Solar Power Water Lifting and Application to Orchard through Drip Irrigation [巴基斯坦]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Madhav Dhakal
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Rima Mekdaschi Studer
technologies_5610 - 巴基斯坦
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
关键资源人
SLM专业人员:
Maqsood Muhammad Mudassar
International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development
巴基斯坦
SLM专业人员:
Shah Ghulam Muhammad
International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development
巴基斯坦
SLM专业人员:
Bhatti Ahmad Zeeshan
Pakistan Council of Research in Water Resources
巴基斯坦
SLM专业人员:
Khan Muhammad Zafar
Karakorum International University
巴基斯坦
SLM专业人员:
Khan Babar
World Wide Fund For Nature
巴基斯坦
SLM专业人员:
Ali Rehmat
World Wide Fund For Nature
巴基斯坦
SLM专业人员:
Ali Amjad
Karakorum International University
巴基斯坦
SLM专业人员:
Ali Ajaz
International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development
巴基斯坦
SLM专业人员:
Dhakal Madhav
International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development
尼泊尔
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
Agricultural Water, Energy, and Hazard Management for Improved Livelihood in the Upper Indus Basin, Pakistan (UIB, Pakistan)有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
ICIMOD International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development (ICIMOD) - 尼泊尔1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.4 所述技术的可持续性声明
这里所描述的技术在土地退化方面是否存在问题,导致无法被认为是一种可持续的土地管理技术?:
否
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
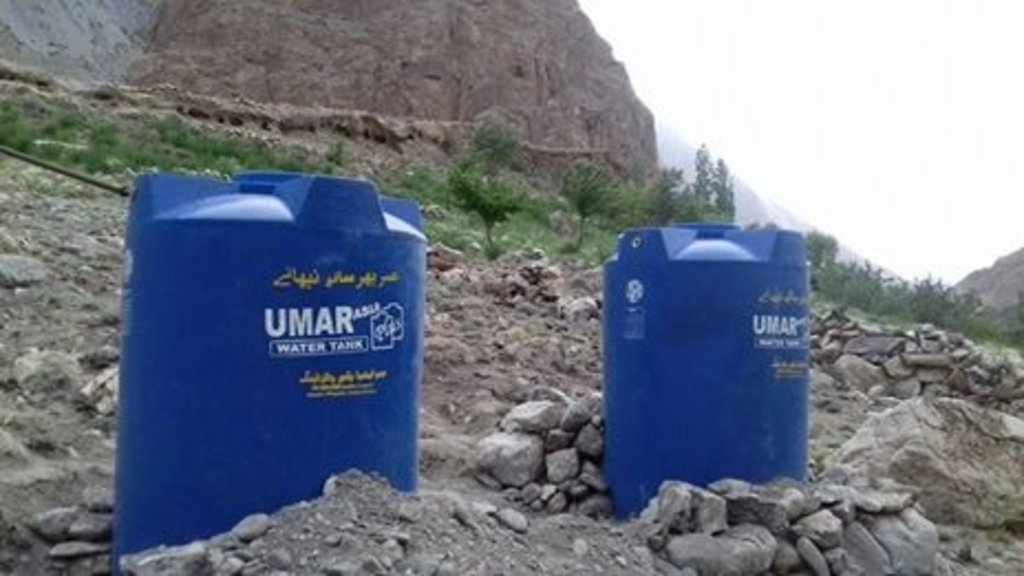
Water from the Hunza river was lifted through solar powered pump, stored above ground plastic tanks and applied to newly planted apple orchards through efficient drip irrigation. Mulch was applied to the plants to conserve soil moisture.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
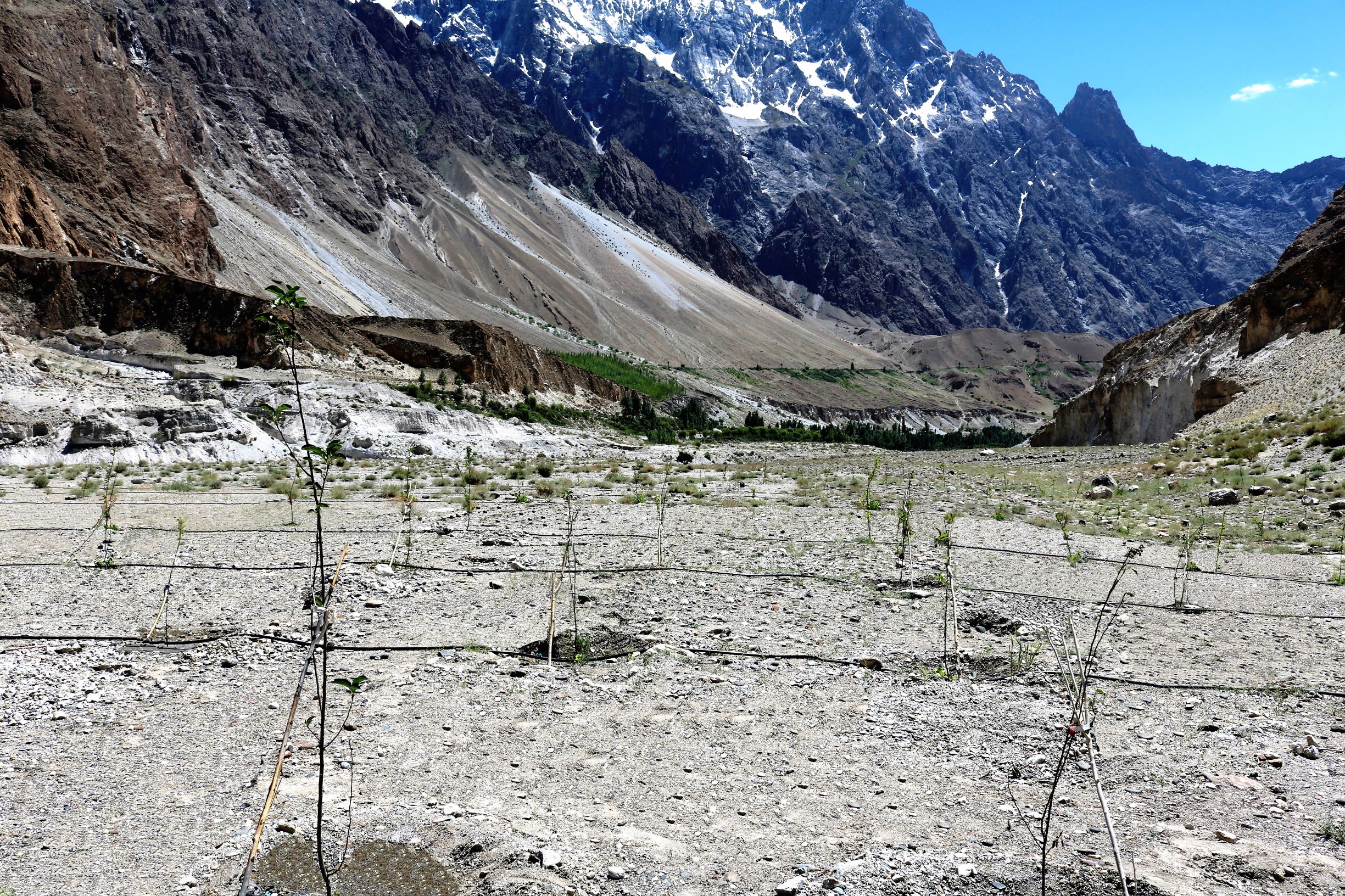
The fragile rouged mountains prone to the effect of climate change makes the mountain com-munities in Gilgit-Baltistan of Pakistan more vulnerable. Agriculture is the major source of their livelihoods and it purely dependents on glacier meltwater which makes the community more susceptible due to the unstable behaviour of the glaciers. Irrigation is practised with traditional irrigation canals, intake of which is located at glacier terminus. On one hand lowering of glacier surface disconnects many irrigation canals. Uncertain glacier behaviour has resulted in the decline of water availability and even forced some communities to abandon their agricultural land. On the other hand, only 2% of land in Gilgit-Baltistan is used for agriculture purposes whereas a huge chunk of barren land lays above the Hunza River, which cannot be cultivated through the traditional irrigation system hence it remains unutilized.
To address both issues, ICIMOD together with a local level partner’s consortia piloted solar water lifting to irrigate barren land for establishing apple orchards along Hunza River at Passu and Morkhun Villages. These two villages are located far from each other. In each village, orchards of 2.5 hectare area were established and the drip irrigation system installed was efficiently used to irrigate apple plants. Similar technological packages (solar pump, drip irrigation and mulch) were applied in both the villages.
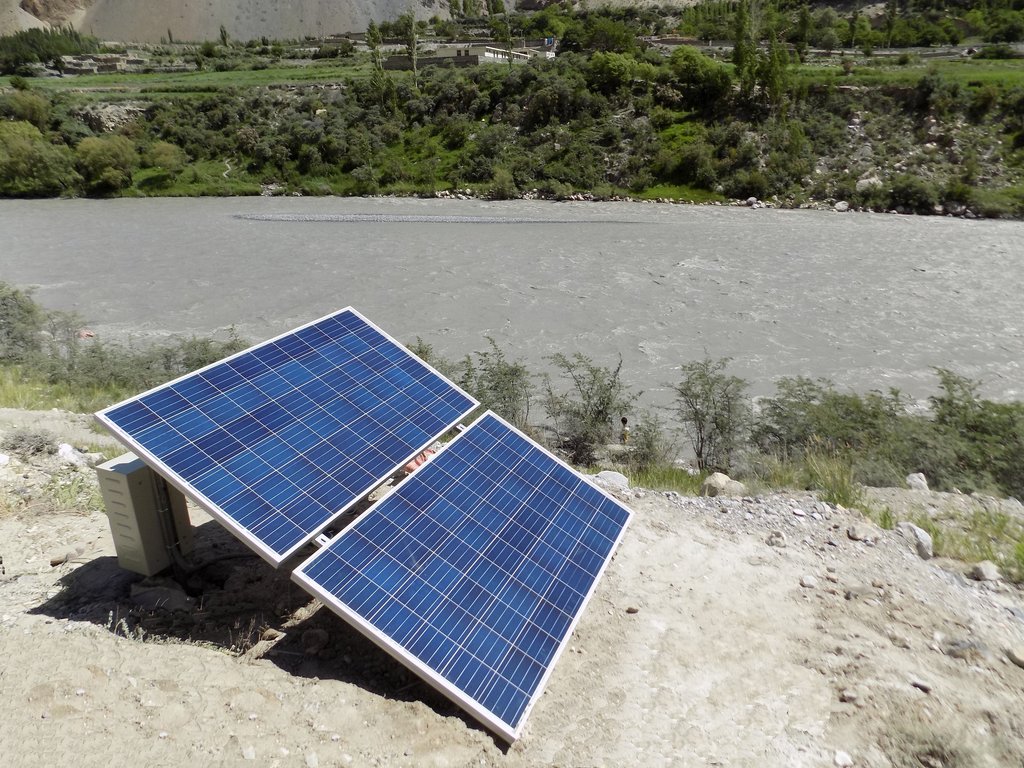
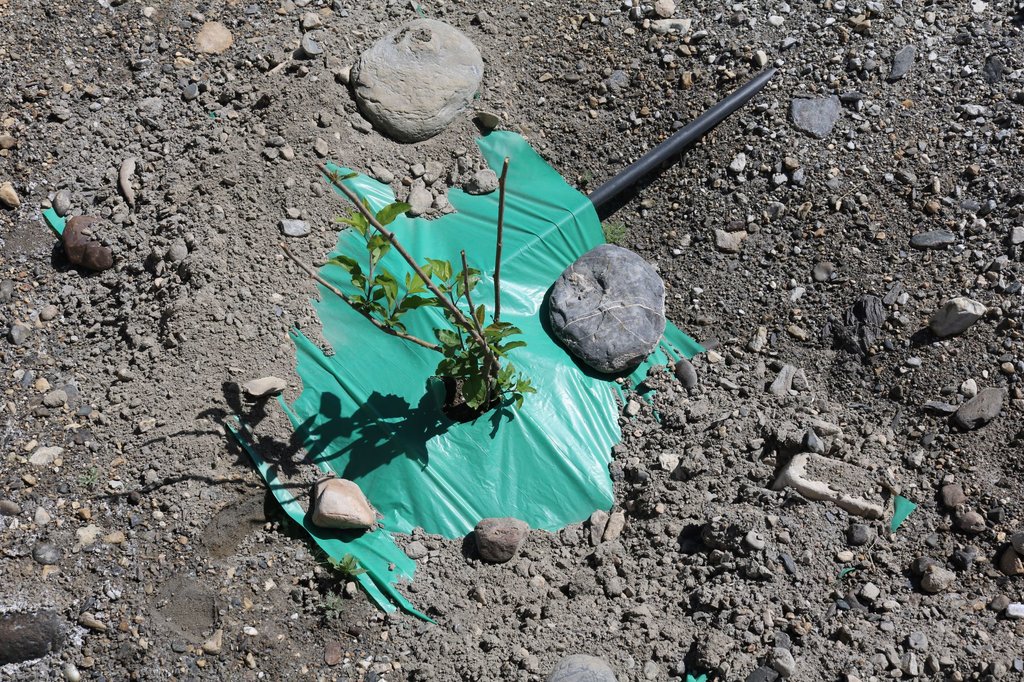
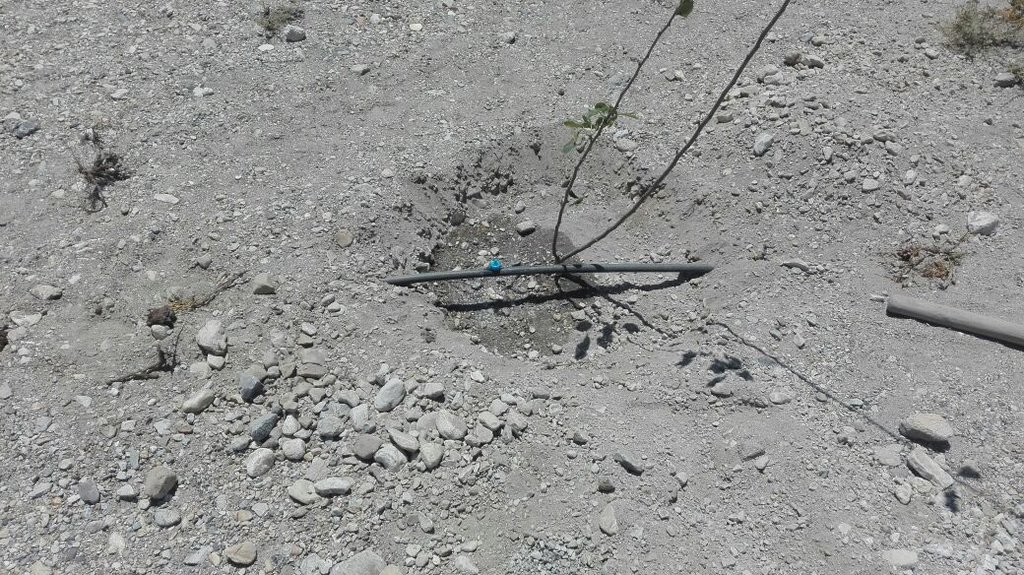
The pumping system comprises a submersible pump (Lorentz, Germany 1 HP) powered by 500 watts solar panels to carry the water to storage tanks (500 litres) made up of plastic that has been placed upslope at 100 feet vertical height from the river. The water from the storage tanks was routed/led to the apple saplings through the surface and pressure compensating drip irrigation system. The pumping capacity of the pump is 7.5 litres/minute, which is irrigating around 3300 apple plants at Passu and Morkhun. The storage tank was kept 60 feet vertical height from the orchard field to be irrigated. Tree to tree distance and row to row distance of apple was maintained at 15 feet in Passu and 10 feet in Morkhun. Drip irrigation (surface and pressure compensating) system was established to irrigate each apple plant, the emitter of the drip system was adjusted according to the plant to plant distance of apple seedlings to be irrigated. Pits were constructed for planting apples and later they also served as water harvesting pits /check basins. Plastic mulch was applied to each apple plants covering a radius around the trunk to minimize soil moisture losses, reduce weed and reduce soil erosion by water and wind.
The cost of an integrated package including solar pumps with accessories, storage tanks, intake and distribution systems (i.e. from river to tank and tank to trees), drip irrigation, apple plants and operational expenses (manpower) for both the sites was US$ 42000 for 5 ha of land. Village Development Organizations (VDO) of both villages take care of maintenance of technological package through a maintenance fund, which is being raised by participating households (HHs). Benefit sharing mechanism has been agreed among the participating HHs. The total income would be divided equally among participating 72 HHs in Morkhun and 135 HHs in Passu.
The technological package was applied in arid climate at an elevation ranging from 2340m to 4877 m above sea level. Passu is located at 36.49o latitude and 74.90o longitude and Morkhun is located at 36.6o N latitudes and 74.86o E longitudes. The area receives 150-200 mm annual rain-fall. The temperature ranges from 11 degree Celsius to 29 degree Celsius. The population of Passu and Morkhun is 1168 and 653 persons respectively. Both villages are semi nomadic and depend mainly on livestock rearing.
2.3 技术照片
2.4 技术视频
日期:
09/10/2018
位置:
Morkhun and Passu
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
巴基斯坦
区域/州/省:
Gilgit Baltistan Province
有关地点的进一步说明:
Morkhun and Passu
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 适用于特定场所/集中在较小区域
技术现场是否位于永久保护区?:
否
Map
×2.6 实施日期
注明实施年份:
2016
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 不到10年前(最近)
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过项目/外部干预
注释(项目类型等):
This package of practices was jointly implemented by Pakistan Council of Research in Water Resources (PCRWR), Worldwide Fund for Nature (WWF) - Pakistan, and ICIMOD
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 改良生产
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
- 适应气候变化/极端天气及其影响
- 创造有益的经济影响
- 创造有益的社会影响
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型
同一土地单元内混合使用的土地::
否

农田
- 乔木与灌木的种植
- Apple
每年的生长季节数:
- 1
具体说明:
April to October, rest months the region is covered with snow
采用间作制度了吗?:
否
采用轮作制度了吗?:
否
3.3 由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?
由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?:
- 是(请在技术实施前填写以下有关土地利用的问题)
同一土地单元内混合使用的土地::
否

农田
- Unproductive
采用间作制度了吗?:
否
采用轮作制度了吗?:
否
3.4 供水
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 充分灌溉
注释:
Water supply with solar pump and distribution to apple with drip irrigation
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 灌溉管理(包括供水、排水)
- 地表水管理(泉、河、湖、海)
- 节能技术
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

植物措施
- V1:乔木和灌木覆盖层

管理措施
- M1:改变土地使用类型
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀

土壤风蚀
- Et:表土流失

水质恶化
- Ha:干旱化

其它
具体说明:
Damage and dysfunction of irrigation canal .
注释:
Damage and dysfunction of irrigation canal intake by shifting nature of glacier as intakes are located at the glacier terminus.
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 修复/恢复严重退化的土地
注释:
due to water access cultivation was possible and vegetation cover improved.
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
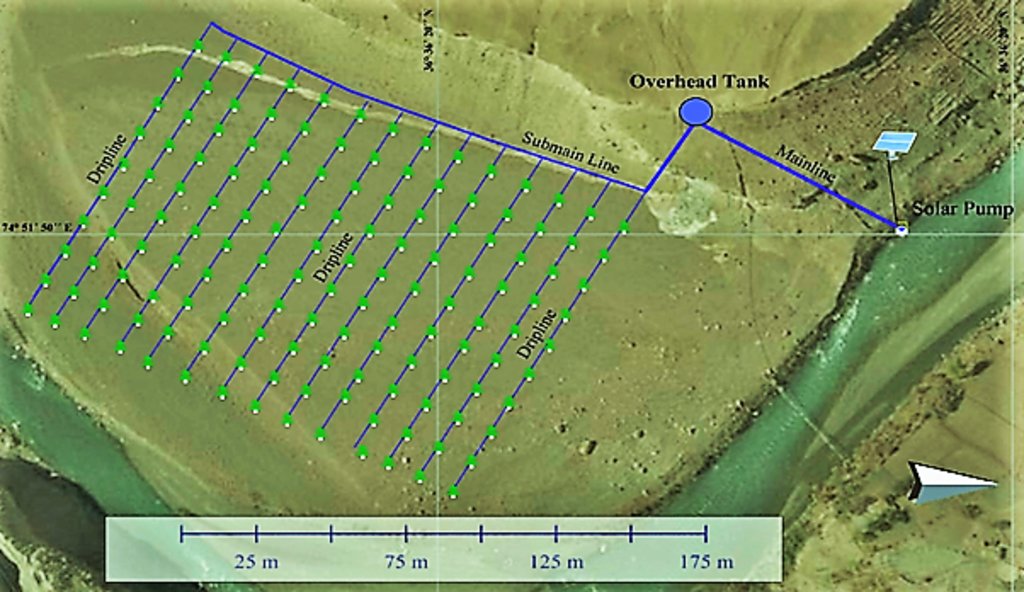
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
Solar Pump: DC submersible (Lorentz, Germany 1 HP), the capacity of Panels: 500 watts, and pumping capacity of the pump: 7.5 litres/minute.
The capacity of storage tank: 500 litres, location of storage tank: 100 feet height (vertical) from the river and 60 feet height (vertical) from the orchard field.
Drip Irrigation: Surface and pressure compensating. The spacing of dripping points: 10 feet in Morkhun and 15 feet in Passu. Water application per plant by drip irrigation is 2 litres per day.
Plant to plant and row to row distance of apple 10 feet in Morkhun and 15 feet ( both plant to plant and row to row) in Passu coinciding with the dripping holes.
Pits: Constructed for planting apples, later they served as water harvesting pits /check basins.
Plastic mulch: In each plant. Shape of the plastic mulch is rectangular and dimension is variable, average about 5 ft long and 3 feet wide. It is an opaque plastic sheet.
作者:
Muhammad Mudassar Maqsood)
日期:
09/10/2018
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
具体说明成本和投入是如何计算的:
- 每个技术单元
指定单位:
Technological package at two sites ( solar system, water storage tank, drip, orchard establishment, and mulch) , same package is applied in two sites separately. Total area of two sites is 5 ha
具体说明成本计算所用货币:
- 美元
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
US$ 14.5 for skilled person and US$ 7.5 for unskilled person
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Site identification in consultation with the communities | Pre Monsson (March) |
| 2. | Detailed engineering surveys, design formulation, tendering and work orders etc | Pre Monsson (March ) |
| 3. | Implementation agreement with the community | Pre Monsson (March) |
| 4. | Installation of solar-powered pumping units with four poly-crystalline solar panels. | Pre Monsson (April) |
| 5. | Installation of storage (plastic tank) with a line filter attached to it for the operation of the drip system and avoid sediment entry into the tank | Pre Monsson (April) |
| 6. | Digging of pits for plantation of the apple orchard at the plant to plant and row distance of 10 feet (Morkhun) and 15 feet (Passu)) | Pre Monsson (April) |
| 7. | Constructed pits for each plant used for application of compost | Pre Monsson (April) |
| 8. | Laying of drip irrigation systems | Pre Monsson (May) |
| 9. | Laying down plastic mulch | Pre Monsson (May) |
| 10. | Plantation of tubed apple (Kala Kolu variety) it is bought from the local nursery | Pre Monsson (May) |
| 11. | Training to selected farmers as caretakers of the technologies for its days to day repair and maintenance | Pre Monsson ( May) |
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Skilled | Person days | 136.0 | 14.43 | 1962.48 | |
| 劳动力 | Unskilled | Person days | 745.0 | 7.7 | 5736.5 | |
| 设备 | Spade | Number | 20.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Shovel | Number | 20.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Plumbing tool kit | Kit box | 1.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 100.0 |
| 植物材料 | Apple Plants | Number | 3300.0 | 0.087 | 287.1 | |
| 施工材料 | Solar panel, pump with all accessories | sites | 2.0 | 6490.0 | 12980.0 | |
| 施工材料 | Water storage, intake, distribution pipes and mulch | sites | 2.0 | 6861.0 | 13722.0 | |
| 施工材料 | Drip irrigation | sites | 2.0 | 4173.0 | 8346.0 | |
| 施工材料 | -Check basin (pits) | number | 3300.0 | 0.466 | 1537.8 | |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 44571.88 | |||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 44571.88 | |||||
如果土地使用者负担的费用少于100%,请注明由谁负担其余费用:
The technological package was designed and implemented by ICIMOD's Indus Basin Initiative with partners and contributes to the sustainable Development Investment Portfolio and is supported by the Australian Aid program.
注释:
Establishment costs and inputs for a solar pump –drip irrigation - mulch system was estimated for apple orchards piloted on a 5 hectares of total land in two villages.
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Monitoring of water pumping, storage, and drip system by a regular visit to the site. | Regular (annually) |
| 2. | Repair and maintenance of solar pump panel and drip irrigation: fixing clogged drip lines and replacement of broken solar panel and cleaning of impellers of the solar pump. | Regular (annually) |
| 3. | Replacement of dead apple plants | As and when required |
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Unskilled | Number | 26.0 | 7.7 | 200.2 | |
| 设备 | Spade | Number | 10.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Plumbing tool kit | Kit box | 1.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 100.0 |
| 植物材料 | Apple ( replacement of dead plants) | number | 330.0 | 0.087 | 28.71 | |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 228.91 | |||||
| 技术维护总成本,美元 | 228.91 | |||||
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
Equipment and labor
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
指定年平均降雨量(若已知),单位为mm:
150.00
有关降雨的规范/注释:
it varies from 150 mm to 200 mm
注明所考虑的参考气象站名称:
Passu ghar
农业气候带
- 干旱
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
说明该技术是否专门应用于:
- 不相关
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 粗粒/轻(砂质)
土壤质地(地表以下> 20厘米):
- 粗粒/轻(砂质)
表土有机质:
- 低(<1%)
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
5-50米
地表水的可用性:
好
水质(未处理):
仅供农业使用(灌溉)
水质请参考::
地表水
水的盐度有问题吗?:
否
该区域正在发生洪水吗?:
是
规律性:
频繁
关于水质和水量的注释和进一步规范:
Water is available in the river but fields are higher up than river
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 低
栖息地多样性:
- 低
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
定栖或游牧:
- 半游牧的
生产系统的市场定位:
- 生计(自给)
非农收入:
- > 收入的50%
相对财富水平:
- 平均水平
个人或集体:
- 团体/社区
机械化水平:
- 手工作业
- 畜力牵引
性别:
- 男人
土地使用者的年龄:
- 中年人
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Relative level of wealth: Poor 35 %, average 65%
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 小规模的
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 个人,有命名
土地使用权:
- 个人
用水权:
- 社区(有组织)
土地使用权是否基于传统的法律制度?:
是
具体说明:
Most of the uncultivated land is communal, community decides uses of the land
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
生产区域
SLM之后的数量:
5 ha
注释/具体说明:
Production area increased as uncultivated land brought under cultivation, but crop production has not increased yet because orchard just established.
能源生产
注释/具体说明:
Use of renewable solar energy for fruit cultivation
水资源可用性和质量
灌溉用水的可用性
注释/具体说明:
Irrigation water availability increased with innovative technological packages.
社会文化影响
社区机构
注释/具体说明:
Community institution (village development organizations) strengthened due to the approach of farming in a group.
SLM/土地退化知识
注释/具体说明:
Land management skills of community enhanced due to various training such as crop cultivation, operation and maintenance of water conservation and management technologies.
生态影响
土壤
土壤水分
注释/具体说明:
Improved soil moisture as a result of water harvesting pits, mulching and efficient drip irrigation.
土壤覆盖层
注释/具体说明:
improved soil cover due to mulch.
土壤流失
注释/具体说明:
Reduced soil loss ( from wind and water erosion) due to application of mulch and also due to vegetation cover and above-ground biomass.
其它生态影响
注释/具体说明:
The technological package is climate change resilient as compared to the melt water dependant surface flood irrigation. Melt water of glacier and snow is very sensitive to climate change. Glaciers are dynamic, their depth and volume fluctuation happens each year.
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
下游洪水
注释/具体说明:
Reduced risk of downstream flooding though the amount is very less.
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气象灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 局地风暴 | 好 |
气候灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 极端冬季条件 | 好 |
| 干旱 | 好 |
水文灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 山洪暴发 | 适度 |
其他与气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
| 其它(具体说明) | 该技术是如何应对的? |
|---|---|
| Heavy load of suspended river sediment | 好 |
注释:
Drip is sensitive to temperature increase; but tolerant to wind storms/dust storms and floods. Solar panel is tolerant to temperature increase.
The solar panel is sensitive to wind storm. The pump is sensitive to flood and sediment load in the river, emitters of drip clog due to sediment. Mulch is sensitive to windstorm. Apple plants at an earlier stage are sensitive to wind storm, plants are sensitive to extreme winter conditions (low temp and snowfall)
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
消极
长期回报:
积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
消极
长期回报:
非常积极
注释:
The initial cost of investment would be fully recovered in 10.9 years, hence the payback period of the project is around 11 years, and the repayment of the investment would start from the eight years. Benefit-Cost Ratio is found to be 4.96.
6.5 技术采用
- 1-10%
如若可行,进行量化(住户数量和/或覆盖面积):
45 Households
注释:
None
6.6 适应
最近是否对该技术进行了修改以适应不断变化的条件?:
是
若是,说明它适应了哪些变化的条件:
- 气候变化/极端气候
具体说明技术的适应性(设计、材料/品种等):
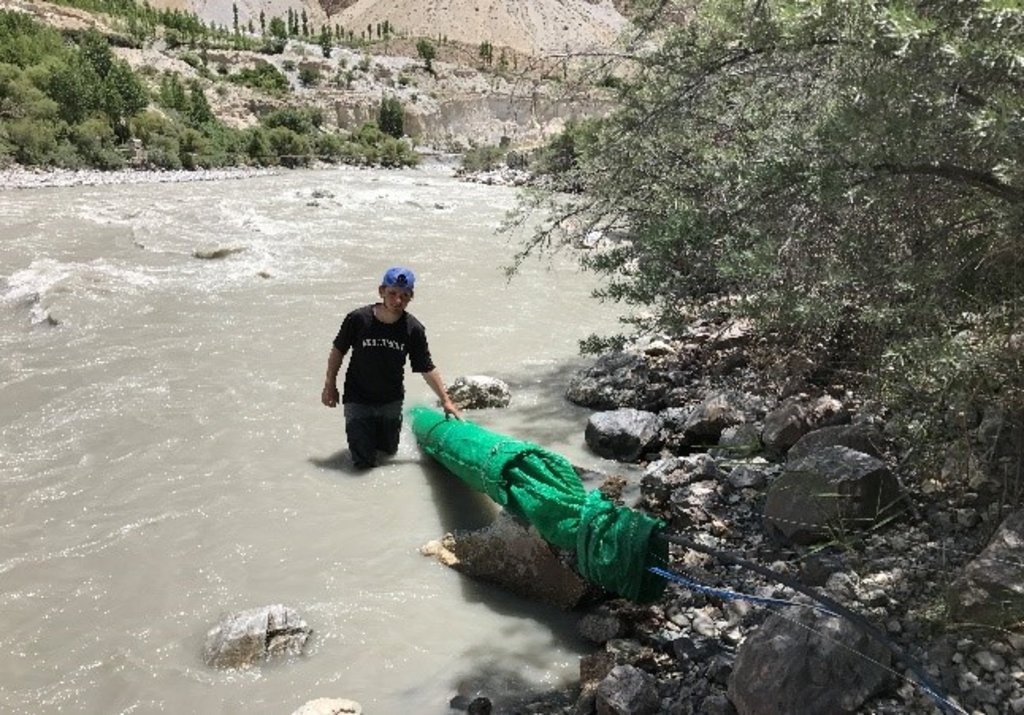
Due to heavy load of suspended sediment flowing in the Hunza River, impellers of the solar pump couldn’t function properly. Site-specific customiza-tion of the pump was carried out to make the system functional and to sustain it in the long run.
For that, an outer filter was developed for the pump to avoid sediment entry into the pump. The outer filter is UPVC pipe (of 10-inch diameter and 13 ft long) wrapped with a finely-meshed green net. The out filter was tightly bound together with the pump. The filter with the pump was placed in the river, transverse to the direction of flow. The farmers are also trained to open the clogged drip to release the sediments from time to time.
Damaged solar panel sometimes was replaced. A portion of mulch was buried under the soil. Apple plants were tied together with support stakes. Application of mulch helped to protect apple plants from low winter temperature.
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| The solar powered water lifting and drip irrigation is the first of its kind in the upper Indus basin. The system is simple and anyone once trained can operate it. It will contribute to nearly 50% of the additional income of the Passu community. |
| The technological package is environmentally friendly and are effective adaptation measures in the context of climate change. |
| Women are often most involved in agricultural activities and this intervention has provided them relief by making it possible for them to work nearer to their valley. More over, once the trees bear fruit, women will be able to sell them to generate income. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| The first innovative technological package in GB that is climate-resilient as compare to meltwater-dependent flood irrigation is operated by renewable solar energy. |
| Water application through drip irrigation is very efficient as compared to flood irrigation, per plant water applied trough drip is 2 litres/day as compared to 30 litres/day through flood irrigation. Integration of mulch enhances soil moisture. |
| The technological package can last more than 20 years. Maintenance cost is nominal, it is US$ 100 at the initial stage and later stage it is US$ 300. |
| As women are predominantly responsible for farming activities, im-proved water access and application through drip reduces their work-load and frees up time for other activities |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Frequent maintenance operation and maintenance of the solar pump due to high sediment concentration of the river from where water is pumped. | Include capacity building activities as an integral part of the technology implementation process. |
| Drip irrigation and parts of solar panel may not available locally | A spare parts should be made available locally for immediate replacement as and when required. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| The investment cost is high . | Explain cost-benefit analysis to aware farmers that the benefit is high in the long run. |
| Techniques of multiple cropping were not practised to get short term benefits from the orchard field. | Engage the agricultural department to demonstrate and train farmers on multiple cropping in the dry land. |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
- 实地考察、实地调查
Field visits was done several times as this was a part of the project activity. Cost benefit analysis was done in 2019.
- 与土地使用者的访谈
Frequently with beneficiaries of the SLM technological packages (around 50 households) .
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
ICIMOD 2017. An Innovative Approach to Agricultural Water Management in the Upper Indus basin: the Water_Energy-Food Nexus at the Local Level
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
http://lib.icimod.org/record/32794/files/Innovative%20Approach.pdf
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Kifayat, U., Khan, F. A., & Ejaz, A. (2014). Determinants of poverty in the mountain region of Gilgit-Baltistan, Pakistan. Developing Country Studies, 4(7), 10-19.
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
Google scholar
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Amjad Ali 2019. Unpublished report on cost-benefit analysis of UIB phase 1 intervention in Upper Hunza
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
ICIMOD
7.4 一般注释
It has been improved a lot as compared to past 10 years .
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块