Piggery-Banana-Coffee technology [乌干达]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Tonny Kyambadde
- 编辑者: Beatrice Nabukenya, Michael Mulindwa, Kyagaba Prossy, Annika Reimann
- 审查者: William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer
Obusa bwe mbizzi kumwanyi ne bitooke
technologies_5914 - 乌干达
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
co-compiler:
Kyagaba Prossy
Caritas MADDO
乌干达
co-compiler:
co-compiler:
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
Euregio-East Africa Livelihood Improvement Programme (EEALIP)有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Caritas Masaka Diocesan Development Organisation (Caritas MADDO) - 乌干达1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.4 所述技术的可持续性声明
这里所描述的技术在土地退化方面是否存在问题,导致无法被认为是一种可持续的土地管理技术?:
否
注释:
The technology under documentation is practically proven for its efficiency and effectiveness in conserving land and improving productivity.
1.5 参考关于SLM方法(使用WOCAT记录的SLM方法)的调查问卷

MADDO SLM approach [乌干达]
This integrated soil fertility management approach aims at identifying and promoting practices in land management that can increase soil fertility, reduce land degradation and improve production. Under this specific example, organic manure from a piggery was applied to banana and coffee plantations.
- 编制者: Tonny Kyambadde
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
The "Piggery-Banana-Coffee" sustainable land management technology is a proven practice that significantly improves soil fertility and productivity in an integrated farming system for smallholder farmers in Uganda.
2.2 技术的详细说明
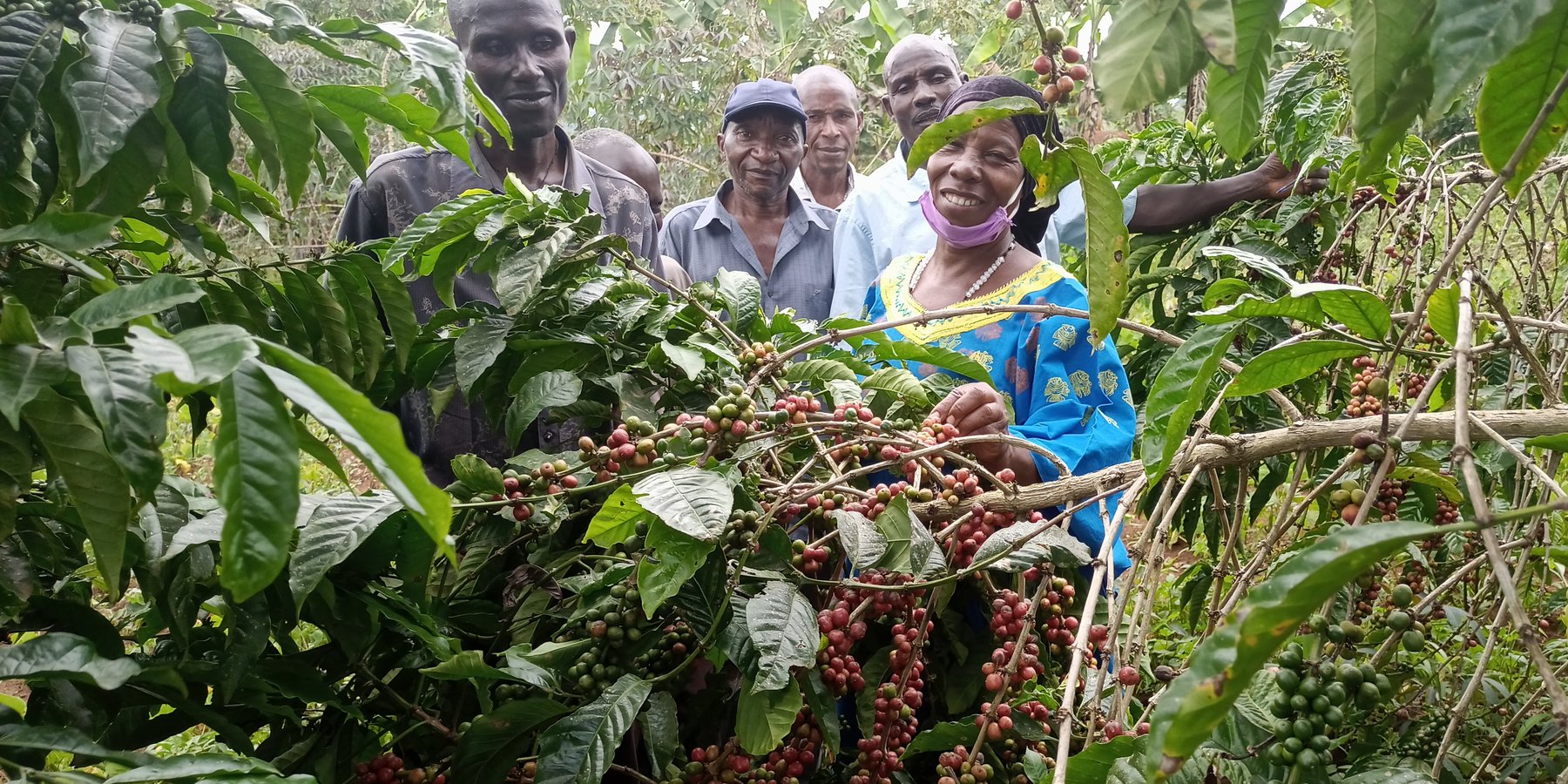
说明:
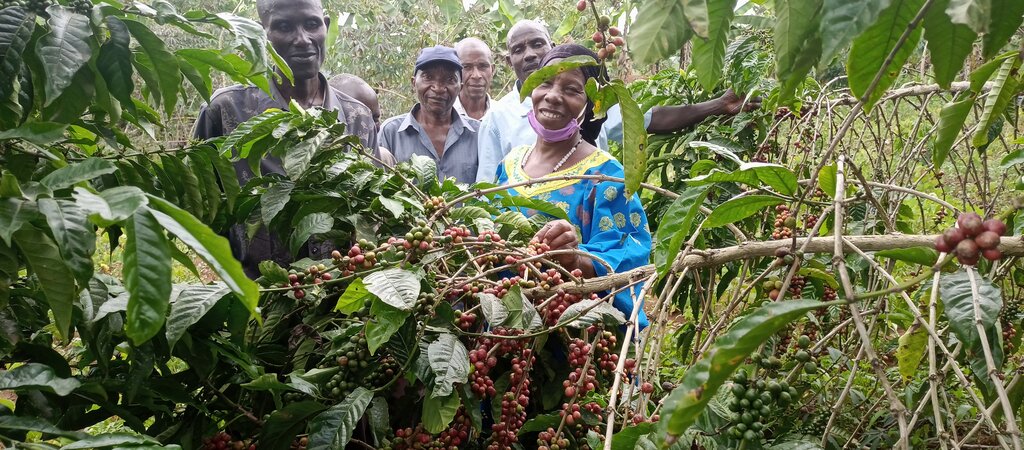
The “piggery-banana-coffee” SLM technology has been widely practiced by smallholders in Bukumansimbi District, Central Uganda for many years. The technology is proven due to its manifold functions and benefits, including increased productivity and improved soil biodiversity leading to better food security with organic, healthy produce. It simultaneously contributes to environmental protection. The technology has been applied for many years in Bukumansimbi but it needed a promotion by the implementer Caritas MADDO for wider adaption by the community.
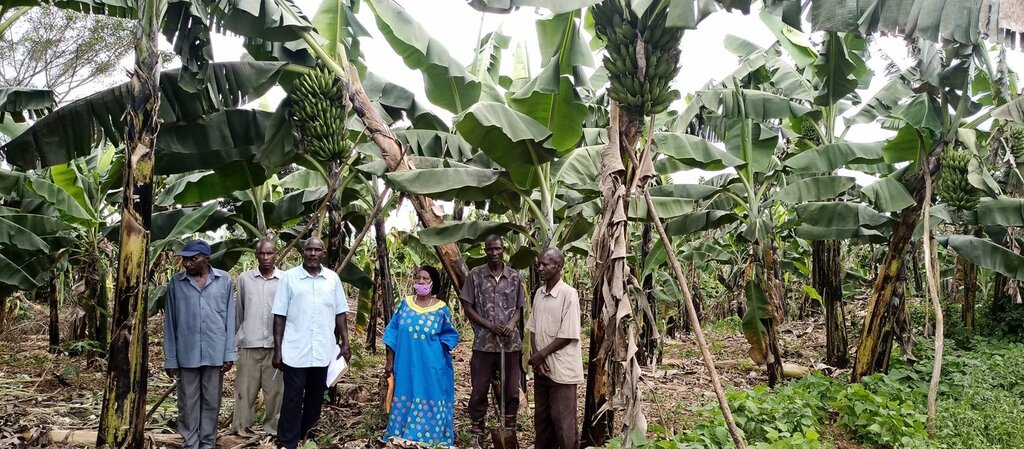
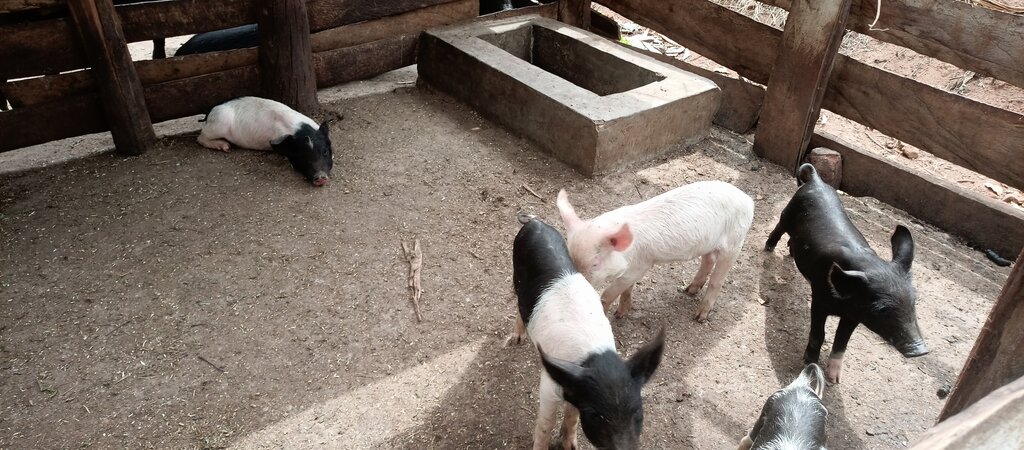
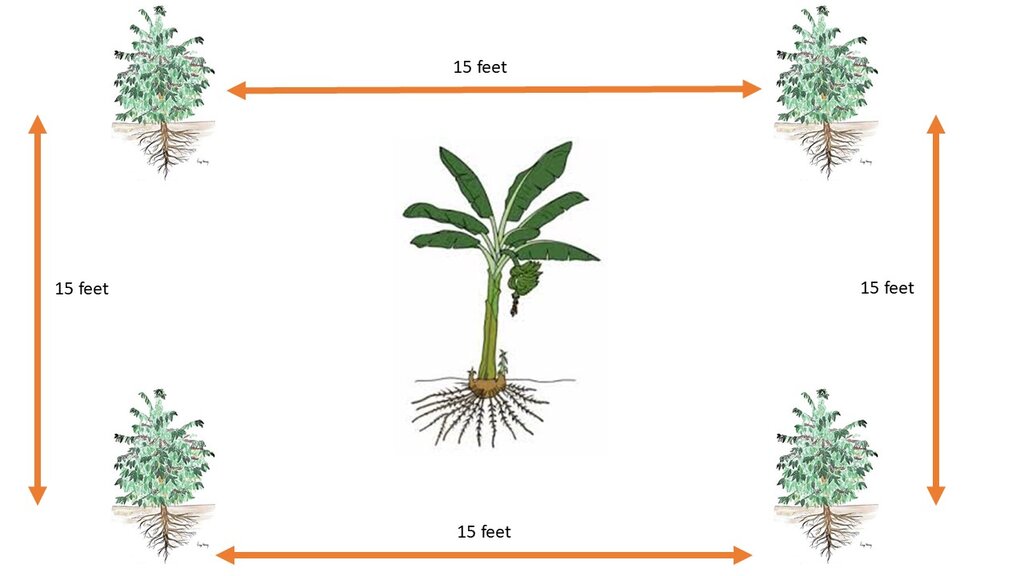
The technology can be applied in a natural environmental setting with no controlled conditions. Taking a case of one acre (0.4 ha) of land the farmer will need 450 coffee seedlings and 150 banana suckers to establish an integrated banana-coffee plantation. Then there is a requirement for 10 pigs to supply enough manure (urine and dung) to maintain the fertility of the soil in the plantation. Bananas provide shade to the coffee and reduce the impact of wind and soil erosion. Manure from the piggery is applied to the mixed plantation. Manure application increases soil biodiversity and improves both the physical and chemical properties of the soil, including soil structure, aeration, and moisture retention. Integrating piggery components into the system requires shed construction, purchase of piglets, feeding costs, treatment, and vaccinations. The pigsty occupies a space of 50 ft by 25 ft (approx. 15 m x 7.5 m). Each enterprise is complementary to the other: manure from pigs goes to the coffee and banana plantation and in return the banana peelings as well as the household food leftovers are served as important food resources for the pigs.
The land users under the pilot project acknowledge the significance of the technology because of its ability to sustain production and the other benefits listen above. However, swine fever disease is one of the limiting factors to the technology, as the pigs are prone to its outbreak. Moreover, some farmers report the high feeding costs for the pigs’ maintenance - particularly in the dry season (when there are few weeds that can be supplemented to the diet of the pigs).
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
乌干达
区域/州/省:
Central region
有关地点的进一步说明:
Bigasa Sub County in Bukomansimbi District
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果不知道精确的区域,请注明大致覆盖的区域:
- 0.1-1 平方千米
技术现场是否位于永久保护区?:
否
Map
×2.6 实施日期
注明实施年份:
2017
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 不到10年前(最近)
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 作为传统系统的一部分(> 50 年)
- 通过项目/外部干预
注释(项目类型等):
The "piggery-banana-coffee” SLM technology has been practiced as a traditional system in the area for more than 50 years, however the project rebooted the technology and its adoption under the EEALIP project starting in 2017.
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 改良生产
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
- 保护生态系统
- 保持/提高生物多样性
- 创造有益的经济影响
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型
同一土地单元内混合使用的土地::
是
具体说明混合土地使用(作物/放牧/树木):
- 农林业

农田
- 多年一作(非木材)
多年生(非木质)作物 - 指定作物:
- 香蕉/芭蕉/蕉麻
- Coffee
每年的生长季节数:
- 2
具体说明:
For banana the harvest is continuous through the year whiles as coffee has two harvesting seasons
采用间作制度了吗?:
是
如果是,说明哪些作物是间作的:
Banana and coffee are intercropped
采用轮作制度了吗?:
否

森林/林地
- 植树造林
植树造林:说明树种的起源和组成:
- 混交品种
- Ficus natalensis (mutuba in luganda) tree
以上的树木是落叶树还是常绿树?:
- 常绿
产品和服务:
- 木材
- 薪材
- 其它森林产品
- 放牧/啃牧
- 自然保持/保护
- 娱乐/旅游
- 自然灾害防护
- Backcloth

水道、水体、湿地
- 沼泽、湿地
主要产品/服务:
Swamp is nearby for water supply
3.3 由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?
由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?:
- 是(请在技术实施前填写以下有关土地利用的问题)
同一土地单元内混合使用的土地::
是
具体说明混合土地使用(作物/放牧/树木):
- 农林牧业

农田
- 多年一作(非木材)
多年生(非木质)作物 - 指定作物:
- 香蕉/芭蕉/蕉麻
- coffee
采用间作制度了吗?:
是
如果是,说明哪些作物是间作的:
Banana and coffee are intercropped
采用轮作制度了吗?:
否

森林/林地
- 植树造林
植树造林:说明树种的起源和组成:
- 混交品种
- Ficus natalensis (mutuba in luganda) tree
以上的树木是落叶树还是常绿树?:
- 常绿
产品和服务:
- 木材
- 薪材
- 其它森林产品
- 放牧/啃牧
- 自然保持/保护
- 娱乐/旅游
- 自然灾害防护

水道、水体、湿地
- 沼泽、湿地
主要产品/服务:
Swamp is nearby for water supply
注释:
Pigs are kept on zero grazing. There are not allowed to roam in the bananas or coffee farm.
3.4 供水
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
注释:
The land is mulched with dry grass and banana materials to conserve rainfed water from evaporation.
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 农业林学
- 农畜综合管理
- 土壤肥力综合管理
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

农艺措施
- A1:植被和土壤覆盖层
- A2:有机质/土壤肥力
- A3:土壤表面处理
- A7:其它
A3:区分耕作制度:
A 3.2: Reduced tillage (> 30% soil cover)

植物措施
- V1:乔木和灌木覆盖层
- V2:草和多年生草本植物
- V3:植被的清理

结构措施
- S1:阶地
- S9:动植物庇护所
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀
- Wo:场外劣化效应

化学性土壤退化
- Cp:土壤污染

生物性退化
- Bq:数量/生物量减少
- Bs:质量和物种组成/多样性的下降
- Bl:土壤寿命损失
- Bp:害虫/疾病增加,捕食者减少

水质恶化
- Hq:地下水水质下降
注释:
The technology is promoting better quality of groundwater on two grounds. Firstly, by applying the organic manure of the pigs on the coffee and banana farm instead of chemical fertilizers no pollution of the waterbodies is given. Secondly, the pigs are confined in their pigs sty and thus due not have the opportunity to go to the water bodies and pollute the water with urine or dung.
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 防止土地退化
- 减少土地退化
注释:
The major purpose for this technology is to prevent soil degradation and improve soil fertility.
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
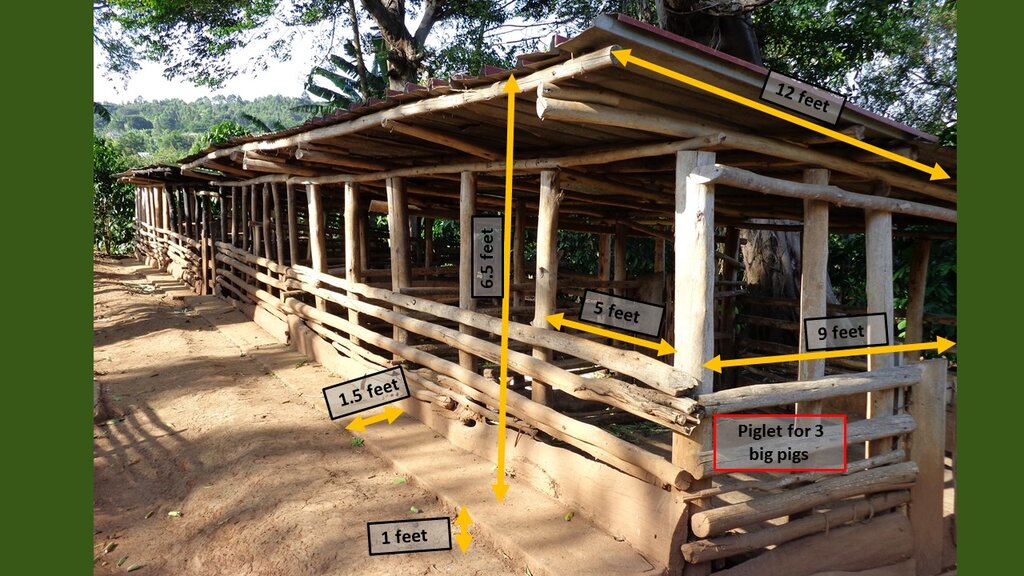
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
Technical specifications of the pig sty construction
作者:
Kyambadde, Tonny
日期:
19/04/2021
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
Technical specifications of the coffee and banana integration
作者:
Kyambadde, Tonny
日期:
13/07/2023
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
具体说明成本和投入是如何计算的:
- 每个技术区域
注明尺寸和面积单位:
one hectare
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
Uganda Shilling
如相关,注明美元与当地货币的汇率(例如1美元=79.9巴西雷亚尔):1美元=:
3750.0
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
no labour was hired
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Land clearing and preparation | once a year |
| 2. | Hole digging | once |
| 3. | Coffee and banana planting | once |
| 4. | Pig sty (house) construction | once |
| 5. | Purchase of pigs | once |
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
如果您无法分解上表中的成本,请估算建立该技术所需要的总成本。:
5300000.0
如果土地使用者负担的费用少于100%,请注明由谁负担其余费用:
The Euregio project contributed two pigs and some starter coffee seedlings and banana suckers (roughly 35 % of total establishment costs were catered by the project).
注释:
These costs include the clearing of the land and prior establishment of the coffee and banana plantation. The majority of the costs are attributed to the purchase of pigs and the construction of the pig sty (roughly 3 million UGX).
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Weeding and garden clearing | Twice a seaon |
| 2. | Manure application | At the onset of rain season |
| 3. | Feeding and watering of pigs | On daily basis |
| 4. | Treatment and deworming of pigs | On monthly basis |
| 5. | Mulching of the garden | Once a year or more |
| 6. | Contour digging | once a year |
| 7. | Pruning of coffee and banana plantation | For banana its done twice a season and for coffee its done every after harvesting season. |
| 8. | Maintenance of piggery sty | once a year |
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
如果您无法分解上表中的成本,请估算维护该技术所需要的总成本。:
500000.0
注释:
Estimation of 500,000 UGX per year. Most costs are for the treatment for the pigs and the maintenance of the pigsty. The rest is covered by family labour.
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
Most costs are connected to the piggery in particular the maintenance of the pigs. Animal diseases and the resulting costs for the treatments are unplanned expenses.
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
指定年平均降雨量(若已知),单位为mm:
1200.00
有关降雨的规范/注释:
The rainfall pattern is bimodal, having two seasons. The two dry spell seasons are between January - March and between June to August, with the winter seasons between March to May and September to December.
注明所考虑的参考气象站名称:
Uganda metrological authority
农业气候带
- 半湿润
The average maximum temperature doesn't exceed 30 degrees Celcius and the minimum temperature is not below 10 degrees Celcius with almost equal length of the day and night through out the year.
The humidity level is relatively low through out the area.
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
土壤质地(地表以下> 20厘米):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 中(1-3%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
The soils ranging from red laterite, sandy loam and loam.
Soils are generally ferrallisol characterized by red colored sandy clay loams and sandy loams, but relatively productive.
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
5-50米
地表水的可用性:
中等
水质(未处理):
不良饮用水(需要处理)
水质请参考::
地下水和地表水
水的盐度有问题吗?:
否
该区域正在发生洪水吗?:
否
关于水质和水量的注释和进一步规范:
Major source of water supply is swamp and readily available all the time in both seasons dry and rain season
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 高
栖息地多样性:
- 中等
关于生物多样性的注释和进一步规范:
No official statistics available, but Banana plantations usually have higher diversity with up to 15 species of other crops within.
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
定栖或游牧:
- 定栖的
生产系统的市场定位:
- 混合(生计/商业)
- 商业/市场
非农收入:
- 低于全部收入的10%
相对财富水平:
- 贫瘠
个人或集体:
- 团体/社区
机械化水平:
- 手工作业
性别:
- 女人
- 男人
土地使用者的年龄:
- 青年人
- 中年人
- 老年人
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 小规模的
注释:
In Central Uganda 1-2 ha is considered small scale. It might be different in other regions of Uganda.
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 个人,未命名
- 个人,有命名
土地使用权:
- 个人
用水权:
- 自由进入(无组织)
土地使用权是否基于传统的法律制度?:
是
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
SLM之前的数量:
1
SLM之后的数量:
3
注释/具体说明:
Significant improvement in coffee production was noticed jumping from an average yield increase of 300kg to 700kg of coffee harvest in one acre per season. Size of banana bunches with an average increase in weight from from 12kg to 30kg.
作物质量
SLM之前的数量:
0
SLM之后的数量:
2
注释/具体说明:
Coffee beans improved a lot in terms of size and quality, with over 70% coffee beans harvested in the category of screen 18 (super beans). The banana size and its fingers improved in size, and the taste of banana food greatly improve with a pleasant aroma, softer on eating and cooks faster compared to previously produced bananas.
畜牧生产
注释/具体说明:
The production of pigs increased substantially in a time period of a year. The participating farmers started with 3 pigs at the beginning and reached an increase of pigs to an average 15 pigs after a year (2 breeding cycles per pig per year).
土地管理
SLM之前的数量:
-2
SLM之后的数量:
3
注释/具体说明:
The farming system employed by the farmers previously before introduction of the technology was not sustainable. Resources were being continuously depleted by crop practices employed without replacement of what is lost from the soil during harvest. integration of piggery into the system improved soil fertility with manure composted from piggery wastes. Besides boosting soil fertility, biodiversity on the farm improved as well (the soil organisms, new plant species emerged, insect species among others) the green biomass and overall soil health improved.
收入和成本
农业收入
注释/具体说明:
The average farm income before the technology was very little and did not support the family's basic home needs. With the introduction of the technology, the household income improved from an average of monthly 45.000 UGX to 150.000 UGX. However, it is important to note that this is not a fixed monthly income and is depending on the harvest season. Thus, there are peak income phases followed by low seasons.
收入来源的多样性
注释/具体说明:
More income sources were established through the three enterprises (coffee, banana and piggery).
社会文化影响
食品安全/自给自足
SLM之前的数量:
0
SLM之后的数量:
2
注释/具体说明:
With improved soil fertility resulting in bigger sizes of banana bunches, improved food security was achieved. The increased income from coffee and piggery ensured availability of alternative food supply though their sale.
健康状况
SLM之前的数量:
-1
SLM之后的数量:
2
注释/具体说明:
There was less exposure to agriculture chemical by farmers and the entire community at large which poses health threat to the people and cause environment damage. the quality of food produced was free from any chemical residues emanating from synthetic fertilizers.
SLM/土地退化知识
注释/具体说明:
Through the technology farmers were able to learn how important it is to use organic sources of fertilizer and its benefits to the environment and soil health. MADDO facilitated roughly 15 different training sessions for the participating farmer group targeting the soil and water conservation practices.
社会经济弱势群体的情况
注释/具体说明:
The situation of women (average between 40-55 years old) was improved through the technology by giving them access and knowledge to this pilot project. The mobilization and right selection of participants were crucial for the improvement.
生态影响
土壤
土壤水分
注释/具体说明:
Higher retention of soil moisture
土壤有机物/地下C
注释/具体说明:
Better composition of soil nutrients with increased population of soil organisms (micro and macro)
生物多样性:植被、动物
生物量/地上C
栖息地多样性
注释/具体说明:
Organic manure provided a conducive environment for multiplication and survival of living organisms
对现场影响的评估(测量)进行具体说明:
All the impacts are based on estimations. Thereby, assessments by farmers have been added with observations from the staff to get a clear understanding of the impacts.
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
Pollution of water
注释/具体说明:
The usage of organic manure instead of chemical fertilizers reduced the pollution of downstream water from fields
对场外影响(测量)的评估进行具体说明:
This impact is based on estimation by the project staff as well as some observations from participants.
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
注释:
The technology was piloted in a 3-year program and climate-related consequences cannot be measured yet.
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
非常积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
稍微积极
注释:
After the establishment of the technology, the returns from coffee are attained in period of two years, for banana returns observed in less than one year and for piggery profits attained in period of less than two years.
6.5 技术采用
- 11-50%
如若可行,进行量化(住户数量和/或覆盖面积):
Mainstreaming of the technology was promoted through copying from the participants and also due to the promotion by the district field staff. The technology has been in existence for years and that is why a high adoption can be observed.
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发的,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 51-90%
注释:
The technology is commonly used in the area. However, those who were not part of the program take short-cuts or do not have such high positive progress as the others.
6.6 适应
最近是否对该技术进行了修改以适应不断变化的条件?:
否
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Contributes positively to the soil fertility. |
| Improves the food security and household income |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Farmers were able to local available resources for this technology. |
| It improved the soil health and contributed to environmental conservation. |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Diseases that affect the piggery (swine fewer). | No mitigation (vaccination) available. |
| The vet officers are not always available for vaccinations or treatments for the pigs. Moreover, there are quite expensive. | Farmers group together to lobby for the service. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Follow up on the management practices for the piggery were time consuming. | Establishment of community-based trainers (CBT) that take over |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
- 与土地使用者的访谈
About 30 participants
- 与SLM专业人员/专家的访谈
Interview with two experts from the district (agriculture officer and production officer).
- 根据报告和其他现有文档进行编译
The following sources was used:
Ministry of Agriculture, Animal Industry and Fisheries (2014): Uganda Training Materials for Coffee Production. Trainer's Guide. First Edition.
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
26/05/2021
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Benefits of sustainable land management, UNCCD
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
https://catalogue.unccd.int/838_Benefits_of_SLM_eng.pdf
7.3 链接到网络上的相关信息
标题/说明:
Sustainable Agriculture in Africa,
URL:
https://wedocs.unep.org/bitstream/handle/20.500.11822/34621/RSRSA.pdf?sequence=3&isAllowed=y
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接

MADDO SLM approach [乌干达]
This integrated soil fertility management approach aims at identifying and promoting practices in land management that can increase soil fertility, reduce land degradation and improve production. Under this specific example, organic manure from a piggery was applied to banana and coffee plantations.
- 编制者: Tonny Kyambadde
模块
无模块