhanced? Maintenance of water harvesting ditches and replacement of mulching materials |
|
Soil fertility improvement How can they be sustained / enhanced? Regular application of manure and mulch |
|
Improvement of soil structure and aeration How can they be sustained / enhanced? Manure and mulch application |
|
Control of soil erosion How can they be sustained / enhanced? Maintenance of plant cover and water retention ditches, manure and mulch application |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| High labour and capital demand | Phase in implementation and regular maintenance of the technology |
| High risk of fire | Use of fire breaks |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Improving Productivity of Field Crops and Post Harvest Management in North west Tanzania,United Republic of Tanzania Ministry of Agriculture, Food and Cooperatives,2008
7.3 链接到网络上的相关信息
标题/说明:
Kagera TAMP project website
URL:
http://www.fao.org/nr/kagera/en/
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接

Integrated farm knowledge adoption [坦桑尼亚联合共和国]
The way and means through which a performing farmers adopt and use a combination of indigenous and scientific to maximaze production.
- 编制者: Jasson Rwazo
模块
无模块