Roof Top Rain Water Harvesting - Concrete Tank [塔吉克斯坦]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Sa'dy Odinashoev
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Deborah Niggli, David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano, Joana Eichenberger
Чамоварии оби борон
technologies_1460 - 塔吉克斯坦
- Roof Top Rain Water Harvesting - Concrete Tank: Aug. 21, 2019 (inactive)
- Roof Top Rain Water Harvesting - Concrete Tank: Nov. 2, 2021 (public)
- Roof Top Rain Water Harvesting - Concrete Tank: April 4, 2018 (inactive)
- Roof Top Rain Water Harvesting - Concrete Tank: July 21, 2017 (inactive)
- Roof Top Rain Water Harvesting - Concrete Tank: May 6, 2017 (inactive)
- Roof Top Rain Water Harvesting - Concrete Tank: March 16, 2017 (inactive)
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
SLM专业人员:
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
Book project: Water Harvesting – Guidelines to Good Practice (Water Harvesting)有助于对技术进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
Pilot Program for Climate Resilience, Tajikistan (WB / PPCR)有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
CARITAS (Switzerland) - 瑞士有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
CAMP - Central Asian Mountain Partnership (CAMP - Central Asian Mountain Partnership) - 吉尔吉斯斯坦有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
NCCR North-South (NCCR North-South) - 吉尔吉斯斯坦1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
The roof top rain water harvesting system using a concrete tank was designed to improve household access to water for irrigation of kitchen garden plots during the hot and dry summer months.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
A 16 cubic metre concrete tank situated in the shadow of the house constructed to retain rainwater that collects in the roof guttering.
Purpose of the Technology: The purpose of the tank is to retain water to be used for drinking, sanitation and irrigation during the hot and dry summer months. The retained water allows for the irrigation of kitchen garden plots and more diverse crops, and hence should improve the livelihoods of households involved.
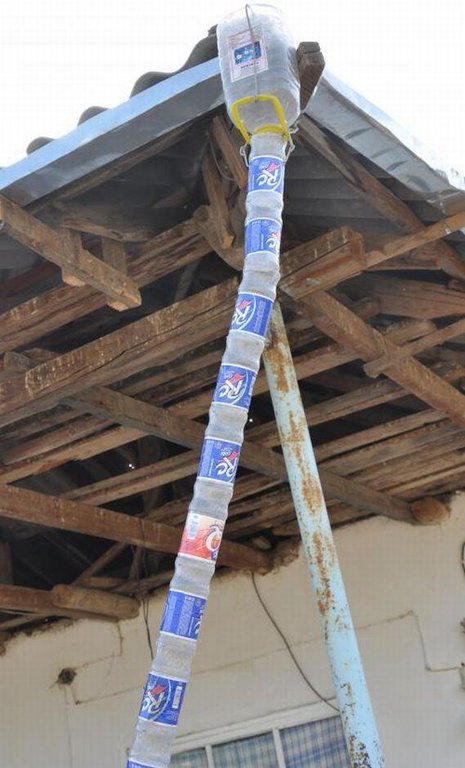
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: There are three main elements to the construction of the rainwater harvesting system. The first is the construction of a metal gutter on wooden supports around the perimeter of the roof; second, the construction of a concrete pool in the shadow of the house; and finally the provision of a connection pipe between the gutter and the pool. The pool needs to be cleaned periodically to prevent contamination and build up of algae around the edge the pool.
Natural / human environment: During the Soviet period the water supply for the village was supplied through a concrete storage tank located at the foot of the hills above the village. After the collapse of the Soviet Union the concrete tank and its associated infrastructure fell into disrepair. As a result the inhabitants were faced with water shortages, especially during the hot dry summers. In response to this issue the residents invested time, finance and resources into constructing rainwater collection systems.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
塔吉克斯坦
区域/州/省:
Tajikistan
有关地点的进一步说明:
Rudaki, Boshkengash
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 适用于特定场所/集中在较小区域
注释:
Система сбора дождевой воды с крыш, которая продускает воду в бетонную цистерну, существует во многих сельских домах
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 10-50年前
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过土地使用者的创新
注释(项目类型等):
The land owner built the concrete tank in 2010, however numerous other tanks have been constructed during the last 10 years.
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- access to water
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

农田
- 一年一作
- 乔木与灌木的种植
年作 - 具体指明作物:
- 蔬菜 - 其他
乔木和灌木种植 - 指定作物:
- 水果、其他
每年的生长季节数:
- 1
具体说明:
Вегетативный период (дни): 220. Вегетативный период по месяцам: Март-Ноябрь

森林/林地
产品和服务:
- 水果和坚果

定居点、基础设施
- 定居点、建筑物
注释:
Населенный пункт с небольшими огородами
注释:
Основные проблемы землепользования (по мнению составителя): В районе кишлака выпадает 600мм/год осадков, однако они выпадают только в период двух месяцев года. Земля в пределах кишлака стала сильно сухой и, таким образом, более оголенной и непригодной для культивации.
Основные проблемы землепользования (по мнению землепользователя): Недостаток воды в критические периоды года.
Экологические услуги леса: плоды и орехи
Будущее землепользование (после внедрения УЗП технологии): Пашня: Ct: выращивание кустов и деревьев
Тип севооборота: Вода собранная с крыш используется для полива приусадебных участков. На этих участках обычно выращивают лук, картошку и морковку, а также фруктовые деревья.
Ограничение поселения: земля, где будет построена цистерна, может быть используется для выращивания овощей
Если использование земель изменилось с началом применения Технологии, укажите тип землепользования до применения Технологии:
Смешанный: Mo: другое
3.3 由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?
由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?:
- 是(请在技术实施前填写以下有关土地利用的问题)

农田
- 乔木与灌木的种植
采用间作制度了吗?:
是
如果是,说明哪些作物是间作的:
Недостаток воды в критические периоды года.
Экологические услуги леса: плоды и орехи

森林/林地

定居点、基础设施
注释:
Вода собранная с крыш используется для полива приусадебных участков. На этих участках обычно выращивают лук, картошку и морковку, а также фруктовые деревья.
3.4 供水
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 集水
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

农艺措施
- A7:其它

结构措施
- S5:大坝、集水斗、水池
注释:
Main measures: structural measures
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀

土壤风蚀
- Et:表土流失
注释:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Et: loss of topsoil
Main causes of degradation: over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use (The domestic plots were over used due to poor water supply.)
Secondary causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (This occured previously and the trees were not replaced.), other human induced causes (specify) (After the collapse of the Soviet Union the concrete tank and it's associated infrastructure fell into disrepair.), change of seasonal rainfall (Less rainfall at critical times impacted on cultivation activity.), Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts) (Lack of vegetation results in higher losses of soil erosion during heavy rainfall events.), droughts (Longer dry periods in the summer months.), population pressure (The population and number of houses in the village is increasing.)
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 减少土地退化
注释:
Main goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
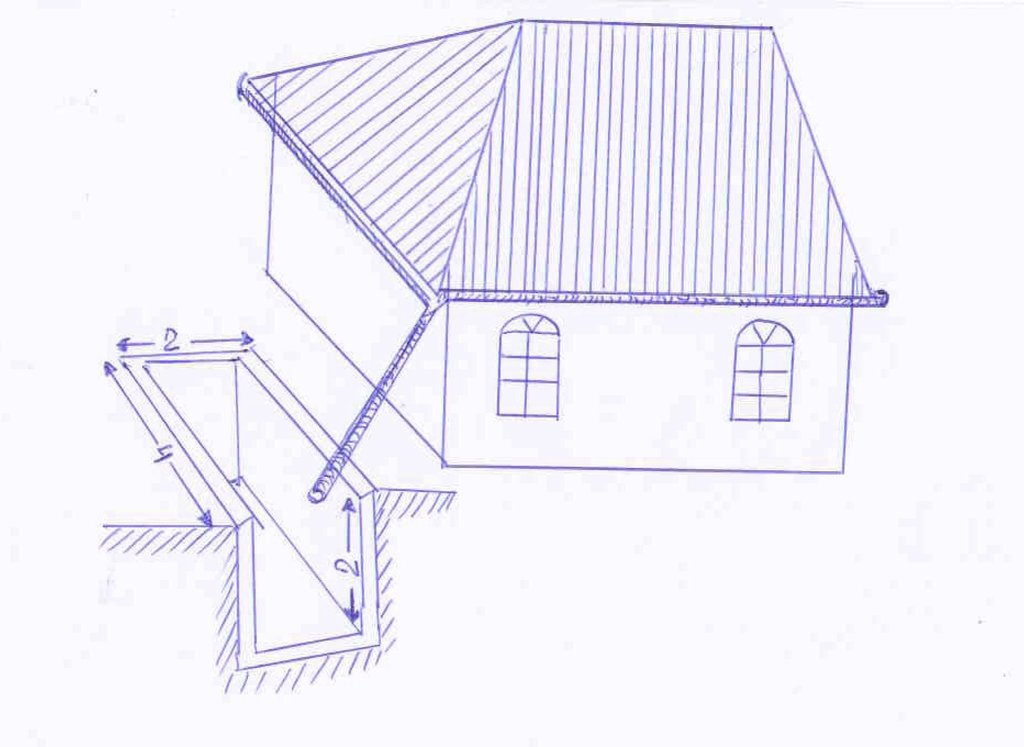
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
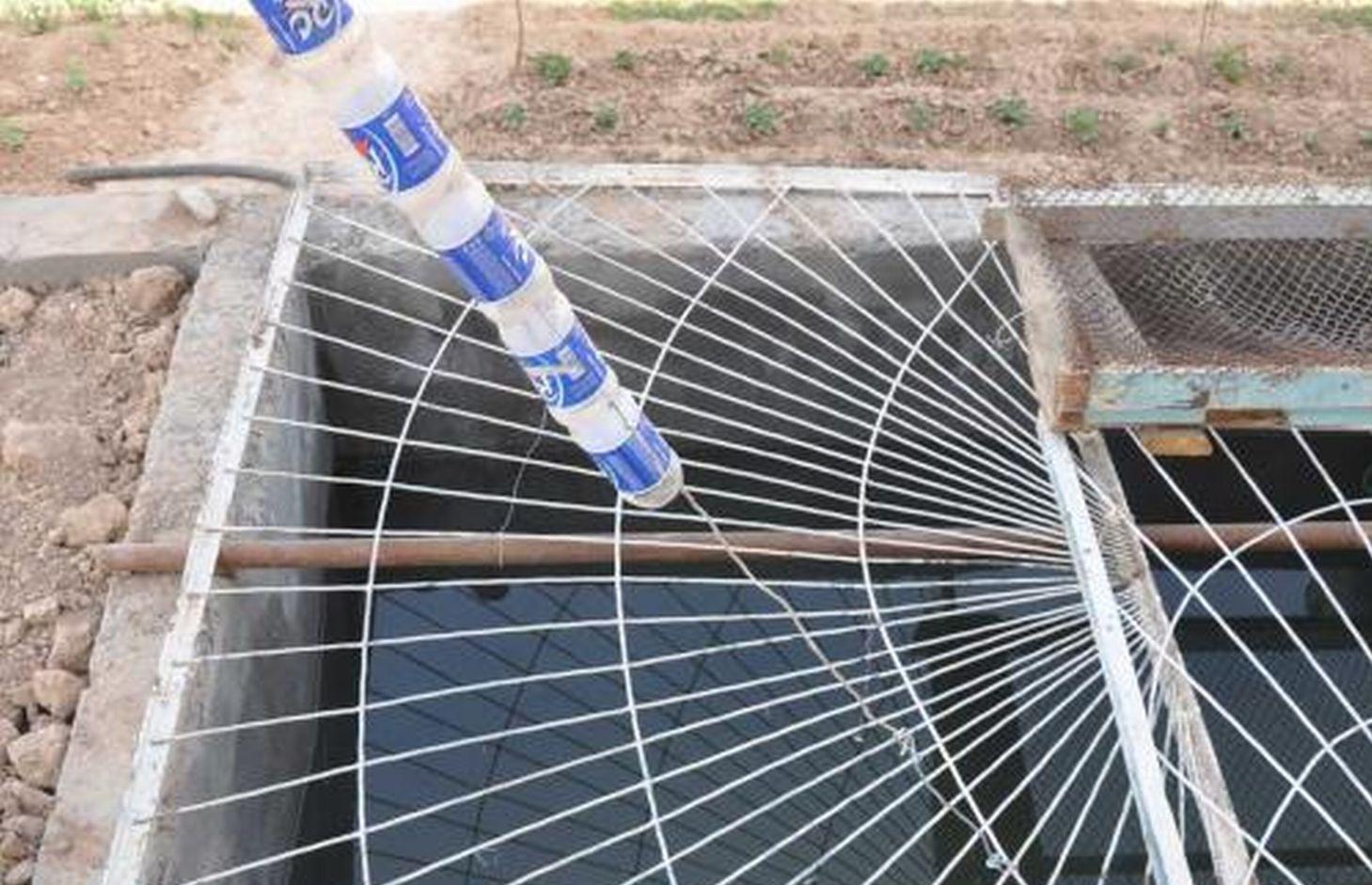
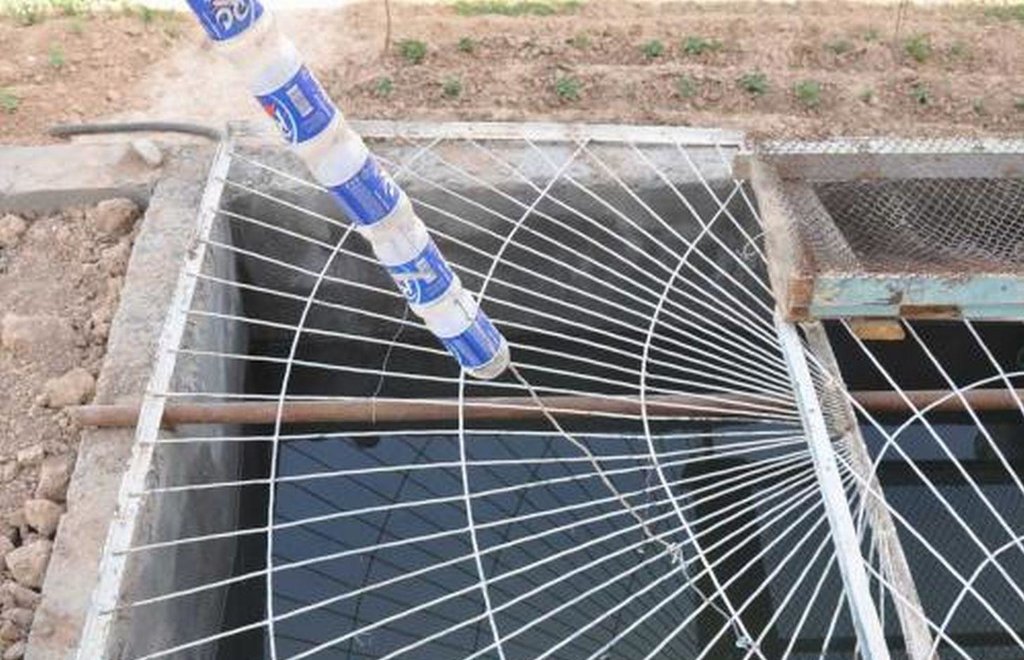
Чертеж показывает металлический желоб (0,15м шириной), располагаемый по периметру верхушки крыши. Желоб собирает дождевую воду с крыши и через пластиковую трубу, сделанную из старых бутылок, соединенных друг с другом путем обвязки, пропускает ее в бетонную цистерну. В данном примере, протяженность цистерны 4м, ширина -2м, глубина – 2м и расположена она в тени дома для того, чтобы снизить уровень испарения. Цистерна расположена с уклоном и частично заглублена вверх по склону. Цистерна закрыта в целях безопасности и предотвращения внешнего загрязнения.
Место расположения: Бошкенгаш. Рудаки
Дата: 20011-05-06
Необходимые технические навыки для землепользователей: средний (Требуется техническое знание, иначе конструкция рухнет)
Основные технические функции: сбор воды / повышение водоснабжения
яма/ цистерна/ пруд
Глубина канав/ям/дамб (м): 2
Ширина канав/ям/дамб (м): 2
Длина канав/ям/дамб (м): 4
Особенность ямы/ цистерны/ пруда: емкость 16м3
Площадь, с которой собирается вода: 20м2
Крутизна склона внутри ямы: 0%;
Крутизна склона снаружи ямы: 0%
Другие особенности: размер цистерны 2*2*4м
Сбор воды: разница между площадью, с которой собирается вода, и площадью, куда она собирается: 1:0.5
Lieu: Boshkengash. Rudaki, Tadjikistan
Date: 20011-05-06
Connaissances techniques requises pour les utilisateurs fonciers: moyen (Certaines connaissances technique sont requises ou alors la structure ne tient pas).
Principales fonctions techniques: récupération de l'eau / augmentation des réserves d'eau
Barrage / bassin / étang
Profondeur des fossés / puits / barrages (m): 2
Largeur des fossés / puits / barrages (m): 2
Longueur des fossés / puits / barrages (m): 4
Spécifications des barrages / bassins / bassins: Capacité 16m3
Zone de collecte: 20 m2m2
Zone bénéfique: 0,2 h.am2
Pente de la paroi du barrage à l'intérieur: 0%;
Pente du mur du barrage à l'extérieur: 0%
Dimensions des spillings: 0m
Autres spécifications: dimension du réservoir 2 * 2 * 4m
Pour la récolte de l'eau: le rapport entre la zone où l'eau récoltée est appliquée et la superficie totale à partir de laquelle l'eau est collectée est: 1: 0,5
作者:
Soisin Peter
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
Somoni
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
10.00
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | construction of concrete tank and guttering | spring |
| 2. | None | None |
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Construction of concrete tank and guttering | Persons/day | 20.0 | 22.5 | 450.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Tools | pieces | 6.0 | 11.1666666 | 67.0 | 100.0 |
| 施工材料 | Concrete sand, stone | tons | 2.0 | 337.5 | 675.0 | 100.0 |
| 施工材料 | Metal guttering | tons | 0.5 | 900.0 | 450.0 | 100.0 |
| 施工材料 | Wood | tons | 0.5 | 240.0 | 120.0 | 100.0 |
| 施工材料 | Plastic pipes | pieces | 1.0 | 10.0 | 10.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 1772.0 | |||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 1772.0 | |||||
注释:
Duration of establishment phase: 2 month(s)
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Cleaning | annually |
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Cleaning | Person/day | 1.0 | 25.0 | 25.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 25.0 | |||||
| 技术维护总成本,美元 | 25.0 | |||||
注释:
The costs were calculated based on 2010 prices per tank.
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
Labour, tools and piping can be provided by the land user and stone for the foundation is locally available, however, there is an initial outlay of $300 for the cement, wood and metal guttering. In this example the money for the initial outlay was collected by family members working in Russia and from local salaries.
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
有关降雨的规范/注释:
Estimated to be at the lower end of the range
农业气候带
- 半干旱
Thermal climate class: temperate
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
关于地形的注释和进一步规范:
Altitudinal zone = 800m
Slopes on average: The village is located on a flat plain at the foothill of a slope.
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 中(1-3%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Soil texture: Loess soils.
Soil fertility has a potential to be high when cultivated under good conditions.
Soil drainage / infiltration is medium but can be reduced under dry conditions. i.e crusts.
Soil water storage capacity is low-medium since loess material does contain some clay soils.
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
5-50米
地表水的可用性:
中等
水质(未处理):
良好饮用水
关于水质和水量的注释和进一步规范:
Availability of surface water is good during spring rains and poor/none in the summer months.
Water quality (untreated) is good drinking water during winter and spring (snow and rainfall), but poor during summer.
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 中等
关于生物多样性的注释和进一步规范:
Mixture of vegetables and orchards being grown.
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
生产系统的市场定位:
- 生计(自给)
非农收入:
- 收入的10-50%
相对财富水平:
- 平均水平
个人或集体:
- 个人/家庭
机械化水平:
- 手工作业
性别:
- 女人
- 男人
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: 100-200 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 1% - 2%
15% of the land users are rich.
70% of the land users are average wealthy (for the land user used for this example).
15% of the land users are poor.
Off-farm income specification: The residents do not have a significant income from their garden plots.
Market orientation of production system: The water is for personal use.
Level of mechanization: All work is done by hand.
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 小规模的
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 州
土地使用权:
- 个人
用水权:
- 个人
注释:
In regards to the water in the tank, household plots are allocated by the local government. All land is owned by the state.
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
注释/具体说明:
Due to access to water in the summer months
木材生产
注释/具体说明:
From the increased number of fruit trees.
生产故障风险
产品多样性
水资源可用性和质量
饮用水的可用性
SLM之后的数量:
16 cub m
注释/具体说明:
Readily available especially in the summer months.
家畜用水的可用性
SLM之后的数量:
16 cub m
注释/具体说明:
Dramatically increased, in the summer months.
灌溉用水的可用性
SLM之后的数量:
16 cub m
注释/具体说明:
During the drought periods.
收入和成本
农业投入费用
注释/具体说明:
In some households water had to be purchased.
工作量
注释/具体说明:
No collection of water from distant sources.
其它社会经济效应
Potential debt issues if finance is borrowed for the initial outlay
注释/具体说明:
Initial outlay in the region of $400
社会文化影响
食品安全/自给自足
注释/具体说明:
Able to grow more and of a better quality.
冲突缓解
注释/具体说明:
Previously residents had to wait at water points.
Hygiene and sanitation
注释/具体说明:
Constant access to water dramatically improves sanitation levels in the village.
Livelihood and human well-being
注释/具体说明:
Permanent access to water has dramatically improved the sanitation and hygiene levels, and increased crop quality and diversification. It has also improved the quality of and access to drinking water, and therefore has significant health benefits.
生态影响
水循环/径流
水量
SLM之后的数量:
16 cub m
注释/具体说明:
Readily available water supply.
水质
SLM之后的数量:
16 cub m
水的回收/收集
SLM之后的数量:
16 cub m
注释/具体说明:
The technology concentrates on harvesting water.
蒸发
注释/具体说明:
Tank is built in the shadow of the house.
土壤
土壤水分
生物多样性:植被、动物
植物多样性
注释/具体说明:
Able to grow crops at different times of the year.
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
水资源可用性
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 增加或减少 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年温度 | 增加 | 好 |
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气象灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 局地暴雨 | 好 |
气候灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 干旱 | 不好 |
其他气候相关的后果
其他气候相关的后果
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 缩短生长期 | 好 |
注释:
In times of heavy rainfall and prolonged summer drought the size of the tank could be increased.
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
非常积极
长期回报:
非常积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
非常积极
长期回报:
非常积极
注释:
If it is constructed to a reasonable standard then it will not need any significant maintenance.
6.5 技术采用
- > 50%
如若可行,进行量化(住户数量和/或覆盖面积):
900 household (70 percent of the area covered)
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发的,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 91-100%
注释:
Comments on spontaneous adoption: The urban roof top rainwater harvesting has been replicated by many members of the community without external support.
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: People observed, and experienced the benefits, and decided that it was worth the initial investment.
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Improved the standard of living, and the increased access to water allowed the households to have more automony over what that grow and eat. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
Improves the provision of irrigated water for the hot dry summer periods. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Further dissemination to other households. |
|
Allowed for the improvement and expansion of kitchen gardens. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Training on keeping a kitchen garden. |
| Improved the quality and quantity of fruit yields |
|
Improved the access of water for sanitation and drinking water purposes How can they be sustained / enhanced? Education on sanitation methods. |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| The perception was that the water was not clean in the concrete pool. | However, it was tested and proved to be safe to use. This provided reassurance to the household members. It would be a major benefit if the water tank remains covered and is cleaned periodically. |
| The initial outlay may be considered expensive for some families. | Many families have adopted this, possibly if many were built at once the material costs would be reduced. The technology could be tied in with micro finance activities. |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块