Marab - Water Harvesting Based Floodplain Agriculture [约旦]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Joren Verbist
- 编辑者: Mira Haddad, Enrico Bonaiuti
- 审查者: Rima Mekdaschi Studer
Marab in Arabic “المرب”
technologies_5770 - 约旦
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
关键资源人
SLM专业人员:
Strohmeier Stefan
International Center of Agriculture Research in the Dry Areas (ICARDA)
约旦
SLM专业人员:
SLM专业人员:
Natural Resources Economist Social, Economy & Policy Research:
Dhehibi Boubaker
International Center of Agriculture Research in the Dry Areas (ICARDA)
约旦
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
ICARDA Institutional Knowledge Management Initiative有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
International Center for Agricultural Research in the Dry Areas (ICARDA) - 黎巴嫩1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.4 所述技术的可持续性声明
这里所描述的技术在土地退化方面是否存在问题,导致无法被认为是一种可持续的土地管理技术?:
否
注释:
This technology conserves soil and water; it reduces surface water and sediment losses from dryland watersheds. The technology is located in downstream/lowland floodplains, and ideally, it is implemented in an integrated watershed approach. In the present case study, the ‘Marab’ is linked with two main upstream measures: Upland micro-water harvesting (Vallerani system) and gully/channel measures (gully plugs)
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
The Marab is a local downstream water harvesting measure in an integrated watershed context, where up/midstream users and applied land management practices affect the Marab.
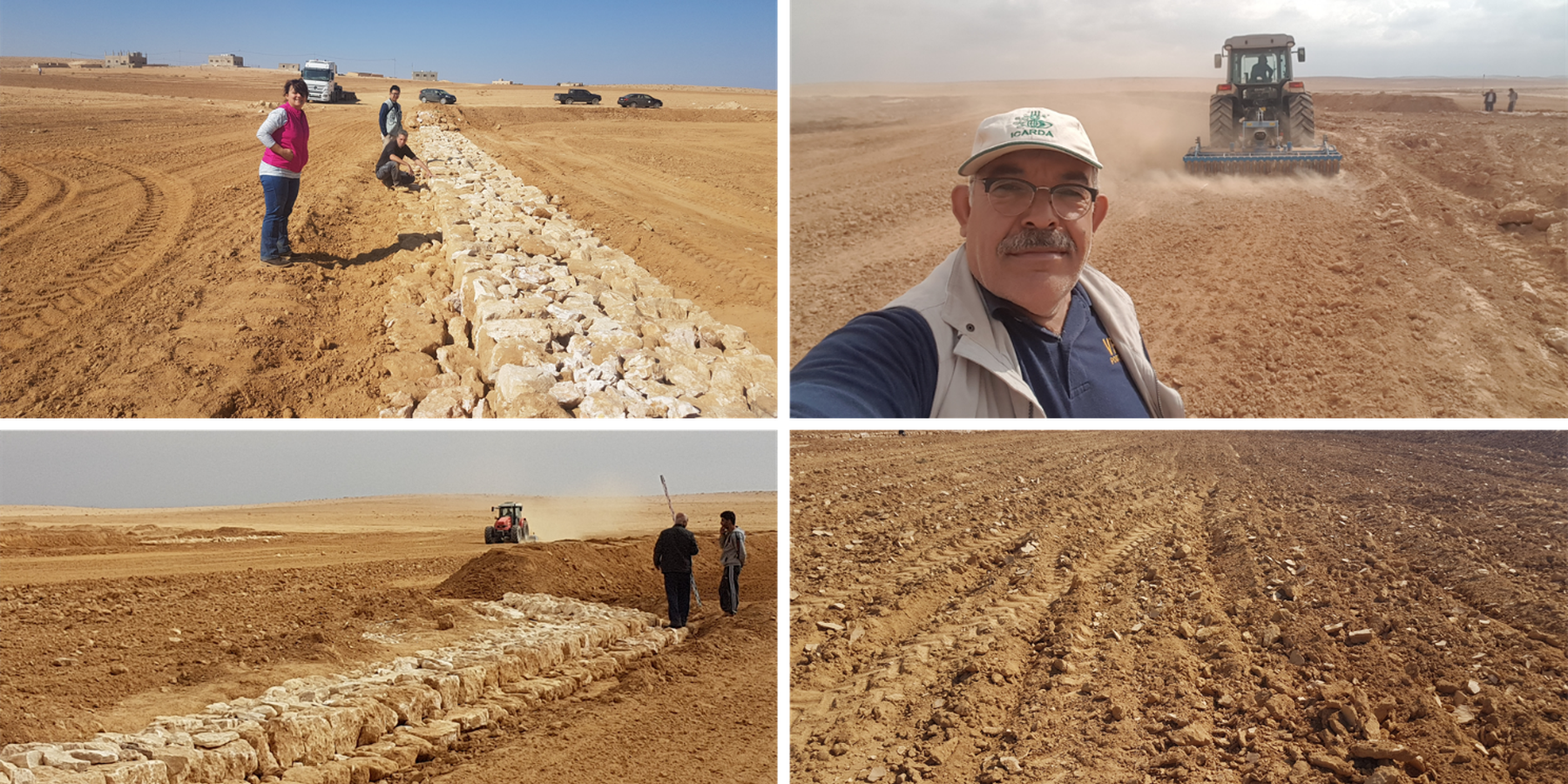
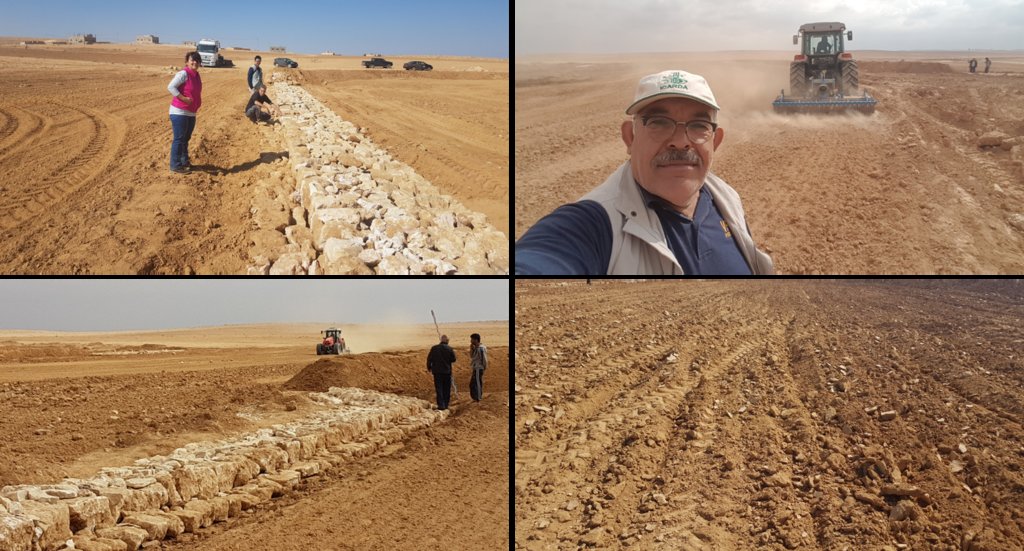
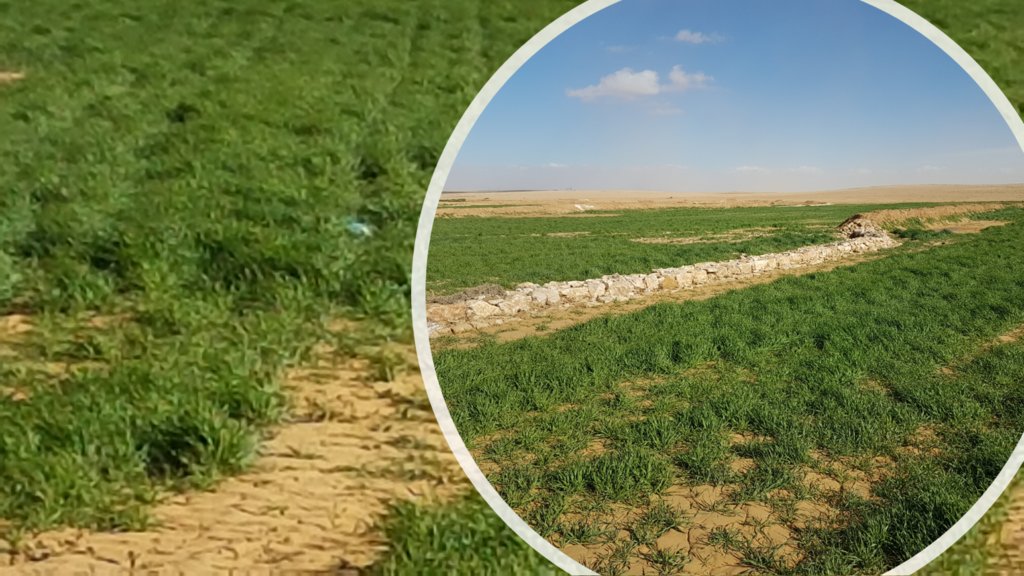
The technology diverts and spreads excess runoff over deep-soil flood plains. The technology comprises local gully-filling, grading/leveling of seed bed, and construction of a bund-and-spillway system creating several compartments for flood-irrigated agriculture.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
Arid drylands of Jordan receive less than 200mm average annual rainfall. The specific site is located close by Al Majeddyeh village, around 30km south-east of Amman. The average annual rainfall at the site is around 130mm. The average temperature is above 18 degrees Celsius. The human environment is characterized by agro-pastoralists. These are farmers that live in permanent houses but transport their livestock to graze. As consequence of the natural environment and mis-management (e.g. overgrazing) desertification has been an increasingly problem, not only from an environmental perspective (e.g. carbon stocking; lack of water), but also from an socio-economic perspective, because desertification leads to reduced productive lands, consequently resulting in less income for the rural population.
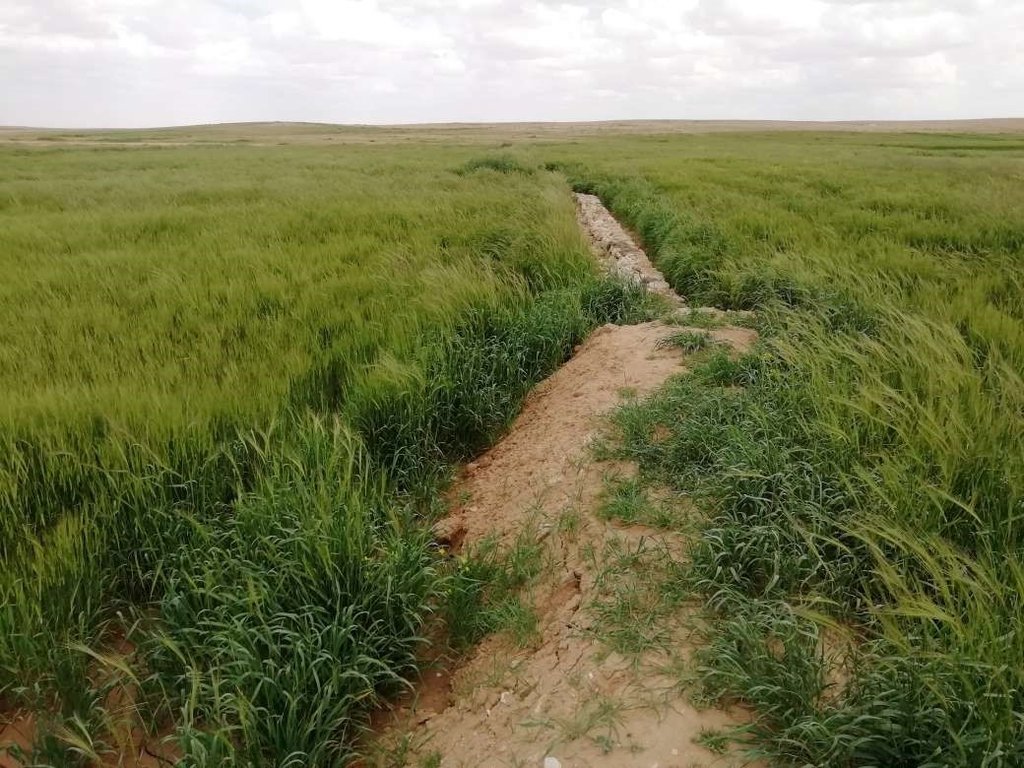
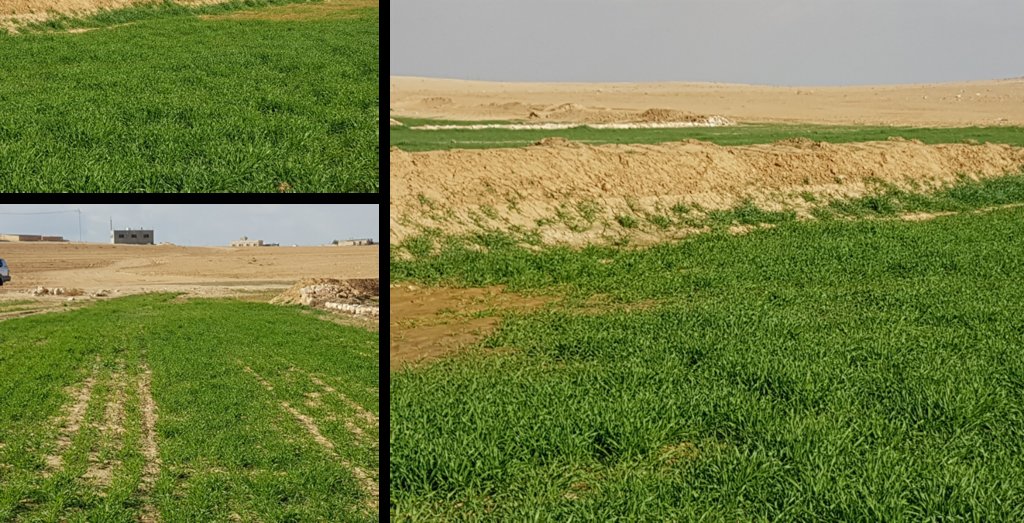
Therefore, the aim of the technology is to achieve high-yield agriculture through flood/macro-catchment water harvesting in arid environments commonly unsuitable for field crop agriculture, creating beneficial impact for local land users. The high yield barley is fed to the livestock (goats and sheeps) of the local agro-pastoralists. Applied in an integrated watershed approach, it meets agricultural demands and motivates sustainable dryland ecosystem management in the uplands. The Marab-technology has a buffering effect on extreme runoff through water retention, for further use in downstream areas, including the trapping of relative fertile sediments from upstream. As the Marab increases yields, it also improves the livelihood of the local population.
The Marab-technology is a macro-catchment water harvesting technology. The Marab is located in the natural depression of the watershed (10 square kilometres), therefore most of the water from the watershed is captured here, instead of being spilled away. Combining this natural depression with the construction of bunds and specific soil leveling, leads to decreased run-off, thus highly increased water infiltration and soil moisture. Thereby, the biomass-production increased as well.
The watershed is characterized by degraded lands upstream (720 ha), where low yield and subsidized barley cultivation is practiced, and by gullies. In a limited part (12 ha) of the upstream area, Vallerani micro-catchments are implemented as a pilot-plot. This might seem contradicting since upstream micro-catchment water harvesting decreases the water in the Marab downstream. However, the Vallerani micro-catchments also have beneficial impacts on the watershed and the Marab, such as flattening peak water flows, reducing erosion and providing fodder. The reduction in water run-off for the Marab as consequence of the Vallerani structures is not significant, due to the small size of the pilot area. But the relations between upstream and downstream should be taken into account.
Upstream watershed measures to buffer and/or avoid extreme runoff events (extreme downstream flooding) in the Marab such as micro-catchment water harvesting structures (Vallerani tractor plow system) and the out-planting of native shrub seedlings, as well as the stabilization of erosive gully systems through gully plugging and revegetation of side banks are advised to be taken before implementing the Marab technology downstream, as they safeguard and protect the Marab. But they are not further into account in this documentation.
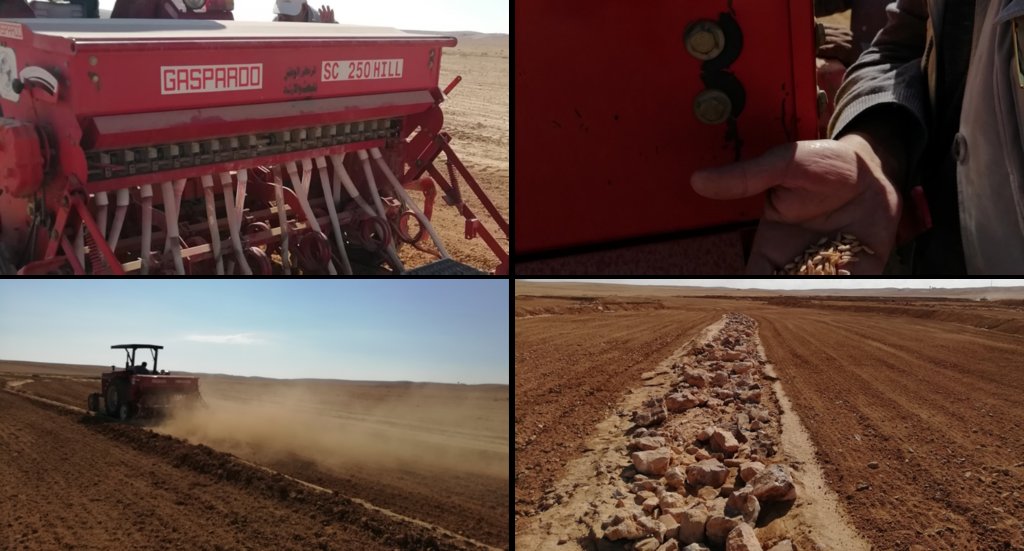
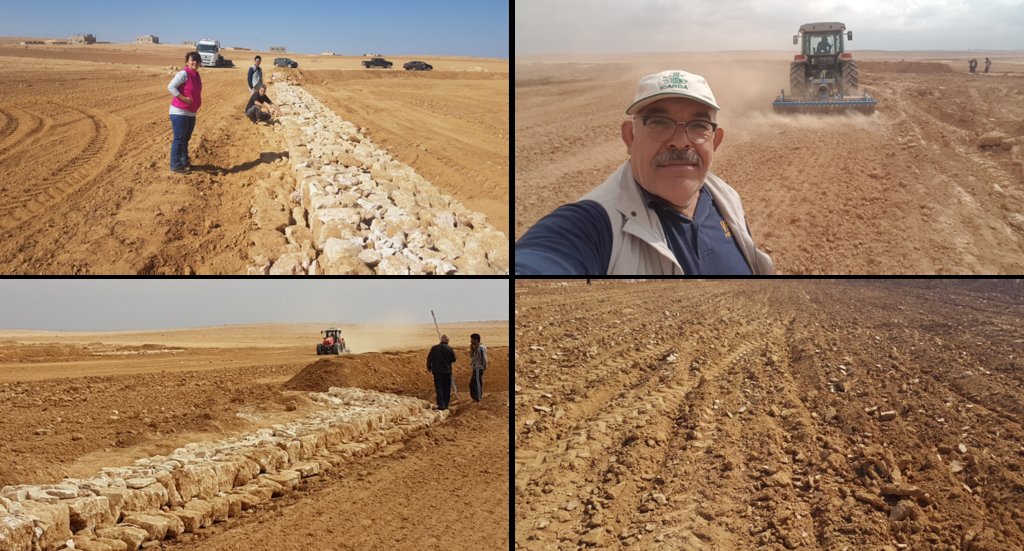
Establishment of the downstream Marab system includes:
•Local filling of downstream gull(system) with deep soil
•Leveling/grading of flood plains
•Construction of earth bunds
•Construction of the spillways (stone made)
• Seedbed preparation for planting annual crop such as barley
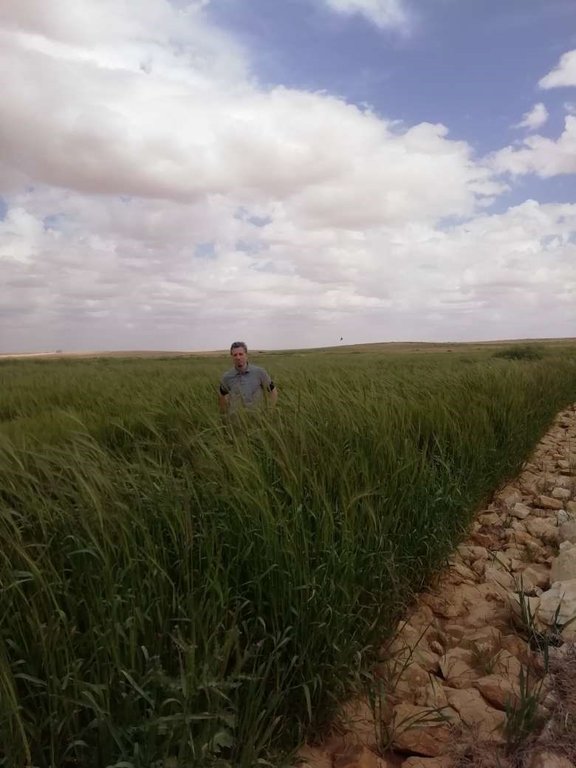
Marab agricultural production is high and stable. It can reach around 5-6 t ha-1 of barley, compared with the low and strongly varying yields of around 0.05-0.30 t ha-1 in traditionally, without macro water harvesting, cultivated barley. Marab barley produces grains (for fodder and reseeding purposes) and requires local inputs, such as fertilizer. The Marab mitigates downstream flooding and loss of sediments from the watershed. Local farmers applying the Marab technology are very satisfied, because of the extremely increased yield as consequence of the technology. However, as water is captured in the watershed, tensions may arise between the downstream (Marab) users and the upstream users.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
约旦
区域/州/省:
Al Jiza District
有关地点的进一步说明:
Al Majeddyeh Village
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 适用于特定场所/集中在较小区域
技术现场是否位于永久保护区?:
否
Map
×2.6 实施日期
注明实施年份:
2017
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 在实验/研究期间
- 通过项目/外部干预
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 改良生产
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
- 降低灾害风险
- 适应气候变化/极端天气及其影响
- 创造有益的经济影响
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型
同一土地单元内混合使用的土地::
是
具体说明混合土地使用(作物/放牧/树木):
- 农牧业(包括农牧结合)

农田
- 一年一作
年作 - 具体指明作物:
- 谷类 - 大麦
每年的生长季节数:
- 1
采用间作制度了吗?:
否
采用轮作制度了吗?:
否

牧场
粗放式放牧:
- 半游牧畜牧业
集约放牧/饲料生产:
- 收割和携带/零放牧
动物类型:
- 山羊
- 绵羊
是否实行作物与牲畜的综合管理?:
否
3.3 由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?
由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?:
- 否(继续问题3.4)
3.4 供水
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
注释:
The Marab facilitates uniform distribution of excess rainwater obtained from the upland (partly Vallerani micro-catchments) and the water is conveyed through rehabilitated gullies to the Marab. (Some) Micro catchments and rehabilitated gullies are essential to avoid damaging water peaks, harming the Marab-structures. The Marab is rainfed and naturally flood irrigated.
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 改良的地面/植被覆盖
- 集水
- 引水和排水
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

农艺措施
- A3:土壤表面处理
- A4:地表下处理

结构措施
- S2:堤、岸
- S3:分级沟渠、渠道、水道
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀
- Wg:冲沟侵蚀/沟蚀
- Wo:场外劣化效应

物理性土壤退化
- Pk:熟化和结壳

生物性退化
- Bc:植被覆盖的减少
- Bq:数量/生物量减少

水质恶化
- Ha:干旱化
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 减少土地退化
注释:
Retaining surface runoff and locally infiltrating water through bunds increase soil moisture hence agricultural yield increases (e.g. biomass, vegetation cover) , soil crusting decreases (in some selected ponding areas it might increase) - and because of trapping top-soil sediments and residues from the uplands, soil fertility increases likewise.
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
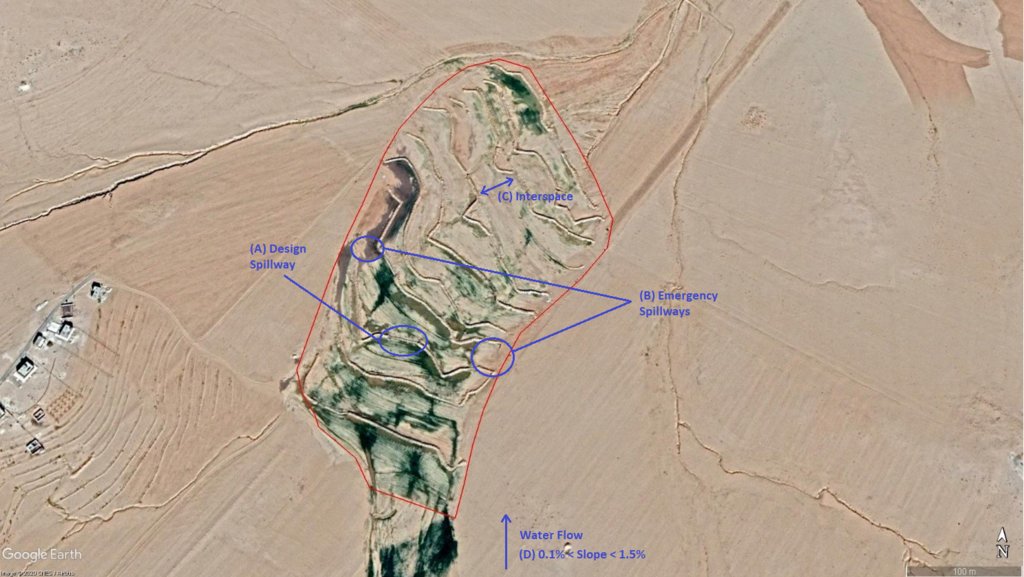
The overall Marab (reshaped flood plain) area is 10 hectares. The natural flood plain was leveled up to the sides; the natural slope in flow direction ranges between 0.1 and 1.5% (D). The later stone bund construction (soil relocation) and siltation/erosion processes over time develop a slight step-terraced bund compartment system, with the single compartments having much smaller slope than the overall Marab. At the sides, the levelled area slightly increases towards the natural terrain (natural terrain at the sides is around 0.1 to 0.3m higher compared with the leveled Marab). This avoids side outflow of water during design storms (*). Bund structures, along the contour, are built with a loader up to around 0.7 to 1.0m height and around 2.0 – 3.0m bottom width. The bunds are built with compaction through the loader. Interspace between the bunds is between 10-50 meters (C), depending on the local slope in the flow direction, having around 0.1 to 0.3m soil surface elevation difference between the bunds. Stone made design-spillways (A) are being constructed around the middle of each bund, with certain position change between the bund in downstream direction. Thus, spillways do not perfectly align with respect to the bund, but create a meandering flow around the center. The stone-protected design-spillways are designed to safely route at least the expected 2-5 year return period flood event. The Marab plain is not perfectly even, especially at the sides, to avoid water flowing around the bunds during design storms. However, the Marab-technology is also designed to cope with more extreme events, a storm of 5-10 return period, without significant damages. Therefore, there are emergency-spillways (**) implemented at the sides of each bund (B). These emergency-spillways allow excess water to flow out sideways rather than flow over the bund which would damage the structures. Note:
Based on above considerations and calculations bund spillway lengths reach 50-60m in the specific watershed.
* A design storm is a rainfall event that results in a flood event as water accumulates throughout the watershed. The Marab is designed to harvest the water optimally by (design) spill ways that keep the water in the Marab. A design storm relates to a certain return period. In general a longer return period (i.e. less frequent) accounts for a more intense event hence a more severe flooding event.
** An emergency spill way is a structure that is designed to discharge excess water coming from storms more extreme than the design storm (i.e. with less frequent storms). In practice this means that the Marab is protected from excess water.
作者:
Joren Verbist (Extracted from Google Earth Pro on Jan 7th 2019)
日期:
19/12/2020
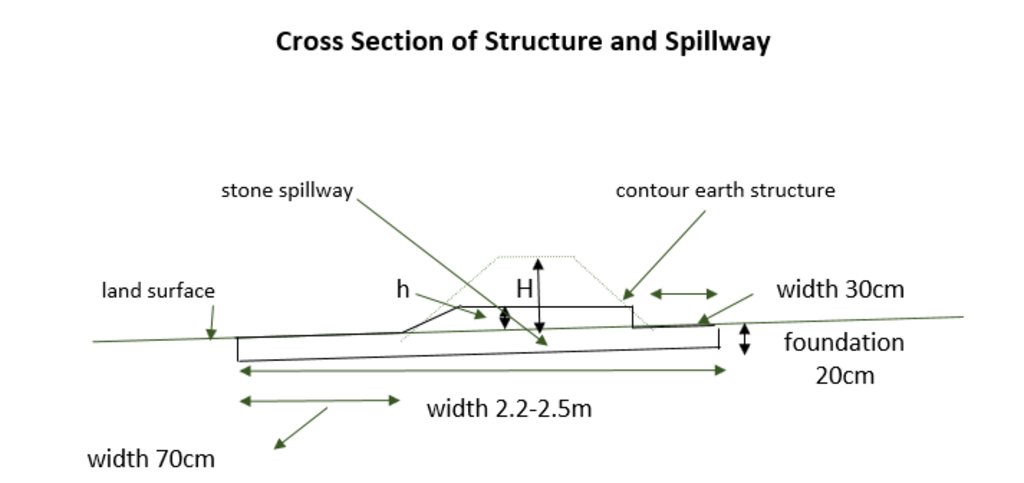
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
The cross-section shows the dimensions. Downstream of a bund the width is 70 centimeter. The foundation is 20 centimeter high. The upstream width is 30 centimeter. The total width of the bund varies between 2.2 meter and 2.5 meter.
作者:
Stefan Strohmeier
日期:
01/07/2020
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
具体说明成本和投入是如何计算的:
- 每个技术区域
注明尺寸和面积单位:
10 ha
具体说明成本计算所用货币:
- 美元
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
35
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Implement upstream watershed rehabilitation measure (e.g. Upstream Vallerani micro water harvesting) | Prior of Marab-Technology construction |
| 2. | Implement gully rehabilitation measure (e.g. Midstream gully rehabilitation) | Prior of Marab-Technology construction |
| 3. | Marab site selection (flood plain): topographic assessment (slope, soil depth, etc.) and consideration of watershed hydrology (e.g. for bund and spillway design) | Before the rainy season |
| 4. | Grading/levelling of natural flood plain incl. gully fill (with soil material) | season (Aug. – Nov.) |
| 5. | Implement bund structures (based on step 4) | season (Aug. – Nov.) |
| 6. | Construct stone made design and emergence spillways (based on step 5) | season (Aug. – Nov.) |
| 7. | Preparation of compartmentalized agricultural fields (bund interspaces) for field crop agriculture | season (Aug. – Nov.) |
注释:
The upstream measures as the Vallerani System and gully rehabilitation are strongly recommended but are not taken into account as costs in this documentation. Because this documentation focuses specifically on the Marab-technology.
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Local Workers | person-days | 50.0 | 35.0 | 1750.0 | |
| 劳动力 | Land Survey | person-days | 6.0 | 35.0 | 210.0 | |
| 劳动力 | Engineer (+assistance) | person-days | 15.0 | 50.0 | 750.0 | |
| 劳动力 | Drivers of heavy machinery | person-days | 12.0 | 35.0 | 420.0 | |
| 设备 | Grader | machine-days | 3.0 | 250.0 | 750.0 | |
| 设备 | Loader | machine-days | 10.0 | 250.0 | 2500.0 | |
| 设备 | Deep Plow | machine-days | 3.0 | 200.0 | 600.0 | |
| 设备 | Tractor (to pull the shallow and deep plow) | machine-days | 5.0 | 200.0 | 1000.0 | |
| 设备 | Shallow Plow | machine-days | 2.0 | 200.0 | 400.0 | |
| 设备 | Water Tank Truck | Tank | 1.0 | 50.0 | 50.0 | |
| 设备 | Small Equipment (Shovel, pickaxe, buckets) | Equipment | 1.0 | 200.0 | 200.0 | |
| 施工材料 | Stones | Kubic Metre | 200.0 | 10.0 | 2000.0 | |
| 其它 | Transportation of heavy machinery | 1.0 | 2000.0 | 2000.0 | ||
| 其它 | Security | 1.0 | 300.0 | 300.0 | ||
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 12930.0 | |||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 12930.0 | |||||
如果土地使用者负担的费用少于100%,请注明由谁负担其余费用:
ICARDA and National Agricultural Research Centre (NARC)
注释:
These costs are for establishment (so one-time) and are for the total Marab-technology i.e. 10 ha.
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Maintaining the structures based on observations and possible damages after the rainy season, so no clear maintenance plans | Before the rainy season (Oct. – Nov.)/upon observation |
注释:
Excludes annual farming costs (e.g. seedbed preparation)
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Engineer | person days per year | 2.0 | 50.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Worker | person days per year | 6.0 | 35.0 | 210.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Loader | machine days per year | 1.0 | 250.0 | 250.0 | 100.0 |
| 施工材料 | Stones | Kubic Metre | 10.0 | 10.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 660.0 | |||||
| 技术维护总成本,美元 | 660.0 | |||||
注释:
The costs of practicing agriculture (e.g. cost of seeds and fertilizer) are not taken into account, since these costs were also made before the implementation of this technology.
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
The special and heavy machinery affect the cost significantly, since these were not available in the area. The implementation of the technology is labour intensive, therefore labour costs are significant as well. However, these costs are initially, so these specific costs are almost zero after establishment. In addition, all the maintenance is payed for by the land users. So, only the establishment was payed for by external parties.
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
指定年平均降雨量(若已知),单位为mm:
130.00
有关降雨的规范/注释:
In the specific site/dry areas of Jordan rainy season usually ranges from November until April
Queen Alia International Airport long-time avergae annual rainfall is around 150 mm (around 10km west of the site)
At the site a rainfall tipping bucket has been installed in 2016.
注明所考虑的参考气象站名称:
Queen Alia International Airport
农业气候带
- 干旱
The maximum temperature usually occurres in August.
The average daily maximum temperature is 25.01 °C.
The average daily minimum temperature is 8.5 °C
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
说明该技术是否专门应用于:
- 凸形情况
关于地形的注释和进一步规范:
The Marab itself is rather concave (depression shape) / natural depression. However, the bund structures are convex, spreading water over the field.
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
- 细粒/重质(粘土)
土壤质地(地表以下> 20厘米):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 低(<1%)
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
> 50米
地表水的可用性:
匮乏/没有
水质(未处理):
不可用
水质请参考::
地表水
水的盐度有问题吗?:
否
该区域正在发生洪水吗?:
是
规律性:
频繁
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 低
栖息地多样性:
- 低
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
定栖或游牧:
- 半游牧的
生产系统的市场定位:
- 混合(生计/商业)
非农收入:
- 低于全部收入的10%
相对财富水平:
- 贫瘠
- 平均水平
个人或集体:
- 个人/家庭
机械化水平:
- 机械化/电动
性别:
- 男人
土地使用者的年龄:
- 青年人
- 中年人
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
The actual land users are often poor Jordanians or Syrian refugees. However, the owners of the livestock are relatively rich. The landowners are responsible for the maintenance of the intervention.
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 中等规模的
注释:
10ha
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 个人,有命名
土地使用权:
- 租赁
- 个人
- NA
土地使用权是否基于传统的法律制度?:
是
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
注释/具体说明:
The crops produced are used as fodder
饲料生产
SLM之前的数量:
0.05ton/ha
SLM之后的数量:
5ton/ha
注释/具体说明:
The production of the fodder is increased as the barley yield is mostly used to feed animals and also the stubble is grazed.
饲料质量
注释/具体说明:
The barley is fed to the livestock
生产区域
注释/具体说明:
Due to the bunds (but very limited and inevitable)
土地管理
收入和成本
农业投入费用
注释/具体说明:
Expenses are slightly increased due to possible maintenance of the Marab. However, the increased yield justifies this.
农业收入
工作量
注释/具体说明:
Due to possible maintenance
社会文化影响
食品安全/自给自足
SLM/土地退化知识
注释/具体说明:
During the construction, local community were hired as workers, this has significantly boosted their knowlegde about SLM.
生态影响
水循环/径流
水的回收/收集
地表径流
多余水的排放
地下水位/含水层
土壤
土壤水分
土壤覆盖层
土壤流失
土壤堆积
土壤结壳/密封
土壤有机物/地下C
生物多样性:植被、动物
植被覆盖
生物量/地上C
减少气候和灾害风险
洪水影响
干旱影响
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
下游洪水
注释/具体说明:
Reduced downstream flooding is desired
下游淤积
注释/具体说明:
Reduced downstream siltation is desired
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 增加或减少 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年降雨量 | 减少 | 好 |
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气象灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 局地暴雨 | 非常好 |
水文灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 山洪暴发 | 非常好 |
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
轻度消极
长期回报:
积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
非常积极
注释:
The initial investment is quite large. Therefore, the short term returns is classified as slightly negative. After some seasons with good (stable) crop yield the return of investment is positive. Long term benefits are classified positively.
6.5 技术采用
- 1-10%
如若可行,进行量化(住户数量和/或覆盖面积):
These are some farmers that live near the Marab. They try to copy the Marab in their fields.
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发的,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 91-100%
注释:
The local farmers like the technology and acknowledge its positive impacts. They would like to have a Marab themselves (even if their locally owned lands are not suitable in many cases). Local agro-pastoralists copy and apply parts of the technology (especially the bund
system). However, it strongly recommended that implementing a Marab-technology is done as a community-based project/intervention; the Marab technology should be part of an integrated watershed management plan, located at the most suitable location for the entire community.
6.6 适应
最近是否对该技术进行了修改以适应不断变化的条件?:
是
若是,说明它适应了哪些变化的条件:
- 气候变化/极端气候
具体说明技术的适应性(设计、材料/品种等):
The spillway design can be adapted to variable surface runoff occurrence (affected by climate change).
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| The farmers highly appreciate the improved economic situation as consequence of the increased yield. |
| A strength of the Marab technology is that water is harvested and minimally spilled away, preventing top-soil erosion and accumulating soil organic matter consequently preserving soil fertility. |
| The crop produces grains: can be (partially) used for re-seeding in the coming seasons; economic gain + increase resilience. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Economic improvement through targeted agricultural interventions in the most suitable location(s) of a watershed. This aims at decreasing the pressure on the fragile dry land ecosystem. The locally increased yield raises awareness on non-sufficient field crop agriculture in uplands (commonly achieved) and might increase the willingness for more nature-based sustainable land management measures in the less fertile and runoff generating (more vulnerable uplands) parts of the watershed. Therefore, the Marab technology could be a starting point for a watershed rehabilitation initiative. |
| The Marab technology creates an opportunity for multiple crop introduction (due to natural flood irrigation) – aside from barley monoculture (agro-diversity). |
| Increased water infiltration conserves water and might lead to deep percolation (groundwater recharge). |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| The Marab depends on upstream water users; can lead to increased tensions | Agreement among the community - conducting contacts/contracts among upstream and downstream farmers. Joint watershed management and benefit share could be mediate these tension. And might even lead to watershed rehabilitation. |
| High initial investment and partially high maintenance costs (including machinery) | Once the implementation is linked with larger environmental benefits – communities might receive funds from the government or international donors. |
| Loss of cultivation area where the bunds are placed | Unavoidable. However, the gain of interspaces exceeds these losses several times. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Tensions among multiple actors in the watershed (selection of Marab area) | Develop institutions that could avoid these tensions by establishing agreements, contracts, rules, or regulations. |
| Heavy machinery in a vulnerable ecosystems – can induce other requests/use by locals (improper use) | Targeted policies in place & enforcements |
| Increasing wealth inequality between farmers and/or communities. | Creation of institutions, which assure fair distribution. This would benefit the whole watershed. |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
- 实地考察、实地调查
- 与土地使用者的访谈
- 与SLM专业人员/专家的访谈
- 根据报告和其他现有文档进行编译
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
15/04/2020
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Strohmeier, S. (2017). Dimensioning of Marab in Majidyya.
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Strohmeier, S. (2017). Watershed Restoration in Baia Areas of Jordan Technology Packages for Controlling and Monitoring Gully Erosion.
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
https://mel.cgiar.org/projects/jordan-watershed-restoration-project
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Mira Haddad, Stefan Strohmeier. (12/12/2017). Treated upland areas map. Jordan: International Center for Agricultural Research in the Dry Areas (ICARDA).
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
https://hdl.handle.net/20.500.11766/9108
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Stefan Strohmeier, Mira Haddad, Ismail Shukri. (8/11/2018). Marab - water harvesting based agriculture.
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
https://hdl.handle.net/20.500.11766/9069
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Boubaker Dhehibi, Mira Haddad, Stefan Strohmeier, Masnat El-Hiary. (24/7/2020). Enhancing a Traditional Water Harvesting Technique in Jordan’s Agro-pastoral Farming System. Lebanon: International Center for Agricultural Research in the Dry Areas (ICARDA).
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
https://hdl.handle.net/20.500.11766/11506
7.3 链接到网络上的相关信息
标题/说明:
WATER HARVESTING FOR RESTORING RANGELANDS IN JORDAN
URL:
https://www.icarda.org/media/drywire/water-harvesting-restoring-rangelands-jordan
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块