Natural spring catchment protection [塔吉克斯坦]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Giuseppe Bonati
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
technologies_1465 - 塔吉克斯坦
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
SLM专业人员:
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
CESVI (CESVI) - 塔吉克斯坦1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
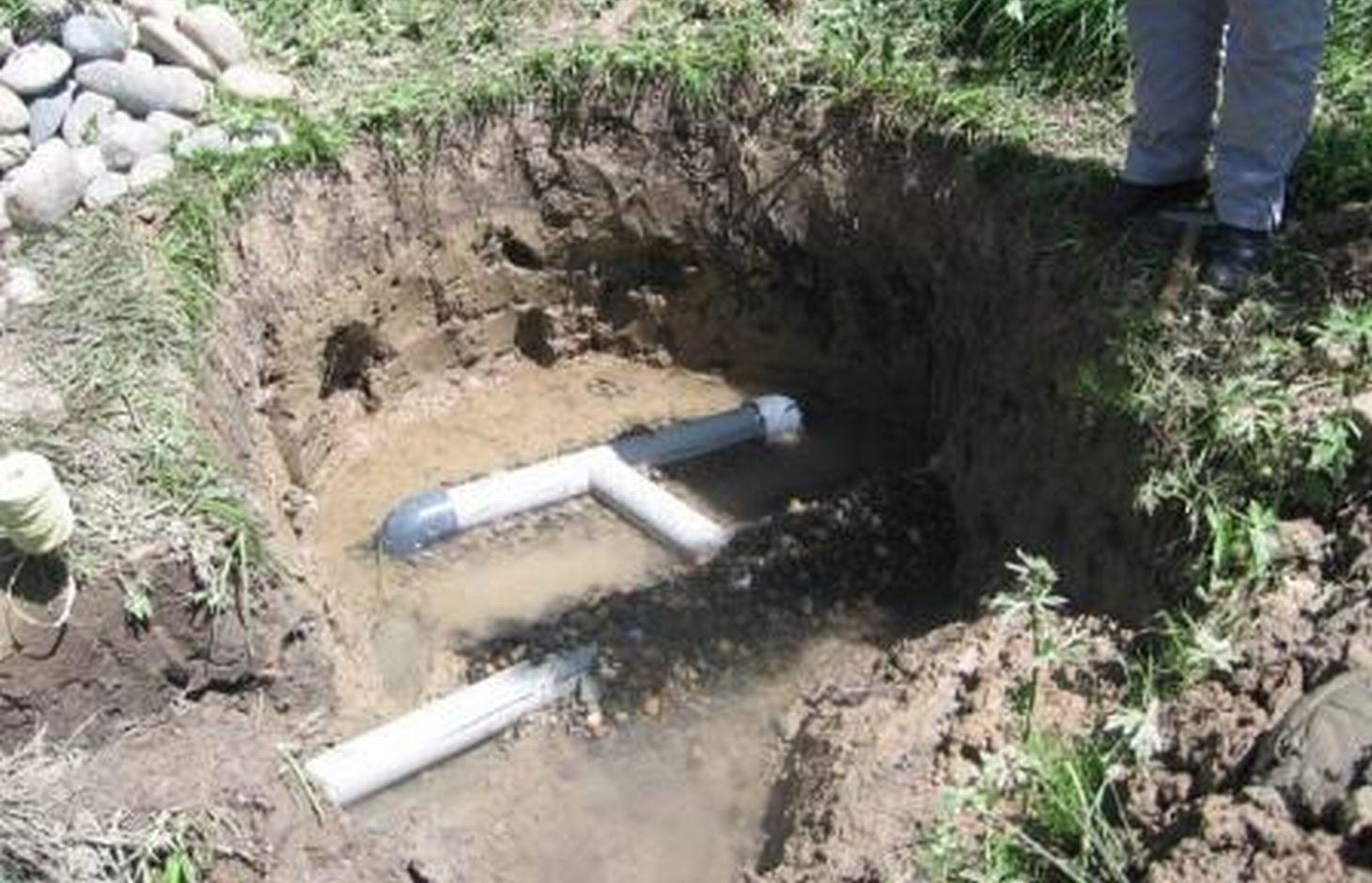
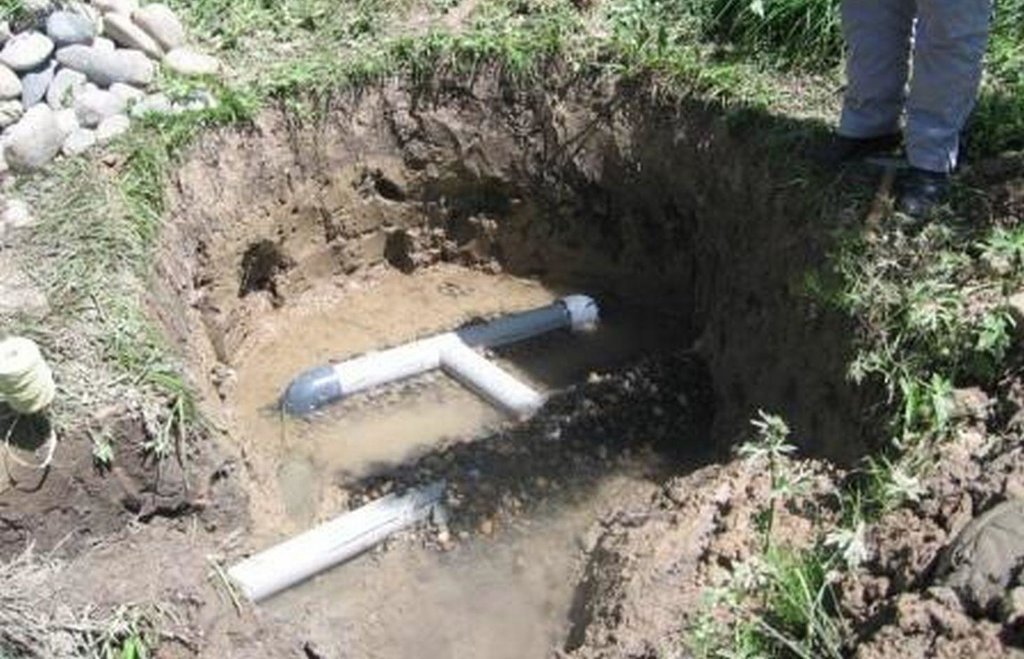
The construction of a natural spring catchment pit for the collection and distribution of uncontaminated ground water.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
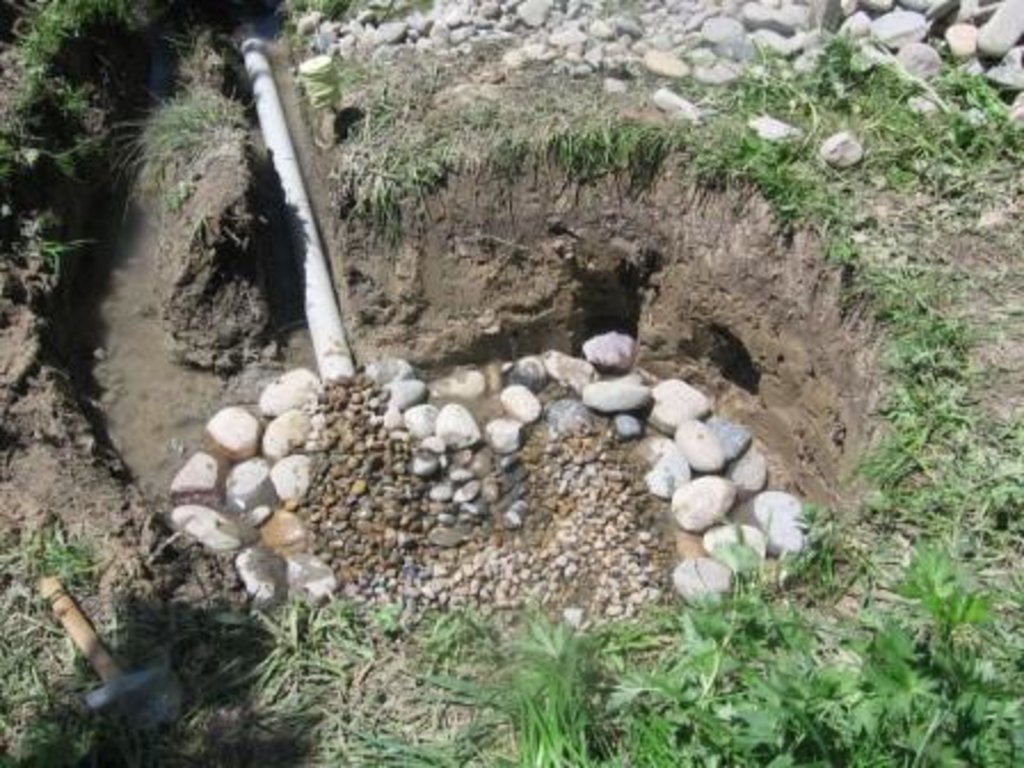
The technolgy consists of digging of a pit around the spring outlet and placing a 15cm perforated plastic pipe on a bed of gravel. The gravel acts as a natural sediment filter and protects the pipe from clogging. The pipe is buried in more gravel and covered with a plastic sheet to prevent animals from contaminating the spring source. The plastic pipe can be extended and attached to a flexible pipe to deliver clean ground water to the final destination.
Purpose of the Technology: There are two main aims of the technology, the first is to prevent contamination of the spring source from livestock which uses the spring head as a watering hole. The second goal is to optimise the springs capacity for irrigation and human consumption by capturing the water in the perforated pipe and channelling to the usage point.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The construction of the spring catchment is relatively straight forward. A 1m deep pit is dug around the spring head approximately 2m wide. A bed of washed gravel is placed in the foot of the pit, and a 15cm perforated plastic pipe is embedded into the gravel, this is attached to a flexible tube to transport the clean water away. The perforated pipe is covered in more clean gravel and covered with a heavy polythene sheet and covered in earth. The construction process can be completed in one day if the materials are available.
The only substantial maintenance required would be the cleaning of the pipe and gravel if it gets clogged with earth.
Natural / human environment: In many parts of Tajikistan water for human use and irrigation is scarce and plays a critical role in securing the livelihoods of the local population. The construction of the spring catchment increases not only the volume but also improves the quality of water available. This can and does have a dramatic effect on the productivity of the land and the health of the land users.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
塔吉克斯坦
区域/州/省:
Khatlon region
有关地点的进一步说明:
Khovaling
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果不知道精确的区域,请注明大致覆盖的区域:
- < 0.1 平方千米(10 公顷)
注释:
This technology is in one location.
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 不到10年前(最近)
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过项目/外部干预
注释(项目类型等):
Spring Protection Project
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- improved access to water
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

农田
- 乔木与灌木的种植
乔木和灌木种植 - 指定作物:
- 水果、其他
每年的生长季节数:
- 1
具体说明:
Longest growing period in days: 180Longest growing period from month to month: april - october

森林/林地
产品和服务:
- 薪材
- 水果和坚果
- 自然灾害防护
注释:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Lack of access to water. Contamination of the water due to animals using the spring.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Provides a better cleaner source of water for the land and the people.
Plantation forestry: Fruit tree orchards.
Problems / comments regarding forest use: The spring is located in natural woodland, however the water supply is directed towards the fruit orchards.
Forest products and services: fuelwood, fruits and nuts, protection against natural hazards
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Forests / woodlands: Fn: Natural
3.3 由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?

森林/林地
- (半天然)天然森林/林地
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 集水
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

结构措施
- S3:分级沟渠、渠道、水道

管理措施
- M6:废物管理(回收、再利用或减少)
注释:
Main measures: structural measures
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀
- Wm:块体运动/滑坡

生物性退化
- Bc:植被覆盖的减少

水质恶化
- Hs:地表水良变化
- Hp:地表水水质下降
注释:
Main type of degradation addressed: Bc: reduction of vegetation cover, Hs: change in quantity of surface water, Hp: decline of surface water quality
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Wm: mass movements / landslides
Main causes of degradation: other natural causes (avalanches, volcanic eruptions, mud flows, highly susceptible natural resources, extreme topography, etc.) specify (The land degradation was caused by uncontrolled natural spring run off.)
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 防止土地退化
- 减少土地退化
注释:
Main goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
Secondary goals: prevention of land degradation
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
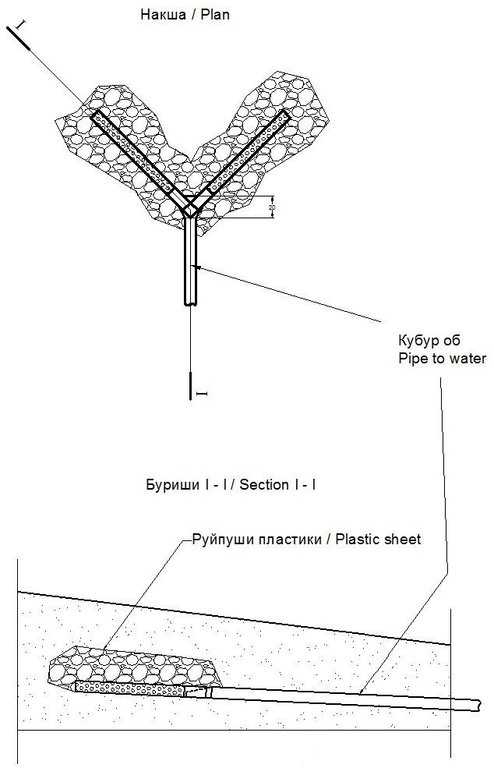
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
Basic sketch of perferated drainage collecting the spring water and flowing into a pipe. To take an increased quantity of water you can install more pipes (See section 2.1.3).
Location: Gulizor Nursary. Khovaling/Khatlo/Tajikistan
Date: 19/05/2011
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high (After training to increase their capacity)
Technical knowledge required for land users: high (After training to increase their capacity)
Main technical functions: control of concentrated runoff: drain / divert, water harvesting / increase water supply
Diversion ditch/ drainage
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 1
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 1.5
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 1.5
Construction material (earth): The spring head is dug into the earth.
Construction material (stone): The stone is used to line the base of the spring head.
作者:
Foteh, CESVI
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
TJS
如相关,注明美元与当地货币的汇率(例如1美元=79.9巴西雷亚尔):1美元=:
4.5
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
25
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Digging of the spring head | Spring |
| 2. | pipe positioning | Spring |
| 3. | Gravel positioning and covering with plastic sheet | Spring |
| 4. | Fill back the drainage | Spring |
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Digging of the spring head | Persons/day | 2.0 | 25.0 | 50.0 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Pipe positioning | Persons/day | 2.0 | 25.0 | 50.0 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Gravel positioning | Persons/day | 2.0 | 25.0 | 50.0 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Fill back the drainage | Persons/day | 2.0 | 25.0 | 50.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Tools | Pieces | 4.0 | 10.0 | 40.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Drill | Pieces | 1.0 | 250.0 | 250.0 | |
| 施工材料 | Drainage pipe | meter | 10.0 | 1.5 | 15.0 | |
| 施工材料 | Stone | tons | 0.5 | 136.0 | 68.0 | |
| 施工材料 | Plastic sheet to cover | sq m | 1.5 | 5.333333 | 8.0 | |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 581.0 | |||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 129.11 | |||||
如果土地使用者负担的费用少于100%,请注明由谁负担其余费用:
CESVI
注释:
Duration of establishment phase: 1 month(s)
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Cleaning the water channel after drainage | Spring |
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Cleaning the water channel | Persons/day | 2.0 | 25.0 | 50.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Tools | Pieces | 2.0 | 10.0 | 20.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 70.0 | |||||
| 技术维护总成本,美元 | 15.56 | |||||
注释:
Machinery/ tools: Shovel
Costs are based upon one spring at a depth of 1m at 2010 prices.
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
The cost is determined by the depth of the spring head. If it needs to be deeper it requires additonal labour and material costs.
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
农业气候带
- 半干旱
Thermal climate class: temperate
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 细粒/重质(粘土)
表土有机质:
- 中(1-3%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Soil fertility is low
Soil drainage / infiltration is medium
Soil water storage capacity is medium
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
< 5米
地表水的可用性:
好
水质(未处理):
良好饮用水
关于水质和水量的注释和进一步规范:
Availability of surface water is good at the location of the spring, but medium where the water is needed for the lands.
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 中等
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
非农收入:
- 收入的10-50%
相对财富水平:
- 非常贫瘠
- 贫瘠
个人或集体:
- 团体/社区
性别:
- 女人
- 男人
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly Leaders / privileged
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 1% - 2%
80% of the land users are poor.
20% of the land users are poor.
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 大规模的
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 州
土地使用权:
- 社区(有组织)
用水权:
- 社区(有组织)
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
水资源可用性和质量
饮用水的可用性
灌溉用水的可用性
社会文化影响
食品安全/自给自足
健康状况
SLM/土地退化知识
Livelihood and human well-being
注释/具体说明:
It has improved access to running water for sanitation, hygiene, irrigation and animal husbandry purposes.
生态影响
水循环/径流
水量
水质
水的回收/收集
地表径流
多余水的排放
减少气候和灾害风险
干旱影响
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
水资源可用性
旱季稳定可靠的水流
下游洪水
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 增加或减少 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年温度 | 增加 | 好 |
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气象灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 局地暴雨 | 好 |
| 局地风暴 | 好 |
气候灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 干旱 | 好 |
水文灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 比较和缓的(河道)洪水 | 未知 |
其他气候相关的后果
其他气候相关的后果
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 缩短生长期 | 好 |
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
稍微积极
长期回报:
积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
积极
6.5 技术采用
- 单例/实验
如若可行,进行量化(住户数量和/或覆盖面积):
1 houshold
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发的,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 0-10%
注释:
Comments on spontaneous adoption: In the course of the project 24 springs will be refurbished (2011-2013).
There is no trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: The technology is new and in its infancy.
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Pleased at the increase in water and ability to improve the yield of his crops. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
Increased access to water through controlled piping. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Provision of guidance of which pipes to use. |
| Reduced the contamination at the spring head by animals. |
|
It is quick and cheap to install. How can they be sustained / enhanced? provide further training and support on maintenance. |
| It is easy to teach people how to install it. |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Difficult at times to find good cheap plastic pipe. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| It incurs an initial financial outlay, which may be considerable if the spring is located far from where the water is needed. |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块