Animal manure use in a citrus orchard [乌干达]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Jalia Namakula
- 编辑者: JOY TUKAHIRWA
- 审查者: Drake Mubiru, Nicole Harari, Alexandra Gavilano
Anyukwa
technologies_2254 - 乌干达
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
关键资源人
土地使用者:
Ojoadi Charles
Green Valley enterprise
乌干达
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
Scaling-up SLM practices by smallholder farmers (IFAD)有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Uganda Landcare Network (ULN) - 乌干达1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.4 所述技术的可持续性声明
这里所描述的技术在土地退化方面是否存在问题,导致无法被认为是一种可持续的土地管理技术?:
否
注释:
Application of animal manure improves the soil organic matter content, hence improving soil fertility.
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
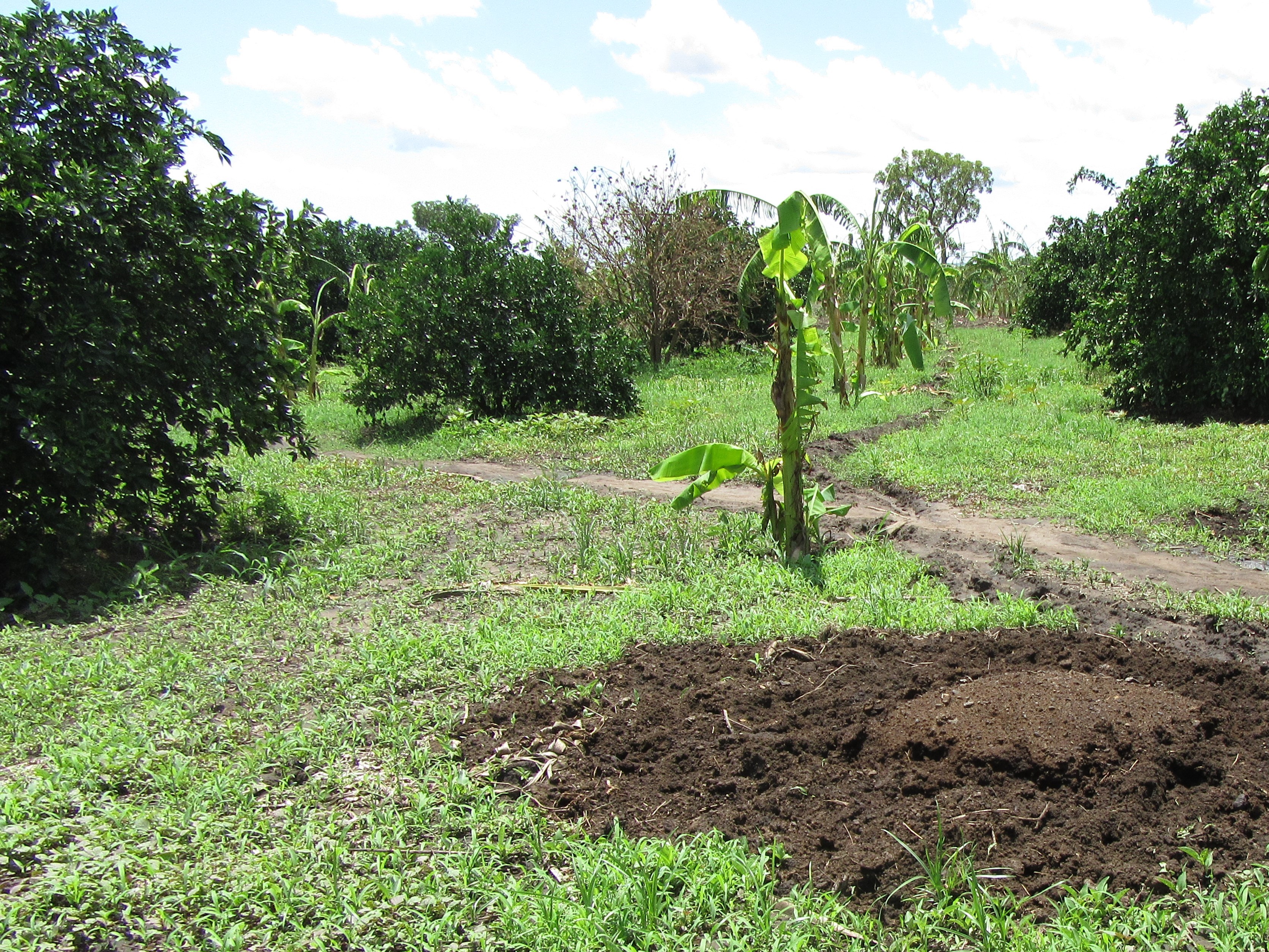
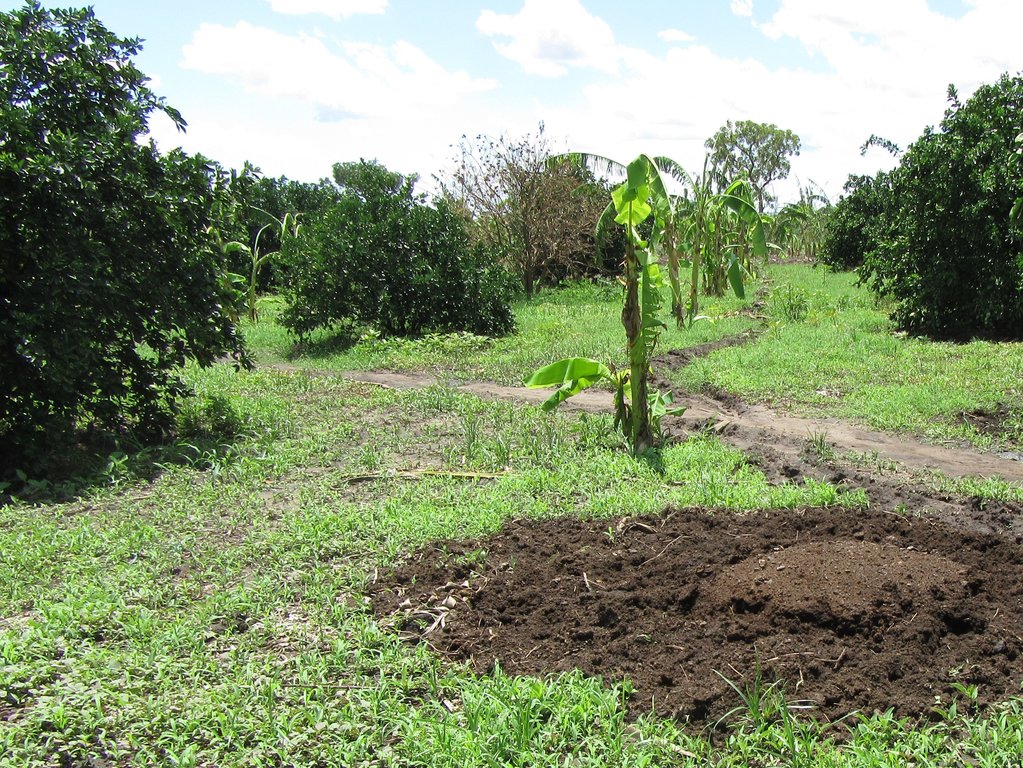
Application of animal manure on citrus trees (citrus sinensis) for improving soil productivity. Every beginning of season (March and August) 40 kg of animal manure are applied, 60 cm away from the tree trunk, using the ring method to improve soil fertility for increased yields and farm income.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
Use of animal manure is a recommended agronomic practice for soil fertility enhancement in agro-ecosystems. Animal manure application contributes to the build-up of soil organic matter and supplies most of the required nutrients, both of which ultimately improve soil health and productivity. Additionally, manure improves the soil’s water holding capacity, improves soil structure, resulting into improved water infiltration and reduced runoff.
Animal manure is applied on citrus trees at the Green Valley Enterprise farm located in Adjumani District found in Northern Uganda. The farm lies on a gentle slope in an area with predominantly sandy soils. This area experiences a bimodal rainfall pattern with an annual average of 1000 mm. The farm is strategically located close to River Adidi, which is used to provide water for irrigation during the dry months. The purpose of animal manure application on the citrus trees is to increase soil fertility and health, thus improving fruit quality and quantity. Since the soils on the farm are sandy, the land user needs to have a good soil fertility and water management plan in place.
At the beginning of every cropping season, 70 bags of animal manure from cows, each weighing about 100 kg are bought and applied on over 111 citrus trees planted on an acre of land. The citrus trees are a mixture of Washington navel and Hamlin, planted at a spacing of 6×6 m. Before application, the animal manure is collected, heaped and left to decompose under shade at the owner’s kraal for 4 months. At the farm, the manure is applied using the ring method, that is, 60 cm radius from the tree trunk and covered with grass mulch. Forty (40) kg of the manure is applied per tree per season. Application of the animal manure on one acre is estimated to cost UGX 540,000, while maintenance costs are estimated to be UGX 50,000 per season.
At this farm, animal manure application has increased citrus fruit yields up to seven folds. When covered with grass mulch it improves soil moisture retention, hence the farmer is able to have two major harvests annually. In addition, the trees on which manure is applied are more tolerant to dry spells. The main disadvantages of use of animal manure are intensive labour requirement for handling, and variability in manure quality depending on the source.
2.3 技术照片
2.4 技术视频
注释、简短说明:
Video showing animal manure being applied on oranges.
日期:
10/05/2017
位置:
Elegu Central
摄影师的名字:
Isa Yiga
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
乌干达
区域/州/省:
Northern Uganda
有关地点的进一步说明:
Elegu Central
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 适用于特定场所/集中在较小区域
注释:
3.52880,32.00569 is located in Adjumani District, Northern Uganda.
The manure is applied in this case around the citrus trees 60cm away from the tree trunk.
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 10-50年前
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过土地使用者的创新
注释(项目类型等):
Land user started applying manure 10 years ago after realizing low yields without the use of any fertilizers on his crops.
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 改良生产
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
- 创造有益的经济影响
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

农田
- 多年一作(非木材)
- 乔木与灌木的种植
多年生(非木质)作物 - 指定作物:
- 香蕉/芭蕉/蕉麻
乔木和灌木种植 - 指定作物:
- 柑橘属
每年的生长季节数:
- 2
具体说明:
Oranges are harvested in July and December
3.3 由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?
注释:
The land use has not changed since application of animal manure, the oranges were grown 10 years ago.
3.4 供水
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 混合雨水灌溉
注释:
During the dry season, water is pumped from a stream that flows through the farm to irrigate the citrus trees .
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 土壤肥力综合管理
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

农艺措施
- A2:有机质/土壤肥力
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

化学性土壤退化
- Cn:肥力下降和有机质含量下降(非侵蚀所致)

生物性退化
- Bc:植被覆盖的减少
- Bl:土壤寿命损失
注释:
Application of animal manure enhances soil micro biomass
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 防止土地退化
- 修复/恢复严重退化的土地
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
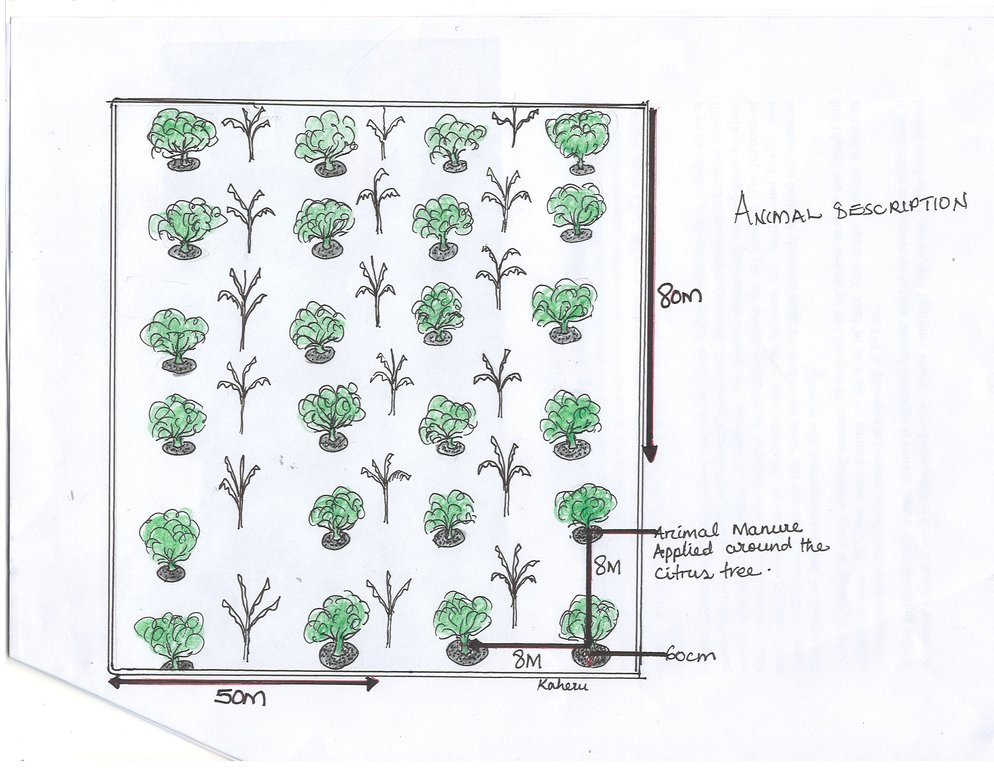
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
40 kg of animal manure are applied per citrus tree
citrus is planted at 8×8m
111 orange trees were planted, oranges planted are the Washington navel and Hamline type
The manure is applied using the ring method 60cm away from the tree trunk and covered with mulch
作者:
Prossy Kaheru
日期:
10/05/2017
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
具体说明成本和投入是如何计算的:
- 每个技术区域
注明尺寸和面积单位:
1 acre
如果使用本地面积单位,注明转换系数为1公顷(例如1公顷=2.47英亩):1公顷=:
0.40 ha
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
Ug Shillings (UGX)
如相关,注明美元与当地货币的汇率(例如1美元=79.9巴西雷亚尔):1美元=:
3650.0
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
6660
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | heaping of manure | Twice annually |
| 2. | transporting | Twice annually |
| 3. | loading and offloading | Twice annually |
| 4. | manure application | Twice annually |
注释:
The animal manure is applied twice annually, application is done at the beginning of the season, that is in March and September.
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Heaping manure | heaps | 20.0 | 2000.0 | 40000.0 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Transporting | heaps | 20.0 | 5000.0 | 100000.0 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Application | acre | 1.0 | 50000.0 | 50000.0 | 100.0 |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | animal manure | bags | 70.0 | 5000.0 | 350000.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 540000.0 | |||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 147.95 | |||||
如果土地使用者负担的费用少于100%,请注明由谁负担其余费用:
the land user bore all the costs
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | collecting and heaping manure | Twice |
| 2. | transporting | Twice |
| 3. | application of manure | Twice |
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | collecting | heap | 10.0 | 5000.0 | 50000.0 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | 1.0 | |||||
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 50000.0 | |||||
| 技术维护总成本,美元 | 13.7 | |||||
如果土地使用者负担的费用少于100%,请注明由谁负担其余费用:
Costs are borne by land user
注释:
When it comes to application of animal manure, most of the costs are borne by the land user.
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
Quantities of the manure
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
指定年平均降雨量(若已知),单位为mm:
1217.00
有关降雨的规范/注释:
The rainfall on set have delayed for the last 2 seasons (2016, 2017) from March-April
农业气候带
- 潮湿的
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
说明该技术是否专门应用于:
- 不相关
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
土壤质地(地表以下> 20厘米):
- 细粒/重质(粘土)
表土有机质:
- 低(<1%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
The soils according to the farmer are very poor.
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
< 5米
地表水的可用性:
过量
水质(未处理):
良好饮用水
水的盐度有问题吗?:
否
该区域正在发生洪水吗?:
是
规律性:
偶然
关于水质和水量的注释和进一步规范:
sometimes it rains and the stream fills up causing flooding but this doesn't happen every season
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 中等
栖息地多样性:
- 高
关于生物多样性的注释和进一步规范:
He is growing a number of crops on his farm (tomatoes, sugar cane, citrus and bananas), on the farm there is also a woodlot.
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
定栖或游牧:
- 定栖的
生产系统的市场定位:
- 混合(生计/商业)
非农收入:
- 收入的10-50%
相对财富水平:
- 丰富
个人或集体:
- 个人/家庭
机械化水平:
- 机械化/电动
性别:
- 男人
土地使用者的年龄:
- 中年人
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
He is an ex soldier who retired into farming and he has a number of on-farm income generating activities.
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 大规模的
注释:
Average land holding of the people here is 2 ha. but he owns 5 ha of land.
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 社区/村庄
- customary
土地使用权:
- 社区(有组织)
用水权:
- 社区(有组织)
注释:
This land tenure system land is owned communally
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
SLM之前的数量:
75 oranges per tree
SLM之后的数量:
200 oranges per tree
作物质量
注释/具体说明:
with application of animal manure fruit sizes have increased
收入和成本
农业收入
注释/具体说明:
farm income has increased though no records are given
社会文化影响
食品安全/自给自足
注释/具体说明:
The oranges are consumed by the family therefore providing nutritional benefits to family.
生态影响
土壤
土壤水分
注释/具体说明:
Using manure has increased soil organic matter, which in turn increases fertility and soil moisture retention,
减少气候和灾害风险
干旱影响
注释/具体说明:
Because it increases soil fertility and soil moisture retention animal manure helps the citrus trees to tolerate dry spells.
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
对场外影响(测量)的评估进行具体说明:
No off site impacts have been observed, however, continuous application of animal manure due to runoff can lead to eutrophication of streams
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 增加或减少 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年温度 | 增加 | 好 | |
| 年降雨量 | 减少 | 好 |
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
其他与气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
| 其它(具体说明) | 该技术是如何应对的? |
|---|---|
| Dry spells | 好 |
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
非常积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
非常积极
注释:
The land user attests that benefits surpass both establishment and maintenance costs
6.5 技术采用
- 单例/实验
6.6 适应
最近是否对该技术进行了修改以适应不断变化的条件?:
否
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Animal manure increases the quantity and quality of the citrus |
| It increases the water holding capacity |
| It improves soil fertility |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| It is improves agro-ecosystem functioning |
| increases farm income |
| improves food security of family |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| If not proper covered with soil or mulch, nutrients can easily be eroded | cover it properly or apply beneath the soil |
| manure is not readily accessible | outsource from different farmers |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| it is slow in action hence easily affected by weather | it is applied on perennial crops |
| May contain excess salts |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
- 实地考察、实地调查
one informant
- 与土地使用者的访谈
one informant
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
10/05/2017
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块