Building Walls's stones to protect lands and building outlet to drain excess water [也门]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: ahmed algalal
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
الجدران الحجرية والمفيضات
technologies_1578 - 也门
- Building Walls's stones to protect lands and building outlet to drain excess water: June 24, 2017 (inactive)
- Building Walls's stones to protect lands and building outlet to drain excess water: Aug. 11, 2019 (inactive)
- Building Walls's stones to protect lands and building outlet to drain excess water: April 4, 2024 (public)
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
SLM专业人员:
Sallam Ahmed
Agricultural Research and Extension Authority
也门
SLM专业人员:
Alhadrami Yahya
General Directorate for irrigation
也门
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
General Directorate of Irrigation - 也门有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Agricultural Research and Extension Authority (AREA) - 也门1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.5 参考关于SLM方法(使用WOCAT记录的SLM方法)的调查问卷
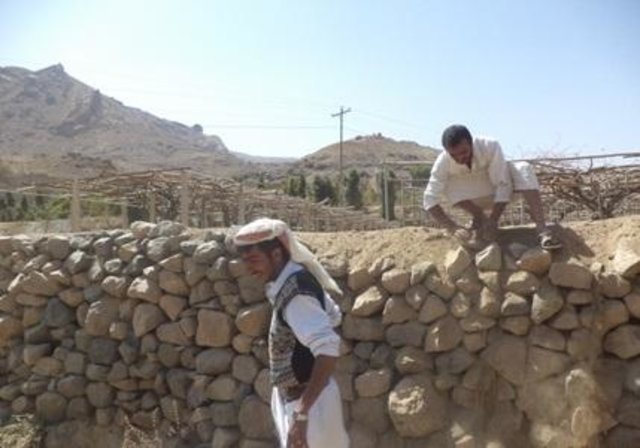

Rehabilitation of terraces and diversion construction with gates … [也门]
The rehabilitation of walls and outlets of the terraces and diversion construction with accessories from channels and gates are carried out by the local community in a regular way
- 编制者: ahmed algalal
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
use the stones to build walls around agricultural terraces to protect them from erosion and make outlets (Spillway) to discharge excess water and prevent the destruction of the stands
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
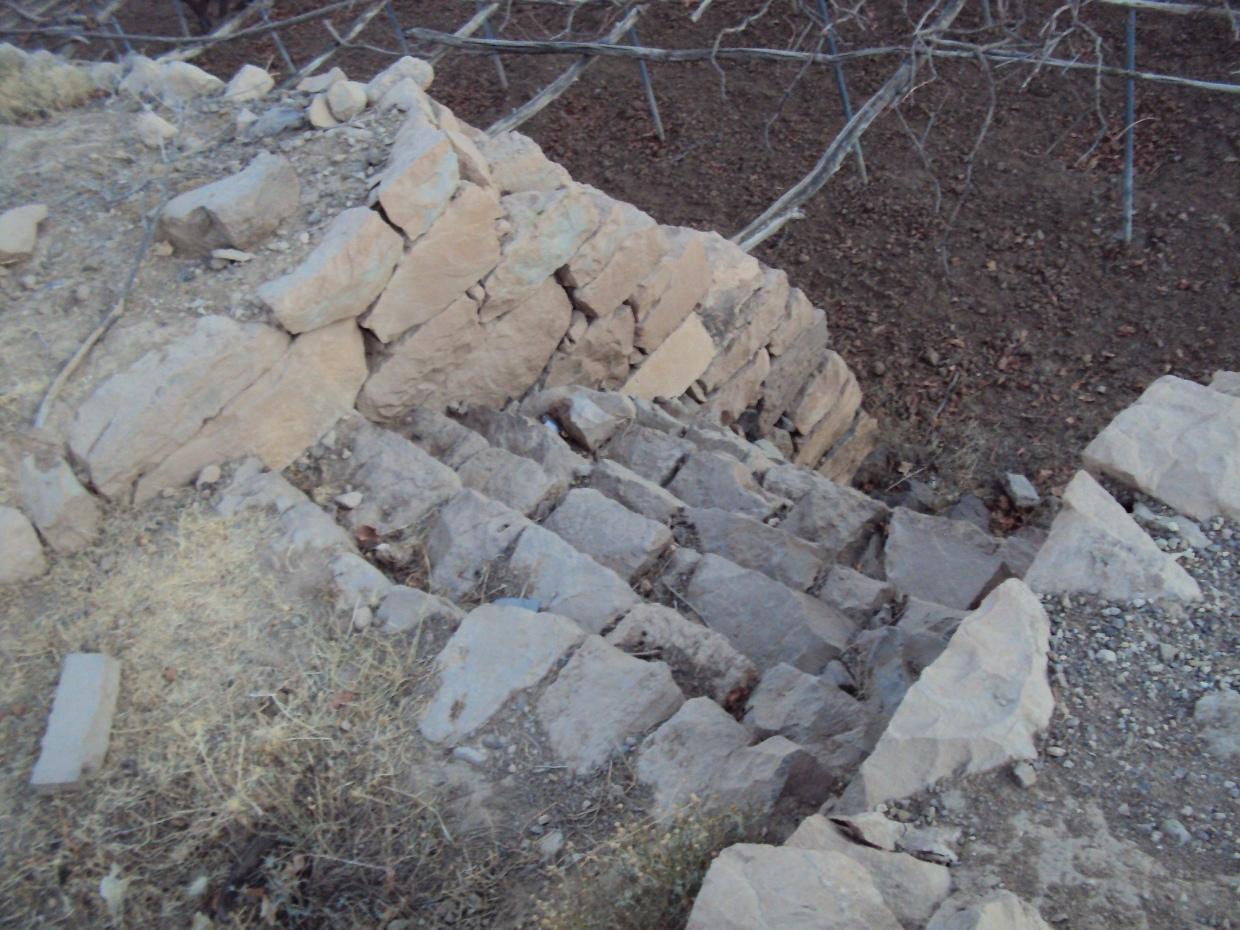
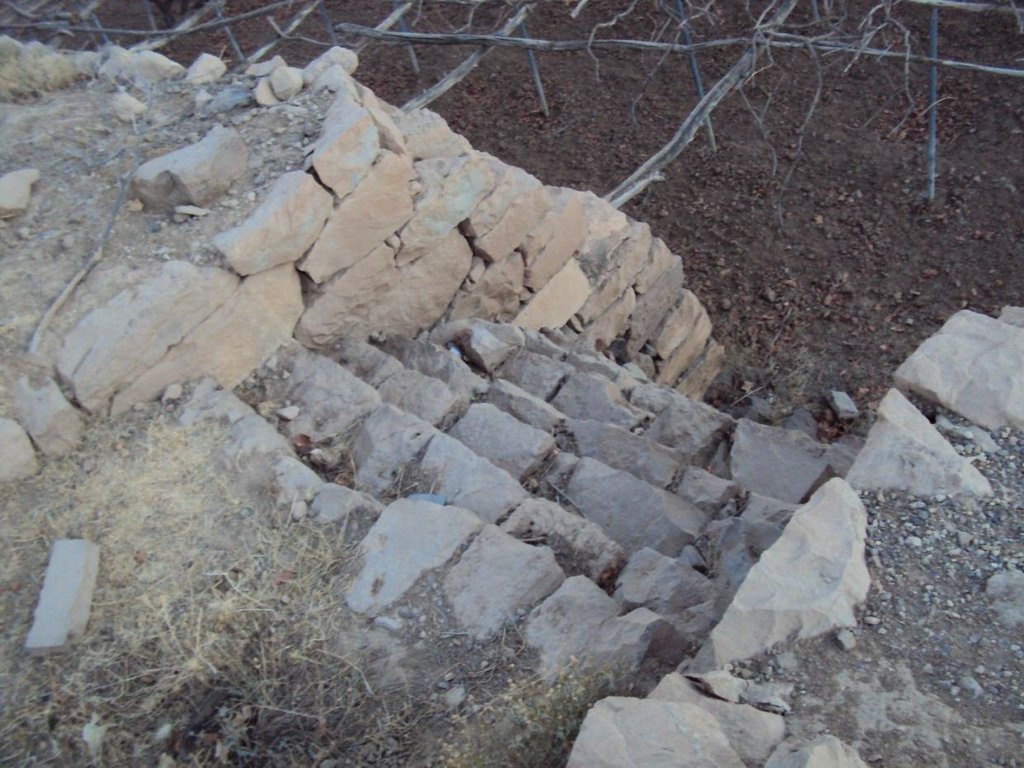
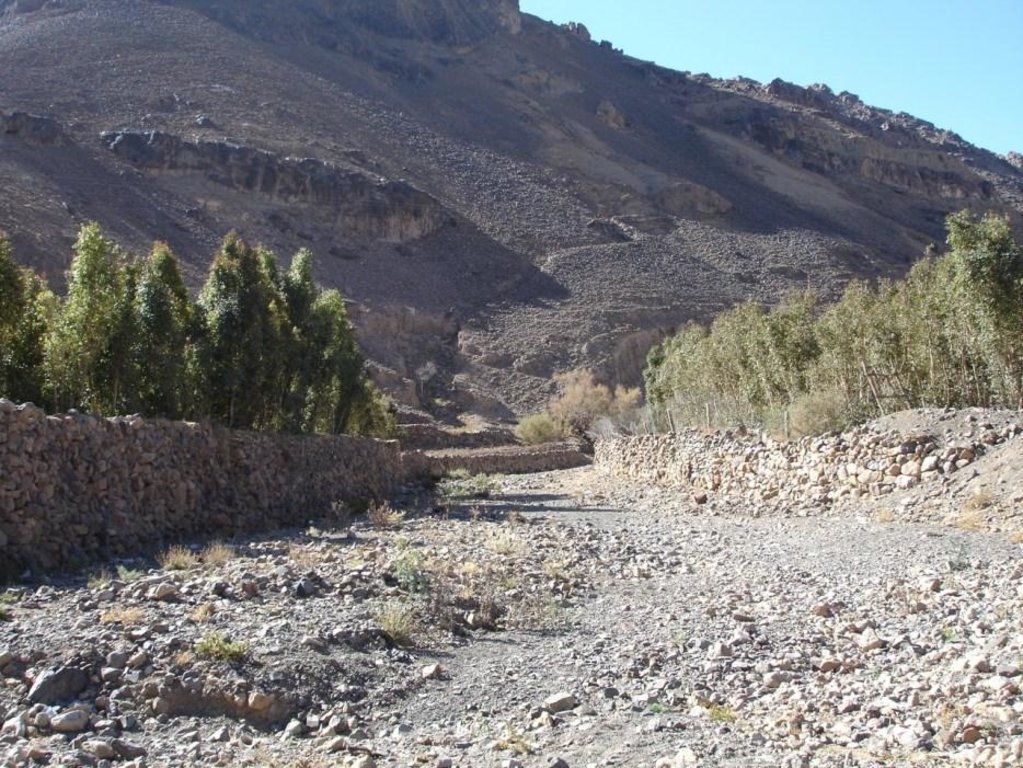
Is a structural one of the types of measures and that is where build walls around the land of stones available in the area to protect agricultural terraces from erosion as a result of the speed of the water flow.
This process starts of building walls to collect stones available and building walls around the agricultural terraces, which is beside the waterway and then land agricultural away from the stream where are building walls around land terraces threatened drift ranges wall height 2-3 meters and a width of 30 cm and is accompanied by building outlets with the construction of the walls. Different view slot spillway and the number depending on the amount of water entering the agricultural land terraces which is used irrigation number of agricultural terraces about 4 - 5 terraces (pieces) where irrigation start from the top-down system of first come through outlets which works to protect the land from erosion and destruction by water pressure due process flood irrigation .
walls and outlets Were built by hands where the process of building need a long time, the walls are built gradually according to the height of the surface of the soil where you are collecting sediment , which requires him to do to raise the walls and well outlets .
The implementation of this technique in filled valleys on the slope moderate 5% of the irrigation system mixed and used to irrigate crop of grapes , mainly for the purpose of self-sufficiency and to go to the market to trade, is the technology of long-term investments that need to be high costs in the process of starch and because of the natural conditions of flow velocity and the output from a pool of water in the mountain slopes , the process of maintenance necessary to sustain and maintain the technology .
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
也门
区域/州/省:
Sana
有关地点的进一步说明:
Bani Hushaish district
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果不知道精确的区域,请注明大致覆盖的区域:
- 10-100 平方千米
注释:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 20.6 km2.
Alrawanah Bani Hushaish, which is located on the eastern side of the capital Sanaa, and is about 16 km away
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 50多年前(传统)
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 作为传统系统的一部分(> 50 年)
注释(项目类型等):
It is a very old technology but was rehabilitated in 1956 by the community
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

农田
- 乔木与灌木的种植
乔木和灌木种植 - 指定作物:
- 葡萄
- Qat
每年的生长季节数:
- 1
具体说明:
Longest growing period in days: 90
注释:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Erosion of riparian valley resulting from the floods in addition to gully erosion on agricultural land
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Erosion of agricultural terraces
3.4 供水
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
注释:
Water supply: Also mixed rainfed - irrigated and post-flooding
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 横坡措施
- 灌溉管理(包括供水、排水)
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

结构措施
- S1:阶地
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wg:冲沟侵蚀/沟蚀
- Wr:河岸侵蚀

物理性土壤退化
- Ps:有机土壤沉降,土壤沉降
注释:
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Ps: subsidence of organic soils, settling of soil
Main causes of degradation: floods (As a result of flow velocity and rainwater collected from many places)
Secondary causes of degradation: over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use (For domestic use due to lack of alternatives such as gas), poverty / wealth (poverty), education, access to knowledge and support services
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 减少土地退化
- 修复/恢复严重退化的土地
注释:
Secondary goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
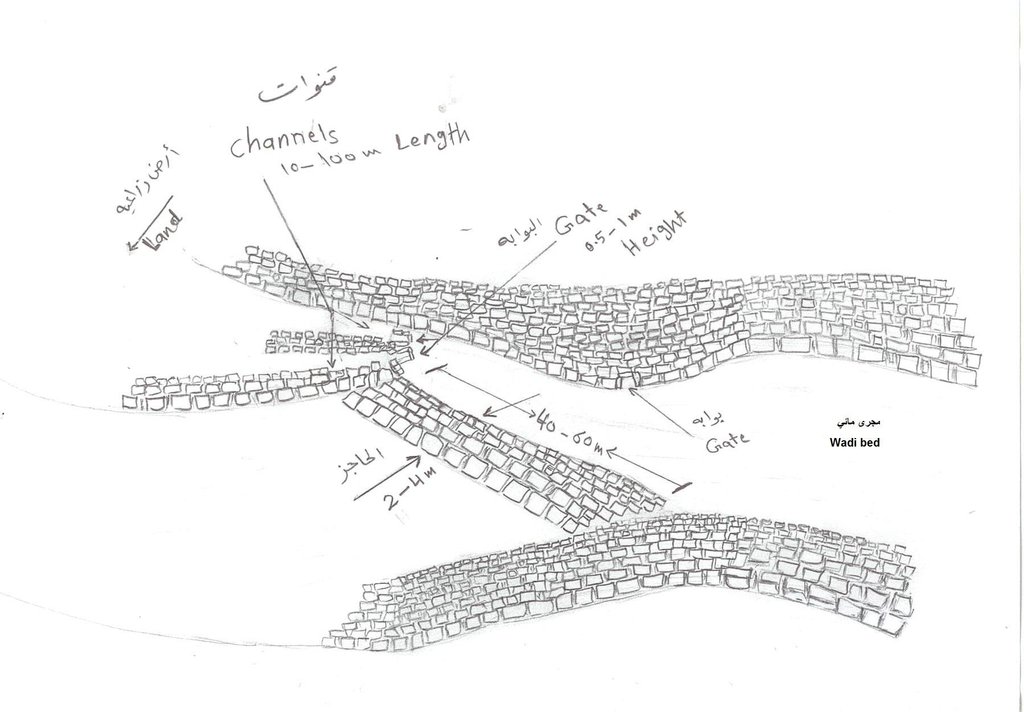
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
Stone walls with outlets
Location: Bani Hushaish district. Sana'a
Date: 15-3-2013
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high (The construction process requires skills and experiences)
Technical knowledge required for land users: low (Has enough experience)
Main technical functions: control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap, water spreading, Reduce runoff
Secondary technical functions: increase of groundwater level / recharge of groundwater, water harvesting / increase water supply, sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting
Spillway
Vertical interval between structures (m): S
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 2 - 3
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 1– 1.5
Structural measure: Stone walls
Vertical interval between structures (m): S
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 2 - 3
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.3
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 60-100
Construction material (stone): Available stones in the region
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 5%
For water harvesting: the ratio between the area where the harvested water is applied and the total area from which water is collected is: 1:1
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
具体说明成本计算所用货币:
- 美元
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
7.00
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Collecting stones | Before the rainy season |
| 2. | Building outlets walls | Before the rainy season |
| 3. | Packing the soil behind walls and outlets | Before the rainy season |
| 4. | Settlement of the Earth's surface and filling the grooves | Before the rainy season |
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Collecting stones | persons/day/ha | 150.0 | 7.0 | 1050.0 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Building outlets walls | persons/day/ha | 500.0 | 7.0 | 3500.0 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Packing the soil behind walls and outlets | persons/day/ha | 10.0 | 7.0 | 70.0 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Settlement of the Earth's surface and filling the grooves | persons/day/ha | 10.0 | 7.0 | 70.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Collecting stones (animal traction) | ha | 1.0 | 69.76 | 69.76 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Tools | ha | 1.0 | 14.0 | 14.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Settlement of the Earth's surface and filling the grooves (animal traction) | ha | 1.0 | 23.25 | 23.25 | 100.0 |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 4797.01 | |||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 4797.01 | |||||
注释:
Duration of establishment phase: 12 month(s)
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Repair walls and outlets | annually after the rainy season |
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Repair walls and outlets | persons/day/ha | 20.0 | 7.0 | 140.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 140.0 | |||||
| 技术维护总成本,美元 | 140.0 | |||||
注释:
Machinery/ tools: A Leveler , shovel and a big hammer
The calculated costs are based on the current situation and a length of the wall of 500 meters and a height of 2 meters and a width of 0.3 meters.
It should be noted that the walls do not work in all agricultural terraces, but they are working in areas threatened by drift but for outlets it is built in each of agricultural land terraces. Construction costs were calculated for walls with outlets including the number of working days per person. In fact most of the activities are at the same time and with the participation of a large number of people.
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
The most determinate factors affecting the costs are the collection and the transport of stones, and the difficulty of the road
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
农业气候带
- 半干旱
Thermal climate class: temperate
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
关于地形的注释和进一步规范:
Altitudinal zone: 2400 m a.s.l.
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
- 细粒/重质(粘土)
表土有机质:
- 中(1-3%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Soil depth on average: 150 cm
Soil texture: Flood deposits
Topsoil organic matter: After falling grape leaves and weeds developing
Soil fertility is low - medium (output of the flood deposits)
Soil drainage / infiltration is medium - good
Soil water storage capacity is medium - high
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
> 50米
地表水的可用性:
匮乏/没有
水质(未处理):
不良饮用水(需要处理)
关于水质和水量的注释和进一步规范:
Ground water table: 400 m
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 低
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
生产系统的市场定位:
- 混合(生计/商业)
非农收入:
- 收入的10-50%
相对财富水平:
- 贫瘠
- 平均水平
个人或集体:
- 团体/社区
机械化水平:
- 手工作业
- 畜力牵引
性别:
- 男人
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Difference in the involvement of women and men: Women could not do the hard work, therefore, men do work on the farm and women do the house works.
Population density: > 500 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 3% - 4%
70% of the land users are average wealthy and own 90% of the land.
30% of the land users are poor and own 10% of the land.
100% of the land users are poor and own 100% of the land.
Level of mechanization: Also mechanized, but less common
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 中等规模的
注释:
0.45 – 0.9 fragmentation of tenure is the cause of the small ownership per household
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 个人,有命名
土地使用权:
- 租赁
- 个人
- Waqf
用水权:
- 社区(有组织)
- Waqf
注释:
There are three types of land ownership owned, Waqf, and a share at 70%, 20%, 10% respectively.
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
生产故障风险
生产区域
土地管理
水资源可用性和质量
灌溉用水需求
收入和成本
农业收入
收入来源的多样性
工作量
社会文化影响
食品安全/自给自足
SLM/土地退化知识
livelihood and human well-being
注释/具体说明:
As a result of reduced labor and increased production, standard of living is improved and children can go to school.
生态影响
水循环/径流
地表径流
多余水的排放
地下水位/含水层
土壤
土壤水分
土壤流失
生物多样性:植被、动物
栖息地多样性
减少气候和灾害风险
洪水影响
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
下游淤积
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 增加或减少 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年温度 | 增加 | 好 |
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气象灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 局地暴雨 | 好 |
水文灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 比较和缓的(河道)洪水 | 不好 |
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
中性/平衡
长期回报:
积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
非常积极
6.5 技术采用
如若可行,进行量化(住户数量和/或覆盖面积):
537 households covering 100 percent of the stated area
注释:
537 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: The technology is implemented at the level of the entire region, but due to a lack of capital the adoption is hindered.
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
Protection of the land from erosion How can they be sustained / enhanced? Continue the process of maintenance to maintain walls and outlets |
|
Increase in soil moisture How can they be sustained / enhanced? Maintenance of the outlets to ensure that they are working |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| The inability of the walls to withstand severe flooding due to the use of only stones in construction | The use of stone and cement materials in the construction of walls |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Report of traditional knowledge and customs (sallam, et al, 2008)- General Census of Population, Housing and Establishment (Census, 2004). - 45.Guide of agricultural climate in Yemen (Al Khorasani, 2005).
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
Agricultural Research and ExtensionAuthority, AREACentral Bureau of StatisticsAgricultural Research and ExtensionAuthority, AREA
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接

Rehabilitation of terraces and diversion construction with gates … [也门]
The rehabilitation of walls and outlets of the terraces and diversion construction with accessories from channels and gates are carried out by the local community in a regular way
- 编制者: ahmed algalal
模块
无模块