Flower strips on field margins to attract beneficial insects [比利时]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Alan Radbourne
- 编辑者: David Norris, Sabine Reinsch
- 审查者: William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer
technologies_5620 - 比利时
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
关键资源人
co-compiler:
D’Hooghe Mathias
agrobeheercentrum Eco²
比利时
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
European Interreg project FABulous Farmers有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
UK Centre for Ecology & Hydrology (CEH) - 英国有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Biobest Group (Biobest Group) - 比利时1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.4 所述技术的可持续性声明
这里所描述的技术在土地退化方面是否存在问题,导致无法被认为是一种可持续的土地管理技术?:
否
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
Field margins in agricultural areas are sown with specific flowers to attract insects which help combating pests of crops and livestock and reduce the need for pesticides.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
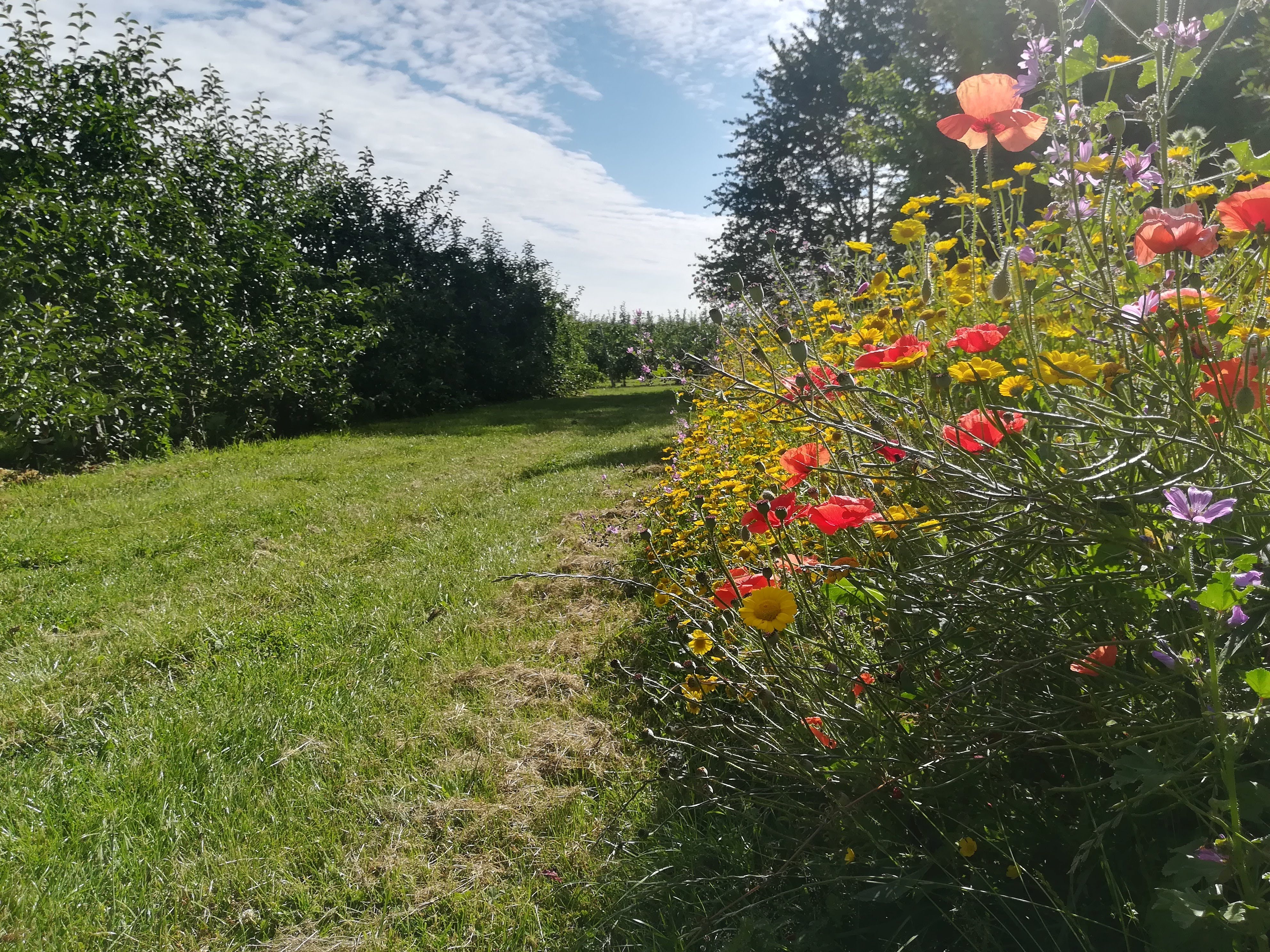
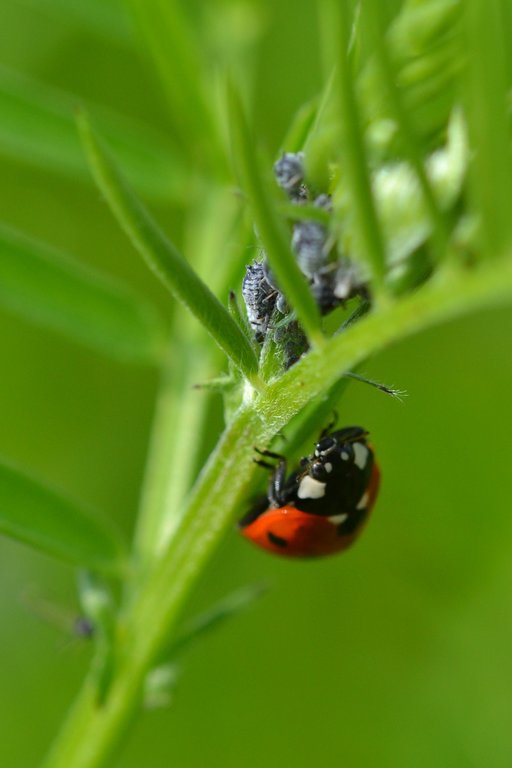
Flower strips on field margins have been established in the centre of Belgium in the region ‘Pajottenland’. The Pajottenland is predominantly farmland and lies mostly between the rivers Dender and Senne in close proximity to Brussels. Pajottenland has historically provided food and drink for the citizens of Brussels. This SLM practice was established in September 2019 on parcels on 7 different farms in Pajottenland. Such flower strips are 3-12 metres wide and are established at the edges of fields to provide nectar and pollen to attract beneficial species that control pest species. It is estimated the beneficial effect of the flower strips on field margins extends about 50 metres into the field.
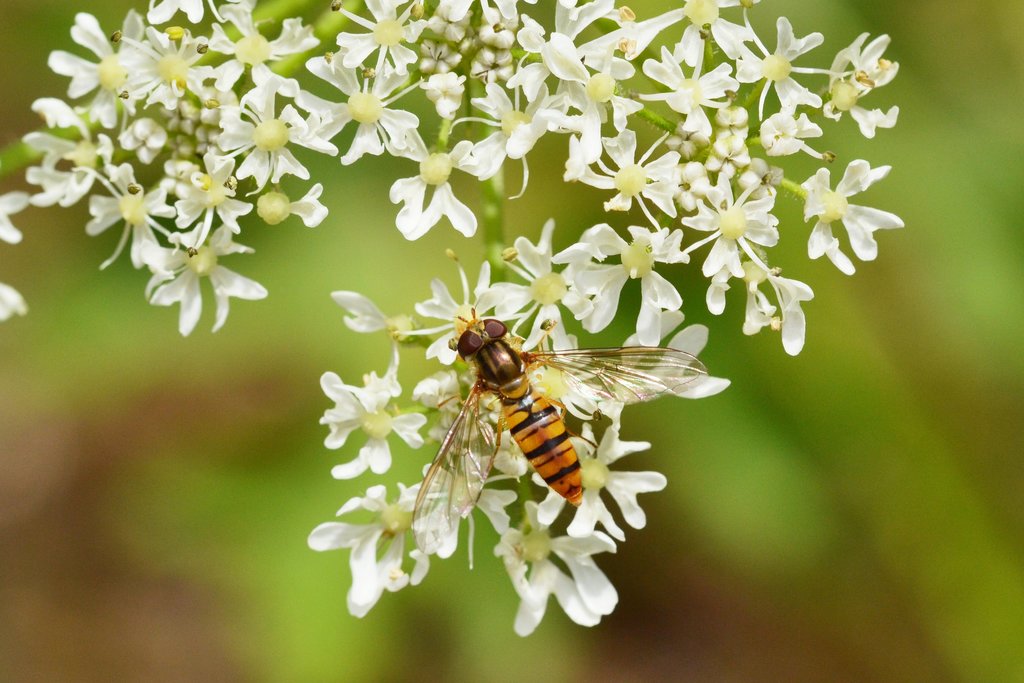
The strips provide a habitat for natural enemies of various crop and livestock pests to control and decrease their population and to reduce the necessity of spraying pesticides. Care it taken in choosing and sowing flower species that attract arthropods with a role in biocontrol, such as hoverflies, lacewings, parasitoids and ladybirds. The flower strips conserve ecosystems and improve biodiversity, also facilitating ecosystem-based disaster risk and integrated soil fertility management.
Farmers dedicate strips of land on field margins to flowers (perennial herbaceous plants). Work includes management of the soil, sowing seeds, mowing flowers and removal of residues. Costs are related to farmers working hours, sowing and mowing equipment, pesticides (if necessary) and seed costs. Savings are related to providing a habitat for natural pest controls, thereby reducing pest in crops and increasing yields.
What do land users like about the technology?
- increased recreational impact for humans due to the beauty of the flower strips
- increased biodiversity (beyond natural pest enemies)
What do land users dislike about the technology?
- reduced overall income from crops (due to reduced area)
- the costs - unless subsidies become more widely available
The compilation of this SLM is a part of the European Interreg project FABulous Farmers which aims to reduce the reliance on external inputs by encouraging the use of methods and interventions that increase the farm’s Functional AgroBiodiversity (FAB). Visit www.fabulousfarmers.eu and www.nweurope.eu/Fabulous-Farmers for more information.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
比利时
区域/州/省:
Flemisch Brabant
有关地点的进一步说明:
Pajottenland
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 适用于特定场所/集中在较小区域
技术现场是否位于永久保护区?:
否
Map
×2.6 实施日期
注明实施年份:
2019
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 在实验/研究期间
- 通过项目/外部干预
注释(项目类型等):
Interreg North West Europe: FABulous farmers
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 保持/提高生物多样性
- Reduced pesticide use
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型
同一土地单元内混合使用的土地::
否

农田
- 一年一作
- Various crop types used in a regional effort to implement flowerstrips
每年的生长季节数:
- 1
采用间作制度了吗?:
否
采用轮作制度了吗?:
否
3.3 由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?
由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?:
- 否(继续问题3.4)
3.4 供水
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 病虫害综合管理(包括有机农业)
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

农艺措施
- A1:植被和土壤覆盖层

植物措施
- V2:草和多年生草本植物
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

生物性退化
- Bp:害虫/疾病增加,捕食者减少
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 不适用
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
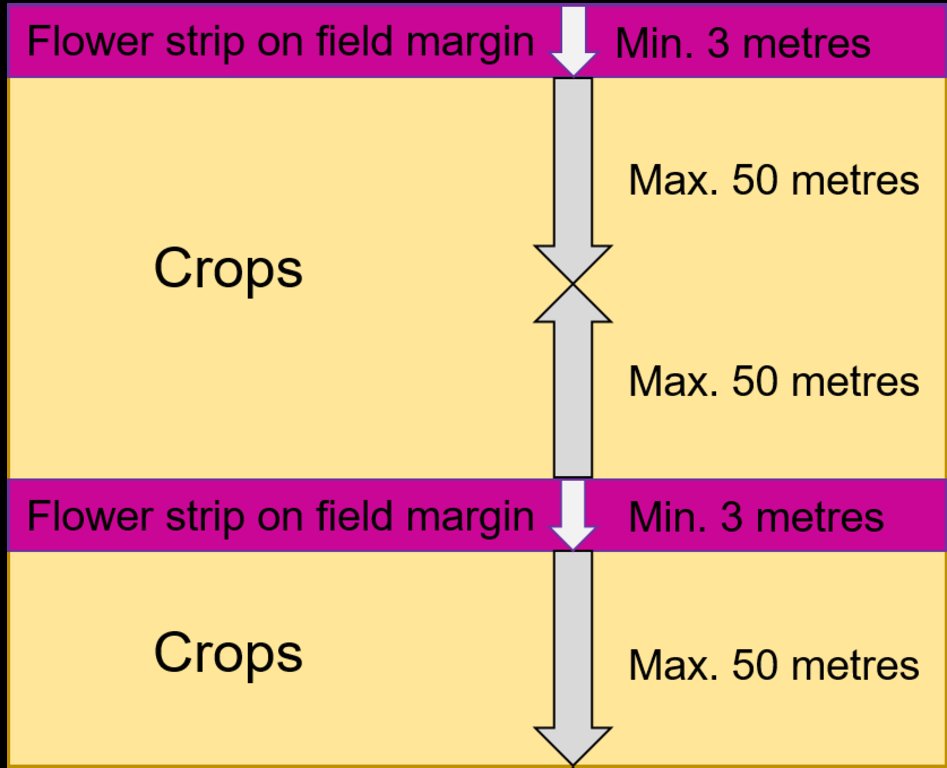
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
Dimension flower strip: minimum 3 metres wide
Effect of the flower strips goes up to 50 metres
Sowing= 2 g seeds/m²= 20 kg seeds/hectare
作者:
Mathias D’Hooghe
日期:
02/10/2019
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
具体说明成本和投入是如何计算的:
- 每个技术区域
注明尺寸和面积单位:
1 ha
如果使用本地面积单位,注明转换系数为1公顷(例如1公顷=2.47英亩):1公顷=:
1ha - 2.47 acres
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
€
如相关,注明美元与当地货币的汇率(例如1美元=79.9巴西雷亚尔):1美元=:
0.91
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
240
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Soil strip preparation | Spring |
| 2. | Planting wildflower seed | Spring |
| 3. | Mowing wildflowers | Late-Summer |
| 4. | Residue removal | Late-Summer (before crop harvest) |
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Farmer time for establishment | Days per establishment | 3.0 | 240.0 | 720.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Machine to cultivate the land (already owned by farmer) | 1 | 1.0 | 100.0 | ||
| 设备 | Machine for sowing after cultivating (already owned by farmer) | 1 | 1.0 | 100.0 | ||
| 设备 | Mower to cut and clear flowers (already owned by farmer) | 1 | 1.0 | 100.0 | ||
| 植物材料 | Flower seeds | per ha | 1.0 | 900.0 | 900.0 | 30.0 |
| 其它 | Loss of income with reduction of cultivated area for crops due to flower strips | ha | 1.0 | 500.0 | 500.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 2120.0 | |||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 2329.67 | |||||
注释:
In 2019 farmers working with VLM who provide a subsidy to sow and maintain field margins at ~70% of the costs to embed and maintain the flower margins.
4.5 维护/经常性活动
注释:
No on-going maintenance. The technology would be re-established as required
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
Cost of seed mix
Cost of machines to embed and maintain the flower strips if not already available to farmer
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
指定年平均降雨量(若已知),单位为mm:
751.00
有关降雨的规范/注释:
Rain spread throughout the year
注明所考虑的参考气象站名称:
KMI, VMM
农业气候带
- 半湿润
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
说明该技术是否专门应用于:
- 不相关
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
土壤质地(地表以下> 20厘米):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 中(1-3%)
- 低(<1%)
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
< 5米
地表水的可用性:
好
水质(未处理):
不良饮用水(需要处理)
水质请参考::
地下水
水的盐度有问题吗?:
否
该区域正在发生洪水吗?:
否
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 中等
栖息地多样性:
- 中等
关于生物多样性的注释和进一步规范:
To be increased by SLM.
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
定栖或游牧:
- 定栖的
生产系统的市场定位:
- 混合(生计/商业)
- 商业/市场
非农收入:
- 低于全部收入的10%
相对财富水平:
- 平均水平
个人或集体:
- 个人/家庭
机械化水平:
- 机械化/电动
性别:
- 男人
土地使用者的年龄:
- 中年人
- 老年人
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 中等规模的
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 个人,有命名
土地使用权:
- 租赁
用水权:
- 自由进入(无组织)
土地使用权是否基于传统的法律制度?:
是
具体说明:
Royal decrees, rent legislation
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物质量
注释/具体说明:
Beneficial species control pests that leads to improved crop quality
收入和成本
农业投入费用
注释/具体说明:
More beneficial species and fewer pests reduces reliance on pesticide use
生态影响
生物多样性:植被、动物
有益物种
注释/具体说明:
Flowers attract more beneficial species
害虫/疾病控制
注释/具体说明:
Flowers attract more beneficial species that can control pests and diseases
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
积极
注释:
'Positive' with the support of subsidies.
6.5 技术采用
- 1-10%
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发的,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 0-10%
注释:
Support provided by SLM expert and subsidised establishment costs
6.6 适应
最近是否对该技术进行了修改以适应不断变化的条件?:
否
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Reduced reliance on pesticide use |
| Landscape diversity and colourful appearance |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Improved crop quality and health with natural pest control and more beneficial species for pollination, reduces inputs and labour |
| Social benefit with attractive flower strips in landscape |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Loss of production land for crops | Costs offset by reduced pesticide use and potential for improved crop quality |
| Expensive seed mix | Subsidy for implementation |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Speciailst knowledge required for right seed mix | SLM expert support and more training opportunities provided through projects like FAB Farmers |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
- 实地考察、实地调查
SLM expert supported implementation thorough the FAB Farmers Project
- 与土地使用者的访谈
SLM expert supported implementation thorough the FAB Farmers Project
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
01/09/2019
7.4 一般注释
This SLM technology is an excellent and easy way to reduce pesticide use and provide other benefits in-kind. The key challenge is to use the correct flower seed mix to attract the most beneficial species for the farm and crop.
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块